Linked list: it is a kind of discontinuous storage structure in physical storage structure.
Schematic diagram of headless one-way acyclic chain list: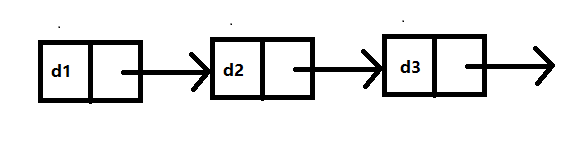
Next, we will implement such a headless one-way acyclic list.
1. head insertion
public void addFirst(int elem) {
LinkedNode node = new LinkedNode(elem); //Create a node
if(this.head == null) { //Empty linked list
this.head = node;
return;
}
node.next = head; //Not empty list, normal
this.head = node;
return;
}2. tail insertion method
public void addLast(int elem) {
LinkedNode node = new LinkedNode(elem);
if(this.head == null) { //Empty linked list
this.head = node;
return;
}
LinkedNode cur = this.head; //Create a node to find the last node if it is not empty
while (cur != null){ //At the end of the loop, cur points to the last node
cur = cur.next;
}
cur.next = node; //Place the inserted element after the last node
}3. Insert anywhere, the first data node is subscript 0
public void addIndex(int index,int elem) {
LinkedNode node = new LinkedNode(elem);
int len = size();
if(index < 0 || index > len) { //Verification of validity
return;
}
if(index == 0) { //Head insertion
addFirst(elem);
return;
}
if(index == len) { //Tail insertion
addLast(elem);
return;
}
LinkedNode prev = getIndexPos(index - 1); //Find where to insert
node.next = prev.next;
prev.next = node;
}How to calculate the length of the chain list:
public int size() {
int size = 0;
for(LinkedNode cur = this.head; cur != null; cur = cur.next) {
size++;
}
return size;
}To find a location in a linked list:
private LinkedNode getIndexPos(int index) {
LinkedNode cur = this.head;
for(int i = 0; i < index; i++){
cur = cur.next;
}
return cur;
}4. Check whether the keyword toFind is included in the single chain table
public boolean contains(int toFind) {
for(LinkedNode cur = this.head; cur != null; cur = cur.next) {
if(cur.data == toFind) {
return true;
}
}
return false;
}5. Delete the node with the first key
public void remove(int key) {
if(head == null) {
return;
}
if(head.data == key) {
this.head = this.head.next;
return;
}
LinkedNode prev = seachPrev(key);
LinkedNode nodeKey = prev.next;
prev.next = nodeKey.next;
}Before deleting, you should find the previous element to delete:
private LinkedNode seachPrev(int key){
if(this.head == null){
return null;
}
LinkedNode prev = this.head;
while (prev.next != null){
if(prev.next.data == key){
return prev;
}
prev = prev.next;
}
return null;
}6. Delete all nodes whose value is key
public void removeAllkey(int key){
if(head == null){
return;
}
LinkedNode prev = head;
LinkedNode cur = head.next;
while (cur != null){
if(cur.data == key){
prev.next = cur.next;
cur = prev.next;
} else {
prev = cur;
cur = cur.next;
}
}
if(this.head.data == key){
this.head = this.head.next;
}
return;
}7. Print single chain table
public void display(){
System.out.print("[");
for(LinkedNode node = this.head; node != null; node = node.next){
System.out.print(node.data);
if(node.next != null){
System.out.print(",");
}
}
System.out.println("]");
}8. Clear single chain table
public void clear(){
this.head = null;
}