1, Start to understand the general of the project
1. Project background
As the name suggests, online education is a teaching method based on the network. Through the network, students and teachers can carry out teaching activities even if they are thousands of miles apart; In addition, with the help of network courseware, students can study anytime and anywhere, which really breaks the restrictions of time and space. For workplace people with busy work and uncertain learning time, network distance education is the most convenient way of learning.
2. Mode adopted by the project
1. C2C mode (Consumer To Consumer platform mode)
User to user, the essence of this model is to resell their own traffic or users to video or live content providers, and make profits by selling content.
The platform model avoids very heavy content and services and expands rapidly, but in fact, this model also has defects. The development of online education in the past two years has devalued the content rapidly, making it difficult to bring more free users and traffic.
Representative website:
51cto http://edu.51cto.com/
Tencent classroom https://ke.qq.com/
2. B2C mode (Business To Customer member mode) is the mode used this time
Merchants to users, this mode is to make a large number of videos with their own copyright and put them on their own platform, so that users can pay monthly or annual fees. This model is simple and fast. It can develop rapidly as long as you concentrate on recording a large number of videos. It was hot because of lynda's sky high financing. However, in China, due to weak awareness of copyright protection, easy reproduction of educational content and many competitors with massive free resources, it is difficult to obtain decent cash flow.

Representative website:
lynda https://www.lynda.com/
Muke network https://www.imooc.com/
Grain College http://www.gulixueyuan.com/
3. B2B2C (merchant to merchant to user)
The platform links third-party educational institutions and users. Generally, the platform does not directly provide course content, but more undertakes the role of Internet carrier of education, providing all-round support and services for all links of the teaching process.

Representative website:
51cto http://edu.51cto.com/
Tencent classroom https://ke.qq.com/
4. Vertical field
This mode requires a combination of recording, broadcasting, live broadcasting, help services and other means to be responsible for students' learning a certain content. This model has high charges and strong barriers. Once this product forms a reputation, it will have a stable user base and income, but the product is very complex, difficult and high threshold. Even a single project will consume a lot of human and material resources, so the development speed is slow.
Representative website:
51cto micro position http://edu.51cto.com/
Micro specialty of Netease cloud classroom https://study.163.com/
5. Live broadcast and interaction
This model moves the feedback, interaction and Q & A in the traditional classroom online. It is easy for users to accept. As long as the service is considerate, users are willing to pay, so they have rich cash flow. However, the defect is that users can only be attracted through the platform, resulting in a low threshold for competition, The model is the same, there are many competitors, and the revenue is always a large platform with traffic or users.
Representative website:
Tencent Classroom: https://ke.qq.com/
Learning and thinking https://www.xueersi.com
6. 1 to 1
Let a lecturer tutor a student within a certain period of time, and the students pay according to the time. This model is easy to charge, The cash flow is good, the product is not difficult and the market space is large, but the acquisition and consumption of human resources is huge. If the teachers are not well controlled, such as the excellent lecturers cannot be retained, or the overall cost is too large, it will lead to the development of the 1-to-1 model.
Representative website:
VIPKID https://www.vipkid.com.cn/
Learning and thinking https://www.xueersi.com
7. O2O mode (Online To Offline)
That is, through free content or operation, let the online platform obtain users and traffic, attract users to offline classes, or Participants are invited to attend classes in affiliated offline institutions. This model has simple form and high income. As long as we control the needs of users and attract users, the charging is not a problem, and it is in line with the traditional consumption habits.
Representative website:
Kai Tak Education https://www.eic.org.cn/
8. freemium (free value-added)
Freemium was first proposed by Fred Wilson of AVC in 2006. It refers to attracting users with free services, and then converting some free users into charging users through value-added services to realize cash. The freemium model has the "28 law" factor, that is, a small number of price insensitive high-end users are willing to pay for some additional functions and bring most of the revenue to service providers.
Representative website:
Chinese University Course http://www.icourse163.org
Establish cooperation with colleges and universities through free famous school courses to attract users. Provide postgraduate entrance examination column and school cloud value-added service online http://www.xuetangx.com/
The course is free. If you want to get the certification certificate of the course, you have to pay the corresponding fee
3. Project function module
4. Technology used
2, Introduction to online education project
1. Function introduction
Grain college is a B2C vocational skills online education system, which is divided into foreground user system and background operation platform.
2. System module
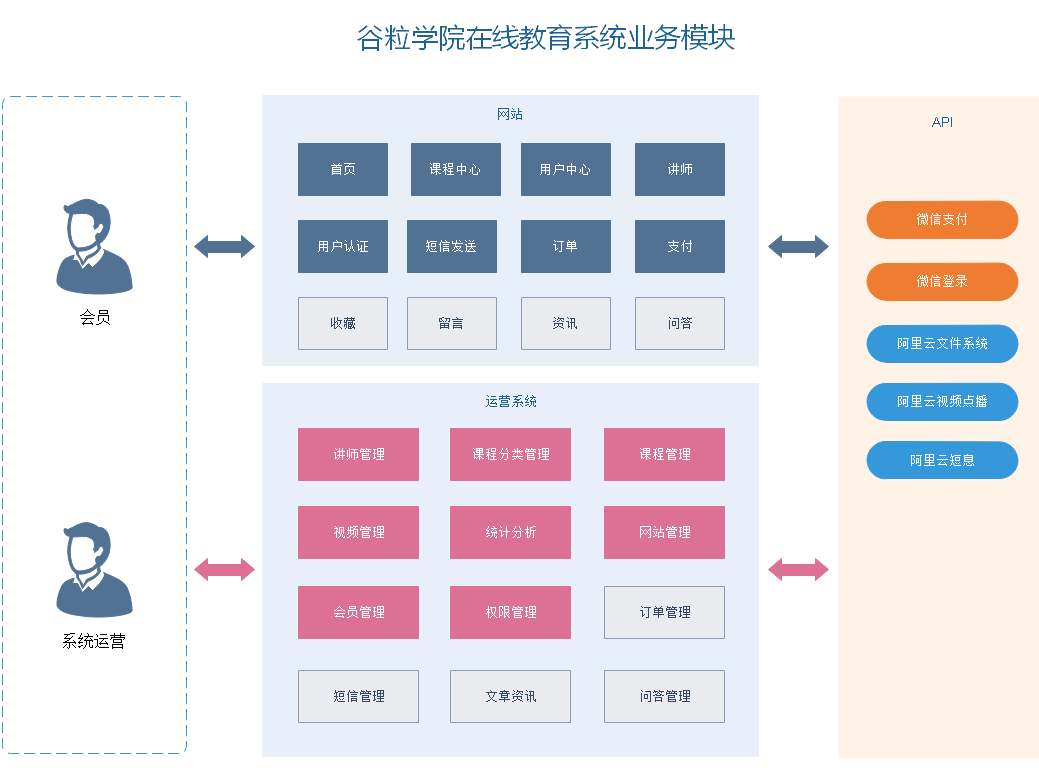
3, System architecture
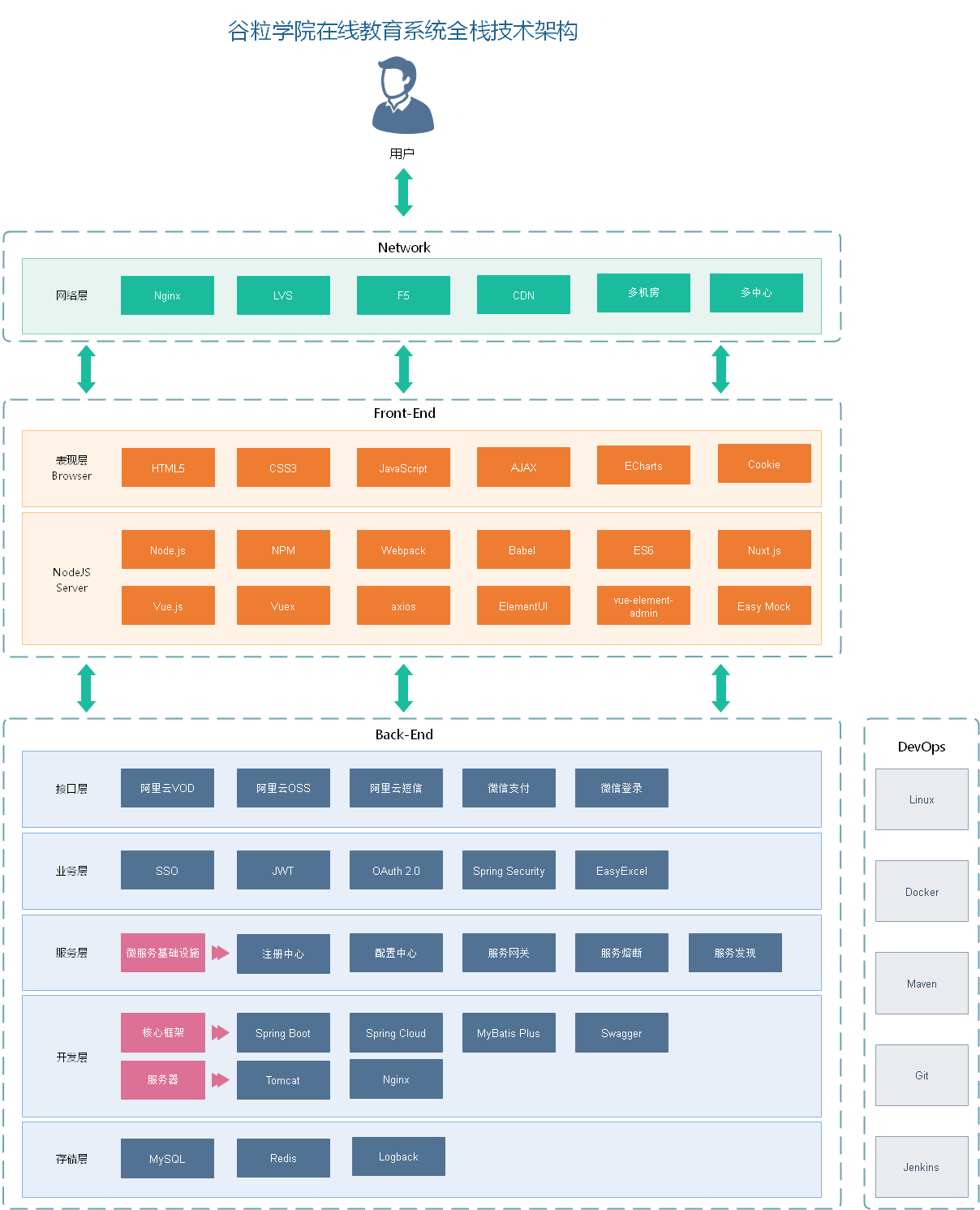 4, Learn about mybatis puls
4, Learn about mybatis puls
1. Introduction
Official website: http://mp.baomidou.com/
Reference tutorial: http://mp.baomidou.com/guide/
2. Characteristics

3. Quick start
Quick start reference: http://mp.baomidou.com/guide/quick-start.html
Test item: mybatis_plus
Database: mybatis_plus
3.1 creating database
mybatis_plus
3.2 creating tables
The table structure is as follows
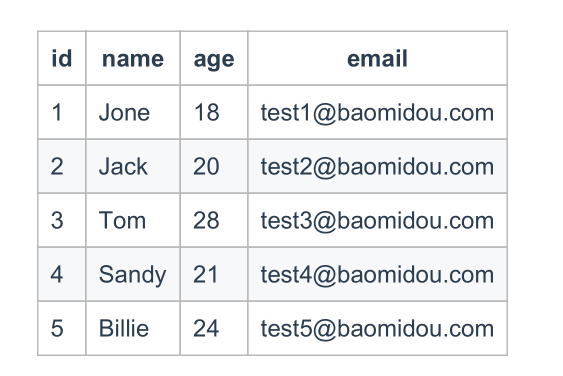
The corresponding database sql script is as follows:
DROP TABLE IF EXISTS user; CREATE TABLE user ( id BIGINT(20) NOT NULL COMMENT 'Primary key ID', name VARCHAR(30) NULL DEFAULT NULL COMMENT 'full name', age INT(11) NULL DEFAULT NULL COMMENT 'Age', email VARCHAR(50) NULL DEFAULT NULL COMMENT 'mailbox', PRIMARY KEY (id) );
Insert corresponding data
DELETE FROM user; INSERT INTO user (id, name, age, email) VALUES (1, 'Jone', 18, 'test1@baomidou.com'), (2, 'Jack', 20, 'test2@baomidou.com'), (3, 'Tom', 28, 'test3@baomidou.com'), (4, 'Sandy', 21, 'test4@baomidou.com'), (5, 'Billie', 24, 'test5@baomidou.com');
5. Initialization works
use Spring Initializr Quickly initialize a Spring Boot project
Group: com.yy
Artifact: mybatis-plus
Version: 2.2.1.RELEASE
1. Introduce dependency
spring-boot-starter,spring-boot-starter-test
Add: mybatis plus boot starter, MySQL, lombok
Using Lombok in a project can reduce the writing of a lot of repetitive code. For example, the preparation of getter/setter/toString and other methods
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-test</artifactId>
<scope>test</scope>
<exclusions>
<exclusion>
<groupId>org.junit.vintage</groupId>
<artifactId>junit-vintage-engine</artifactId>
</exclusion>
</exclusions>
</dependency>
<!--mybatis-plus-->
<dependency>
<groupId>com.baomidou</groupId>
<artifactId>mybatis-plus-boot-starter</artifactId>
<version>3.0.5</version>
</dependency>
<!--mysql-->
<dependency>
<groupId>mysql</groupId>
<artifactId>mysql-connector-java</artifactId>
</dependency>
<!--lombok Used to simplify entity classes-->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.projectlombok</groupId>
<artifactId>lombok</artifactId>
</dependency>
Note: after introducing MyBatis plus, please do not introduce MyBatis and MyBatis spring again to avoid problems caused by version differences.
2. Install lombok
3. Configuration
Add the relevant configuration of MySQL database in the application.properties configuration file:
mysql5
#mysql database connection spring.datasource.driver-class-name=com.mysql.jdbc.Driver spring.datasource.url=jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/mybatis_plus spring.datasource.username=root spring.datasource.password=00000
mysql8
Note: driver and url changes
spring.datasource.driver-class-name=com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver spring.datasource.url=jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/mybatis_plus?serverTimezone=GMT%2B8 spring.datasource.username=root spring.datasource.password=123456
be careful:
1. What is the url used here? serverTimezone=GMT%2B8 suffix, because Spring Boot 2.1 integrates the jdbc driver of version 8.0,
This suffix needs to be added to this version of jdbc driver. Otherwise, run the test case and report the following error:
java.sql.SQLException: The server time zone value 'Öйú±ê׼ʱ¼ä' is unrecognized or representsmore
2. The driver class name here uses com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver. It is recommended to use this driver in jdbc 8. The previous com.mysql.jdbc.Driver has been abandoned, otherwise there will be warning information when running the test case.
6. Write code
1. Startup class
Add the @ MapperScan annotation on the startup class and scan the mapper folder
@SpringBootApplication
@MapperScan("com.yy.mybatisplus.mapper")
public class MybatisPlusApplication {
......
}2. Entity class
create package entity Writing entity classes User.java (used here) Lombok Simplify the code and omit the get, set method and toString)
@Data
public class User {
private Long id;
private String name;
private Integer age;
private String email;
}
3. Create mapper file
Create package mapper authoring Mapper interface: UserMapper.java
be careful:
IDEA reports an error at userMapper because the injected object cannot be found because the class is created dynamically, but the program can execute correctly.
To avoid error reporting, you can add an interface on the dao layer @ Repository annotation
@Repository
public interface UserMapper extends BaseMapper<User> {
}
4. Start using
s add a test class and test in the test class
@SpringBootTest
class MybatisPlusApplicationTests {
@Autowired
private UserMapper userMapper;
@Test
void testSelectList(){
System.out.println(("----- selectAll print ------"));
//The parameter of the selectList() method in UserMapper is the MP built-in conditional Wrapper
//Do not fill in and query all data
List<User> list = userMapper.selectList(null);
list.forEach(System.out::println);
}
}
5. Console output
----- selectAll method test ------ User(id=1, name=Jone, age=18, email=test1@baomidou.com) User(id=2, name=Jack, age=20, email=test2@baomidou.com) User(id=3, name=Tom, age=28, email=test3@baomidou.com) User(id=4, name=Sandy, age=21, email=test4@baomidou.com) User(id=5, name=Billie, age=24, email=test5@baomidou.com)
Some simple curd operations can be queried directly with the condition constructor in mybatis puls without writing xml sql statements. If it involves linked table queries, you must write sql statements in the xml file yourself
6. Configure mybatis log file
#mybatis log mybatis-plus.configuration.log-impl=org.apache.ibatis.logging.stdout.StdOutImpl
5, CURD operation of mybatis puls
1.insert
@SpringBootTest
class MybatisPlusApplicationTests {
@Autowired
private UserMapper userMapper;
@Test
void testInsert(){
User user = new User();
user.setAge(18);
user.setName("Helen");
user.setEmail("55317332@qq.com");
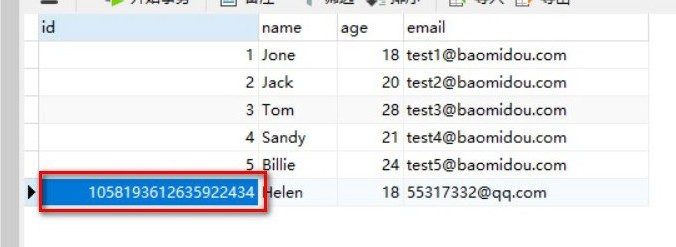
int result = userMapper.insert(user);
System.out.println(result); //Number of rows affected
System.out.println(user); //id auto backfill
}
}
Note: the database insert id value defaults to globally unique id
1.1. Primary key policy
1.1.1 ID_WORKER
The default primary key policy of mybatis plus is ID_WORKER globally unique ID
Reference: distributed system unique ID generation scheme summary: https://www.cnblogs.com/haoxinyue/p/5208136.html
1.1.2 auto increment strategy
To automatically increase the primary key, you need to configure the following primary key policies
~You need to set primary key auto increment when creating a data table
~Configure @ TableId(type = IdType.AUTO) in the entity field
@Data
public class User {
@TableId(type = IdType.AUTO) //id self increment
private Long id;
private String name;
private Integer age;
private String email;
}
To affect the configuration of all entities, you can set the global primary key configuration
#Global setting primary key generation policy mybatis-plus.global-config.db-config.id-type=auto
Other primary key strategies: analyze the IdType source code
@Getter
public enum IdType {
/**
* Database ID self increment
*/
AUTO(0),
/**
* The type is not set with primary key
*/
NONE(1),
/**
* User input ID
* This type can be populated by registering its own auto fill plug-in
*/
INPUT(2),
/* The following three types are automatically filled only when the inserted object ID is empty. */
/**
* Globally unique ID (idWorker)
*/
ID_WORKER(3),
/**
* Globally unique ID (UUID)
*/
UUID(4),
/**
* String globally unique ID (string representation of idworker)
*/
ID_WORKER_STR(5);
private int key;
IdType(int key) {
this.key = key;
}
}
2.update operation
1. Update operation by Id
Note: the sql generated during update is dynamic sql automatically: UPDATE user SET age=? WHERE id=?
@Test
void testUpdate(){
User user = new User();
user.setId(1L);
user.setAge(28);
int result = userMapper.updateById(user);
System.out.println(result);
}
2. Auto fill
Some data are often encountered in the project, which are filled in the same way every time, such as the creation time and update time of the record.
We can use the auto fill function of MyBatis Plus to complete the assignment of these fields:
(1) Add autofill fields to database tables
Add a new field create of type datetime to the User table_ time,update_time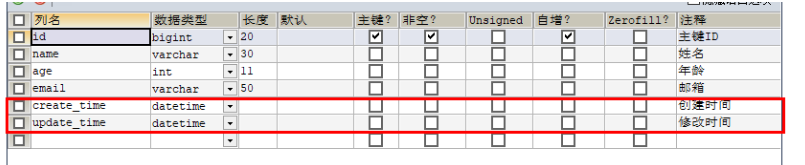
(2) Add annotation to entity
@Data
public class User {
......
@TableField(fill = FieldFill.INSERT)
private Date createTime;
// @TableField(fill = FieldFill.UPDATE)
@TableField(fill = FieldFill.INSERT_UPDATE)
private Date updateTime;
}
( 3) Create a MyMetaObjectHandler class and implement the MetaObjectHandler to override the insertFill and updateFill methods
@Component
public class MyMetaObjectHandler implements MetaObjectHandler {
private static final Logger LOGGER = LoggerFactory.getLogger(MyMetaObjectHandler.class);
//This method performs the add operation using mp
@Override
public void insertFill(MetaObject metaObject) {
LOGGER.info("start insert fill. . . ");
this.setFieldValByName("createTime", new Date(), metaObject);
this.setFieldValByName("updateTime", new Date(), metaObject);
}
//Using mp to implement the modification operation, this method performs
@Override
public void updateFill(MetaObject metaObject) {
LOGGER.info("start update fill ....");
this.setFieldValByName("updateTime", new Date(), metaObject);
}
}
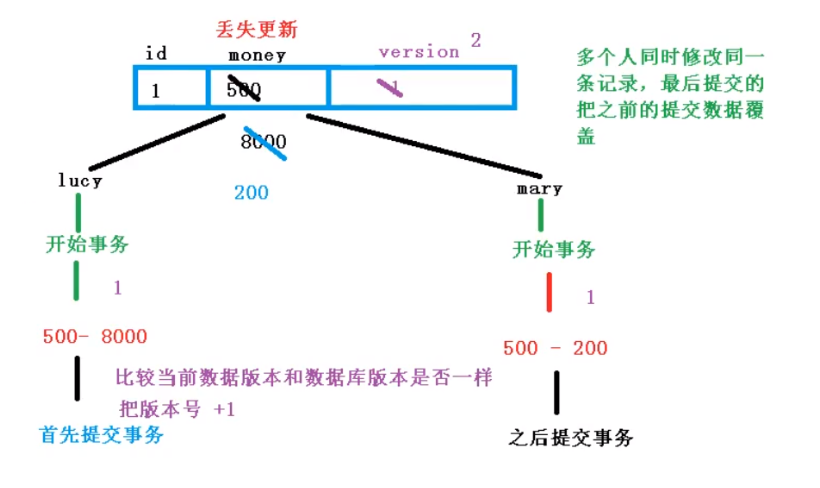
3. Optimistic lock
Main applicable scenarios: when a record is to be updated, it is hoped that the record has not been updated by others, that is, thread safe data update is realized
Optimistic lock implementation method:
1. When fetching the record, get the current version
2. Bring this version when updating
3. When updating, set version = newVersion where version = oldVersion. If the version is wrong, the update fails
| When submitting data, compare whether the current version number is consistent with the database version number. If it is consistent, submit it, and add the version number + 1; Submit failed if inconsistent |
( 1) Add version field to database
ALTER TABLE `user` ADD COLUMN `version` INT

( 2) Add the Version field to the entity class and add @ Version annotation
@Version @TableField(fill = FieldFill.INSERT) private Integer version;
(3) Add the insert default value of version to the meta object processor interface
@Component
public class MyMetaObjectHandler implements MetaObjectHandler {
//This method performs the add operation using mp
@Override
public void insertFill(MetaObject metaObject) {
...
this.setFieldValByName("version",1,metaObject);
}
}
Special note:
The only supported data types are int, integer, long, long, date, timestamp and localdatetime
Integer type: newVersion = oldVersion + 1
newVersion will write back entity in
Only supported updateById(id) And update(entity, wrapper) method
stay update(entity, wrapper) Under the method, wrapper Cannot reuse!!!
(4) Register the Bean in MybatisPlusConfig and use the optimistic lock plug-in
@EnableTransactionManagement
@Configuration
@MapperScan("com.yy.mybatisplus.mapper")
public class MybatisPlusConfig {
//Optimistic lock plug-in
@Bean
public OptimisticLockerInterceptor optimisticLockerInterceptor() {
return new OptimisticLockerInterceptor();
}
}
(5) The test lock can be modified successfully
After the test, analyze the printed sql statement and add 1 to the value of version
@Test
void testOptimisticLocker(){
//query
User user = userMapper.selectById(1364080977348956166L);
//Modify data
user.setName("Helen Yao");
user.setEmail("helen@qq.com");
//Execute update
userMapper.updateById(user);
}
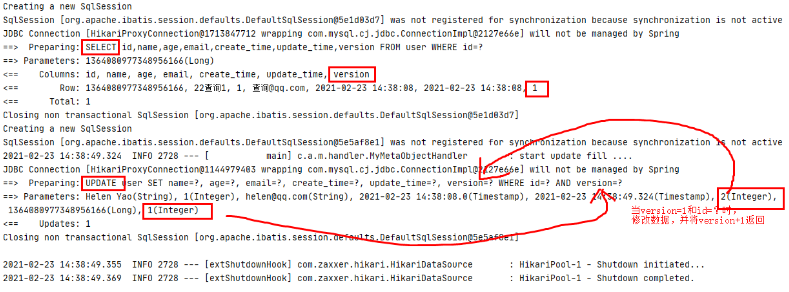
( 6) Test lock modification failed
//Test lock modification failed
@Test
public void testOptimisticLockerFail() {
//query
User user = userMapper.selectById(1L);
//Modify data
user.setName("Helen Yao1");
user.setEmail("helen@qq.com1");
//After the simulation fetches the data, the actual version data in the database is larger than the fetched value, that is, the version has been modified and updated by other threads
user.setVersion(user.getVersion() - 1);
//Execute update
userMapper.updateById(user);
}
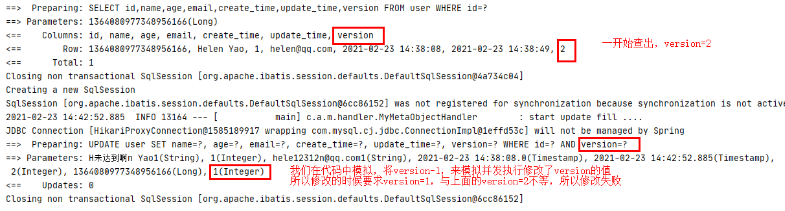
3.select operation
1. Query records by id
@Test
void testSelectById(){
User user = userMapper.selectById(1);
System.out.println(user);
}
2. Batch query through multiple IDS
The foreach function of dynamic sql is completed
//Batch query of multiple IDS
@Test
void testSelectBatchIds(){
//Batch query data through collection
List<User> users = userMapper.selectBatchIds(Arrays.asList(1, 2, 3));
users.forEach(System.out::println);
}
3. Simple conditional query
Encapsulate query criteria through map
Note: the key in the map corresponds to the column name in the database. For example, database user_id, and the entity class is userId. In this case, the key of map needs to be filled in user_id
@Test
void testSelectByMap(){
HashMap<String, Object> map = new HashMap<>();
map.put("name","Tester");
map.put("age",18);
List<User> users = userMapper.selectByMap(map);
users.forEach(System.out::println);
}
4. Pagination
MyBatis Plus comes with a paging plug-in, which can realize paging function with simple configuration
(1) Create configuration class
At this point, you can delete the @ MapperScan scan annotation in the main class
//Paging plug-in
@Bean
public PaginationInterceptor paginationInterceptor() {
return new PaginationInterceptor();
}
(2) Test selectPage paging
Test: finally obtain relevant data through the page object
//Paging query
@Test
void testPage(){
//1. Create page object
//Incoming parameters: current page and number of records displayed per page
Page<User> userPage = new Page<>(1,3);
//Call mp paging query method
//In the process of calling mp paging query, the bottom layer will encapsulate and sub load all paging data into the page object
userMapper.selectPage(userPage,null);
//Get data through page object
userPage.getRecords().forEach(System.out::println);//Traverse the paged data of the query
System.out.println(userPage.getCurrent());//Get current page
System.out.println(userPage.getSize());//Number of records per page
System.out.println(userPage.getTotal());//Total records
System.out.println(userPage.getPages());//PageCount
System.out.println(userPage.hasNext());//Determine whether there is a next page
System.out.println(userPage.hasPrevious());//Determine whether there is a previous page
}
(3) Test selectMapsPage paging: the result set is Map
Note: this line must use mapIPage to obtain the record list, otherwise there will be data type conversion errors
//Test selectMapsPage paging: the result set is Map
@Test
void testSelectMapsPage(){
//1. Create page object
//Incoming parameters: current page and number of records displayed per page
Page<User> page = new Page<>(1,3);
//Call mp paging query method
//In the process of calling mp paging query, the bottom layer will encapsulate and sub load all paging data into the page object
IPage<Map<String, Object>> mapIPage = userMapper.selectMapsPage(page, null);
//Note: this line must use mapIPage to obtain the record list, otherwise there will be data type conversion errors
mapIPage.getRecords().forEach(System.out::println);
System.out.println(page.getCurrent());
System.out.println(page.getPages());
System.out.println(page.getSize());
System.out.println(page.getTotal());
System.out.println(page.hasNext());
System.out.println(page.hasPrevious());
}
5.delete operation
1. Delete record by id
@Test
public void testDeleteById(){
int result = userMapper.deleteById(1364080977348956166L);
System.out.println(result);
}
2. Batch deletion
@Test
public void testDeleteBatchIds() {
int result = userMapper.deleteBatchIds(Arrays.asList(8, 9, 10));
System.out.println(result);
}
3. Simple conditional query deletion
@Test
public void testDeleteByMap() {
HashMap<String, Object> map = new HashMap<>();
map.put("name", "Helen");
map.put("age", 18);
int result = userMapper.deleteByMap(map);
System.out.println(result);
}
4. Logical deletion
Physical delete: real delete, delete the corresponding data from the database, and then query the deleted data
Logical deletion: false deletion. Change the status of the field representing whether to be deleted in the corresponding data to deleted status. After that, you can still see this data record in the database
(1) Add deleted field to database
ALTER TABLE `user` ADD COLUMN `deleted` boolean

(2) Add deleted field to entity class
And add @ TableLogic Notes and @ TableField(fill = FieldFill.INSERT) annotation
@TableField(fill = FieldFill.INSERT_UPDATE)
@TableLogic
private Boolean isDeleted;(3) Add the deleted insert default value to the meta object processor interface
@Override
public void insertFill(MetaObject metaObject) {
......
this.setFieldValByName("deleted", 0, metaObject);
}
(4) application.properties add configuration
mybatis-plus.global-config.db-config.logic-delete-value=1 mybatis-plus.global-config.db-config.logic-not-delete-value=0
(5) Register beans in MybatisPlusConfig
@Bean
public ISqlInjector sqlInjector() {
return new LogicSqlInjector();
}
(6) Test logical deletion
/**
* Test logical deletion
*/
@Test
public void testLogicDelete() {
int result = userMapper.deleteById(1L);
System.out.println(result);
}(7) Query after test logic deletion
The query operation in MyBatis Plus will also automatically add the judgment of logically deleting fields
/**
* Query after test logic deletion:
* Records deleted logically are not included
*/
@Test
public void testLogicDeleteSelect() {
User user = new User();
List<User> users = userMapper.selectList(null);
users.forEach(System.out::println);
}
6. Performance analysis plug-in
Performance analysis interceptor, which is used to output each SQL statement and its execution time
SQL performance analysis is performed, the development environment is used, and it stops running after the specified time. Help identify problems
1. Configure plug-ins
1) Parameter description
Parameter: maxTime: the maximum SQL execution time, which exceeds the automatic stop, helps to find problems.
Parameter: Format: whether to format SQL. The default is false.
2) Configuration in MybatisPlusConfig: used in development environment, not recommended online.
//Performance analysis plug-in
/**
* SQL Execute performance analysis plug-in
* It is not recommended to use the development environment online. maxTime refers to the maximum sql execution time
*/
@Bean
@Profile({"dev","test"})// Set dev test environment on
public PerformanceInterceptor performanceInterceptor() {
PerformanceInterceptor performanceInterceptor = new PerformanceInterceptor();
performanceInterceptor.setMaxTime(100);//ms. if the ms set here is exceeded, sql will not be executed
performanceInterceptor.setFormat(true);
return performanceInterceptor;
}
3) Set dev environment in Spring Boot
#Environment settings: dev, test, prod spring.profiles.active=dev
You can create different profiles for each environment
Just configure the startup environment in application.yml, as in 3)
2. Testing
1) Routine test
/**
* Test performance analysis plug-in
*/
@Test
public void testPerformance() {
User user = new User();
user.setName("I am Helen");
user.setEmail("helen@sina.com");
user.setAge(18);
userMapper.insert(user);
}
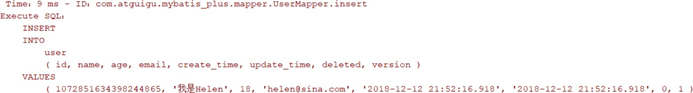
2) Test again after reducing maxTime
performanceInterceptor.setMaxTime(5);//ms, if it exceeds the ms set here, it will not be executed
If the execution time is too long, an exception will be thrown: The SQL execution time is too large,

7. Others
If you want to query complex conditions, you need to use the condition constructor Wapper, which involves the following methods
1,delete
2,selectOne
3,selectCount
4,selectList
5,selectMaps
6,selectObjs
7,update
6, MyBatisPlus condition constructor [wapper]
1. Introduction to wapper
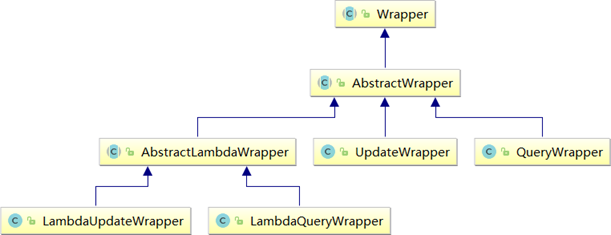
Wrapper: conditional construction abstract class, topmost parent class
AbstractWrapper: used to encapsulate query conditions and generate where conditions for sql. QueryWrapper: Entity object encapsulates operation class instead of lambda syntax UpdateWrapper: Update condition. It is used for Entity object Update operation
AbstractLambdaWrapper: Lambda syntax uses Wrapper to handle and parse Lambda to obtain column. LambdaQueryWrapper: it can be understood from the name. It is the query Wrapper used for Lambda syntax. Lambdaupdatewrapper: Lambda update Wrapper
2,AbstractWrapper
Note: the column s in the method input parameters of the following condition constructor represent database fields
1,ge,gt,le,lt,isNull,isNotNull
See the official website for details: https://mp.baomidou.com/guide/crud-interface.html#service-crud-%E6%8E%A5%E5%8F%A3
@Test
public void testDelete() {
QueryWrapper<User> queryWrapper = new QueryWrapper<>();
queryWrapper
.isNull("name")
.ge("age", 12)
.isNotNull("email");
int result = userMapper.delete(queryWrapper);
System.out.println("delete return count = " + result);
}
UPDATE user SET deleted=1 WHERE deleted=0 AND name IS NULL AND age >= ? AND email IS NOT NULL
2,eq,ne
Note: seletOne returns an entity record. If there are multiple records, an error will be reported
@Test
public void testSelectOne() {
QueryWrapper<User> queryWrapper = new QueryWrapper<>();
queryWrapper.eq("name", "Tom");
User user = userMapper.selectOne(queryWrapper);
System.out.println(user);
}
The executed sql statement is
SELECT id,name,age,email,create_time,update_time,version,deleted FROM user WHERE deleted=0 AND name = ?
3,between,notBetween
Include size boundary
@Test
public void testSelectCount() {
QueryWrapper<User> queryWrapper = new QueryWrapper<>();
queryWrapper.between("age", 20, 30);
Integer count = userMapper.selectCount(queryWrapper);
System.out.println(count);
}
The executed sql statement is
SELECT COUNT(1) FROM user WHERE deleted=0 AND age BETWEEN ? AND ?
4,allEq
@Test
public void testSelectList() {
QueryWrapper<User> queryWrapper = new QueryWrapper<>();
Map<String, Object> map = new HashMap<>();
map.put("id", 2);
map.put("name", "Jack");
map.put("age", 20);
queryWrapper.allEq(map);
List<User> users = userMapper.selectList(queryWrapper);
users.forEach(System.out::println);
}
The executed sql statement is
SELECT id,name,age,email,create_time,update_time,version,deleted FROM user WHERE deleted=0 AND name = ? AND id = ? AND age = ?
5,like,notLike,likeLeft,likeRight
selectMaps returns a list of Map collections
@Test
public void testSelectMaps() {
QueryWrapper<User> queryWrapper = new QueryWrapper<>();
queryWrapper
.notLike("name", "e")
.likeRight("email", "t");
List<Map<String, Object>> maps = userMapper.selectMaps(queryWrapper);//The return value is the Map list
maps.forEach(System.out::println);
}
The executed sql statement is
SELECT id,name,age,email,create_time,update_time,version,deleted FROM user WHERE deleted=0 AND name NOT LIKE ? AND email LIKE ?
6,in,notIn,inSql,notinSql,exists,notExists
in,notIn:
notIn("age",{1,2,3})—>age not in (1,2,3)
notIn("age", 1, 2, 3)—>age not in (1,2,3)
inSql, notinSql: sub query can be implemented
Example: inSql("age", "1,2,3,4,5,6") - > age in (1,2,3,4,5,6)
Example: inSql("Id", "select id from table where id < 3") - > ID in (select id from table where id < 3)
@Test
public void testSelectObjs() {
QueryWrapper<User> queryWrapper = new QueryWrapper<>();
//queryWrapper.in("id", 1, 2, 3);
queryWrapper.inSql("id", "select id from user where id < 3");
List<Object> objects = userMapper.selectObjs(queryWrapper);//The return value is the Object list
objects.forEach(System.out::println);
}
The sql is:
SELECT id,name,age,email,create_time,update_time,version,deleted FROM user WHERE deleted=0 AND id IN (select id from user where id < 3)
7,or,and
Note: the UpdateWrapper is used here
If you do not call or, and is used by default
@Test
public void testUpdate1() {
//Modify value
User user = new User();
user.setAge(99);
user.setName("Andy");
//modify condition
UpdateWrapper<User> userUpdateWrapper = new UpdateWrapper<>();
userUpdateWrapper
.like("name", "h")
.or()
.between("age", 20, 30);
int result = userMapper.update(user, userUpdateWrapper);
System.out.println(result);
}
sql statement:
UPDATE user SET name=?, age=?, update_time=? WHERE deleted=0 AND name LIKE ? OR age BETWEEN ? AND ?
8. Nested or, nested and
lambda expressions are used here, and the expressions in or are finally translated into sql with parentheses
@Test
public void testUpdate2() {
//Modify value
User user = new User();
user.setAge(99);
user.setName("Andy");
//modify condition
UpdateWrapper<User> userUpdateWrapper = new UpdateWrapper<>();
userUpdateWrapper
.like("name", "h")
.or(i -> i.eq("name", "Li Bai").ne("age", 20));
int result = userMapper.update(user, userUpdateWrapper);
System.out.println(result);
}
sql statement:
UPDATE user SET name=?, age=?, update_time=? WHERE deleted=0 AND name LIKE ? OR ( name = ? AND age <> ? )
9,orderBy,orderByDesc,orderByAsc
@Test
public void testSelectListOrderBy() {
QueryWrapper<User> queryWrapper = new QueryWrapper<>();
queryWrapper.orderByDesc("id");
List<User> users = userMapper.selectList(queryWrapper);
users.forEach(System.out::println);
}
sql:
SELECT id,name,age,email,create_time,update_time,version,deleted FROM user WHERE deleted=0 ORDER BY id DESC
10,last
Directly spliced to the end of sql
Note: it can only be called once. The last call shall prevail. There is a risk of sql injection. Please use it with caution
@Test
public void testSelectListLast() {
QueryWrapper<User> queryWrapper = new QueryWrapper<>();
queryWrapper.last("limit 1");
List<User> users = userMapper.selectList(queryWrapper);
users.forEach(System.out::println);
}
sql:
SELECT id,name,age,email,create_time,update_time,version,deleted FROM user WHERE deleted=0 limit 1
11. Specify the columns to query
@Test
public void testSelectListColumn() {
QueryWrapper<User> queryWrapper = new QueryWrapper<>();
queryWrapper.select("id", "name", "age");
List<User> users = userMapper.selectList(queryWrapper);
users.forEach(System.out::println);
}
sql:
SELECT id,name,age FROM user WHERE deleted=0
12,set,setSql
The final sql will merge the fields in user.setAge(), userUpdateWrapper.set() and setSql()
@Test
public void testUpdateSet() {
//Modify value
User user = new User();
user.setAge(99);
//modify condition
UpdateWrapper<User> userUpdateWrapper = new UpdateWrapper<>();
userUpdateWrapper
.like("name", "h")
.set("name", "Lao Li Tou")//In addition to querying, you can also use set to set the modified fields
.setSql(" email = '123@qq.com'");//Can have subqueries
int result = userMapper.update(user, userUpdateWrapper);
}
sql:
UPDATE user SET age=?, update_time=?, name=?, email = '123@qq.com' WHERE deleted=0 AND name LIKE ?