Hibernate Framework Note 03_Table Operation_Multiple-to-Multiple Configuration
Article directory
- Hibernate Framework Note 03_Table Operation_Multiple-to-Multiple Configuration
- 1. Relationships between database tables and tables
- 2. Hibernate's one-to-many association mapping
- 2.1 Create a project and introduce related jar packages
- 2.2. Create databases and tables
- 2.3 Creating Entities
- 2.4 Create mapping files
- 2.5 Create Core Profile
- 2.6 Introducing Tool Classes and Logs
- 2.7 Writing Tests
- 2.8 One-to-many cascade operation
- 3. Hibernate's many-to-many Association mappings
1. Relationships between database tables and tables
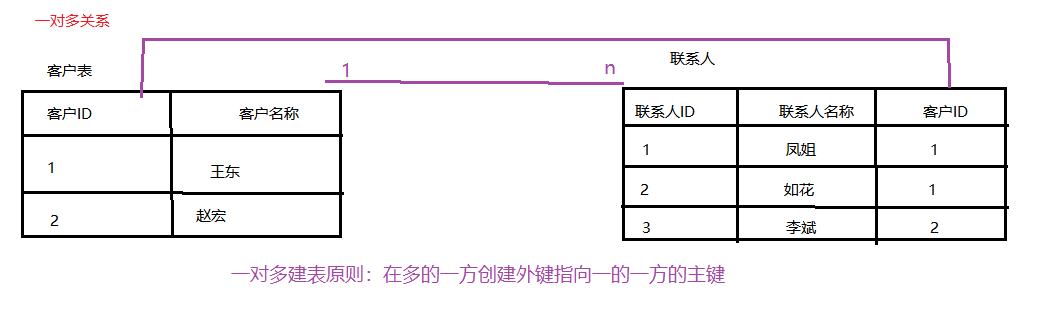
1.1 One-to-many relationship
-
What kind of relationship belongs to one-to-many?
- A Department corresponds to more than one employee, and an employee can only belong to one department.
- A customer corresponds to multiple contacts, and a contact can only belong to one customer.
-
One-to-many tabulation principle: Create the primary key of the foreign key pointing to one side on the multiple side
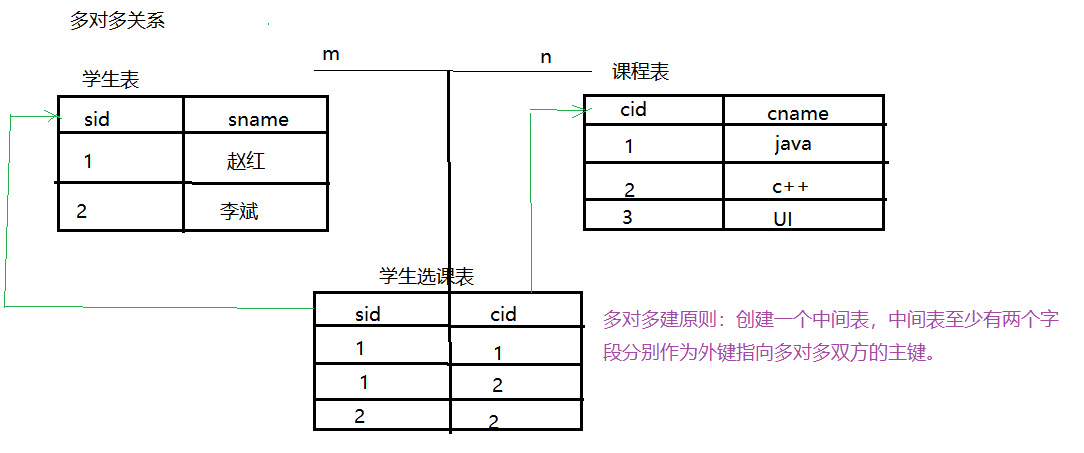
1.2 Many-to-Many Relations
-
What kind of relationship belongs to many-to-many?
- One student can choose more than one course, and one course can be chosen by more than one student.
- A user can select multiple roles, and a role can be selected by multiple users.
-
Multi-to-many table building principle: multi-to-many table building principle: create a middle table, the middle table has at least two fields as foreign keys to point to the main key of many-to-many sides.
1.3 One-to-one relationship [understanding]
- What kind of relationship belongs to one-to-one?
- A company can only have one registration address, and a registration address can only be registered by one company.
- Unique foreign key correspondence: Assuming a one-to-many relationship, it is necessary to create a primary key pointing to one side on one side of the multiple side, and set the foreign key to unique.
- Primary key correspondence: Make the primary key of one table the primary key of another table.
2. Hibernate's one-to-many association mapping
2.1 Create a project and introduce related jar packages
2.2. Create databases and tables
-
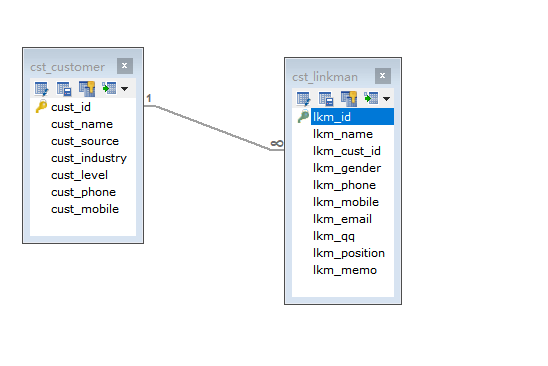
Create a database and create two new tables
-
Cusmer table crm_cst_customer.sql
CREATE TABLE `cst_customer` ( `cust_id` bigint(32) NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT COMMENT 'Customer number(Primary key)', `cust_name` varchar(32) NOT NULL COMMENT 'Customer name(Corporate name)', `cust_source` varchar(32) DEFAULT NULL COMMENT 'Customer Information Sources', `cust_industry` varchar(32) DEFAULT NULL COMMENT 'Customer information', `cust_level` varchar(32) DEFAULT NULL COMMENT 'Customer level', `cust_phone` varchar(64) DEFAULT NULL COMMENT 'Fixed telephone', `cust_mobile` varchar(16) DEFAULT NULL COMMENT 'Mobile phone', PRIMARY KEY (`cust_id`) ) ENGINE=InnoDB AUTO_INCREMENT=1 DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8;
-
LinkMan table crm_cst_linkman.sql
CREATE TABLE `cst_linkman` ( `lkm_id` bigint(32) NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT COMMENT 'Contact Number(Primary key)', `lkm_name` varchar(16) DEFAULT NULL COMMENT 'Name of contact person', `lkm_cust_id` bigint(32) NOT NULL COMMENT 'Customer id', `lkm_gender` char(1) DEFAULT NULL COMMENT 'Contact Gender', `lkm_phone` varchar(16) DEFAULT NULL COMMENT 'Contact office telephone', `lkm_mobile` varchar(16) DEFAULT NULL COMMENT 'Cell Phone', `lkm_email` varchar(64) DEFAULT NULL COMMENT 'Contact mailbox', `lkm_qq` varchar(16) DEFAULT NULL COMMENT 'Contacts qq', `lkm_position` varchar(16) DEFAULT NULL COMMENT 'Contact Title', `lkm_memo` varchar(512) DEFAULT NULL COMMENT 'Contact Remarks', PRIMARY KEY (`lkm_id`), KEY `FK_cst_linkman_lkm_cust_id` (`lkm_cust_id`), CONSTRAINT `FK_cst_linkman_lkm_cust_id` FOREIGN KEY (`lkm_cust_id`) REFERENCES `cst_customer` (`cust_id`) ON DELETE NO ACTION ON UPDATE NO ACTION ) ENGINE=InnoDB AUTO_INCREMENT=1 DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8;
-
The relationship between two tables
2.3 Creating Entities
public class Customer { private Long cust_id; private String cust_name; private String cust_source; private String cust_industry; private String cust_level; private String cust_phone; private String cust_mobile; // Represented by ORM: A customer corresponds to multiple contacts // Place a collection of multiple parties. Hibernate defaults to Set collections private Set<LinkMan> linkMans = new HashSet<LinkMan>(); //get/set method
public class LinkMan { private Long lkm_id; private String lkm_name; private String lkm_gender; private String lkm_phone; private String lkm_mobile; private String lkm_email; private String lkm_qq; private String lkm_position; private String lkm_memo; // Represented by ORM: A contact can only belong to one customer // Objects placed on one side private Customer customer; //set/get method
2.4 Create mapping files
-
Several entities require several mapping files
-
Customer.hbm.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <!DOCTYPE hibernate-mapping PUBLIC "-//Hibernate/Hibernate Mapping DTD 3.0//EN" "http://www.hibernate.org/dtd/hibernate-mapping-3.0.dtd"> <hibernate-mapping> <class name="com.itzhouq.hibernate.domain.Customer" table="cst_customer"> <!-- establish OID Mapping with Primary Key --> <id name="cust_id" column="cust_id"> <generator class="native"></generator> </id> <!-- establish General attributes and database field mapping --> <property name="cust_name" column="cust_name"></property> <property name="cust_source" column="cust_source"></property> <property name="cust_industry" column="cust_industry"></property> <property name="cust_level" column="cust_level"></property> <property name="cust_phone" column="cust_phone"></property> <property name="cust_mobile" column="cust_mobile"></property> <!-- Configure one-to-many mappings: sets of multiple parties placed --> <!-- set Label: * name: The attribute name of a collection of objects of more than one party --> <set name="linkMans"> <!-- column The name of the foreign key of more than one party --> <key column="lkm_cust_id"></key> <!-- class: Fully qualified names of classes of multiple parties --> <one-to-many class="com.itzhouq.hibernate.domain.LinkMan"/> </set> </class> </hibernate-mapping>
-
LinkMan.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <!DOCTYPE hibernate-mapping PUBLIC "-//Hibernate/Hibernate Mapping DTD 3.0//EN" "http://www.hibernate.org/dtd/hibernate-mapping-3.0.dtd"> <hibernate-mapping> <class name="com.itzhouq.hibernate.domain.LinkMan" table="cst_linkman"> <!-- establish OID Mapping with Primary Key --> <id name="lkm_id" column="lkm_id"> <generator class="native"></generator> </id> <!-- Establishing mapping between common attributes and table fields --> <property name="lkm_name"/> <property name="lkm_gender"/> <property name="lkm_phone"/> <property name="lkm_mobile"/> <property name="lkm_email"/> <property name="lkm_qq"/> <property name="lkm_position"/> <property name="lkm_memo"/> <!-- Configuring many-to-one relationships: Placing objects on one side --> <!-- many-to-one Label * name: The property name of an object on one side *class: Fully qualified names of classes of one party column: The name of the foreign key of a table on more than one side --> <many-to-one name="customer" class="com.itzhouq.hibernate.domain.Customer" column="lkm_cust_id"/> </class> </hibernate-mapping>
2.5 Create Core Profile
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <!DOCTYPE hibernate-configuration PUBLIC "-//Hibernate/Hibernate Configuration DTD 3.0//EN" "http://www.hibernate.org/dtd/hibernate-configuration-3.0.dtd"> <hibernate-configuration> <session-factory> <!-- Basic parameters for connecting database --> <property name="hibernate.connection.driver_class">com.mysql.jdbc.Driver</property> <property name="hibernate.connection.url">jdbc:mysql:///hibernate_day03</property> <property name="hibernate.connection.username">root</property> <property name="hibernate.connection.password">2626</property> <!-- To configure Hibernate Dialects (optional) --> <property name="hibernate.dialect">org.hibernate.dialect.MySQLDialect</property> <!-- Printing SQL(Optional) --> <property name="hibernate.show_sql">true</property> <!-- Format SQL(Optional) --> <property name="hibernate.format_sql">true</property> <!-- Automatically create tables --> <property name="hibernate.hbm2ddl.auto">update</property> <!-- To configure C3P0 Connection pool --> <property name="connection.provider_class">org.hibernate.connection.C3P0ConnectionProvider</property> <!--Minimum number of database connections available in connection pool --> <property name="c3p0.min_size">5</property> <!--Maximum number of database connections in connection pool --> <property name="c3p0.max_size">20</property> <!--Setting the expiration time of database connection,In seconds, If a database connection in the connection pool is idle longer than timeout time,It will be cleared from the connection pool --> <property name="c3p0.timeout">120</property> <!--Check free connections in all connection pools every 3000 seconds in seconds--> <property name="c3p0.idle_test_period">3000</property> <!-- Setting transaction isolation level --> <property name="hibernate.connection.isolation">4</property> <!-- Configuring the current thread-bound Session --> <property name="hibernate.current_session_context_class">thread</property> <!-- Configuration mapping file --> <mapping resource="com/itzhouq/hibernate/domain/Customer.hbm.xml"/> <mapping resource="com/itzhouq/hibernate/domain/LinkMan.hbm.xml"/> </session-factory> </hibernate-configuration>
2.6 Introducing Tool Classes and Logs
2.7 Writing Tests
package com.itzhouq.hibernate.demo; import org.hibernate.Session; import org.hibernate.Transaction; import org.junit.Test; import com.itzhouq.hibernate.domain.Customer; import com.itzhouq.hibernate.domain.LinkMan; import com.itzhouq.hibernate.utils.HibernateUtils; /* * One-to-many test classes */ public class Demo1 { @Test // Keep two contacts, three customers public void test() { Session session = HibernateUtils.getCurrentSession(); Transaction transaction = session.beginTransaction(); // Create two customers Customer customer1 = new Customer(); customer1.setCust_name("Wang Dong"); Customer customer2 = new Customer(); customer2.setCust_name("Li Xi"); // Create three contacts LinkMan linkMan1 = new LinkMan(); linkMan1.setLkm_name("Miss Luo Yu Feng"); LinkMan linkMan2 = new LinkMan(); linkMan2.setLkm_name("Flowery"); LinkMan linkMan3 = new LinkMan(); linkMan3.setLkm_name("Dong Dong Wang"); // set relationship linkMan1.setCustomer(customer1); linkMan2.setCustomer(customer1); linkMan3.setCustomer(customer2); customer1.getLinkMans().add(linkMan1); customer1.getLinkMans().add(linkMan2); customer2.getLinkMans().add(linkMan3); // Save data session.save(customer1); session.save(customer2); session.save(linkMan1); session.save(linkMan2); session.save(linkMan3); transaction.commit(); } }
2.8 One-to-many cascade operation
- Cascade: Cascade refers to whether an object will be operated on at the same time when it is operated on.
- Cascade is directional:
- When operating one party, whether to operate more than one party
- Whether to operate to one side when operating more than one side
2.8.1 Cascade Save or Delete
-
Customer Preservation, Cascade Contacts
- The main body of the operation is the customer object, which needs to be configured in Customer.hbm.xml
<!-- set Tags: * name: the attribute name of a collection of objects of more than one party * cascade: cascade --> <set name="linkMans" cascade="save-update"> <! - The name of the foreign key of the party with more than one column - > <key column="lkm_cust_id"></key> Class: The fully qualified name of a class of more than one party - > <one-to-many class="com.itzhouq.hibernate.domain.LinkMan"/> </set>
@Test /** * Cascade save or update operation * Save customer cascade contacts, the main body of the operation is the customer object, which needs to be configured in Customer.hbm.xml */ public void test2() { Session session = HibernateUtils.getCurrentSession(); Transaction transaction = session.beginTransaction(); Customer customer = new Customer(); customer.setCust_name("Zhao Hong"); LinkMan linkMan = new LinkMan(); linkMan.setLkm_name("Flowery"); customer.getLinkMans().add(linkMan); linkMan.setCustomer(customer); session.save(customer); transaction.commit(); }
-
Keep Contacts, Cascade Customers
-
The main body of the operation is the contact object, which needs to be configured in LinkMan.hbm.xml
<many-to-one name="customer" cascade="save-update" class="com.itzhouq.hibernate.domain.Customer" column="lkm_cust_id"/>@Test /** * Cascade save or update operation * Save cascading customer contacts. The main body of the operation is the customer object. It needs to be configured in LinkMan.hbm.xml. */ public void test2() { Session session = HibernateUtils.getCurrentSession(); Transaction transaction = session.beginTransaction(); Customer customer = new Customer(); customer.setCust_name("Zhao Bin"); LinkMan linkMan = new LinkMan(); linkMan.setLkm_name("civic"); customer.getLinkMans().add(linkMan); linkMan.setCustomer(customer); session.save(linkMan); transaction.commit(); }
-
-
Test Object Navigation
@Test /** * Navigation of Test Objects * Prerequisite: cascade="save-update" is set on both sides of one-to-many */ public void test3() { Session session = HibernateUtils.getCurrentSession(); Transaction transaction = session.beginTransaction(); Customer customer = new Customer(); customer.setCust_name("Zhao Bin"); LinkMan linkMan1 = new LinkMan(); linkMan1.setLkm_name("Miss Luo Yu Feng"); LinkMan linkMan2 = new LinkMan(); linkMan2.setLkm_name("Flowery"); LinkMan linkMan3 = new LinkMan(); linkMan3.setLkm_name("Lotus"); linkMan1.setCustomer(customer); customer.getLinkMans().add(linkMan2); customer.getLinkMans().add(linkMan3); // Both sides have cascade s //session.save(linkMan1); // Send several insert statements, four //session.save(customer); // Send several insert statements with three session.save(linkMan2); // Send several insert statements, one transaction.commit(); }
2.8.2 Cascade Delete
-
Cascade deletion: When the cascade deletes once, the other party's data is deleted at the same time.
-
Cascade deletion of contacts when deleting customers
-
The deleted principal is the customer and needs to be configured in Custoemr.hbm.xml
<set name="linkMans" cascade="save-update,delete"> <!-- column The name of the foreign key of more than one party --> <key column="lkm_cust_id"></key> <!-- class: Fully qualified names of classes of multiple parties --> <one-to-many class="com.itzhouq.hibernate.domain.LinkMan"/> </set>
@Test /** * cascading deletion * Delete customer cascade delete contacts, delete the main body is the customer, need to configure in Custoemr.hbm.xml */ public void test4() { Session session = HibernateUtils.getCurrentSession(); Transaction transaction = session.beginTransaction(); // No cascade is set, default: modify the contact's foreign key, delete the customer //Customer customer = session.get(Customer.class, 1L); //session.delete(customer); // Delete the customer and delete the contact <set name="linkMans" cascade="save-update, delete"> Customer customer = session.get(Customer.class, 1L); session.delete(customer); transaction.commit(); }
-
Delete Contacts Cascade Delete Clients (Basically Not Used)
Configuration of 2.8.3 inverse
-
Setting bidirectional associations to one-to-many generates redundant SQL statements
@Test /** * Change Contact No. 2 to Customer No. 2 instead of Contact No. 1 */ public void test5() { Session session = HibernateUtils.getCurrentSession(); Transaction transaction = session.beginTransaction(); // Query No. 2 Contacts LinkMan linkMan = session.get(LinkMan.class, 2L); //Query No. 2 Customer Customer customer = session.get(Customer.class, 2L); //Two-way Association linkMan.setCustomer(customer); customer.getLinkMans().add(linkMan); //Send two update statements and modify the foreign key twice //Automatic updating of persistent objects transaction.commit(); }
-
Analysis
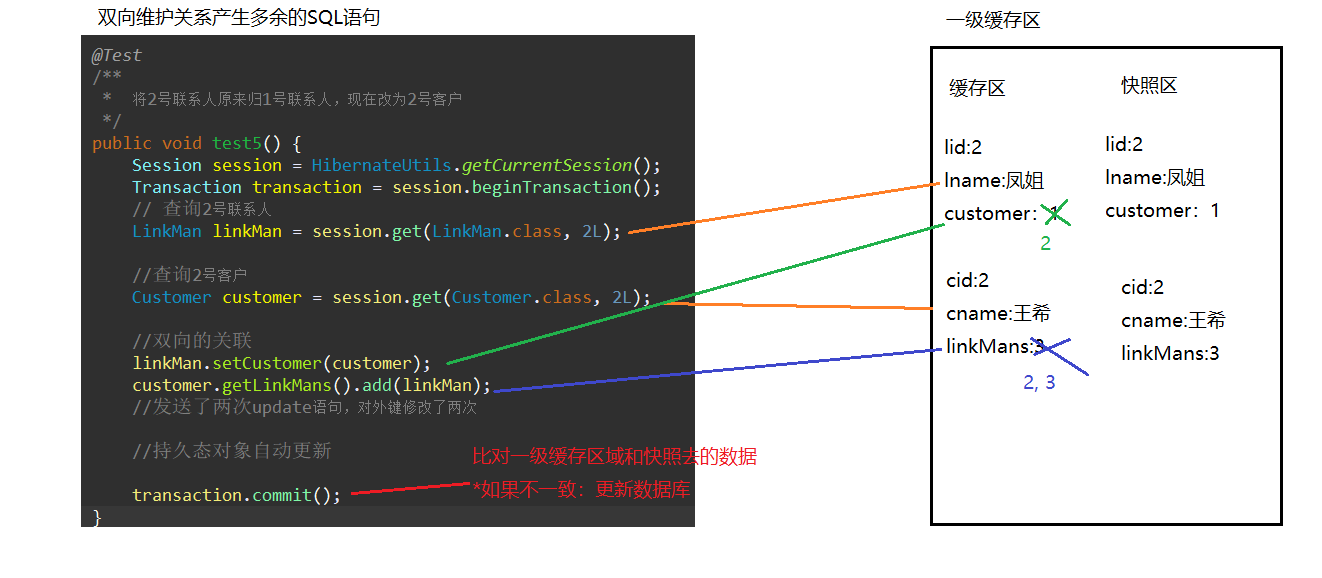
-
Resolve redundant SQL statements
- Unidirectional maintenance
- Cause one party to give up foreign key protection rights: one party to give up. Configure inverse="true" on the set in the configuration file Customer.hbm.xml
-
Distinguish cascade from inverse
-
The cascade operates on the associated objects, such as when the customer is stored in the database, the customer-associated contacts will also be stored in the database.
-
But is there any foreign key controlled by inverse?
@Test /** * Distinguishing the difference between cascade and inverse */ public void test6() { Session session = HibernateUtils.getCurrentSession(); Transaction transaction = session.beginTransaction(); Customer customer = new Customer(); customer.setCust_name("Li Bin"); LinkMan linkMan = new LinkMan(); linkMan.setLkm_name("Miss Luo Yu Feng"); customer.getLinkMans().add(linkMan); //Conditions are configured with cascade="save-update" inverse="true" in the set on Customer.hbm.xml session.save(customer); // The customer will insert back into the database, and the contact will insert into the database, but the foreign key is null. transaction.commit(); }
Customer.hbm.xml related configuration
<!-- set Tags: * name: the attribute name of a collection of objects of more than one party * cascade: cascade * inverse: Whether to abandon foreign key constraints, true means to abandon foreign key constraints --> <set name="linkMans" cascade="save-update,delete" inverse="true"> <! - The name of the foreign key of the party with more than one column - > <key column="lkm_cust_id"></key> Class: The fully qualified name of a class of more than one party - > <one-to-many class="com.itzhouq.hibernate.domain.LinkMan"/> </set>
-
3. Hibernate's many-to-many Association mappings
3.1 Configuration of Hibernate's many-to-many relationship
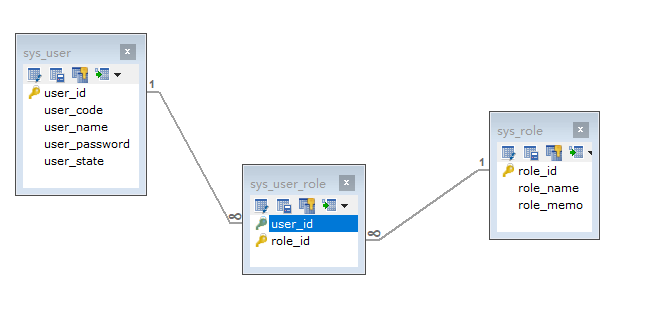
3.1.1 Create tables
- User table
CREATE TABLE `sys_user` ( `user_id` BIGINT(32) NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT COMMENT 'user id', `user_code` VARCHAR(32) COMMENT 'User account', `user_name` VARCHAR(64) COMMENT 'User name', `user_password` VARCHAR(32) COMMENT 'User password', `user_state` CHAR(1) COMMENT '1:normal,0:suspend', PRIMARY KEY (`user_id`) ) ENGINE=INNODB AUTO_INCREMENT=1 DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8;
- Role table
CREATE TABLE `sys_role` ( `role_id` BIGINT(32) NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT, `role_name` VARCHAR(32) COMMENT 'Role name', `role_memo` VARCHAR(128) DEFAULT NULL COMMENT 'Remarks', PRIMARY KEY (`role_id`) ) ENGINE=INNODB AUTO_INCREMENT=6 DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8;
- Intermediate table
CREATE TABLE `sys_user_role` ( `role_id` BIGINT(32) NOT NULL COMMENT 'role id', `user_id` BIGINT(32) NOT NULL COMMENT 'user id', PRIMARY KEY (`role_id`,`user_id`), KEY `FK_user_role_user_id` (`user_id`), CONSTRAINT `FK_user_role_role_id` FOREIGN KEY (`role_id`) REFERENCES `sys_role` (`role_id`) ON DELETE NO ACTION ON UPDATE NO ACTION, CONSTRAINT `FK_user_role_user_id` FOREIGN KEY (`user_id`) REFERENCES `sys_user` (`user_id`) ON DELETE NO ACTION ON UPDATE NO ACTION ) ENGINE=INNODB DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8;
3.1.2 Creating Entities
- User entity
public class User { private Long user_id; private String user_code; private String user_name; private String user_password; private String user_state; // Setting up many-to-many relationships: Indicates that a user chooses multiple roles // Place a collection of roles private Set<Role> roles = new HashSet<Role>(); //set/get method
- Role Entity Role
public class Role { private Long role_id; private String role_name; private String role_memo; // A role is selected by multiple users // Place a collection of users private Set<User> users = new HashSet<User>(); //set/get method
3.1.3 Create Maps
- User mapping User.hbm.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<!DOCTYPE hibernate-mapping PUBLIC
"-//Hibernate/Hibernate Mapping DTD 3.0//EN"
"http://www.hibernate.org/dtd/hibernate-mapping-3.0.dtd">
<hibernate-mapping>
<class name="com.itzhouq.hibernate.domain.User" table="sys_user">
Establishing Primary Key and OID Mapping
<id name="user_id" column="user_id">
<generator class="native"/>
</id>
<! - Establish mapping between common attributes and fields - >.
<property name="user_code" column="user_code"/>
<property name="user_name" column="user_name"/>
<property name="user_password" column="user_password"/>
<property name="user_state" column="user_state"/>
<! - Establish a mu lt i-to-many mapping relationship for roles - >
<!-- set
* name: The property name of the collection of the other party
* table: Many-to-many relationships require the use of intermediate tables, with the names of the intermediate tables.
-->
<set name="roles" table="sys_user_role">
<! -- The column in the key tag refers to the name of the foreign key of the middle table corresponding to the current object - >
Many-to-man tag:
* class: The full path of each other's class
* column: The name of the foreign key of the other party's object in the middle table
-->
<key column="user_id"/>
<many-to-many class="com.itzhouq.hibernate.domain.Role" column="role_id"/>
</set>
</class>
</hibernate-mapping>
- Role mapping. hbm. XML
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <!DOCTYPE hibernate-mapping PUBLIC "-//Hibernate/Hibernate Mapping DTD 3.0//EN" "http://www.hibernate.org/dtd/hibernate-mapping-3.0.dtd"> <hibernate-mapping> <class name="com.itzhouq.hibernate.domain.Role" table="sys_role"> <!-- Establishing Primary Key and OID Attribute --> <id name="role_id" column="role_id"> <generator class="native"/> </id> <!-- Mapping common attributes to fields--> <property name="role_name" column="role_name"/> <property name="role_memo" column="role_memo"/> <!--inverse="true",Role One side waived the right to maintain foreign keys. --> <set name="users" table="sys_user_role" inverse="true"> <key column="role_id"/> <many-to-many class="com.itzhouq.hibernate.domain.User" column="user_id"/> </set> </class> </hibernate-mapping>
3.1.4 Writing Test Classes
-
Introduce User.hbm.xml and Role.hbm.xml into the main configuration file
<!-- Configuration mapping file --> <mapping resource="com/itzhouq/hibernate/domain/User.hbm.xml"/> <mapping resource="com/itzhouq/hibernate/domain/Role.hbm.xml"/>
-
Test class
package com.itzhouq.hibernate.demo2; import org.hibernate.Session; import org.hibernate.Transaction; import org.junit.Test; import com.itzhouq.hibernate.domain.Role; import com.itzhouq.hibernate.domain.User; import com.itzhouq.hibernate.utils.HibernateUtils; /** * Hibernate Many-to-many mapping * @author itzhouq * */ public class Demo2 { @Test /* * Save multiple records: Save multiple users and roles */ public void test() { Session session = HibernateUtils.getCurrentSession(); Transaction transaction = session.beginTransaction(); // 1. Create two users User user1 = new User(); user1.setUser_name("Zhao Hong"); User user2 = new User(); user2.setUser_name("Li Bing"); // 2. Create three roles Role role1 = new Role(); role1.setRole_name("R & D department"); Role role2 = new Role(); role2.setRole_name("Marketing Department"); Role role3 = new Role(); role3.setRole_name("Public Relations Department"); // 3. Setting up bidirectional relationship user1.getRoles().add(role1); user1.getRoles().add(role2); user2.getRoles().add(role2); user2.getRoles().add(role3); role1.getUsers().add(user1); role2.getUsers().add(user1); role2.getUsers().add(user2); role3.getUsers().add(user2); // 4. Preservation: A bidirectional relationship between many-to-many must be forgiven by one party. // 5. Generally, the passive side abandons the foreign key maintenance role, and needs to configure inverse=true in the Role.hbm.xml file. // For example, when a student chooses a course, the course is chosen, so one side of the course abandons foreign key maintenance and needs to configure inverse=true in the course mapping file. session.save(user1); session.save(user2); session.save(role1); session.save(role2); session.save(role3); transaction.commit(); } }
-
Configuration in Role.hbm.xml file
<!--inverse="true",Role One side waived the right to maintain foreign keys. --> <set name="users" table="sys_user_role" inverse="true"> <key column="role_id"/> <many-to-many class="com.itzhouq.hibernate.domain.User" column="user_id"/> </set>
3.2 Hibernate's many-to-many operations
3.2.1 Is it OK to save only one side?
@Test /* * Many-to-many operation * Is it okay to save only one side? No, transient anomaly */ public void test2() { Session session = HibernateUtils.getCurrentSession(); Transaction transaction = session.beginTransaction(); // 1. Create a user User user1 = new User(); user1.setUser_name("Zhao Hong"); // 2. Create a role Role role1 = new Role(); role1.setRole_name("R & D department"); // 3. Setting up two-way relationship user1.getRoles().add(role1); role1.getUsers().add(user1); // 4. Save Users session.save(user1); transaction.commit(); }
3.2.2 Cascade Save or Update
@Test /* * Many-to-many operation * Multi-to-many cascade storage: * * Save user cascading save roles. The main body is the user. * * Configure cascade="save-update" on set in User.hbm.xml */ public void test3() { Session session = HibernateUtils.getCurrentSession(); Transaction transaction = session.beginTransaction(); // 1. Create a user User user1 = new User(); user1.setUser_name("Li Shimin"); // 2. Create a role Role role1 = new Role(); role1.setRole_name("Board of directors"); // 3. Setting up bidirectional relationship user1.getRoles().add(role1); role1.getUsers().add(user1); // 4. Save Users session.save(user1); transaction.commit(); }
3.2.3 Cascade Delete
- Query before cascading deletion
3.2.4 Other operations
-
Select roles for users
@Test /* * Select roles for users */ public void test4() { Session session = HibernateUtils.getCurrentSession(); Transaction transaction = session.beginTransaction(); // 1. Choose more Roles 3 for User 1 // 2. Query User No. 1 User user = session.get(User.class, 1L); // 3. Query Roles 3 Role role = session.get(Role.class, 3L); // 4. Choosing roles user.getRoles().add(role); transaction.commit(); }
- Note that the <property name="hibernate.hbm2ddl.auto">update</property> of the main configuration file needs to be set before modification.
-
Change roles for users
@Test /* * Change roles for users */ public void test5() { Session session = HibernateUtils.getCurrentSession(); Transaction transaction = session.beginTransaction(); // 1. Change User No. 2's original No. 3 role to No. 2 role // 2. Query User 2 User user = session.get(User.class, 2L); // 3. Query Roles 3 Role role3 = session.get(Role.class, 3L); // 4. Query 2 role Role role2 = session.get(Role.class, 2L); // 5. Changing Roles user.getRoles().remove(role3); user.getRoles().add(role2); transaction.commit(); }
-
Delete roles to users
@Test /* * Delete roles to users */ public void test6() { Session session = HibernateUtils.getCurrentSession(); Transaction transaction = session.beginTransaction(); // 1. Delete the role No. 1 of User No. 2 // 2. Query User 2 User user = session.get(User.class, 2L); // 3. Query role 1 Role role = session.get(Role.class, 1L); // 4. Delete roles user.getRoles().remove(role); transaction.commit(); }