Mapreedce (3)
Project address: https://github.com/KingBobTitan/hadoop.git
MR's Shuffle explanation and Join implementation
First, review
1. MapReduce's history monitoring service: JobHistoryServer
- Function: used to monitor the information of all MapReduce programs running on YARN
- Configure log aggregation of YARN: stored on hdfs
- Launch: web:19888
2. Custom data types: encapsulating JavaBean s in Hadoop
-
Encapsulation requires serialization
-
Implementation interface
- Writable: only serialization is implemented
- write: serialization
- readFields: deserialization
- Writablecompatible: implements serialization and comparator
- write: serialization
- readFields: deserialization
- compareTo: the method of comparison
- If the custom type will go through the shuffle process as a key, you need to implement the writablecompatible interface
- Writable: only serialization is implemented
-
Sorting: custom data types
-
First check whether there is a sorter. If there is one, use the sorter
job.setSortComaparator(RawComparator<T>) => extends WritableComparator
-
If not, the comparableTo of the type is called
-
If neither, it's a mistake
-
-
Sorting: default type: Text, IntWritable
- First check whether there is a sorter. If there is one, use the sorter
- If there is no sorter, a comparer of the default type is called
3. Basic Shuffle process
-
Input
- function
- Change all input data to KeyValue
- Split task: calculate task: slice: 100 pieces
- function
-
Map
- Function: sub
- Start MapTask according to the partition of Input, one partition corresponds to one MapTask
- Each MapTask will call the map method once for each keyvalue in its partition
- Implementation logic
- map method customization
- Function: sub
-
Shuffle
-
function
- Partition: if there are multiple reducers, it determines which one will process the current keyvalue
- Sorting: sorting key s according to the sorting rules
- Grouping: the value s of the same key are combined and put into an iterator, each with only one
-
Implementation logic
-
Partitions: default hash partitions
-
Custom: inherit partitioner < key, value >
getPartition(key,value,numReduceTask)
-
-
Sort: ascending by key dictionary by default
- User 1: define a sorter [highest priority]
- Custom 2: custom data type to implement writablecompatible
-
Group: group by key by default
-
-
-
Reduce
- Function: combination
- Merge the data output by shuffle
- Merge logic
- reduce method
- Function: combination
-
Output
- Output the result of Reduce and save it to the corresponding file system
- Default TextOutputFormat: key and value are tab separated
2, Course objectives
-
Detailed explanation of Shuffle process [key points]
-
Two optimizations in Shuffle
-
Join scheme in MapReduce [Master]
-
Read write database [understand]
3, Detailed explanation of Shuffle process
1, function
- partition
- sort
- Grouping
2, stage
-
Input
-
Input:
-
file1
hadoop hive hbase spark spark hadoop hadoop hadoop
-
file2
hue hive hive spark spark hadoop spark spark hbase
-
-
Functions: fragment and convert keyvalue
-
output
-
split1
key value 0 hadoop hive hbase spark spark 10 hadoop hadoop hadoop
-
split2
key value 0 hue hive hive spark spark 20 hadoop spark spark hbase
-
-
-
Map
-
Function: start the MapTask according to the number of slices, and then call the map method for the data in each MapTask
arr = value.toString.split(" ") for(word:arr){ this.outputKey(word) this.outputValue(1) context.write(key,value) } -
MapTask1
hadoop 1 hive 1 hbase 1 spark 1 spark 1 hadoop 1 hadoop 1 hadoop 1
-
MapTask2
hue 1 hive 1 hive 1 spark 1 spark 1 hadoop 1 spark 1 spark 1 hbase 1
-
-
Shuffle: partition, sort, group
-
Shuffle on the Map side: processing the result of Map
-
spill: over write [write data in memory to disk to file]
-
Each MapTask will put its own processing results into a circular memory buffer [100M]
-
When the buffer reaches 80%, overflow will be triggered, and all the data to be overflowed will be partitioned and sorted
-
Partition: by default, the partition is based on the hash redundancy of the key, and the essence is labeled
-
MapTask1: filea
hadoop 1 reduce1 hive 1 reduce2 hbase 1 reduce1 spark 1 reduce2
-
MapTask1: fileb
spark 1 reduce2 hadoop 1 reduce1 hadoop 1 reduce1 hadoop 1 reduce1
-
MapTask2: filea
hue 1 reduce1 hive 1 reduce2 hive 1 reduce2 spark 1 reduce2 spark 1 reduce2
-
MapTask2:fileb
hadoop 1 reduce1 spark 1 reduce2 spark 1 reduce2 hbase 1 reduce1
-
-
Sorting: call the sorter or compareTo method: implementation method: fast sorting
-
Not the whole batch data is globally ordered, but the same partition is internally ordered
-
MapTask1: filea
hadoop 1 reduce1 hbase 1 reduce1 hive 1 reduce2 spark 1 reduce2
-
MapTask1: fileb
spark 1 reduce2 hadoop 1 reduce1 hadoop 1 reduce1 hadoop 1 reduce1
-
MapTask2: filea
hue 1 reduce1 hive 1 reduce2 hive 1 reduce2 spark 1 reduce2 spark 1 reduce2
-
MapTask2:fileb
hadoop 1 reduce1 hbase 1 reduce1 spark 1 reduce2 spark 1 reduce2
-
-
-
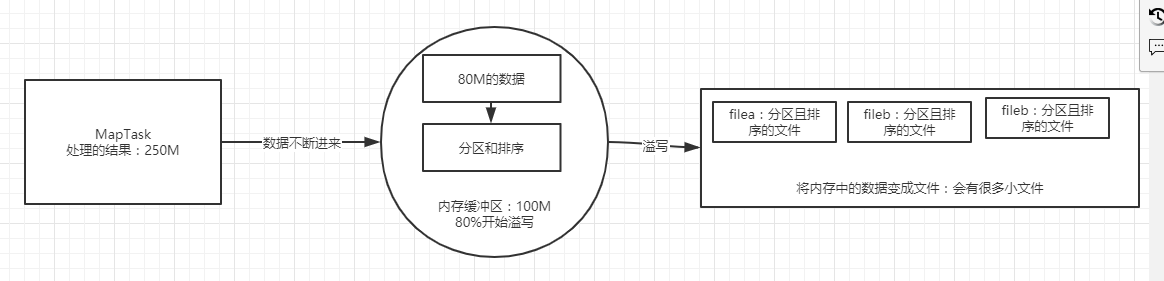
-
Merge: merge. Each MapTask will merge all the small files generated by itself to ensure that each MapTask has only one large file
-
Merge: and sort in the process of merge. The way to achieve this is to merge and sort. Only index is placed in memory
-
The sorting logic still calls the sorter or comparaTo
-
MapTask1
hadoop 1 reduce1 hadoop 1 reduce1 hadoop 1 reduce1 hadoop 1 reduce1 hbase 1 reduce1 hive 1 reduce2 spark 1 reduce2 spark 1 reduce2
-
MapTask2
hadoop 1 reduce1 hbase 1 reduce1 hue 1 reduce1 hive 1 reduce2 hive 1 reduce2 spark 1 reduce2 spark 1 reduce2 spark 1 reduce2 spark 1 reduce2
-
-
-
-
**shuffle on the Reduce side: * * give your results to Reduce
-
merge
-
==Pull: = = through Http protocol, each ReduceTask will get its own data from the results of each MapTask
-
reduceTask1
-
MapTask1
hadoop 1 hadoop 1 hadoop 1 hadoop 1 hbase 1
-
MapTask2
hadoop 1 hbase 1 hue 1
-
-
reduceTask2
-
MapTask1
hive 1 spark 1 spark 1
-
MapTask2
hive 1 hive 1 spark 1 spark 1 spark 1 spark 1
-
-
-
==Merge: = = sort also during merge: implementation method: merge sort [index only in memory]
-
The sorting logic still calls the sorter or comparaTo
-
reduceTask1
hadoop 1 hadoop 1 hadoop 1 hadoop 1 hadoop 1 hbase 1 hbase 1 hue 1
-
reduceTask2
hive 1 hive 1 hive 1 spark 1 spark 1 spark 1 spark 1 spark 1 spark 1
-
-
-
==group: = = merge the value s of the same key into the iterator
-
reduceTask1
hadoop 1,1,1,1,1 hbase 1,1 hue 1
-
reduceTask2
hive 1,1,1 spark 1,1,1,1,1,1
-
-
-
-
Reduce
-
Function: aggregate the results of Shuffle, and call the reduce method for each piece of data
reduce(key,Iterator<value>:values){ for(value:values){ sum+=value.get() } context.write(key,sum) } -
ReduceTask1
hadoop 5 hbase 2 hue 1
-
ReduceTask2
hive 3 spark 6
-
-
Output
-
part-r-00000
hadoop 5 hbase 2 hue 1
-
part-r-00001
hive 3 spark 6
-
3. Flow chart
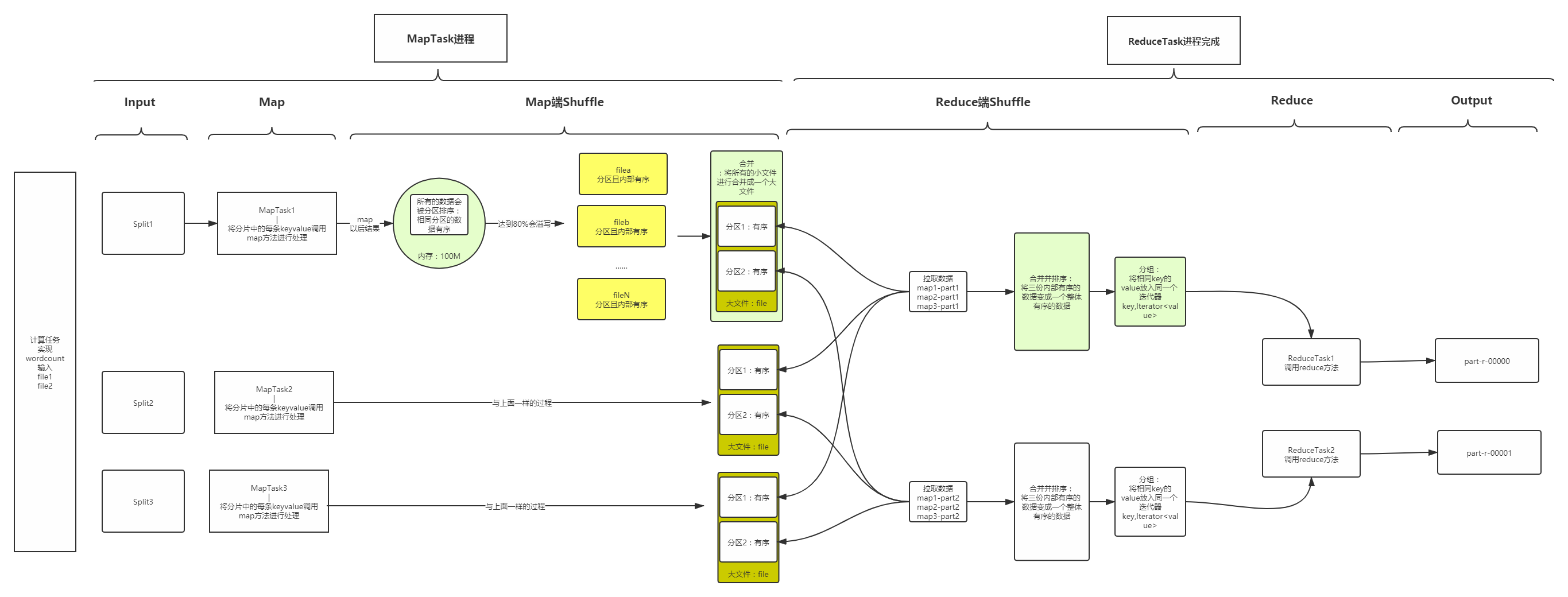
-
Shuffle
-
Process: distributed memory = > disk [do things that cannot be realized in memory] = > memory
-
map1:1 3 => 3 1
-
map2:4 5 => 5 4
-
map3:1 7 => 7 1
-
Requirements: Global reverse order
- Merge: disk: 3 1 5 4 7 1 = > 7 5 4 3 1 = > re read the global order into memory
-
-
4, Two optimizations in Shuffle
1. Combiner: aggregation on the Map side
-
Another function in the Shuffle process, which is off by default, needs to be set manually to enable
-
Not all programs can use Combiner
-
The procedure needs to meet certain conditions
(a+b) * c = a * c+b * c
-
-
Not a combiner
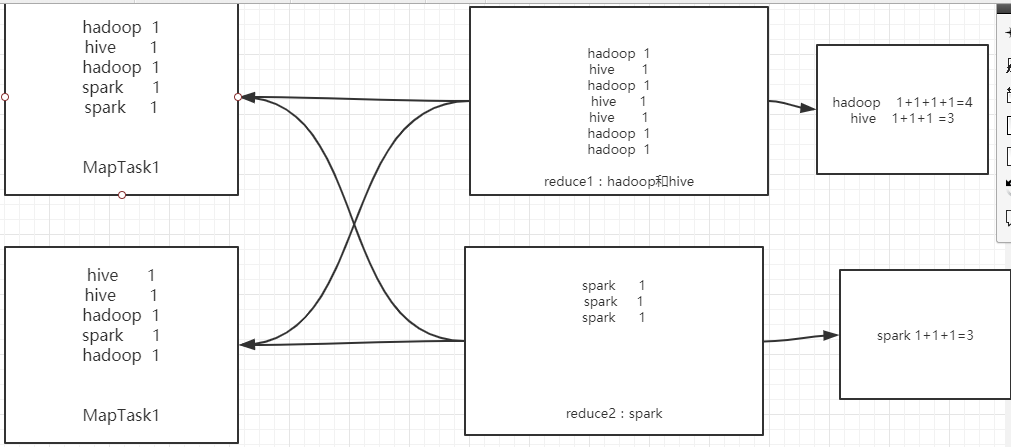
- Using combiner
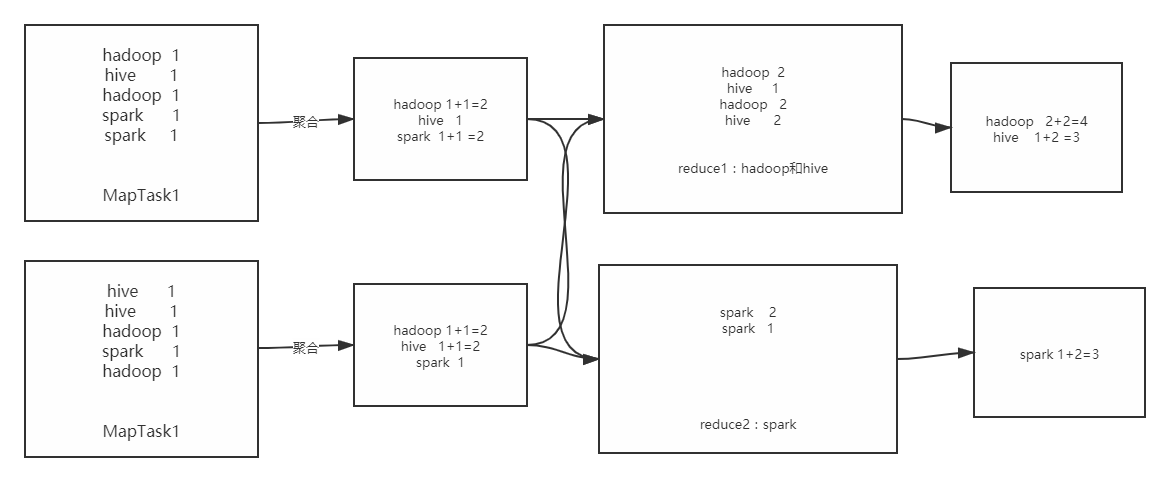
-
Main purpose
-
The number of concurrent maptasks is far greater than the number of Reduce
-
The logic of aggregation is partially completed by each Map, and then the final aggregation is done by Reduce to Reduce the load of Reduce
-
Official wordcount
-
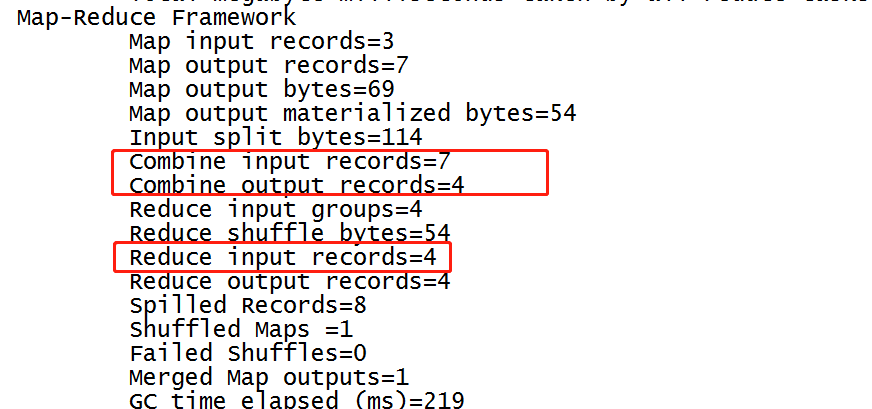
- wordcount developed by ourselves
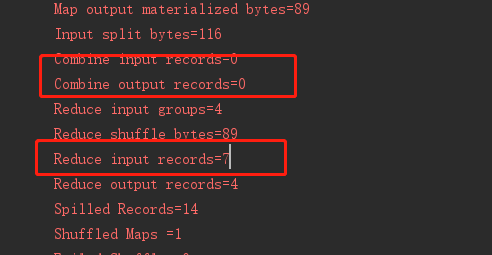
-
You can also enable Combiner when developing by yourself
job.setCombinerClass(WordCountReduce.class);//Set up Combiner
- The Combiner class is generally the Reducer class, and the aggregation logic is consistent
- If you can't tell whether the logic can be split, you can test
- Whether the two results are consistent
- Is the input type of Reduce consistent with the output type of Reduce
- Map output = > reduce input
- Combiner = Reducer
- Combine = > reduce input
2. Compress: compress
-
Compression type in life: zip/rar/7z
-
Compression type in big data: divisible compression type
- 300m = > compression = > 200m
- block1:128M => split1 => MapTask1[node01]
- block2:72M => split2 => MapTask2[node02]
- Type: snappy, lz4, lzo
-
Common compression choices
- Compression and decompression are relatively slow, the algorithm is very complex, but the compression ratio is high [size after compression / original size]
- Compression and decompression are faster, algorithm is simpler, but compression ratio is low
-
Advantage: compression in MapReduce
- Reduce disk and network IO, improve data transmission and storage efficiency
- Shuffle Write: 1t = > hard disk 1s / GB = > 1024s
- Compression: 1t = > compression = > 700g = > hard disk 1s / GB = > 700s + compression time = > 750S
- Shuffle Read: hard disk = > 1t = > 1024s
- Compression: = > hard disk = > 700g = > decompression 1s / GB = > 700s + decompression time = > 750S
- Shuffle Write: 1t = > hard disk 1s / GB = > 1024s
- Reduce disk and network IO, improve data transmission and storage efficiency
-
All the frameworks for storage and computing that I've learned in the future support compression
-
Location in MapReduce where data can be compressed
-
Input: MapReduce can read a compressed file as input [not used]
- The file type of data is determined by data generation
- MapReduce will read the compressed metadata when reading the compressed file
-
Compress in the Shuffle phase: compress the output of Map [main address]
#Enable compression mapreduce.map.output.compress=true #Specify the type of compression mapreduce.map.output.compress.codec=org.apache.hadoop.io.compress.Lz4Codec org.apache.hadoop.io.compress.Lz4Codec org.apache.hadoop.io.compress.SnappyCodec
-
How to modify a configuration
-
mapred-site.xml: always compress all programs
-
In MapReduce program: conf.set(key,value)
-
When running a submit command, you can specify parameters: temporary
yarn jar sougou.jar cn.itcast.hadoop.mapreduce.compress.HotKeyMR -Dmapreduce.map.output.compress=true -Dmapreduce.map.output.compress.codec=org.apache.hadoop.io.compress.Lz4Codec /app/sougou /app/output/sougou1
-
-
-
Output: MapReduce can output compressed file [less use]
mapreduce.output.fileoutputformat.compress=true mapreduce.output.fileoutputformat.compress.codec=org.apache.hadoop.io.compress.DefaultCodec
-
-
bin/hadoop checknative
hadoop: true /export/servers/hadoop-2.6.0-cdh5.14.0/lib/native/libhadoop.so.1.0.0 zlib: true /lib64/libz.so.1 snappy: true /usr/lib64/libsnappy.so.1 lz4: true revision:10301 bzip2: true /lib64/libbz2.so.1
-
Demonstration
-
Demand: count the number of times each search term appears
/** * @ClassName WordCount * @Description TODO Statistics of popular search terms based on Sogou data * @Date 2020/1/9 16:00 * @Create By Frank */ public class HotKeyMR extends Configured implements Tool { /** * Build a MapReduce program, configuration program and submission program * @param args * @return * @throws Exception */ @Override public int run(String[] args) throws Exception { /** * First: construct a MapReduce Job */ //Construct a job object Job job = Job.getInstance(this.getConf(),"mrword"); //Set the class the job runs job.setJarByClass(HotKeyMR.class); /** * Second: configure job */ //Input: set the input class and input path // job.setInputFormatClass(TextInputFormat.class); this is the default Path inputPath = new Path(args[0]);//Take the first parameter of the program as the input path TextInputFormat.setInputPaths(job,inputPath); //map job.setMapperClass(WordCountMapper.class);//Specify Mapper's class job.setMapOutputKeyClass(Text.class);//Specifies the type of key output by the map job.setMapOutputValueClass(IntWritable.class);//Specifies the value type of the map output //shuffle job.setCombinerClass(WordCountReduce.class);//Set up Combiner //reduce job.setReducerClass(WordCountReduce.class);//Specify the class of reduce job.setOutputKeyClass(Text.class);//Specify the key type of reduce output job.setOutputValueClass(IntWritable.class);//Specify the value type of the reduce output // job.setNumReduceTasks(1); / / this is the default //output // job.setOutputFormatClass(TextOutputFormat.class); / / this is the default output class Path outputPath = new Path(args[1]);//Use the second parameter of the program as the output path //Delete if output directory already exists FileSystem hdfs = FileSystem.get(this.getConf()); if(hdfs.exists(outputPath)){ hdfs.delete(outputPath,true); } //Set the output address TextOutputFormat.setOutputPath(job,outputPath); /** * Third: submit job */ //Submit the job to run, return the boolean value, return true for success and false for failure return job.waitForCompletion(true) ? 0 : -1; } /** * The entry of the whole program, which is responsible for calling the run method of the current class * @param args */ public static void main(String[] args) { //Construct a conf object to manage all the configuration of the current program Configuration conf = new Configuration(); //Configuration compression conf.set("mapreduce.map.output.compress","true"); conf.set("mapreduce.map.output.compress.codec","org.apache.hadoop.io.compress.Lz4Codec"); try { //Call the run method of the current class int status = ToolRunner.run(conf, new HotKeyMR(), args); //Exit according to the result of program operation System.exit(status); } catch (Exception e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } /** * Mapper Four generics, inputkey,inputValue,outputKey,outputValue * Generics of input: determined by the input class: TextInputFormat:Longwritable Text * Generics of output: determined by code logic: Text, IntWritable * Rewrite map method */ public static class WordCountMapper extends Mapper<LongWritable, Text,Text, IntWritable>{ //Construct key and value for output private Text outputKey = new Text(); private IntWritable outputValue = new IntWritable(1); /** * map Method: every keyvalue passed by Input calls the map method once * @param key: Current key * @param value: Current value * @param context: Context, responsible for outputting the new keyvalue * @throws IOException * @throws InterruptedException */ @Override protected void map(LongWritable key, Text value, Context context) throws IOException, InterruptedException { //Convert the contents of each line to String String line = value.toString(); //Split the contents of each line String[] words = line.split("\t"); //Take the second field, and the user's search term is the key this.outputKey.set(words[2]); //output context.write(this.outputKey,this.outputValue); } } /** * All Reduce needs to implement four generics * keyvalue of input: the keyvalue type of Map output * Output keyvalue: determined by code logic * Override reduce method */ public static class WordCountReduce extends Reducer<Text, IntWritable,Text, IntWritable>{ private IntWritable outputValue = new IntWritable(); /** * reduce Method, every keyvalue will call the reduce method once * @param key: key passed in * @param values: Iterator, all value s of the current key * @param context * @throws IOException * @throws InterruptedException */ @Override protected void reduce(Text key, Iterable<IntWritable> values, Context context) throws IOException, InterruptedException { //Take the value of the iterator for accumulation int sum = 0; for (IntWritable value : values) { sum += value.get(); } //value encapsulated as output this.outputValue.set(sum); //Output the result of each key context.write(key,outputValue); } } }
-
5, Join scheme in MapReduce
1,Reduce Join
-
join occurs on the reduce side
-
join in SQL
inner join: only when there are results on both sides left join: on the left, there will be right join: if there is one on the right, the result will be full join: on either side, the result is Select * from a join b = select * from a, B = > Cartesian product join: association of columns a id name age sex b id phone addr Query Zhang San's mobile number union: association of rows a id name age sex: Freshman data b id name age sex: sophomore data -
Demand: two pieces of data
-
Order data
1001,20150710,p0001,2 1002,20150710,p0002,3 1002,20150710,p0003,3 Order No., date, commodity id, commodity quantity
-
Commodity data
p0001, helicopter, 10002000 p0002, tank, 10003000 p0003, rocket, 100002000 Commodity id, commodity name, price, inventory
-
Association: get the product name of each order
100120150710, p0001,2 helicopter 100220150710, p0002,3 tank 100220150710, p0003,3 rocket
-
Analysis: MapReduce implementation
-
Step 1: results
- Include product name in addition to order data
-
Step 2: see if there is grouping or sorting
- Grouping: fields of a join
- key: Commodity id
-
Step 3: value
- For order data, other fields besides commodity id are value
- For commodity data, except for commodity id, only commodity name is required
-
Step 4: Verification
-
Input
1001,20150710,p0001,2 1002,20150710,p0002,3 1002,20150710,p0003,3 p0001, helicopter, 10002000 p0002, tank, 10003000 p0003, rocket, 100002000
-
map
- key: Commodity id
- value:
- If it is an order: order number, date, product quantity
- In case of commodity: commodity name
-
shuffle
-
Grouping
- All product and order data corresponding to the same product id are in one iterator
P0001 helicopter, 100120150710, p0001,2 P0002 tank, 100220150710, p0002,3 P0003 rocket, 100220150710, p0003,3
-
-
-
-
-
Realization
/** * @ClassName ReduceJoin * @Description TODO Reduce The process of implementing join * @Date 2020/1/9 17:25 * @Create By Frank */ public class ReduceJoin extends Configured implements Tool { /** * Specific definition of the whole MapReduce job: build, configure and submit * @param args * @return * @throws Exception */ @Override public int run(String[] args) throws Exception { /** * Build a job */ //Create an instance of a job Job job = Job.getInstance(this.getConf(),"mrjob"); //Set the class the job runs job.setJarByClass(ReduceJoin.class); /** * Configure job */ //Input: define the input mode and input path Path orderPath = new Path("datas/mrjoin/orders.txt"); Path productPath = new Path("datas/mrjoin/product.txt"); TextInputFormat.setInputPaths(job,orderPath,productPath); //Map: define the class and output type of map stage job.setMapperClass(MRJoinMapper.class); job.setMapOutputKeyClass(Text.class); job.setMapOutputValueClass(Text.class); //Shuffle: defines the class implemented in the shuffle phase //Reduce: define the class and output type of the reduce phase job.setReducerClass(MRJoinReduce.class); job.setOutputKeyClass(Text.class); job.setOutputValueClass(Text.class); job.setNumReduceTasks(1);//Set the number of Reduce, that is, the number of partitions //Output: defines the output class and output path Path outputPath = new Path("datas/output/join/reducejoin"); //Delete if output exists FileSystem hdfs = FileSystem.get(this.getConf()); if(hdfs.exists(outputPath)){ hdfs.delete(outputPath,true); } TextOutputFormat.setOutputPath(job,outputPath); /** * Submit job: and return according to the result of job running */ return job.waitForCompletion(true) ? 0:-1; } /** * Program entry * @param args * @throws Exception */ public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception { //Build a Conf object to manage all the configuration of the current program Configuration conf = new Configuration(); //Call the run method of the current class int status = ToolRunner.run(conf, new ReduceJoin(), args); //Exit the whole program according to the running state of the job System.exit(status); } /** * Define Mapper implementation class and processing logic in Map process */ public static class MRJoinMapper extends Mapper<LongWritable,Text,Text, Text>{ private Text outputKey = new Text(); private Text outputValue = new Text(); @Override protected void map(LongWritable key, Text value, Context context) throws IOException, InterruptedException { //First determine which file the current data is from FileSplit inputSplit = (FileSplit) context.getInputSplit();//First, obtain which file segments this data belongs to String fileName = inputSplit.getPath().getName();//Get file name //If it is order data, key is the third field and value is the other remaining fields if("orders.txt".equals(fileName)){ String[] items = value.toString().split(","); this.outputKey.set(items[2]);//Commodity id this.outputValue.set(items[0]+"\t"+items[1]+"\t"+items[3]);//Other fields context.write(this.outputKey,this.outputValue);//Output order data }else{ //If it is commodity data, key is the first field and value is the second field String[] split = value.toString().split(","); this.outputKey.set(split[0]);//Commodity id this.outputValue.set(split[1]);//Trade name context.write(this.outputKey,this.outputValue);//Export product data } } } /** * Define the implementation class of Reducer and the processing logic in the process of reduction */ public static class MRJoinReduce extends Reducer<Text,Text,Text,Text>{ private Text outputValue = new Text(); @Override protected void reduce(Text key, Iterable<Text> values, Context context) throws IOException, InterruptedException { StringBuilder stringBuilder = new StringBuilder(); for (Text value : values) { stringBuilder.append(value.toString()+"\t");//Splice the names of all products and all corresponding orders } this.outputValue.set(stringBuilder.toString());//Take product name and order as value context.write(key,this.outputValue); } } }
-
Application scenario
-
Big data join big data
-
Very inefficient comparison
-
Commodity data: 60000
-
Order data: 90000
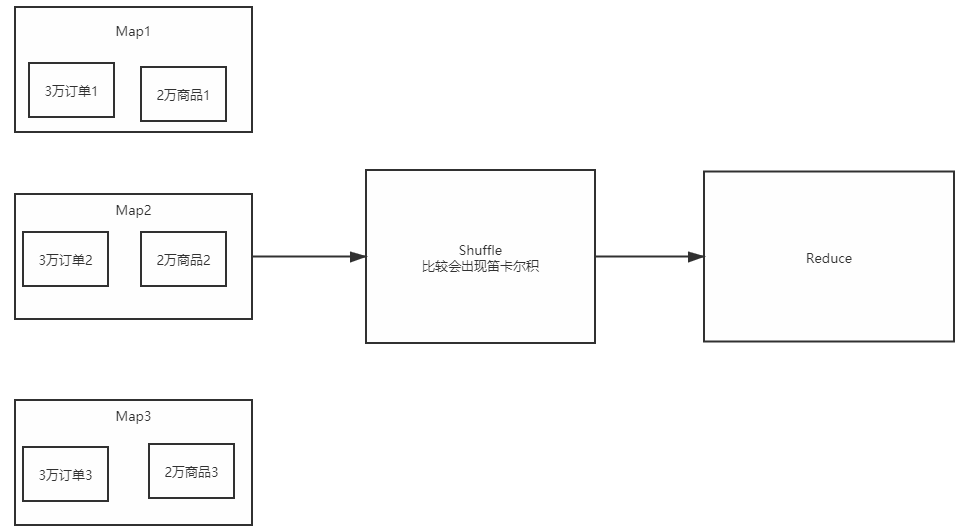
-
2,Map Join
-
Commodity data: 10000
-
Order data: 20 million
-
Small data join big data
-
==Idea: = = put the small data into the distributed cache. When each piece of big data needs to be used, take it directly from the distributed cache, and then complete the join directly on the Map side without shuffling
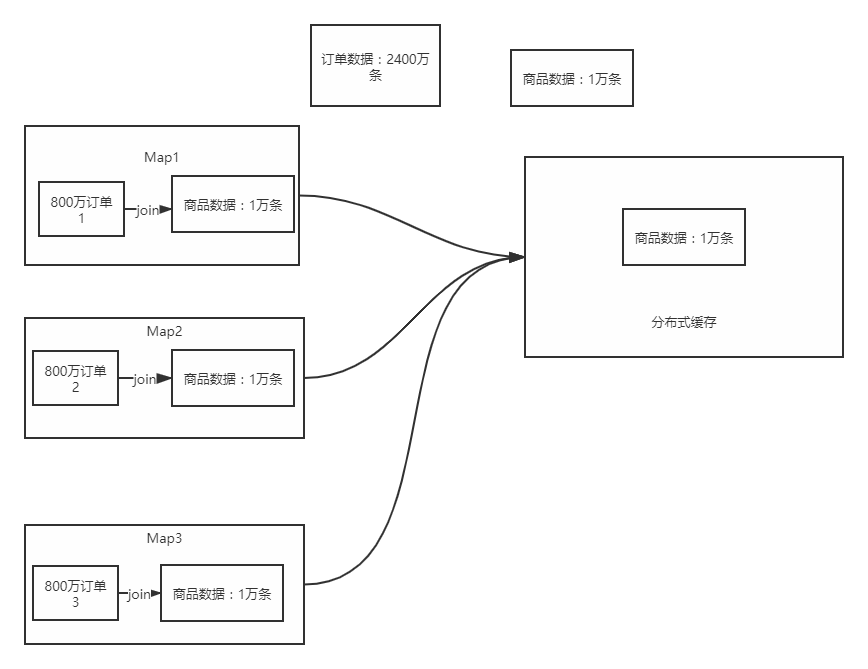
-
Realization
public class MapJoin extends Configured implements Tool { /** * Specific definition of the whole MapReduce job: build, configure and submit * @param args * @return * @throws Exception */ @Override public int run(String[] args) throws Exception { /** * Build a job */ //Create an instance of a job Job job = Job.getInstance(this.getConf(),"mrjob"); //Set the class the job runs job.setJarByClass(MapJoin.class); /** * Configure job */ //Input: define the input mode and input path Path orderPath = new Path("datas/mrjoin/orders.txt"); TextInputFormat.setInputPaths(job,orderPath); //Put product data into distributed cache Path productPath = new Path("datas/mrjoin/product.txt"); job.addCacheFile(productPath.toUri()); //Map: define the class and output type of map stage job.setMapperClass(MRJoinMapper.class); job.setMapOutputKeyClass(Text.class); job.setMapOutputValueClass(Text.class); //Shuffle: defines the class implemented in the shuffle phase //Reduce: define the class and output type of the reduce phase // job.setReducerClass(MRJoinReduce.class); // job.setOutputKeyClass(Text.class); // job.setOutputValueClass(Text.class); job.setNumReduceTasks(0);//Set the number of Reduce, that is, the number of partitions //Output: defines the output class and output path Path outputPath = new Path("datas/output/join/mapjoin"); //Delete if output exists FileSystem hdfs = FileSystem.get(this.getConf()); if(hdfs.exists(outputPath)){ hdfs.delete(outputPath,true); } TextOutputFormat.setOutputPath(job,outputPath); /** * Submit job: and return according to the result of job running */ return job.waitForCompletion(true) ? 0:-1; } /** * Program entry * @param args * @throws Exception */ public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception { //Build a Conf object to manage all the configuration of the current program Configuration conf = new Configuration(); //Call the run method of the current class int status = ToolRunner.run(conf, new MapJoin(), args); //Exit the whole program according to the running state of the job System.exit(status); } /** * Define Mapper implementation class and processing logic in Map process */ public static class MRJoinMapper extends Mapper<LongWritable,Text,Text, Text>{ private Text outputKey = new Text(); private Text outputValue = new Text(); Map<String,String> maps = new HashMap<>(); /** * Map And Reduce: three methods * 1-setup: It will be executed before the map or reduce method * 2-map/reduce: map Logic or reduce logic * 3-close: Final execution method * @param context * @throws IOException * @throws InterruptedException */ @Override protected void setup(Context context) throws IOException, InterruptedException { //Read data from distributed cache URI[] cacheFiles = context.getCacheFiles();//Get all cached data //Read file contents BufferedReader bufferedReader = new BufferedReader(new FileReader(cacheFiles[0].getPath())); String line = null; while(StringUtils.isNotBlank(line = bufferedReader.readLine())){ //Read to each line String pid = line.split(",")[0];//Commodity id String productName = line.split(",")[1];//Trade name //Put commodity id and name into map set maps.put(pid,productName); } } @Override protected void map(LongWritable key, Text value, Context context) throws IOException, InterruptedException { //Get order data String[] items = value.toString().split(","); String pid = items[2]; //Item id in order String productName = maps.get(pid); this.outputKey.set(productName); this.outputValue.set(value.toString()); context.write(this.outputKey,this.outputValue); } } /** * Define the implementation class of Reducer and the processing logic in the process of reduction */ public static class MRJoinReduce extends Reducer<Text,Text,Text,Text>{ private Text outputValue = new Text(); @Override protected void reduce(Text key, Iterable<Text> values, Context context) throws IOException, InterruptedException { StringBuilder stringBuilder = new StringBuilder(); for (Text value : values) { stringBuilder.append(value.toString()+"\t");//Splice the names of all products and all corresponding orders } this.outputValue.set(stringBuilder.toString());//Take product name and order as value context.write(key,this.outputValue); } } }
-
Application scenario
- Suitable for small data join large data scenario
6, Read write database
1. Input and Output
- Input: all input should inherit from InputFormat
- Default: textinputformat extensions fileinputformat extend inputformat
- file
- data base
- Output: all Input should inherit from OutputFormat
- Default: textoutputformat extensions fileoutputformat extensions outputformat
- file
- data base
- Database: JDBC
2, read MySQL
-
Modify the imported class
job.setInputFormatClass(DBInputFormat.class);
-
Customize a data type to receive data from MySQL
-
In addition to the implementation of Writable interface, DBWritable should also be implemented
public class DBReader implements Writable,DBWritable
-
Realize the serialization and deserialization of database objects
public void write(PreparedStatement statement) throws SQLException { // TODO Auto-generated method stub statement.setString(1, word); statement.setInt(2,number); } public void readFields(ResultSet resultSet) throws SQLException { // TODO Auto-generated method stub this.word = resultSet.getString(1); this.number = resultSet.getInt(2); }
-
-
After creating the conf object, you should immediately configure the jdbc connection parameters
Configuration conf = new Configuration(); DBConfiguration.configureDB( conf, "com.mysql.jdbc.Driver", "jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/test", "root", "123456" ); -
Configure read data: tables, SQL statements, fields
DBInputFormat.setInput( job, DBReader.class, //Object to store read results "wcresult", //Indicate null, //Filter condition "number",//Sorted fields fields //Which fields to read ); public static void setInput( Job job, Class<? extends DBWritable> inputClass, //Object to store read results String inputQuery, //SQL statement, the fields returned in the SQL statement must be consistent with the inputClass property String inputCountQuery ) { }
2, write MySQL
-
Configure the output class
job.setOutputFormatClass(DBOutputFormat.class);
-
Configure output parameters: table, field
DBOutputFormat.setOutput(job, "wcresult", fields);
-
The object that the program will output the key to MySQL must implement the DBWritable interface [serialization method]
public static class WriteMap extends Mapper<LongWritable, Text, DBReader, NullWritable>{ private DBReader outputKey = new DBReader(); private NullWritable outputValue = NullWritable.get(); @Override protected void map(LongWritable key, Text value, Context context) throws IOException, InterruptedException { // TODO Auto-generated method stub String line = value.toString(); this.outputKey.setWord(line.split("\t")[0]); this.outputKey.setNumber(Integer.valueOf(line.split("\t")[1])); context.write(outputKey, outputValue); } }

