Title:
M Fibonacci sequence F[n] is an integer sequence, which is defined as follows:
F[0] = a
F[1] = b
F[n] = F[n-1] * F[n-2] ( n > 1 )
Now given a, b, n, can you find the value of F[n]?
Input
The input contains multiple sets of test data
Each group of data takes up one row, including three integers a, b, n (0 < = a, b, n < = 10 ^ 9)
Output
For each group of test data, please output an integer F[n]. Because F[n] may be very large, you only need to output the value of F[n] after taking the module of 100000007, and each group of data output a row.
Sample Input
0 1 0 6 10 2
Sample Output
0 60
Idea: this problem uses Fermat's small theorem {if p is prime number and gcd(a,p)=1, then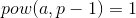 (mod p)}, so I've been stuck for a long time,,,
(mod p)}, so I've been stuck for a long time,,,
set up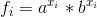 , easy to launch.
, easy to launch.
be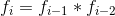
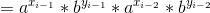
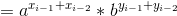
It can be seen that the index of a and B is Fibonacci series. When I do it, the index is mod 1 e 9 + 7.. Silly. Using Fermat's theorem, we can see that every 1e9+6 index will become 1, so the index is mod 1e9+6
After we get the exponent of ab, we can get the fast power
Code:
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
typedef long long ll;
#define maxn 10
#define mod 1000000007
///Matrix of n rows and m columns
struct AA
{
ll n,m,a[maxn][maxn];
void mem1()
{
memset(a,0,sizeof(a));///When n=m, initialize to unit matrix
for(int i=0;i<n;i++)
a[i][i]=1;
}
};
///aa matrix of n rows and m columns * bb matrix of M rows and k columns
AA mul(AA aa,AA bb,int n,int m,int kk)
{
AA cc;
cc.n=cc.m=2;
for(int i=0;i<n;i++)
{
for(int j=0;j<kk;j++)
{
int x=0;
for(int k=0;k<m;k++)
{
x+=(aa.a[i][k]*bb.a[k][j])%(mod-1);
x%=(mod-1);
}
cc.a[i][j]=x;
}
}
return cc;
}
///The m-power of the matrix aa
AA POW(AA aa,ll m)
{
AA d;d.n=d.m=2;
d.mem1();
while(m)
{
if(m&1)
{
d=mul(d,aa,2,2,2);
}
m/=2;
aa=mul(aa,aa,2,2,2);
}
return d;
}
ll pp(ll i,ll j)
{
ll zz=1;
while(j)
{
if(j&1) {zz*=i;zz%=mod;}
j/=2;
i*=i;
i%=mod;
}
return zz;
}
ll n,a,b,x,y;
int main()
{
while(~scanf("%lld%lld%lld",&a,&b,&n))
{
if(n==0)
{
printf("%lld\n",a%mod);
}
else if(n==1)
{
printf("%lld\n",b%mod);
}
else
{
AA aa,bb;aa.n=aa.m=2;
aa.a[0][0]=1;aa.a[0][1]=1;
aa.a[1][0]=1;aa.a[1][1]=0;
AA cc=POW(aa,n-1);
bb.a[0][0]=1;
bb.a[1][0]=0;
cc=mul(cc,bb,2,2,1);
printf("%lld\n",(pp(a,cc.a[1][0])*pp(b,cc.a[0][0]))%mod);
}
}
}