Why use HBase?
Hbase is called Hadoop database. The design idea comes from the paper of bigtable (based on NoSQL database on GFS). HDFS supports the storage of massive data, does not support data modification (record level) and does not support immediate access to massive data. Generally, if you want to random read and write large amounts of data without considering time, you can cooperate with Map Reduce to realize ETL (time-consuming). Hbase is based on a NoSQL database on HDFS to realize random reading and writing of data on HDFS.
The relationship between HBase and HDFS?
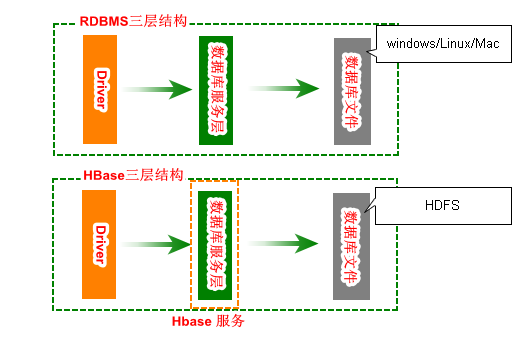
Hbase introduction
HBase is a distributed, extensible, column-oriented open source database. The technology comes from Fay Chang's Google paper Bigtable: A Distributed Storage System for Structured Data. Just as Bigtable takes advantage of the distributed data storage provided by the Google File System, HBase provides Bigtable-like capabilities on top of Hadoop. HBase is a subproject of Apache's Hadoop project. Unlike general relational databases, HBase is a database suitable for unstructured data storage. Another difference is that HBase is column-based rather than row-based. This project's goal is the hosting of very large tables -- billions of rows X millions of columns -- atop clustersof commodity hardware.
Hbase usage scenarios?
[First], make sure you have enough data.If you have hundreds of millions or billions of rows, then HBase is a goodcandidate.
[Second], make sure you can live withoutall the extra features that an RDBMS provides (e.g., typed columns, secondaryindexes, transactions, advanced query languages, etc.)
[Third], make sure you have enoughhardware. Even HDFS doesn't do well with anything less than 5 DataNodes (due tothings such as HDFS block replication which has a default of 3), plus aNameNode.
What is column-oriented storage
1. Row storage problem
RDBMS | 1. Sparse storage (disk) is not supported | |||||
test:t_user | ||||||
id | name | pwd | sex | info | … | |
1 | zs | *** | TRUE |
|
| |
2 | ls | *** |
|
|
| |
3 | ww | *** |
| XXX |
| |
test:t_user_base | test:t_user_info | ||||||
id | name | pwd | id | sex | info | … | |
1 | zs | *** | 1 | TRUE |
|
| |
2 | ls | *** | 3 |
| XXX |
| |
3 | ww | *** | |||||
|
Increase disk and IO utilization and increase table links select id,name from t_user where id =1 IO utilization is not high | |||||||
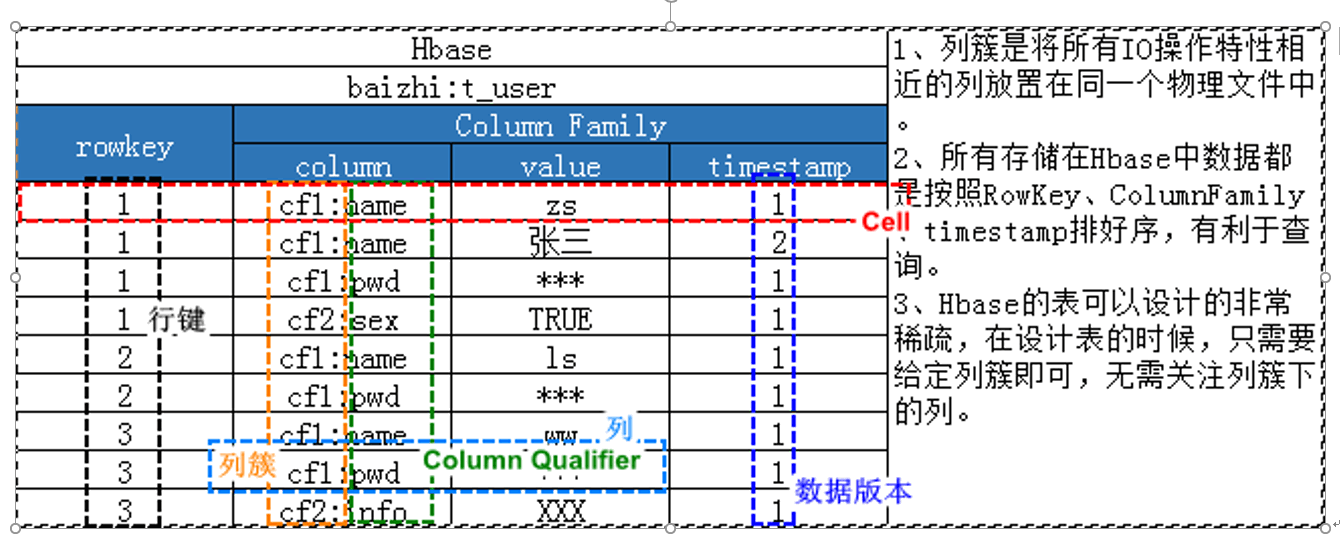
2. Column-oriented storage
Hbase | 1. Column cluster is to place all columns with similar IO operation characteristics in the same physical file. | |||
test:t_user | ||||
rowkey | Column Family | |||
column | value | timestamp | ||
1 | cf1:name | zs | 1 | |
1 | cf1:name | Zhang San | 2 | |
1 | cf1:pwd | *** | 1 | |
1 | cf2:sex | TRUE | 1 | |
2 | cf1:name | ls | 1 | |
2 | cf1:pwd | *** | 1 | |
3 | cf1:name | ww | 1 | |
3 | cf1:pwd | *** | 1 | |
3 | cf2:info | XXX | 1 | |
Noun interpretation
Construction of HBase Environment
1. Ensure that Hadoop's HDFS runs properly (omitted)
2. Start zookeeper (abbreviated)
3. Upload the Hbase installation package hbase-1.2.4-bin.tar.gz to decompress and configure HBASE_HOME in the / usr directory
[root@CentOS ~]# tar -zxf hbase-1.2.4-bin.tar.gz -C /usr/
[root@CentOS ~]# vim .bashrc HBASE_HOME=/usr/hbase-1.2.4 HADOOP_HOME=/usr/hadoop-2.6.0 JAVA_HOME=/usr/java/latest CLASSPATH=. PATH=$PATH:$JAVA_HOME/bin:$HADOOP_HOME/bin:$HADOOP_HOME/sbin:$HBASE_HOME/bin export JAVA_HOME export CLASSPATH export PATH export HADOOP_HOME export HBASE_HOME
[root@CentOS ~]# source .bashrc
4. Modify HBase configuration file hbase-site.xml
[root@CentOS ~]# vim /usr/hbase-1.2.4/conf/hbase-site.xml
<configuration> <property> <name>hbase.rootdir</name> <!-- and hdfs Consistent configuration --> <value>hdfs://CentOS:9000/hbase</value> </property> <property> <name>hbase.cluster.distributed</name> <value>true</value> </property> <property> <name>hbase.zookeeper.quorum</name> <value>CentOS</value> </property> <property> <name>hbase.zookeeper.property.clientPort</name> <value>2181</value> </property> </configuration>
5. Modify the region servers text file (to ensure consistency with the slaves file in hadoop)
[root@CentOS ~]# vim /usr/hbase-1.2.4/conf/regionservers CentOS
6. Modify the hbase-env.sh file
Using external zookeeper to manage cluster metadata
[root@CentOS ~]# vim /usr/hbase-1.2.4/conf/hbase-env.sh 127 # Tell HBase whether it should manage it's own instance of Zookeeper or not. 128 export HBASE_MANAGES_ZK=false
7. Start Close Hbase
[root@CentOS ~]# start|stop-hbase.sh starting master, logging to /usr/hbase-1.2.4/logs/hbase-root-master-CentOS.out CentOS: starting regionserver, logging to /usr/hbase-1.2.4/logs/hbase-root-regionserver-CentOS.out [root@CentOS ~]# jps 11971 NameNode 12750 Jps 1425 QuorumPeerMain 12536 HMaster 12659 HRegionServer 12054 DataNode 12255 SecondaryNameNode
Accessible: http://centos:16010/master-status#userTables
The Hbase shell command is basically used
1) Namespace operation (database operation)
2) Table operation
3) HBASE (Create Retrive update delete[ CRUD] ) DML
Enter the HBASE shell window
[root@CentOS ~]# hbase shell SLF4J: Class path contains multiple SLF4J bindings. SLF4J: Found binding in [jar:file:/usr/hbase-1.2.4/lib/slf4j-log4j12-1.7.5.jar!/org/slf4j/impl/StaticLoggerBinder.class] SLF4J: Found binding in [jar:file:/usr/hadoop-2.6.0/share/hadoop/common/lib/slf4j-log4j12-1.7.5.jar!/org/slf4j/impl/StaticLoggerBinder.class] SLF4J: See http://www.slf4j.org/codes.html#multiple_bindings for an explanation. SLF4J: Actual binding is of type [org.slf4j.impl.Log4jLoggerFactory] HBase Shell; enter 'help<RETURN>' for list of supported commands. Type "exit<RETURN>" to leave the HBase Shell Version 1.2.4, rUnknown, Wed Feb 15 18:58:00 CST 2017 hbase(main):001:0>
Note: Remove the use of ctrl+backspace from the hbase shell
- namespace (database operation):
2) create_namespace (create namespace)hbase(main):003:0> list_namespace NAMESPACE default hbase 2 row(s) in 1.1400 seconds
hbase(main):007:0> create_namespace 'test',{'creator'=>'jeffery'}
0 row(s) in 0.2650 secondshbase(main):008:0> describe_namespace 'test'
DESCRIPTION
{NAME => 'test', creator => 'jeffery'}
1 row(s) in 0.1760 secondshbase> alter_namespace 'namespace', {METHOD => 'set', 'PROPERTY_NAME' => 'PROPERTY_VALUE'}hbase> alter_namespace 'namespace', {METHOD => 'unset', NAME=>'PROPERTY_NAME'}hbase(main):009:0> alter_namespace 'test',{METHOD=>'set','creator'=>'tom'}
0 row(s) in 2.0060 secondshbase(main):010:0> describe_namespace 'test'
DESCRIPTION
{NAME => 'test', creator => 'tom'}
1 row(s) in 0.0420 secondsAdd an attribute
hbase(main):012:0> alter_namespace 'test',{METHOD=>'set','time'=>'2018-07-09'}
0 row(s) in 0.4710 seconds
hbase(main):013:0> describe_namespace 'test'
DESCRIPTION
{NAME => 'test', creator => 'tom', time => '2018-07-09'}
1 row(s) in 0.0230 secondshbase(main):015:0> alter_namespace 'test',{METHOD=>'unset',NAME=>'time'}
0 row(s) in 0.2440 seconds
hbase(main):016:0> describe_namespace 'test'
DESCRIPTION
{NAME => 'test', creator => 'tom'}
1 row(s) in 0.0340 seconds
hbase(main):017:0> drop_namespace 'test' 0 row(s) in 0.7570 seconds
- Table (table operation):
hbase(main):024:0> create 'test:t_user',{NAME=>'cf1',VERSIONS=>3},{NAME=>'cf2',VERSIONS=>3}
0 row(s) in 6.6200 seconds
=> Hbase::Table - test:t_user2) list (showing all user tables)hbase(main):025:0> create 'test:t_user2','cf1','cf2' 0 row(s) in 5.3320 seconds => Hbase::Table - test:t_user2
hbase(main):026:0> list TABLE test:t_user test:t_user2 2 row(s) in 0.5430 seconds => ["test:t_user", "test:t_user2"]
3) describe (view table)
hbase(main):027:0> describe 'test:t_user'
Table test:t_user is ENABLED
test:t_user
COLUMN FAMILIES DESCRIPTION
{NAME => 'cf1', DATA_BLOCK_ENCODING => 'NONE', BLOOMFILTER => 'ROW', REPLICATION_SCOPE => '0', VERSIONS => '3', COMPRESSION =>
'NONE', MIN_VERSIONS => '0', TTL => 'FOREVER', KEEP_DELETED_CELLS => 'FALSE', BLOCKSIZE => '65536', IN_MEMORY => 'false', BLOCK
CACHE => 'true'}
{NAME => 'cf2', DATA_BLOCK_ENCODING => 'NONE', BLOOMFILTER => 'ROW', REPLICATION_SCOPE => '0', VERSIONS => '3', COMPRESSION =>
'NONE', MIN_VERSIONS => '0', TTL => 'FOREVER', KEEP_DELETED_CELLS => 'FALSE', BLOCKSIZE => '65536', IN_MEMORY => 'false', BLOCK
CACHE => 'true'}
2 row(s) in 1.8370 seconds
hbase(main):028:0> describe 'test:t_user2'
Table test:t_user2 is ENABLED
test:t_user2
COLUMN FAMILIES DESCRIPTION
{NAME => 'cf1', DATA_BLOCK_ENCODING => 'NONE', BLOOMFILTER => 'ROW', REPLICATION_SCOPE => '0', VERSIONS => '1', COMPRESSION => '
NONE', MIN_VERSIONS => '0', TTL => 'FOREVER', KEEP_DELETED_CELLS => 'FALSE', BLOCKSIZE => '65536', IN_MEMORY => 'false', BLOCKCA
CHE => 'true'}
{NAME => 'cf2', DATA_BLOCK_ENCODING => 'NONE', BLOOMFILTER => 'ROW', REPLICATION_SCOPE => '0', VERSIONS => '1', COMPRESSION => '
NONE', MIN_VERSIONS => '0', TTL => 'FOREVER', KEEP_DELETED_CELLS => 'FALSE', BLOCKSIZE => '65536', IN_MEMORY => 'false', BLOCKCA
CHE => 'true'}
2 row(s) in 0.0940 secondshbase(main):030:0> disable 'test:t_user2' 0 row(s) in 14.1030 seconds
5) enable (start a disabled table)hbase(main):031:0> drop 'test:t_user2' 0 row(s) in 2.8550 seconds
hbase(main):032:0> enable 'test:t_user' 0 row(s) in 0.0470 seconds
hbase(main):033:0> is_enabled 'test:t_user' true 0 row(s) in 0.0400 seconds
6) Existence of exists judgment tablehbase(main):034:0> is_disabled 'test:t_user' false 0 row(s) in 0.0520 seconds
hbase(main):035:0> exists 'test:t_user' Table test:t_user does exist 0 row(s) in 0.0660 seconds
hbase(main):036:0> exists 'test:t_user2' Table test:t_user2 does not exist 0 row(s) in 0.0520 seconds
- data management
1) put (insert, update)
Syntax: put'ns:table','rowkey','cf:column',value,[ts]
If not, insert
hbase(main):043:0> put 'test:t_user','user:001','cf1:name','zhangsan' 0 row(s) in 0.0610 seconds
hbase(main):042:0> get 'test:t_user','user:001' COLUMN CELL cf1:name timestamp=1527399295854, value=zhangsan 1 row(s) in 0.4010 seconds
Cover data if it exists
hbase(main):043:0> put 'test:t_user','user:001','cf1:name','lisi' 0 row(s) in 0.0610 seconds
2) get (get a column data)hbase(main):044:0> get 'test:t_user','user:001' COLUMN CELL cf1:name timestamp=1527399460905, value=lisi 1 row(s) in 0.0850 seconds
Grammar: get'ns: table','rowkey'...
(1) Get a column data of the latest version
hbase(main):045:0> get 'test:t_user','user:001' COLUMN CELL cf1:name timestamp=1527399460905, value=lisi 1 row(s) in 0.9440 seconds
(2) TIMERANGE takes the data in the time stamp interval (left closed right open interval, left hour node, right large time node)
get 'test:t_user','user:001',{COLUMN=>'cf1',TIMERANGE=>[1527401460239,1527401478060],VERSIONS=>10}hbase(main):092:0> get 'test:t_user','user:001',{COLUMN=>'cf1',TIMERANGE=>[1527401460239,1527401478060],VERSIONS=>10}
COLUMN CELL
cf1:name timestamp=1527401471106, value=wangwu
cf1:name timestamp=1527401466085, value=lisi
cf1:name timestamp=1527401460239, value=zhangsan
3 row(s) in 0.0630 secondsNote: Use TIMERANGE with VERSIONS, otherwise you will get the latest data in the interval.
(3) Get column data of the latest two versions
hbase(main):095:0> get 'test:t_user','user:001',{COLUMN=>'cf1',VERSIONS=>2}
COLUMN CELL
cf1:name timestamp=1527401478060, value=zhaoliu
cf1:name timestamp=1527401471106, value=wangwu
2 row(s) in 0.2140 seconds(4) Get column data for specified timestamp
hbase(main):096:0> get 'test:t_user','user:001',{COLUMN=>'cf1',TIMESTAMP=>1527401471106}
COLUMN CELL
cf1:name timestamp=1527401471106, value=wangwu
1 row(s) in 0.8810 seconds(5) Getting multiple column data
Preparation data hbase(main):099:0> put 'test:t_user','user:001','cf1:age','10' 0 row(s) in 0.4190 seconds
hbase(main):102:0> get 'test:t_user','user:001',{COLUMN => ['cf1:age','cf1:name'],VERSIONS=>1}
COLUMN CELL
cf1:age timestamp=1527403480511, value=10
cf1:name timestamp=1527401478060, value=zhaoliu
2 row(s) in 0.1850 seconds3) scan (get a batch)
Obtain a batch of column data of the latest edition
hbase(main):105:0> scan 'test:t_user' ROW COLUMN+CELL user:001 column=cf1:age, timestamp=1527403480511, value=10 user:001 column=cf1:name, timestamp=1527401478060, value=zhaoliu 1 row(s) in 0.6840 seconds
(2) Paging for a batch of column data (LIMIT for several rowkeys, STARTROW for starting rowkeys)
Preparation data hbase(main):106:0> put 'test:t_user','user:002','cf1:name','jeffery' 0 row(s) in 0.3810 seconds
hbase(main):107:0> scan 'test:t_user', {COLUMNS => ['cf1'], LIMIT =>1, STARTROW => 'user:002'}
ROW COLUMN+CELL
user:002 column=cf1:name, timestamp=1527404037898, value=jeffery
1 row(s) in 0.3700 secondshbase(main):111:0> scan 'test:t_user', {COLUMNS => ['cf1'], LIMIT =>11, STARTROW => 'user:002',REVERSED => true}
ROW COLUMN+CELL
user:002 column=cf1:name, timestamp=1527404037898, value=jeffery
user:001 column=cf1:age, timestamp=1527403480511, value=10
user:001 column=cf1:name, timestamp=1527401478060, value=zhaoliu
2 row(s) in 0.5790 seconds4) delete (delete)
Pre-test data
hbase(main):113:0> get 'test:t_user','user:001',{COLUMN=>'cf1',VERSIONS=>10}
COLUMN CELL
cf1:age timestamp=1527403480511, value=10
cf1:name timestamp=1527401478060, value=zhaoliu
cf1:name timestamp=1527401471106, value=wangwu
cf1:name timestamp=1527401466085, value=lisi
cf1:name timestamp=1527401460239, value=zhangsan
5 row(s) in 0.1440 secondshbase(main):114:0> delete 'test:t_user','user:001','cf1:name',1527401460239 0 row(s) in 0.5630 seconds
hbase(main):115:0> get 'test:t_user','user:001',{COLUMN=>'cf1',VERSIONS=>10}
COLUMN CELL
cf1:age timestamp=1527403480511, value=10
cf1:name timestamp=1527401478060, value=zhaoliu
cf1:name timestamp=1527401471106, value=wangwu
cf1:name timestamp=1527401466085, value=lisi
4 row(s) in 4.9890 secondshbase(main):116:0> delete 'test:t_user','user:001','cf1:name' 0 row(s) in 0.4970 seconds
hbase(main):117:0> get 'test:t_user','user:001',{COLUMN=>'cf1',VERSIONS=>10}
COLUMN CELL
cf1:age timestamp=1527403480511, value=10
1 row(s) in 1.2470 second5) truncate (similar to RDBMS truncate statement, deleting all data quickly but retaining table structure)
hbase(main):118:0> truncate truncate truncate_preserve hbase(main):118:0> truncate 'test:t_user' Truncating 'test:t_user' table (it may take a while): - Disabling table... - Truncating table... 0 row(s) in 16.7690 seconds