hadoop fs
hadoop fs -ls / hadoop fs -lsr hadoop fs -mkdir /user/hadoop hadoop fs -put a.txt /user/hadoop/ hadoop fs -get /user/hadoop/a.txt / hadoop fs -cp src dst hadoop fs -mv src dst hadoop fs -cat /user/hadoop/a.txt hadoop fs -rm /user/hadoop/a.txt hadoop fs -rmr /user/hadoop/a.txt hadoop fs -text /user/hadoop/a.txt hadoop fs -copyFromLocal localsrc dst # Similar to hadoop fs -put function hadoop fs -moveFromLocal localsrc dst # Upload local files to hdfs and delete local files at the same time
hadoop dfsadmin
# Reports basic and statistical information about the file system hadoop dfsadmin -report hadoop dfsadmin -safemode enter | leave | get | wait # Safe mode maintenance command. Security mode is a state of Namenode. In this state, Namenode # 1. Do not accept changes to the namespace (read-only) # 2. Do not copy or delete blocks # Namenode will automatically enter the safe mode at startup. When the configured minimum percentage of blocks meets the minimum number of copies condition, it will automatically leave the safe mode. The safe mode can be entered manually, but in this case, the safe mode must also be turned off manually.
hadoop fsck
Run the HDFS file system check tool.
hadoop fsck [GENERIC_OPTIONS] <path> [-move | -delete | -openforwrite] [-files [-blocks [-locations | -racks]]]
start-balancer.sh
Create code directory
Configure the host name Hadoop, sudo enter the password and add Hadoop to the end of the last line
sudo vim /etc/hosts # Add hadoop to the end of the last line. After modification, it is similar to: (use the tab key to add spaces) # 172.17.2.98 f738b9456777 hadoop ping hadoop
start-up
cd /app/hadoop-1.1.2/bin ./start-all.sh jps#Check the startup process to ensure that the node is started
Create myclass input directory
cd /app/hadoop-1.1.2/ rm -rf myclass input mkdir -p myclass input
Create an example file and upload it to HDFS
get into / app/hadoop-1.1.2/input Directory in which to create quangle.txt File.
cd /app/hadoop-1.1.2/input touch quangle.txt vi quangle.txt
The content is
On the top of the Crumpetty Tree The Quangle Wangle sat, But his face you could not see, On account of his Beaver Hat.
Create a directory in hdfs using the following command / class4
hadoop fs -mkdir /class4 hadoop fs -ls /
Upload the example file to hdfs / class4 Folder
cd /app/hadoop-1.1.2/input hadoop fs -copyFromLocal quangle.txt /class4/quangle.txt hadoop fs -ls /class4
Configure local environment
yes /app/hadoop-1.1.2/conf In the directory hadoop-env.sh Configure as follows:
cd /app/hadoop-1.1.2/conf sudo vi hadoop-env.sh
Join HADOOP_CLASSPATH variable with value / app/hadoop-1.1.2/myclass. After setting, compile the configuration file to make the configuration effective.
export HADOOP_CLASSPATH=/app/hadoop-1.1.2/myclass
Write code
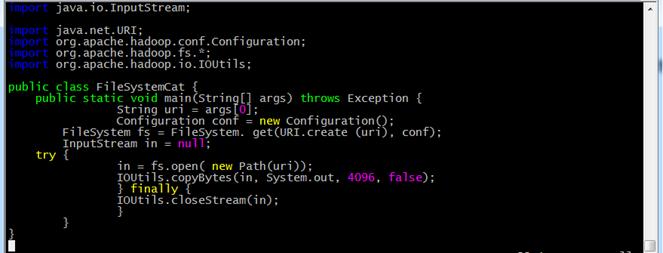
get into / app/hadoop-1.1.2/myclass Directory in which to create FileSystemCat.java Code file, the command is as follows:
cd /app/hadoop-1.1.2/myclass/ vi FileSystemCat.java
Enter code content:
Compile code
stay / app/hadoop-1.1.2/myclass Directory, compile the code with the following command:
javac -classpath ../hadoop-core-1.1.2.jar FileSystemCat.java
Reading HDFS files using compiled code
Use the following command to read the data in HDFS / class4/quangle.txt Content:
hadoop FileSystemCat /class4/quangle.txt
Generate a text file of about 100 bytes in the local file system, write a program to read the file and write its contents of 101-120 bytes into HDFS to become a new file.
//Note: please delete the Chinese notes before compiling!
import java.io.File;
import java.io.FileInputStream;
import java.io.FileOutputStream;
import java.io.OutputStream;
import java.net.URI;
import org.apache.hadoop.conf.Configuration;
import org.apache.hadoop.fs.FSDataInputStream;
import org.apache.hadoop.fs.FileSystem;
import org.apache.hadoop.fs.Path;
import org.apache.hadoop.io.IOUtils;
import org.apache.hadoop.util.Progressable;
public class LocalFile2Hdfs {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
// Get read source file and target file location parameters
String local = args[0];
String uri = args[1];
FileInputStream in = null;
OutputStream out = null;
Configuration conf = new Configuration();
try {
// Get read in file data
in = new FileInputStream(new File(local));
// Get target file information
FileSystem fs = FileSystem.get(URI.create(uri), conf);
out = fs.create(new Path(uri), new Progressable() {
@Override
public void progress() {
System.out.println("*");
}
});
// Skip the first 100 characters
in.skip(100);
byte[] buffer = new byte[20];
// Read 20 characters from the position of 101 into the buffer
int bytesRead = in.read(buffer);
if (bytesRead >= 0) {
out.write(buffer, 0, bytesRead);
}
} finally {
IOUtils.closeStream(in);
IOUtils.closeStream(out);
}
}
}Write code
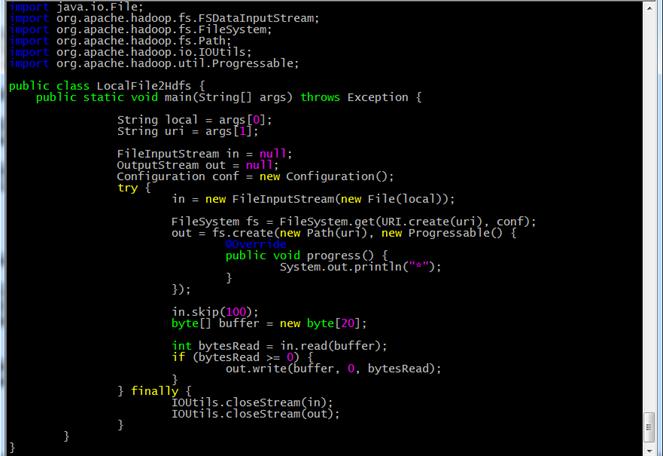
get into / app/hadoop-1.1.2/myclass Directory in which to create LocalFile2Hdfs.java Code file, the command is as follows
cd /app/hadoop-1.1.2/myclass/ vi LocalFile2Hdfs.java
Enter code content:
Compile code
stay / app/hadoop-1.1.2/myclass Directory, compile the code using the following command
javac -classpath ../hadoop-core-1.1.2.jar LocalFile2Hdfs.java
Establish test file
get into / app/hadoop-1.1.2/input Directory in which to create local2hdfs.txt File.
cd /app/hadoop-1.1.2/input/ vi local2hdfs.txt
The content is:
Washington (CNN) -- Twitter is suing the U.S. government in an effort to loosen restrictions on what the social media giant can say publicly about the national security-related requests it receives for user data. The company filed a lawsuit against the Justice Department on Monday in a federal court in northern California, arguing that its First Amendment rights are being violated by restrictions that forbid the disclosure of how many national security letters and Foreign Intelligence Surveillance Act court orders it receives -- even if that number is zero. Twitter vice president Ben Lee wrote in a blog post that it's suing in an effort to publish the full version of a "transparency report" prepared this year that includes those details. The San Francisco-based firm was unsatisfied with the Justice Department's move in January to allow technological firms to disclose the number of national security-related requests they receive in broad ranges.
Upload file contents to HDFS using compiled code
Use the following command to read the 101-120 bytes of local2hdfs and write it to HDFS to become a new file:
cd /app/hadoop-1.1.2/input hadoop LocalFile2Hdfs local2hdfs.txt /class4/local2hdfs_part.txt hadoop fs -ls /class4
Verify success
Use the following command to read local2hdfs_part.txt content
hadoop fs -cat /class4/local2hdfs_part.txt
In the reverse operation of experimental case 3, a text file of about 100 bytes is generated in HDFS, a program is written to read the file, and the contents of the 101st-120th bytes are written into the local file system to become a new file.
import java.io.File;
import java.io.FileInputStream;
import java.io.FileOutputStream;
import java.io.OutputStream;
import java.net.URI;
import org.apache.hadoop.conf.Configuration;
import org.apache.hadoop.fs.FSDataInputStream;
import org.apache.hadoop.fs.FileSystem;
import org.apache.hadoop.fs.Path;
import org.apache.hadoop.io.IOUtils;
public class Hdfs2LocalFile {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
String uri = args[0];
String local = args[1];
FSDataInputStream in = null;
OutputStream out = null;
Configuration conf = new Configuration();
try {
FileSystem fs = FileSystem.get(URI.create(uri), conf);
in = fs.open(new Path(uri));
out = new FileOutputStream(local);
byte[] buffer = new byte[20];
in.skip(100);
int bytesRead = in.read(buffer);
if (bytesRead >= 0) {
out.write(buffer, 0, bytesRead);
}
} finally {
IOUtils.closeStream(in);
IOUtils.closeStream(out);
}
}
}