Introduction to hadoop
Hadoop is a distributed system infrastructure developed by the Apache Foundation. Users can develop distributed programs without knowing the underlying details of the distribution. Take full advantage of the power of clusters for high-speed operations and storage. Hadoop implements a Distributed File System, one of which is HDFS (Hadoop Distributed File System).HDFS is fault-tolerant and is designed to be deployed on low-cost hardware; and it provides high throughput to access application data for applications with large data set s. HDFS relax es POSIX requirements and streaming access Data in the file system.
The core design of Hadoop's framework is HDFS and MapReduce, which provides storage for massive amounts of data while MapReduce provides calculation for massive amounts of data.
Hadoop main modules:
- hadoop Common: Includes commonly used Hadoop tool classes, including system configuration tool Configuration, remote procedure call RPC, serialization mechanism, and Hadoop Abstract file system FileSystem.
- Hadoop Distributed File System (HDFS): A distributed file system that provides high throughput, scalability, and fault-tolerant access to application data.
- Hadoop YARN: Task scheduling and cluster resource management.
- Hadoop MapReduce: A large data set parallel processing system based on YARN. It is a computational model for large data volumes.
hadoop installation
Official hadoop documentation:
https://hadoop.apache.org/docs/stable/hadoop-project-dist/hadoop-common/SingleCluster.html
Prepare the hadoop installation package and jdk source tar package first
 Create user hadoop and set password
Create user hadoop and set password
useradd hadoop echo westos | passwd --stdin hadoop

Move rpm and tar packages to hadoop's home directory, switch to Hadoop users, and unzip and create soft links to upgrade and update versions
mv * /home/hadoop/ su - hadoop tar zxf jdk-8u181-linux-x64.tar.gz tar zxf hadoop-3.2.1.tar.gz ls ln -s jdk1.8.0_181/ java ln -s hadoop-3.2.1/ hadoop
Enter the default configuration directory for hadoop
cd hadoop/etc/hadoop/
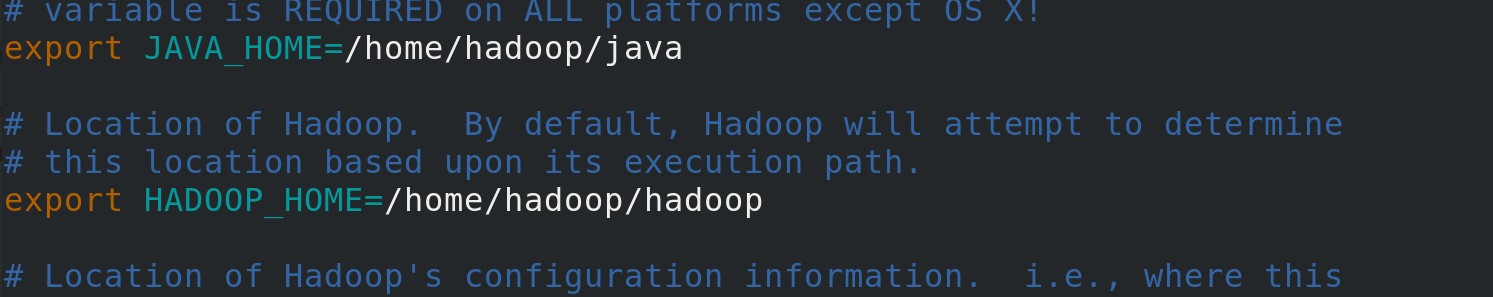
Modify environment variables to specify java and hadoop home directories
vim hadoop-env.sh
Standalone Operation (single machine mode)
Return to the hadoop soft connection directory, create the input directory, copy the xml file suffix of the default profile directory to the input directory, use the jar command to filter the contents of the input directory file starting with dfs, and automatically create the output directory
mkdir input cp etc/hadoop/*.xml input bin/hadoop jar share/hadoop/mapreduce/hadoop-mapreduce-examples-3.2.1.jar grep input output 'dfs[a-z.]+'
View filtered information
[hadoop@server1 hadoop]$ cat output/* 1 dfsadmin
Pseudo-Distributed Operation (pseudo-distributed deployment)
Hadoop can also run on a single node in pseudo-distributed mode, where each Hadoop daemon runs in a separate Java process.
Enter the hadoop soft connection directory
Viewing workers is native
cat etc/hadoop/workers

Modify Profile
Set Native as master
vim etc/hadoop/core-site.xml
<configuration>
<property>
<name>fs.defaultFS</name>
<value>hdfs://localhost:9000</value>
</property>
</configuration>
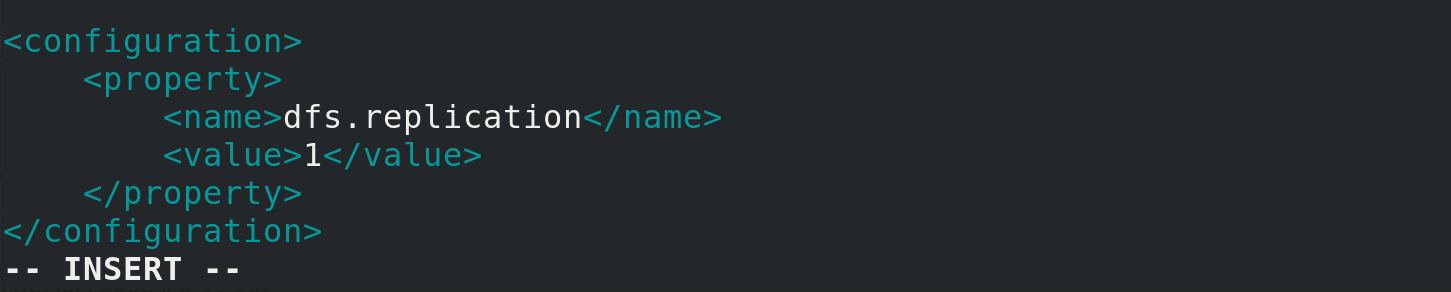
 Set the number of distributed copies to 1, defaulting to 3
Set the number of distributed copies to 1, defaulting to 3
vim etc/hadoop/hdfs-site.xml
<configuration>
<property>
<name>dfs.replication</name>
<value>1</value>
</property>
</configuration>
Now check if you can use ssh to connect to the local host without a passphrase. We need to do a secret-free login
ssh-keygen ssh-copy-id localhost #Password is user hadoop's password ssh localhost #Secret-free login if no password is required exit #Exit ssh with exit, otherwise the shell will be overlaid, causing confusion
Format File System
bin/hdfs namenode -format
Start the NameNode daemon and the DataNode daemon
sbin/start-dfs.sh
jps is a gadget provided by jdk to view the current java process
jps / bin in soft-connected java directory
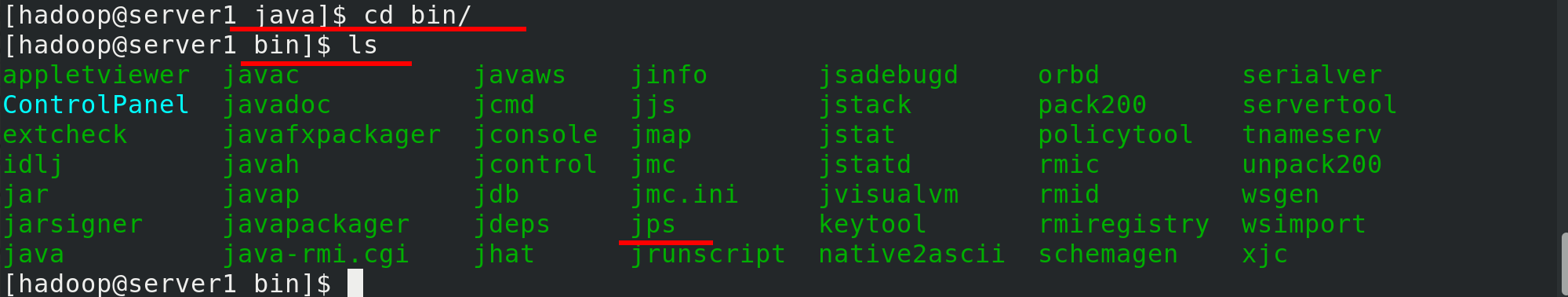 Write environment variables
Write environment variables
vim ~/.bash_profile
Because our Java soft connection directory is in the user's home directory, $HOME/java/bin directly
 Apply the following environment variables and view the java process
Apply the following environment variables and view the java process
source ~/.bash_profile jps
You can see that both the NameNode daemon and the DataNode daemon are open
 Browse NameNode's web interface, which opens port 9870 by default
Browse NameNode's web interface, which opens port 9870 by default
Visit:
172.25.21.1:9870
You can see that the main port of matser is 9000
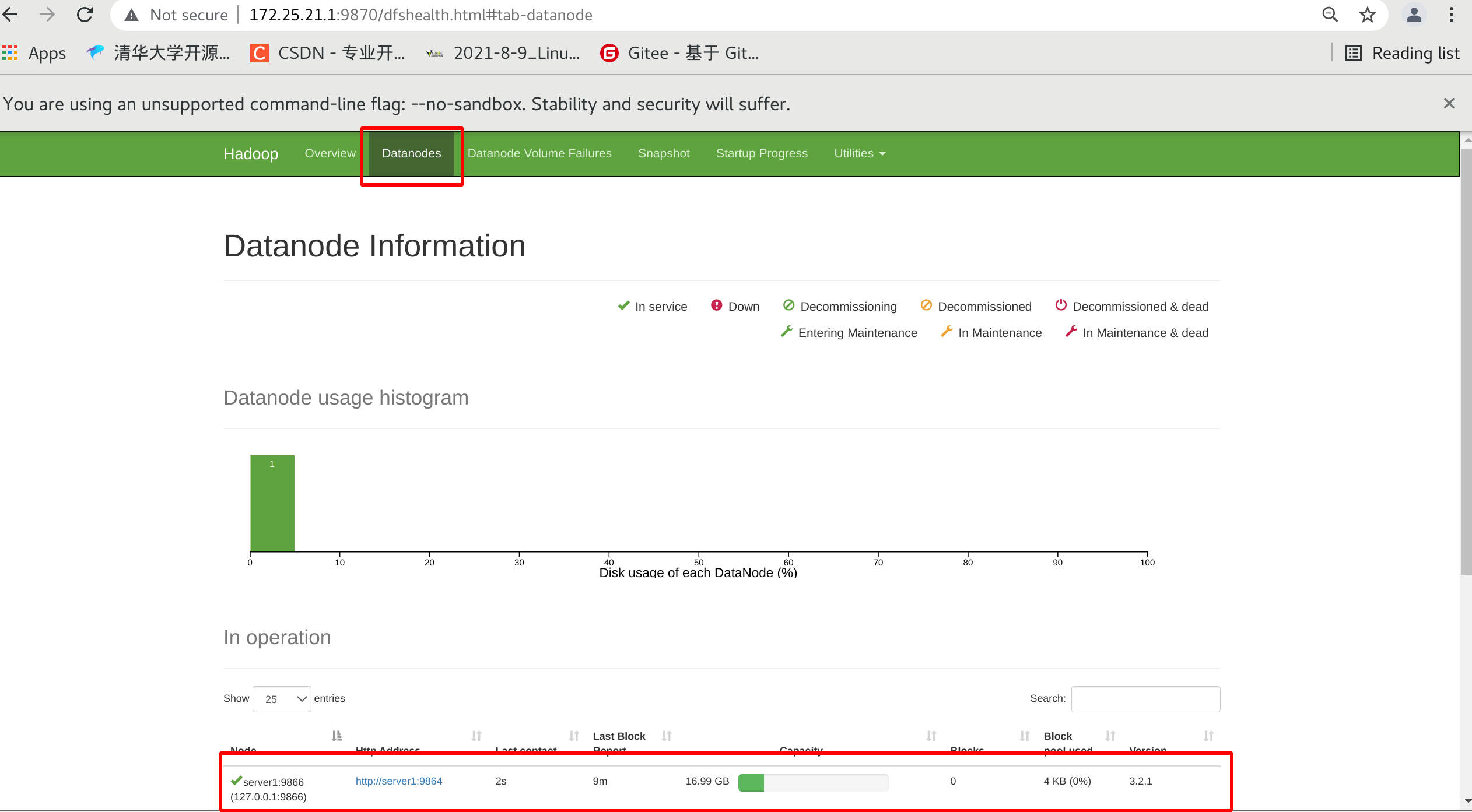
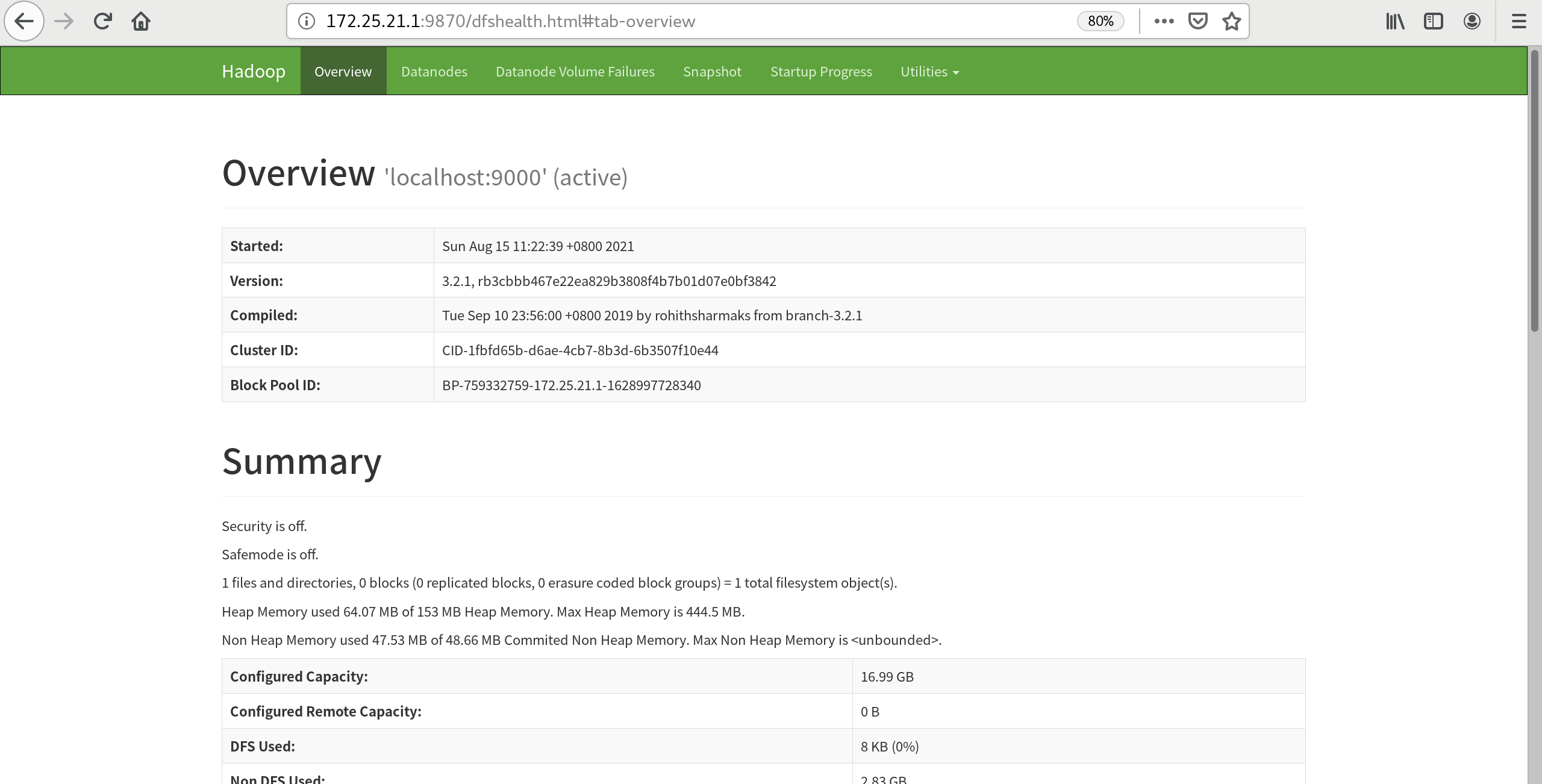 You can also see that the datanode host is listening on port 9866 at this time
You can also see that the datanode host is listening on port 9866 at this time
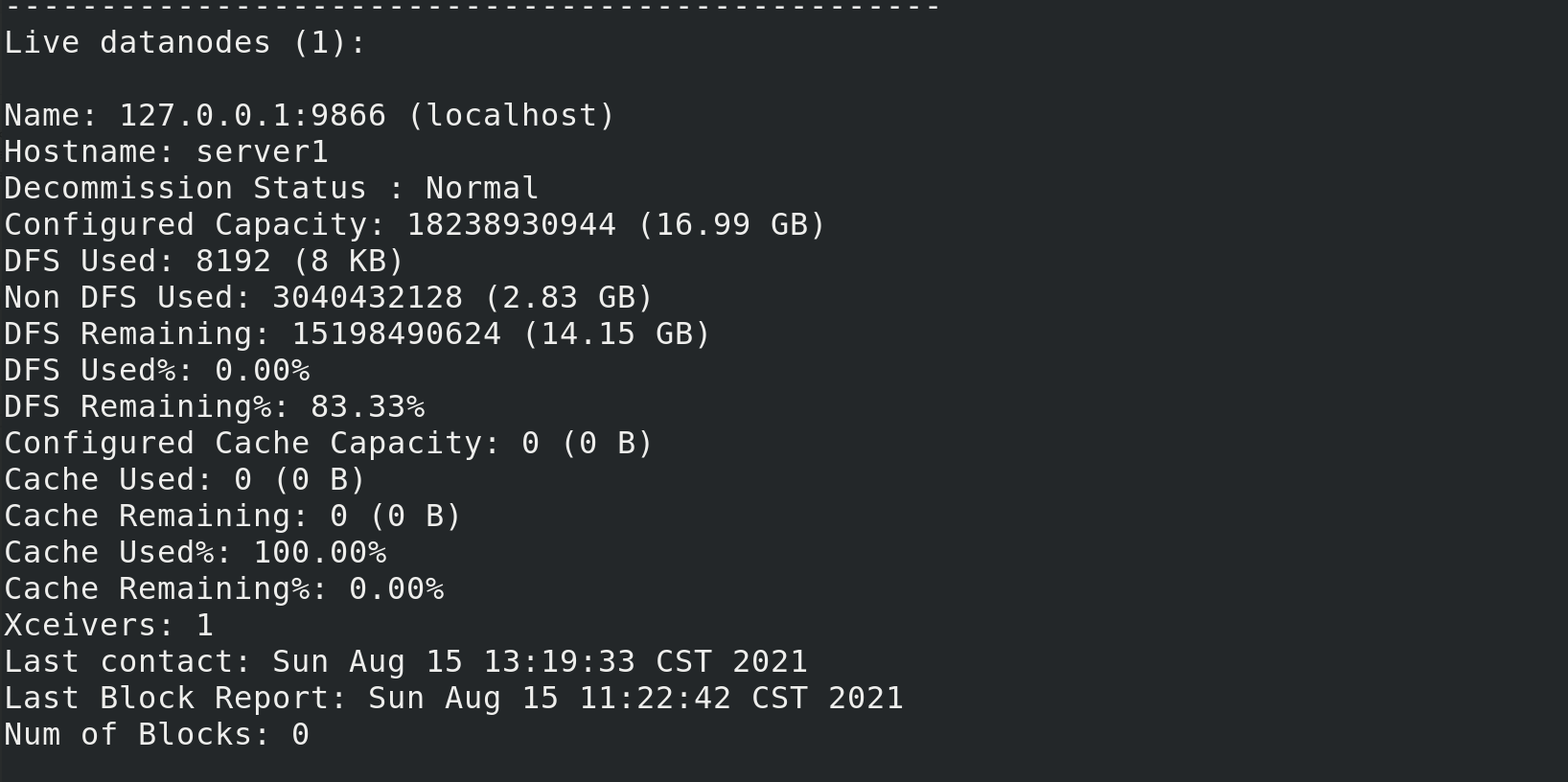
Can view related information
bin/hdfs dfsadmin -report
 Create a user in a pseudo-distributed file system and a user home directory with the same user name
Create a user in a pseudo-distributed file system and a user home directory with the same user name
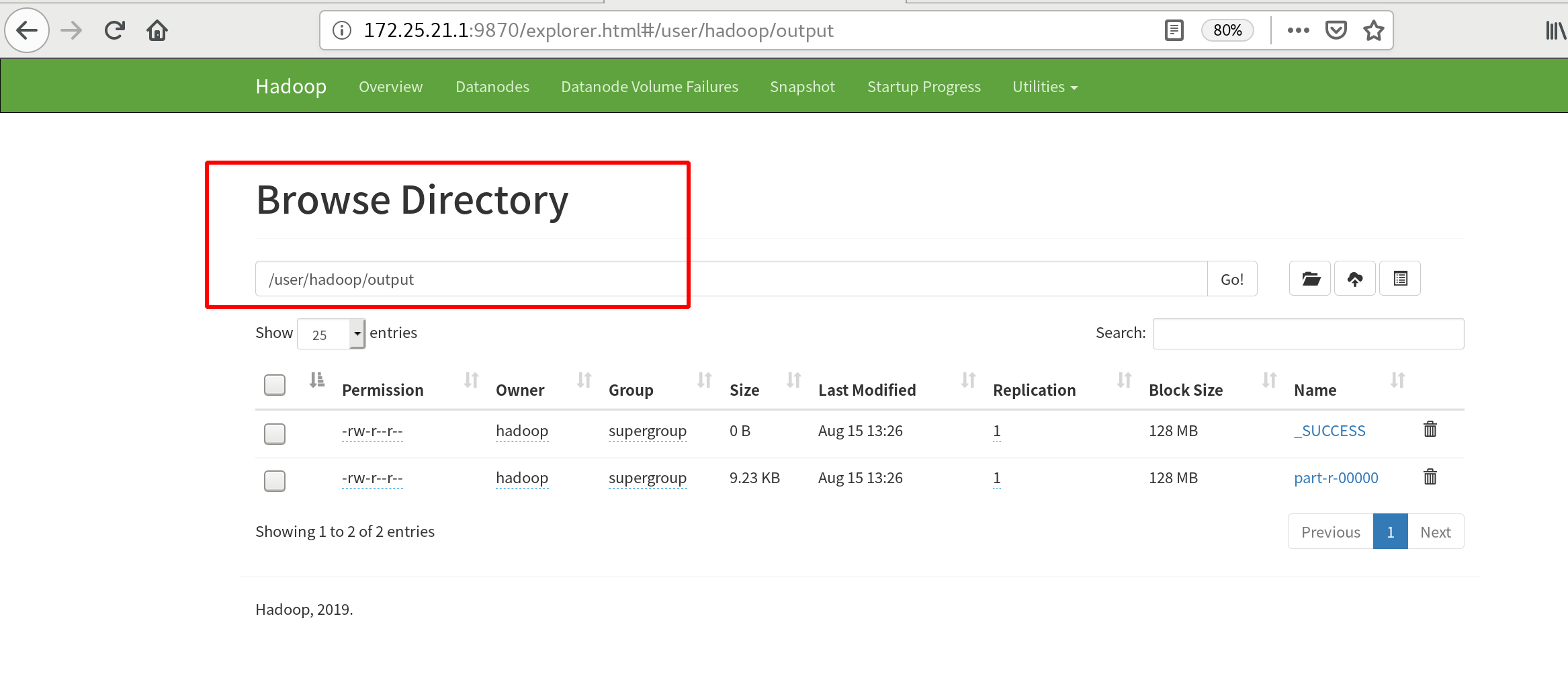
[hadoop@server1 hadoop]$ bin/hdfs dfs -mkdir /user [hadoop@server1 hadoop]$ id uid=1000(hadoop) gid=1000(hadoop) groups=1000(hadoop) [hadoop@server1 hadoop]$ bin/hdfs dfs -mkdir /user/hadoop
Looking at the file system at this point, you can see the user
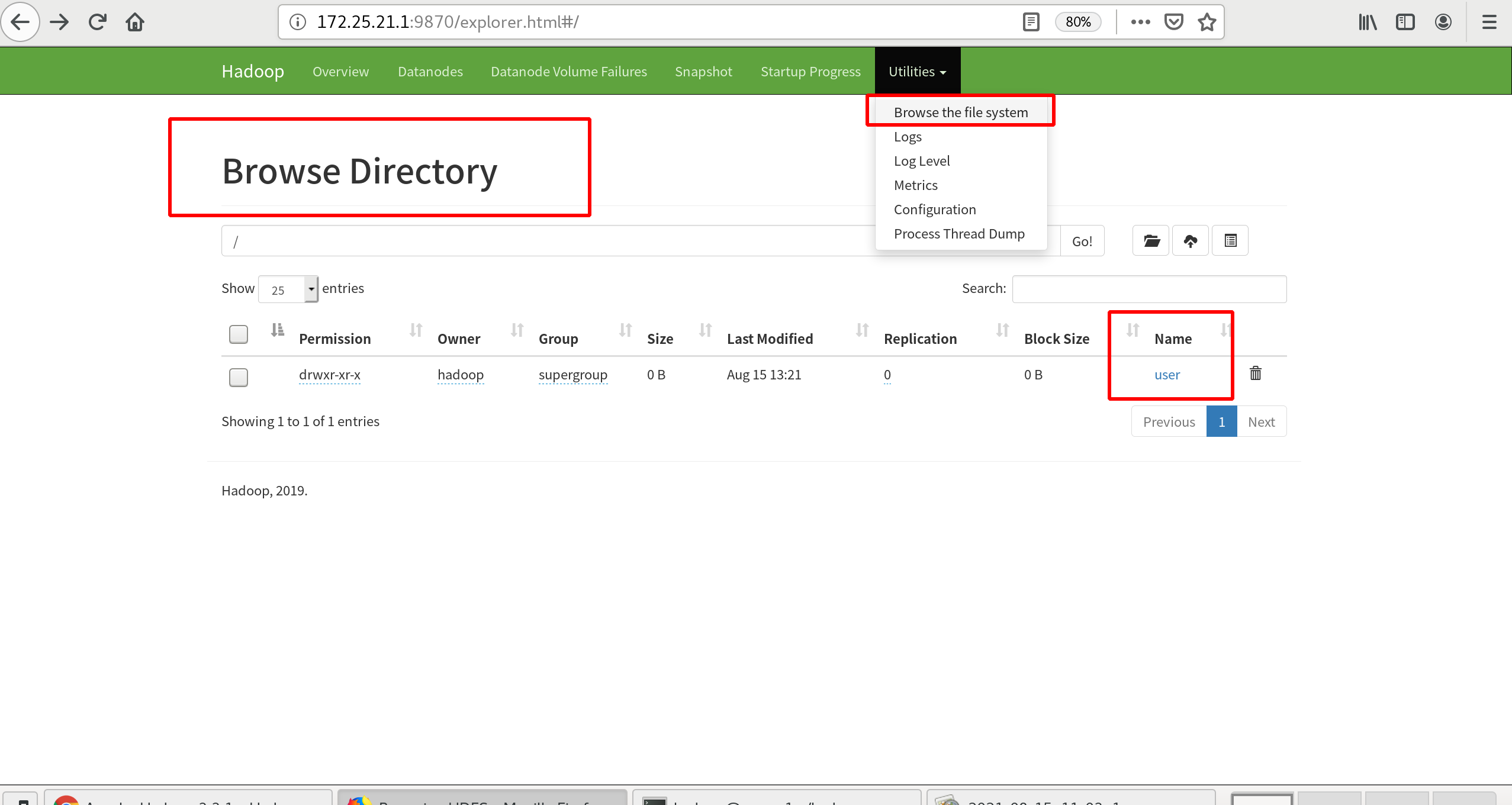
Create an input directory in the distributed file system to copy the input files to the distributed file system
bin/hdfs dfs -mkdir input bin/hdfs dfs -put etc/hadoop/*.xml input
Check the contents of the file
[hadoop@server1 hadoop]$ bin/hdfs dfs -ls Found 1 items drwxr-xr-x - hadoop supergroup 0 2021-08-15 13:23 input [hadoop@server1 hadoop]$ bin/hdfs dfs -ls input/ Found 9 items -rw-r--r-- 1 hadoop supergroup 8260 2021-08-15 13:23 input/capacity-scheduler.xml -rw-r--r-- 1 hadoop supergroup 884 2021-08-15 13:23 input/core-site.xml -rw-r--r-- 1 hadoop supergroup 11392 2021-08-15 13:23 input/hadoop-policy.xml -rw-r--r-- 1 hadoop supergroup 867 2021-08-15 13:23 input/hdfs-site.xml -rw-r--r-- 1 hadoop supergroup 620 2021-08-15 13:23 input/httpfs-site.xml -rw-r--r-- 1 hadoop supergroup 3518 2021-08-15 13:23 input/kms-acls.xml -rw-r--r-- 1 hadoop supergroup 682 2021-08-15 13:23 input/kms-site.xml -rw-r--r-- 1 hadoop supergroup 758 2021-08-15 13:23 input/mapred-site.xml -rw-r--r-- 1 hadoop supergroup 690 2021-08-15 13:23 input/yarn-site.xml
It can also be viewed on the web interface
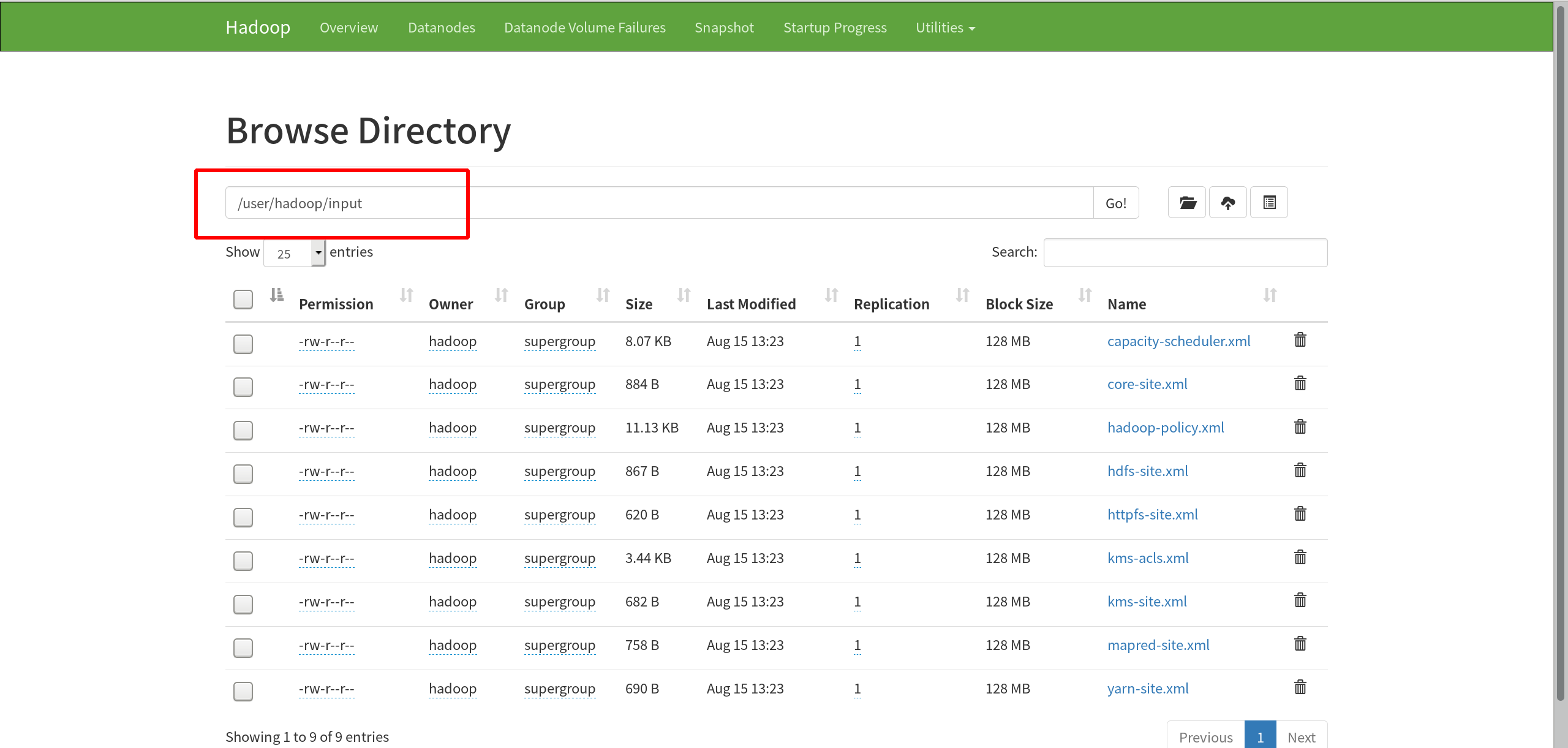
Execute Hadoop's own test package to count words in input and output to output
bin/hadoop jar share/hadoop/mapreduce/hadoop-mapreduce-examples-3.2.1.jar wordcount input output bin/hdfs dfs -ls bin/hdfs dfs -cat output/*
The ouput directory generated at this time is in a distributed file system, independent of local output
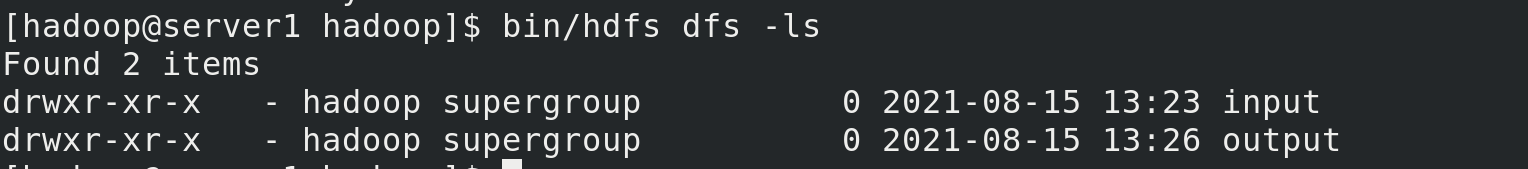
View on the web side
Fully-Distributed Operation (Fully Distributed Deployment)
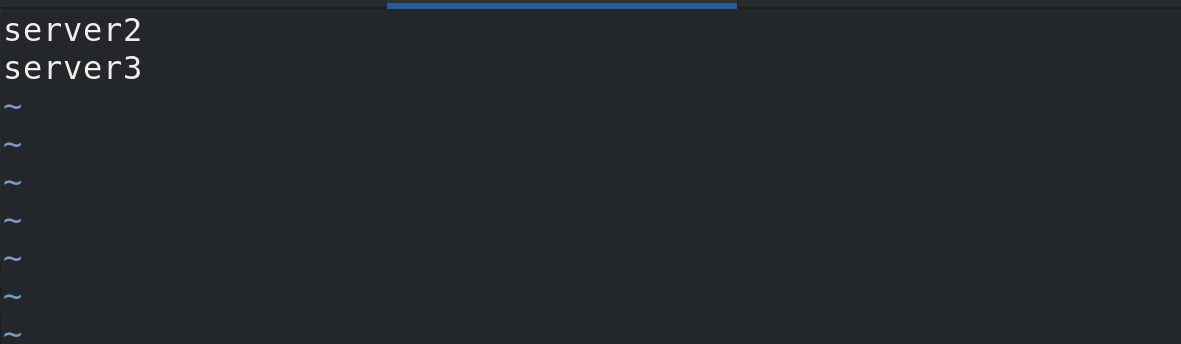
Experimental environment: three virtual machines server1 as master, server2 and server3 as worker
First, stop the hdfs file system!
sbin/stop-dfs.sh

Enter the Hadoop soft connection directory to modify the specified node etc/hadoop/workers
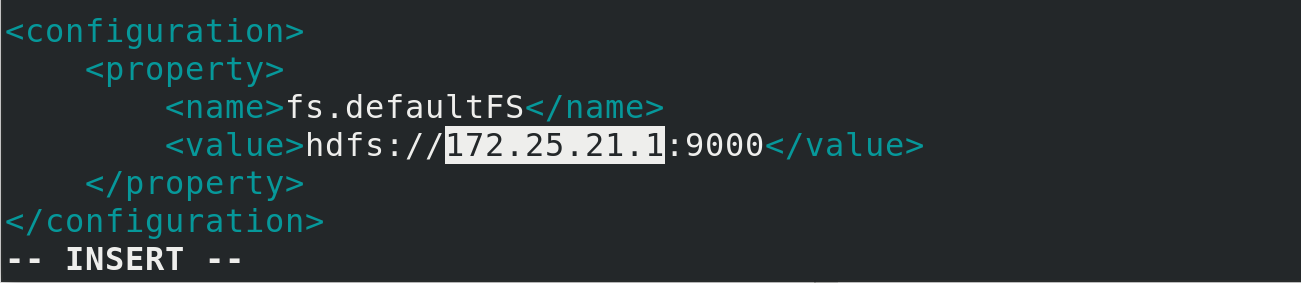
 Modify core profile etc/hadoop/core-site.xml by entering the Hadoop soft connection directory
Modify core profile etc/hadoop/core-site.xml by entering the Hadoop soft connection directory
ip modified to master
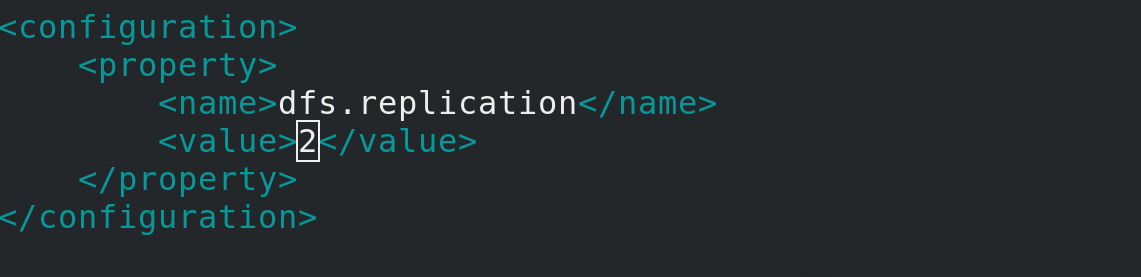
Modify hdfsetc/hadoop/hdfs-site.xml by entering the Hadoop soft connection directory
Change the value to 2 with two nodes
server1, 2, 3 install nfs and set up boot-up self-start nfs
yum install nfs-utils -y systemctl enable --now nfs
server2, 3 create the user hadoop, and then view the IDS to keep the Hadoop user IDs of the three hosts consistent
useradd hadoop id hadoop
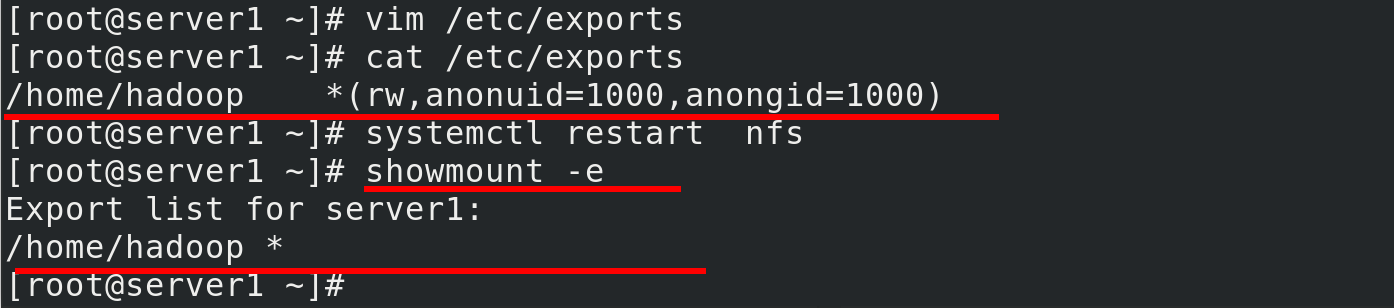
server1 configures network share/home/hadoop, gives Hadoop users read and write access, and restarts the nfs service
[root@server1 ~]# cat /etc/exports /home/hadoop *(rw,anonuid=1000,anongid=1000) [root@server1 ~]# systemctl restart nfs
 server2, 3 to mount server1's / home/hadoop directory
server2, 3 to mount server1's / home/hadoop directory
mount 172.25.21.1:/home/hadoop/ /home/hadoop/ su - hadoop ls
You can see that the network files are synchronized. As long as they are modified on server1, 2 and 3 will also be modified at the same time.

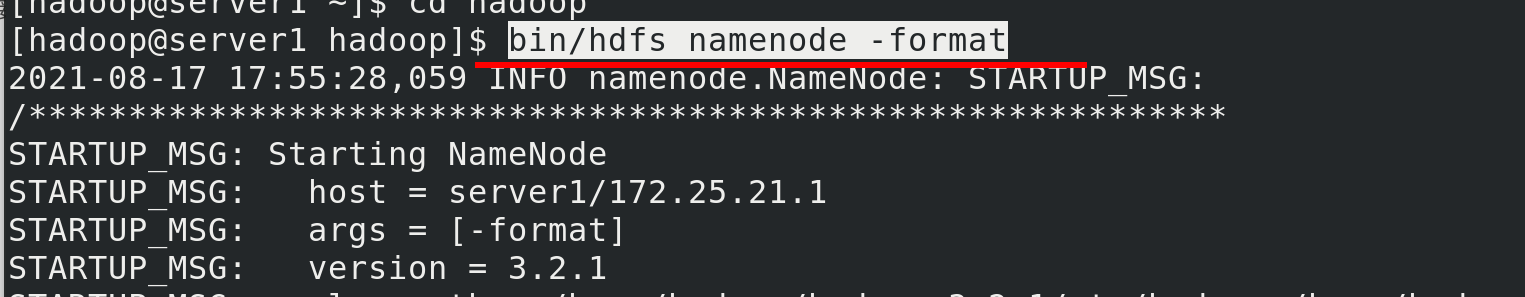
Once configured, at server1, enter the hadoop soft connection directory and perform hadoop initialization
bin/hdfs namenode -format
Open the namenode on server1 and the datanode s for server2 and 3 will be opened using ssh-free (make sure ssh-free)
sbin/start-dfs.sh
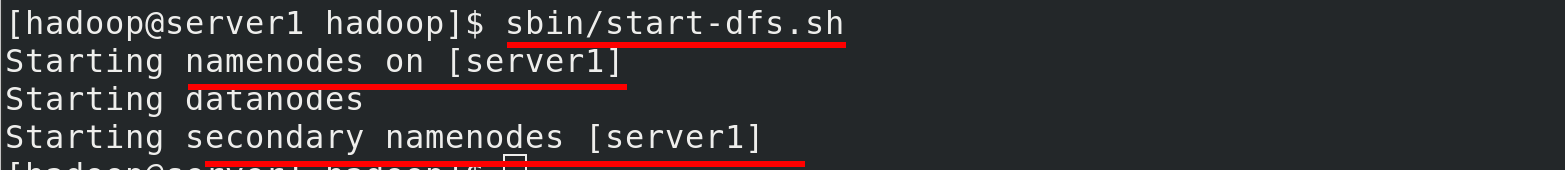
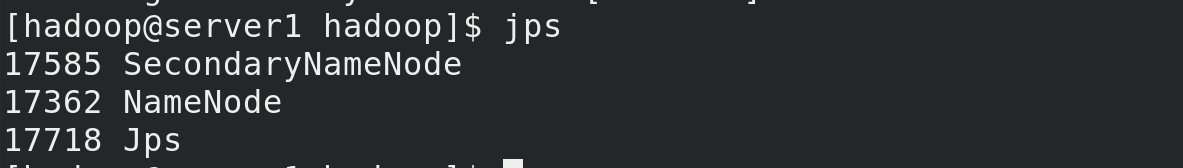
Viewing java processes with jps
server1 is nn
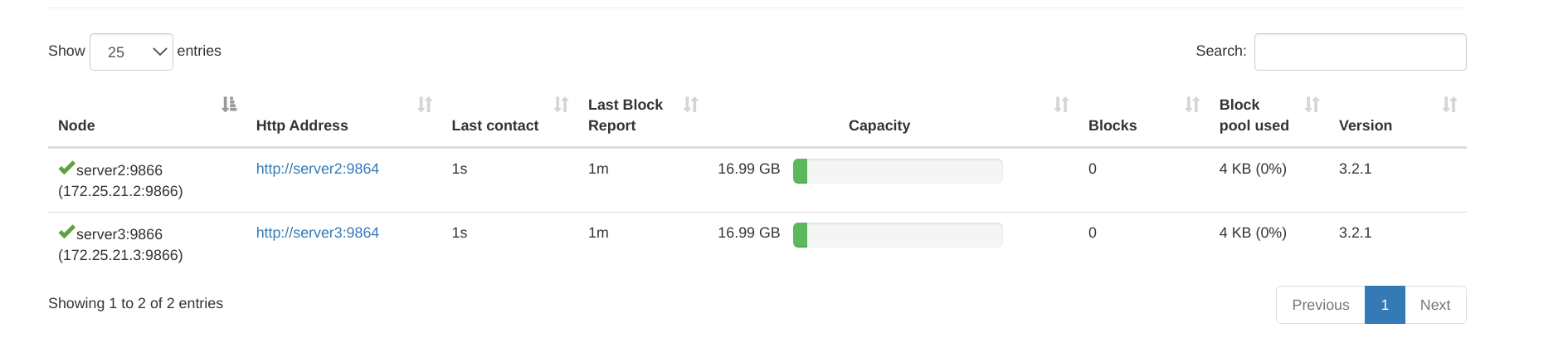
 server2 is dn
server2 is dn
 server3 is dn
server3 is dn

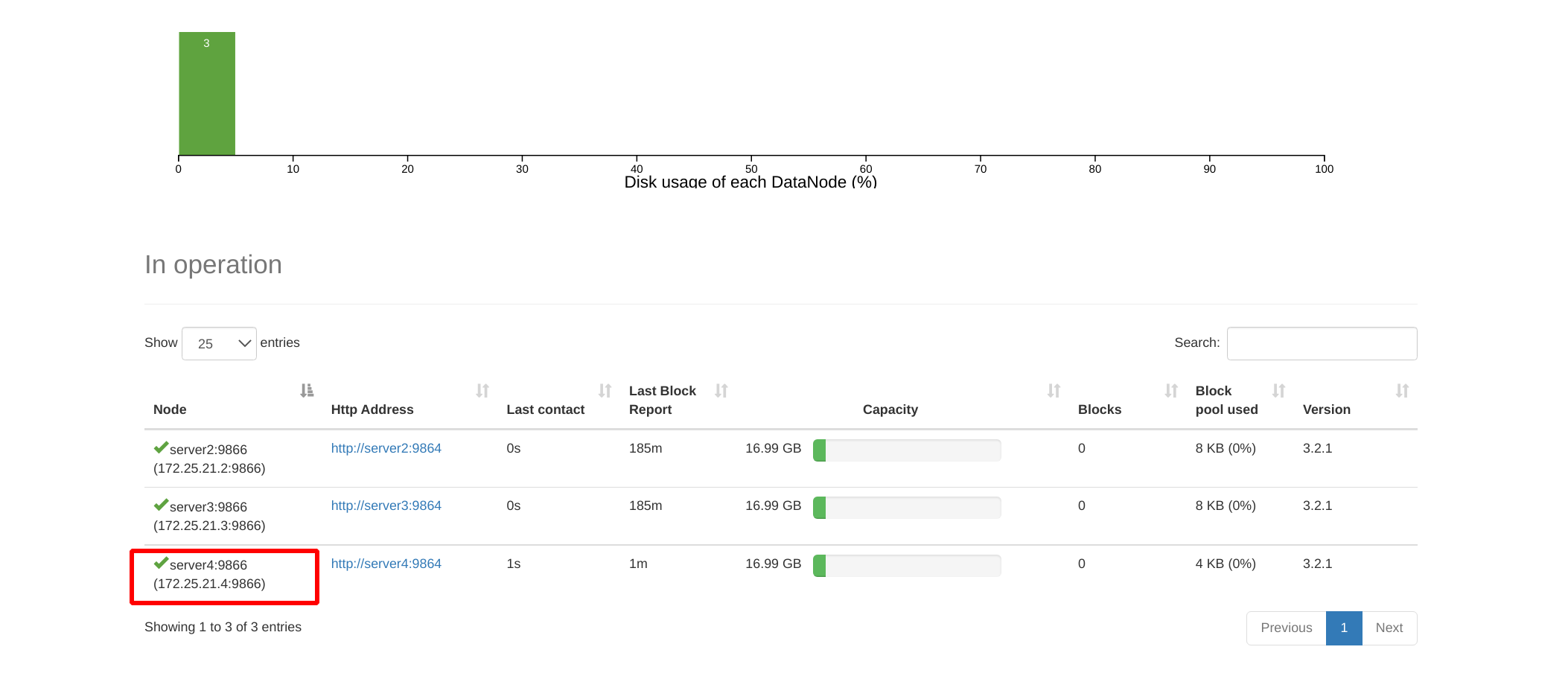
At this point, you can see two DNS from 172.25.21.1:9870 (the web side of nn)
How to expand nodes?
Start with a virtual machine server4
yum install -y nfs-utils.x86_64 #Install nfs useradd hadoop ##Create hadoop user id hadoop #Make sure both uid and gid are 1000 mount 172.25.21.1:/home/hadoop/ /home/hadoop/ ##Mount Network File Directory df ##View mounts
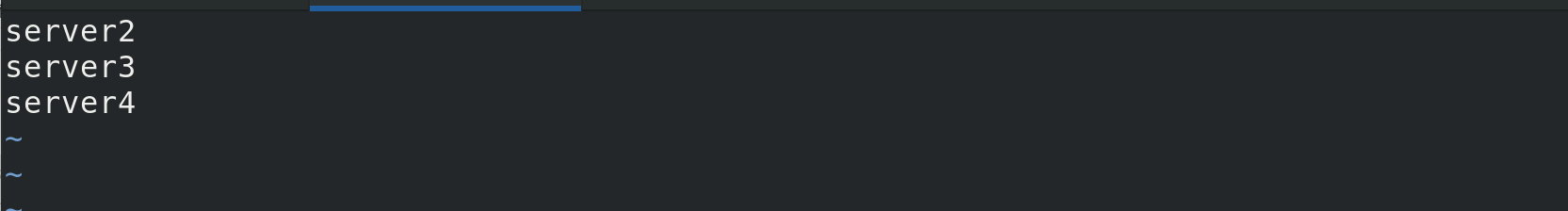
Configure worker files within server1 to join server4 nodes
Within server4, go to the hadoop soft connection directory and execute the node add command
bin/hdfs --daemon start datanode jps ##Query java processes
Serr4 successfully added

On the web side of the namenode, you can see server4