Spring MVC is equivalent to spring+servlet
springBoot tends to be more annotated
We can learn from reading spring MVC source code:
Design patterns:
Singleton pattern
Factory model
Adapter mode
1. Spring IOC container (bean s), control inversion, dependency injection, the underlying equivalent of a HashMap
When we try the following action:
Object object = new Object();
spring puts the objects we create in a container, stores them in memory, and uses HashMap
Class <> clazz = class. forname ("class location")
All bean s will be placed in HashMap after successful startup
map.put("key","object")
IOC==Large MAP
War xxx.war -->.class
@Service
public class Aservice{
}
@Controller
public class Acontroller{
@Autowired
privite Aservice aservice;
}
tomcat: In the process of object.class startup, load the ioc container (Map object) -- instantiate all our declared annotated classes, such as the new object.
1)Aservice aservice = new Aservice();
2)Map.put("aservice",aservice)
3)Acontroller acontroller = new Acontroller();
4)Map.put("acontroller",acontroller)
5) Initialize Autowire to find in map
Aservice aservice = map.get("aservice") This process is dependency injection
Initialization of bean s during startup
tomcat Start Successfully - >
call
Definition of annotations:
@ Docunmented annotations are included in Java DOC
@ When does Retendion use this annotation source, class, runtime
@ Where is the Target annotation used?
@Inherited
Reflection mechanism:
1. Class <? > clazz = class. forname ("class location")
2.Aservice aservice =clazz.newInstance() Reflection creation instance
3. Class <?> clazz = aservice. getClass () Get the class by instance
4.Field[] fields = clazz.getDeclaredFields() Gets all the properties defined in the class
5.Medthod [] medthod = clazz.getMedthods() Gets all methods
6.medthod.invoke(a.args[])
7.request.getRequestURI() Gets the request path
Next, the focus is on the code:
I. Definition Notes
@Autowired in the spring framework
package supmain.annotation;
import java.lang.annotation.*;
@Target(ElementType.FIELD)
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Documented
public @interface SupmainAutowiredanno {
String value() default "";
}
@Controller
package supmain.annotation;
import java.lang.annotation.*;
@Target(ElementType.TYPE)
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Documented
public @interface SupmainControlleranno {
String value() default "";
}@RequrstMapping
package supmain.annotation;
import java.lang.annotation.*;
@Target({ElementType.METHOD,ElementType.TYPE})
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Documented
public @interface SupmainRequestmappinganno {
String value() default "";
}@RequestParam
package supmain.annotation;
import java.lang.annotation.*;
@Target(ElementType.PARAMETER)
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Documented
public @interface SupmainRequestParamanno{
String value() default "";
}@Service
package supmain.annotation;
import java.lang.annotation.*;
@Target(ElementType.TYPE)
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Documented
public @interface SupmainServiceanno {
String value() default "";
}The dao layer is too cumbersome to write here. After all, we can use the mybatis framework instead. That's another thing.
Direct Up service Layer
Simply define a service interface
package supmain.Service;
public interface SupmainService {
String query(String name ,String pwd);
}
Implementation class of service
package supmain.Service.impl;
import supmain.Service.SupmainService;
import supmain.annotation.SupmainServiceanno;
@SupmainServiceanno("SupmainServiceImpl")//When tomcat is started, map. put ("SupmainService Impl", new SupmainService Impl ()) is loaded.
public class SupmainServiceImpl implements SupmainService {
@Override
public String query(String name, String pwd) {
return "name ==== "+name+"pwd===="+pwd;
}
}Next comes the controller layer
package supmain.Controller;
import supmain.Service.SupmainService;
import supmain.annotation.SupmainAutowiredanno;
import supmain.annotation.SupmainControlleranno;
import supmain.annotation.SupmainRequestParamanno;
import supmain.annotation.SupmainRequestmappinganno;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletResponse;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.PrintWriter;
@SupmainControlleranno
@SupmainRequestmappinganno("/supmain")
public class SupmainController {
@SupmainAutowiredanno("SupmainServiceImpl") //map.get("SupmainServiceImpl")
private SupmainService supmainService;//The key used by spring MVC is supmainService
@SupmainRequestmappinganno("/query")
public void query(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response,
@SupmainRequestParamanno("name") String name,
@SupmainRequestParamanno("pwd")String pwd){
try {
PrintWriter writer = response.getWriter();
String str = supmainService.query(name,pwd);
writer.write(str);
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}Finally, the big meal arrived - you all know that the most important core part of Spring MVC is Dispatcher Servlet.
If you don't talk much about BB, here's the core code - - - - >>.
package supmain.servlet;
import supmain.Controller.SupmainController;
import supmain.annotation.*;
import javax.servlet.ServletConfig;
import javax.servlet.ServletException;
import javax.servlet.ServletRequest;
import javax.servlet.ServletResponse;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServlet;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletResponse;
import java.io.File;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.lang.annotation.Annotation;
import java.lang.reflect.Field;
import java.lang.reflect.InvocationTargetException;
import java.lang.reflect.Method;
import java.net.URL;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Map;
public class DispatcherServlet extends HttpServlet {
List<String> classnames = new ArrayList<String>();
//This is our IOC.
Map<String,Object> beans = new HashMap<String,Object>();
//init ensures that all classes are scanned at tomcat startup and bean map IOC is instantiated
//handerMap
Map<String,Object> handerMap = new HashMap<String,Object>();
public void init(ServletConfig servletConfig){
//1. Scan first
basePackageScan("supmain");
//2. Instantiate and create bean s
doInstance();
//3. Injection attributes
doAutowired();
//4. Mapping
doUrlMapping();
}
public void doUrlMapping(){
for (Map.Entry<String,Object> entry:beans.entrySet()){
Object instance = entry.getValue();
//Backstepping, in order to make logical judgments
Class<?> clazz = instance.getClass();
//Only control classes have mapping request paths
if (clazz.isAnnotationPresent(SupmainControlleranno.class)) {
//Get the value of the mapping annotation on the class
SupmainRequestmappinganno requestmappinganno1 = clazz.getAnnotation(SupmainRequestmappinganno.class);
String classPath = requestmappinganno1.value();
Method[] methods = clazz.getMethods();
for (Method method : methods){
if (method.isAnnotationPresent(SupmainRequestmappinganno.class)){
SupmainRequestmappinganno requestmappinganno2 = method.getAnnotation(SupmainRequestmappinganno.class);
String methodPath = requestmappinganno2.value();
String requestPath = classPath+methodPath;
handerMap.put(requestPath,method);
}else {
continue;
}
}
}else {
continue;
}
}
}
public void doAutowired(){
for (Map.Entry<String,Object> entry:beans.entrySet()){
Object instance = entry.getValue();
//Backstepping, in order to make logical judgments
Class<?> clazz = instance.getClass();
if (clazz.isAnnotationPresent(SupmainControlleranno.class)){
//Get all the variables.
Field[] fields = clazz.getDeclaredFields();
for (Field field :fields){
if (field.isAnnotationPresent(SupmainAutowiredanno.class)){
SupmainAutowiredanno autowiredanno = field.getAnnotation(SupmainAutowiredanno.class);
String key = autowiredanno.value();
//Get an object instance
Object bean = beans.get(key);
//Injection First Break Package
field.setAccessible(true);
try {
field.set(instance,bean);
} catch (IllegalAccessException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}else {
continue;
}
}
}else {
continue;
}
}
}
public void doInstance(){
for (String classname: classnames){
//Remove the suffix class
String cn = classname.replace(".class","");
//System.out.println(cn + "open short two doors v");
try {
Class<?> clazz = Class.forName(cn);
if (clazz.isAnnotationPresent(SupmainControlleranno.class)){
//control class
//Instance object
Object instance = clazz.newInstance();
//Get the comment object
SupmainRequestmappinganno requestmappinganno = clazz.getAnnotation(SupmainRequestmappinganno.class);
//Get the key in the comment
String key = requestmappinganno.value();
//Create a map
beans.put(key,instance);
}else if (clazz.isAnnotationPresent(SupmainServiceanno.class)){
//Service class
//Instance object
Object instance = clazz.newInstance();
//Get the comment object
SupmainServiceanno serviceanno = clazz.getAnnotation(SupmainServiceanno.class);
//Get the key in the comment
String key = serviceanno.value();
//Create a map
beans.put(key,instance);
}else {
continue;
}
} catch (ClassNotFoundException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}catch (InstantiationException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (IllegalAccessException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
private void basePackageScan(String basePackage){
//Scanning compiled class paths
URL url = this.getClass().getClassLoader().
getResource(basePackage.replaceAll("\\.","/"));
// System.out.println("milk greatly greatly greatly greatly greatly greatly greatly greatly greatly greatly greatly greatly Garda" +url);
String fileStr = url.getFile();
File file = new File(fileStr);
String [] fileStrs = file.list();
// System.out.println(fileStr+"dadadadadada");
for (String path:fileStrs){
//System.out.println("Hello, your path is 567 - --"+path);
File filepath =new File(fileStr+File.separator+path);
//System.out.println(filepath);
if (filepath.isDirectory()){
//System.out.println("Hello, your path is --"+basePackage+"."+path);
basePackageScan(basePackage+"."+path);
}else {
//System.out.println("Hello, your path is 123 - --"+basePackage +"."+path);
classnames.add(basePackage+"."+filepath.getName());
}
}
}
@Override
protected void doGet(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws ServletException, IOException {
this.doPost(req,resp);
}
@Override
protected void doPost(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws ServletException, IOException {
String url = req.getRequestURI();
//Get the context path
String context = req.getContextPath();
//Cut out the context path from the path
String path = url.replace(context,"");
//Get the method
Method method = (Method) handerMap.get(path);
SupmainController instance = (SupmainController) beans.get("/"+path.split("/")[1]);
Object[] args = hand(req,resp,method);
try {
method.invoke(instance,args);
} catch (IllegalAccessException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (InvocationTargetException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
private static Object[] hand(HttpServletRequest request,HttpServletResponse response,Method method){
//What parameters are available in the currently executed method?
Class<?>[] paramClazzs = method.getParameterTypes();
// System. out. println ("Data in paramClazzs is:"+paramClazzs.toString()));
//Depending on the number of parameters, an array of new parameters assigns all the parameters in the method to args
Object[] args = new Object[paramClazzs.length];
int args_i = 0;
int index = 0;
for (Class<?> paraClazz : paramClazzs){
System.out.println("paraClazz The data are as follows:"+paraClazz);
if (ServletRequest.class.isAssignableFrom(paraClazz)){
args[args_i++]=request;
}
if (ServletResponse.class.isAssignableFrom(paraClazz)){
args[args_i++]=response;
}
Annotation[] paramAns = method.getParameterAnnotations()[index];
if (paramAns.length>0){
for (Annotation paramAn:paramAns) {
if (SupmainRequestParamanno.class.isAssignableFrom(paramAn.getClass())) {
SupmainRequestParamanno requestParamanno = (SupmainRequestParamanno) paramAn;
args[args_i++] = request.getParameter(requestParamanno.value());
}
}
}
index++;
}
return args;
}
}
Finally, my code structure sketch is like this, you can directly copy the code according to my structure, should be able to use.
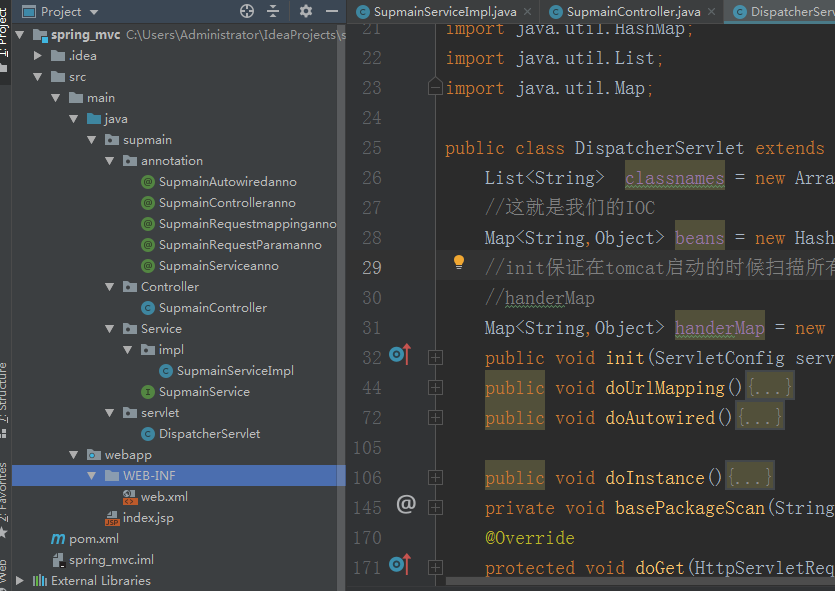
If this article can help you, I am very happy! Hee-hee...