Git branch version management
the mainstream code management tool is basically GIT. Although svn is also used by some people, it is not so much. Git is still accepted by most people. The common people in China use open source git library management, and some people use foreign GitHub to do cloud library management, or even can build git management by themselves Central Library, such as gitlab, etc.
The most important point in using Git to manage is branch management. The official website says:
.
What do you mean by the first and third points? In my understanding, the first point and the third point are temporary branches. They are temporary branches. They are deleted when they are used or not used. They will not be retained. This is temporary branches. The fourth point is the same meaning. This is a feature that Git can use very well. It is convenient for development to test a single function.
Here is a flow chart of Git branch management that I understand
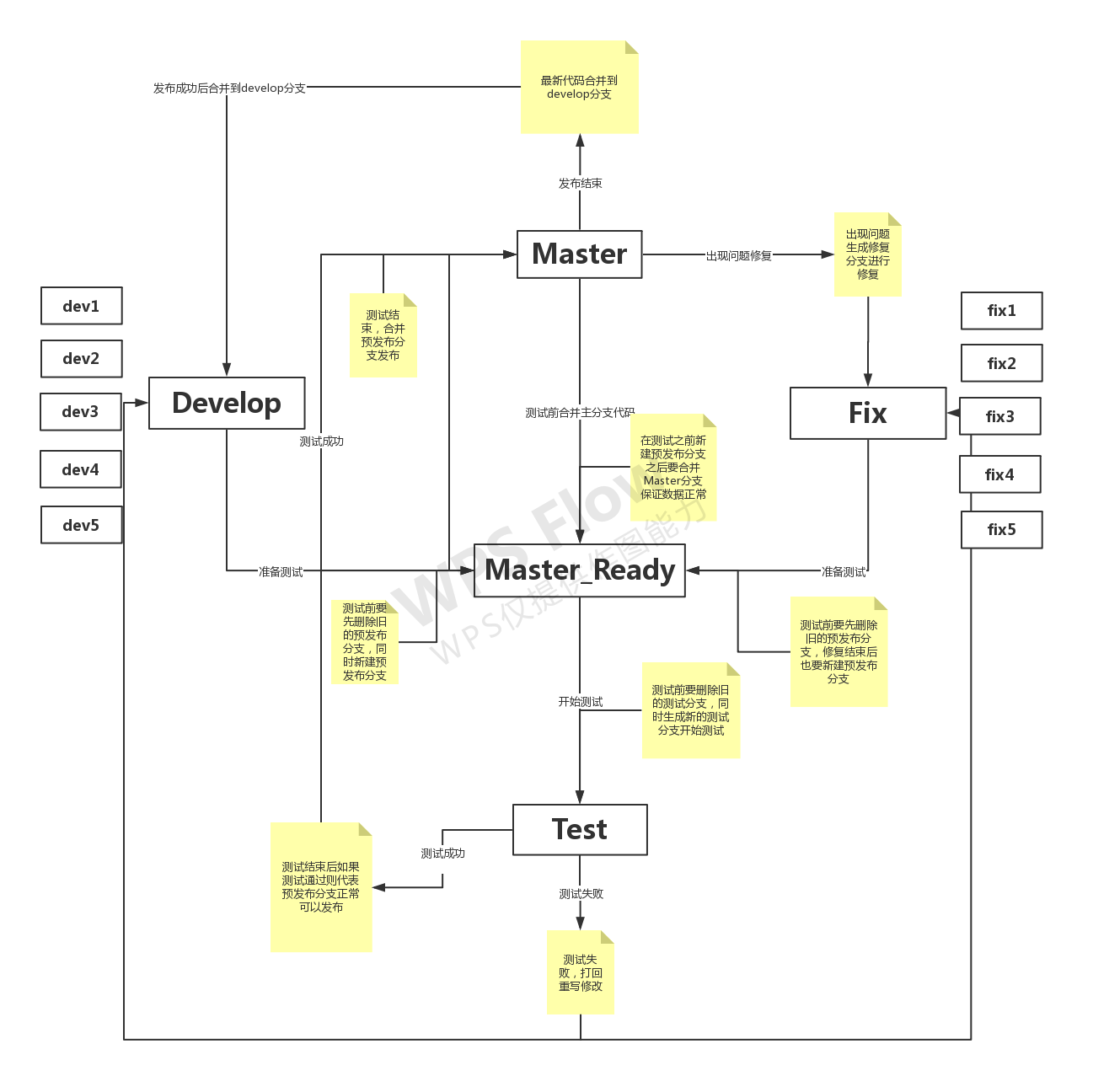
- Master branch: the main branch, which is used to publish production environment code or online code. Only project administrators or publishers have permission to modify it;
- Develop ment Branch: development branch, the branch used by all developers, can also be viewed only by project administrators and developers. After all functions are developed, this branch is the latest code branch;
- Test branch: a test branch, which is dynamically generated and not stored. Each time a single version project is completed, the branch will be generated or deleted to achieve the latest purpose of the code;
- MasterReady branch: the pre release branch is also a dynamically generated branch. It is generated by script before testing, and pushed to the remote end after generation. At the same time, the test branch is dynamically generated after merging development / repair and Master, and then compiled and tested;
- Fix branch: repair branch, which is mainly used when the production environment has problems and needs to be repaired on line. After the problems occur, create a new branch, and then different developers will repair it. After the repair is completed, the development and Test submission process will still be followed;
- devX branch: each developer branch can also operate on the development branch without using the rebase command directly. After the development is completed, it should be merged into the development branch to keep the latest code;
- Fix x branch: the developer branches that fix bug s, as above;
Each development operation process
Development test release process
1.dev1, dev2, dev3 developers develop project function modules and self-test;
2. The developer completes the development, merges all the code into the development branch, and resolves the conflict;
3. Complete the development and submit the test application;
4. Deploy the code through Jenkins script (the deployment script will be given below) (* * script general process: develop masterready – (merge)master – test);
5. Continue to go down after the test is passed, and the failure rewrite and modification start from the first step;
6. Merge and deploy MasterReady branches through Master;
7. After the deployment, reverse the master branch to the development branch;
Repair test release process
1. Fix the problems found in the production environment, and switch out fix branch directly on the master;
2. Repair by the developer, and submit the test application after the repair;
3. Deploy the code through Jenkins script (the deployment script will be given below) (* * script general process: fix masterready - (merge)master - test);
4. Continue to go down after the test is passed, and the failure rewrite and modification start from the first step;
5. Merge and deploy MasterReady branches through Master;
6. After the deployment, reverse the master branch to the development branch;
Script
Test deployment script after development
#!/usr/bin/env bash #Scripts for developers to deploy tests after development is complete #cd Project switch to project root #Switch to the main branch to pull the latest code git checkout master git pull --rebase #Switch to development branch to pull the latest code git checkout develop git pull --rebase #Delete pre release branch git branch | grep -w "master_ready" | xargs git branch -D #Delete test branch git branch | grep -w "test" | xargs git branch -D #Create a new pre release branch from the develop ment branch git checkout -b master_ready #Merge master branch to ensure the latest code git merge master #The current pre release code is the latest code. Delete the remote pre release code. Update the current code to the latest remote code after deletion git push origin :master_ready git push origin master_ready:master_ready #New test branch from current branch after update git checkout -b test #Print current latest submission git log -1 #Start compiling code after switching
Deploy formal script after testing
#!/usr/bin/env bash #Deployment script after testing #cd Project switch to project root #Switch to the main branch to pull the latest code git checkout master git pull --rebase #Delete the current pre release branch and check out the latest one remotely git pull origin master_ready:master_ready #Merge pre release branches git merge master_ready #Push the latest code to the remote end after merging git push origin origin master:master #Deploy compiled code after push #After the deployment is completed, reverse the latest code to develope, and delete the local develope first git branch -D develop #Pull the latest develop ment code git push origin develop:develop #Switch to the development branch and merge the latest master code. If it fails, it will not be processed. If it succeeds, the latest code will be pushed to the remote end git checkout develop git merge master git push origin develop:develop
Test deployment script after repair
#!/usr/bin/env bash #Scripts for developers to deploy tests after development is complete #cd Project switch to project root #Switch to the main branch to pull the latest code git checkout master git pull --rebase #Switch to repair branch pull latest code git checkout fix git pull --rebase #Delete pre release branch git branch | grep -w "master_ready" | xargs git branch -D #Delete test branch git branch | grep -w "test" | xargs git branch -D #Create a new pre release branch from the develop ment branch git checkout -b master_ready #Merge master branch to ensure the latest code git merge master #The current pre release code is the latest code. Delete the remote pre release code. Update the current code to the latest remote code after deletion git push origin :master_ready git push origin master_ready:master_ready #New test branch from current branch after update git checkout -b test #Print current latest submission git log -1 #Start compiling code after switching

