Installation Prerequisites
Hadoop cluster has been installed and configured (single or fully distributed)
Software Download
Hive Installation
Configuring environment variables
Upload the downloaded Live package to the machine and extract it to the specified path
Edit / etc/profile to configure Hive's environment variables
Edit / etc/profile to configure Hive's environment variables
export HIVE_HOME=/.../apache-hive-2.1.0-bin export PATH=$PATH:$HIVE_HOME/bin
Make the environment configuration effective: source/etc/profile
Modify hive-env.sh
Because Hive uses Hadoop, you need to specify the Hadoop installation path in the hive-env.sh file:
At the same time, the path of JAVA_HOME should be modified.
Export JAVA_HOME=/usr/java/jdk-1.8.0_101# Java path
Expo HADOOP_HOME=/usr/hadoop-2.6.4##Hadoop installation path
Export HIVE_HOME=/usr/hadoop-2.6.4/thirdparty/apache-hive-2.1.0-bin# Hive installation path
Expo HIVE_CONF_DIR=$HIVE_HOME/conf# Hive configuration file path
At the same time, the path of JAVA_HOME should be modified.
Export JAVA_HOME=/usr/java/jdk-1.8.0_101# Java path
Expo HADOOP_HOME=/usr/hadoop-2.6.4##Hadoop installation path
Export HIVE_HOME=/usr/hadoop-2.6.4/thirdparty/apache-hive-2.1.0-bin# Hive installation path
Expo HIVE_CONF_DIR=$HIVE_HOME/conf# Hive configuration file path
Configure Hive
Enter the conf directory of hive:
cp hive-env.sh.template hive-env.sh cp hive-default.xml.template hive-site.xml cp hive-log4j2.properties.template hive-log4j2.properties cp hive-exec-log4j2.properties.template hive-exec-log4j2.properties
Modify hive-site.xml
Corresponding to <name/>, change to <value/> as follows:
<property>
<name>hive.exec.scratchdir</name>
<value>/tmp/hive-${user.name}</value>
<description>HDFS root scratch dir for Hive jobs which gets created with write all (733) permission. For each connecting user, an HDFS scratch dir: ${hive.exec.scratchdir}/<username> is created, with ${hive.scratch.dir.permission}.</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.exec.local.scratchdir</name>
<value>/tmp/${user.name}</value>
<description>Local scratch space for Hive jobs</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.downloaded.resources.dir</name>
<value>/tmp/hive/resources</value>
<description>Temporary local directory for added resources in the remote file system.</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.querylog.location</name>
<value>/tmp/${user.name}</value>
<description>Location of Hive run time structured log file</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.server2.logging.operation.log.location</name>
<value>/tmp/${user.name}/operation_logs</value>
<description>Top level directory where operation logs are stored if logging functionality is enabled</description>
</property>Configure Hive Metastore
By default, Hive's metadata is stored in an embedded derby database, but in general, the production environment uses MySQL to store Hive's metadata.
Put mysql-connector-java-5.1.40-bin.jar under $HIVE_HOME/lib.
Configure MySQL database connection information in hive-site.xml.
Put mysql-connector-java-5.1.40-bin.jar under $HIVE_HOME/lib.
Configure MySQL database connection information in hive-site.xml.
<property> <name>javax.jdo.option.ConnectionURL</name> <value>jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/hive?createDatabaseIfNotExist=true&characterEncoding=UTF-8&useSSL=false</value> </property> <property> <name>javax.jdo.option.ConnectionDriverName</name> <value>com.mysql.jdbc.Driver</value> </property> <property> <name>javax.jdo.option.ConnectionUserName</name> <value>hive</value> </property> <property> <name>javax.jdo.option.ConnectionPassword</name> <value>hive</value> </property>
Create HDFS directories for Hive
Before creating tables in Hive, you need to use the following HDFS commands to create / tmp and / user / hive / warehouse directories (the default value of the property item hive.metastore.warehouse.dir in the hive-site. XML configuration file) and assign write permissions to them.
start-dfs.sh hdfs dfs -mkdir /tmp hdfs dfs -mkdir -p /usr/hive/warehouse hdfs dfs -chmod g+w /tmp hdfs dfs -chmod g+w /usr/hive/warehouse
mysql creates user hive
$ mysql -u root -p
mysql> CREATE USER 'hive'@'localhost' IDENTIFIED BY "hive";
mysql> grant all privileges on *.* to hive@localhost identified by 'hive';
mysql> CREATE USER 'hive'@'localhost' IDENTIFIED BY "hive";
mysql> grant all privileges on *.* to hive@localhost identified by 'hive';
Running Hive
When running the hive command on the command line, you must ensure that HDFS is started. You can use start-dfs.sh to start HDFS.
Starting with Hive 2.1, we need to run the schematool command to perform initialization.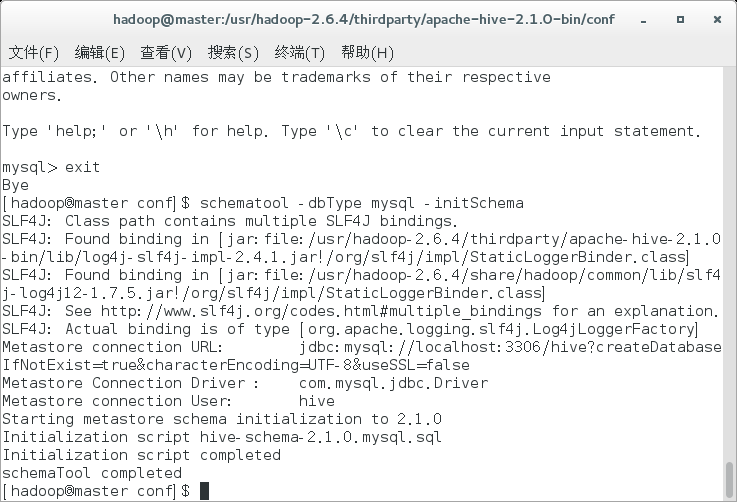
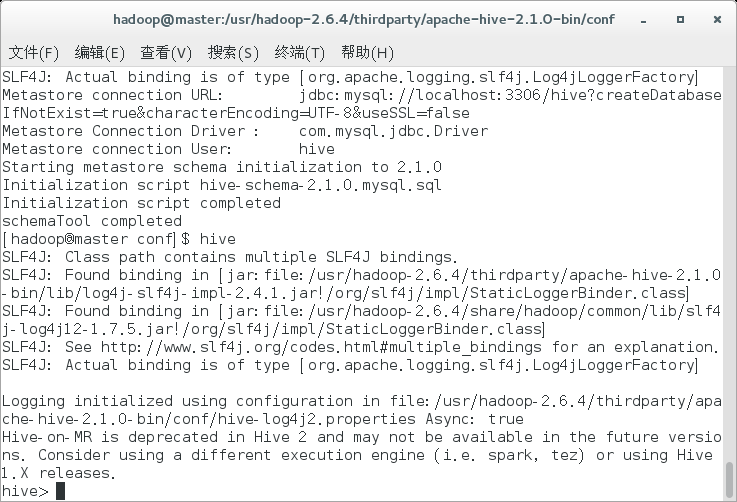
To use Hive CLI (Hive command line interface), you can enter: hive at the terminal
The startup information is as follows:
Test:
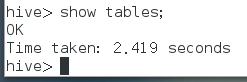
Use show tables to display all tables:
Starting with Hive 2.1, we need to run the schematool command to perform initialization.
schematool -dbType mysql -initSchema

To use Hive CLI (Hive command line interface), you can enter: hive at the terminal
The startup information is as follows:

Test:
Use show tables to display all tables:

Be careful
If MySQL is configured as metadata storage, start the MySQL database service before starting Hive