1. The first problem of HMM: A known HMM model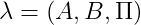 That is, the state transition matrix, the emission matrix, the initial state probability matrix are known, and a sequence of observed values is given.
That is, the state transition matrix, the emission matrix, the initial state probability matrix are known, and a sequence of observed values is given.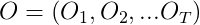 To calculate the probability of occurrence of this observation sequence
To calculate the probability of occurrence of this observation sequence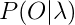 .
.
2. Algorithmic thinking: Actually, it is a dynamic programming algorithm. The key is to find recursive formulas.
2.1 Calculate the forward probabilities of various states at time 1: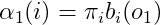 ,
, 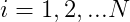
2.2 The probability of recursive 2,3...T time: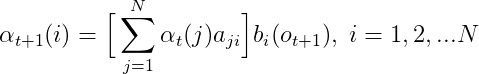
2.3 Calculate the final result: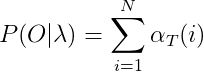
3.c++ code:
// Known: HMM implied state number, state transition probability, state emission probability, and initial state probability distribution, according to the specified visible state chain,
// Seek: The probability of the occurrence of this state chain
// Using forward algorithm to solve time complexity will reduce a lot.
// Following is the C++ version forward algorithm process
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
void forward(double TransProbMatrix[][3], int irow, int icol,
double EmitProbMatrix[][2], int jrow, int jcol,
double PI[], int piLength,
int ObservedChain[], int obLength)
{
// The result matrix is constructed, and each column represents the operation result of each step and state.
const int row = piLength;
const int col = obLength;
double** resultMatrix = new double*[row];
for (int i = 0; i < row; i++)
resultMatrix[i] = new double [col];
for (int i = 0; i < row; i++){
for (int j = 0; j <col; j++)
resultMatrix[i][j] = 0;
}
// The first step is initialization, and the next step is obtained by recursive formula.
for (int i = 0; i < col; i++){
if (i == 0){
for (int j = 0; j < row; j++){
resultMatrix[j][0] = PI[j]*EmitProbMatrix[j][0];
}
}
else{
for (int j = 0; j < row; j++){
for (int k = 0; k < row; k++){
resultMatrix[j][i] += resultMatrix[k][i-1] * TransProbMatrix[k][j] * EmitProbMatrix[j][ObservedChain[i]];
}
}
}
}
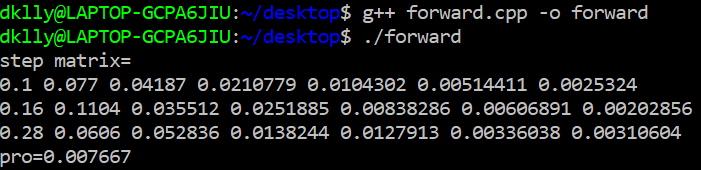
cout<<"step matrix="<<endl;
// Display result matrix
double pro = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < row; i++){
for (int j = 0; j <col; j++){
cout<<resultMatrix[i][j]<<" ";
if (j == col-1)
pro += resultMatrix[i][j];
}
cout<<endl;
}
cout<<"pro="<<pro<<endl;
}
int main()
{
// State transition matrix
double TransProbMatrix[][3] =
{{0.5,0.2,0.3},
{0.3,0.5,0.2},
{0.2,0.3,0.5}};
int tRow = sizeof(TransProbMatrix)/sizeof(*TransProbMatrix);
int tCol = sizeof(*TransProbMatrix)/sizeof(**TransProbMatrix);
// Emission matrix
double EmitProbMatrix[][2] =
{{0.5,0.5},
{0.4,0.6},
{0.7,0.3}};
int eRow = sizeof(EmitProbMatrix)/sizeof(*EmitProbMatrix);
int eCol = sizeof(*EmitProbMatrix)/sizeof(**EmitProbMatrix);
// Initial State Probability Distribution
double PI[] = {0.2, 0.4, 0.4};
int piLen = sizeof(PI)/sizeof(*PI);
// Observation chain
int ObservedChain[] = {0, 1, 0, 1, 0, 1, 0};
int obLen = sizeof(ObservedChain)/sizeof(*ObservedChain);
// Afferent parameter
forward(TransProbMatrix, 3, 3, EmitProbMatrix, 3, 2, PI, 3, ObservedChain, obLen);
}The result is: