Getting started with javaScript
Article directory
1, Basic grammar
What can I do
- Response Click
- Processing forms
- Create pages dynamically according to user's operation
- Set Cookie
Notes
- Where to write js statement
- Write in body
- Uninstall head
- External introduction
- Same as css file
- How to write js comments
- "/ / write comment here": comment line
- "/ * write comments here * /": write comments in the middle
Identifier, literal quantity and variable naming specification
- Identifier: a tool for naming variables. It starts with letters, underscores, and $. It cannot start with numbers, special characters, or reserved words.
- variable
- Create with var keyword
- Naming to conform to identifier specification
- Called by name, case sensitive
- Literal: I understand it as a constant, which can be used directly without storage
data type
- You can use the tyeof operator to view data types
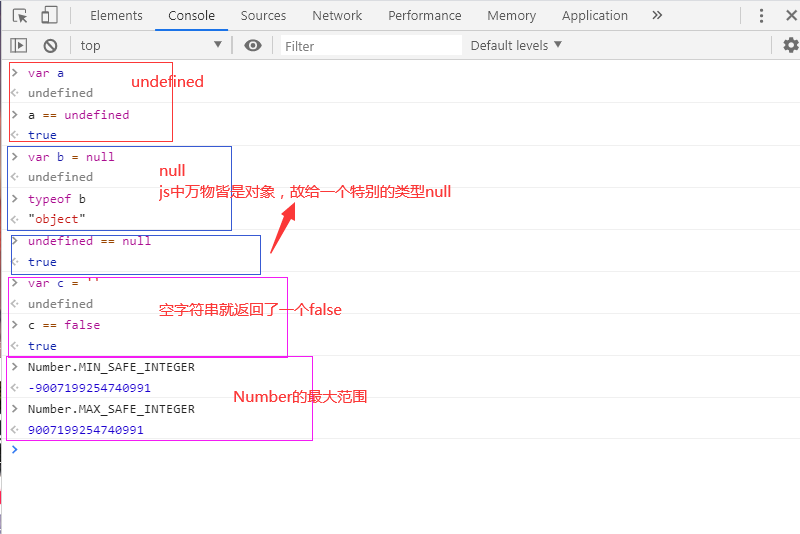
- Basic data type
- undefined
- null
- Number
- Boolean
- String
-
Complex data types
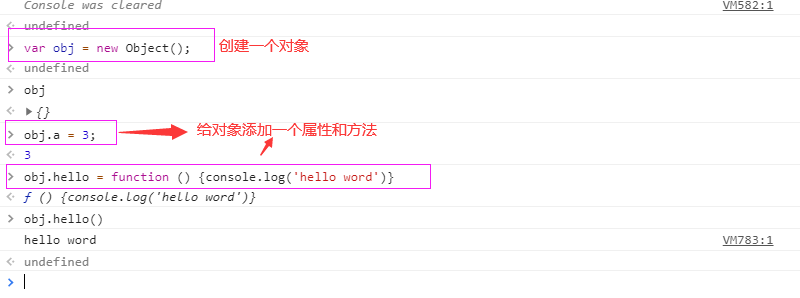
- Object: using new to create an object
Data type conversion, operator
- Data type conversion
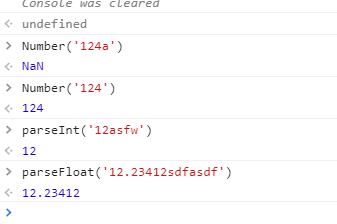
- Number(): other types of conversion value types
- parseInt(): converts a string starting with a number to an integer
- parseFloat(): converts a string starting with a number to a decimal
- Operator
- Arithmetic operators: "+", "-", "*", "/", "%"
- Character operator: + "
- Boolean operators: & &, "" | "
- Assignment operators: '=', '+ =', '- ='
- Unary operators: + +, –
- Comparison operators: '>
2, Common methods of string and array
Character method
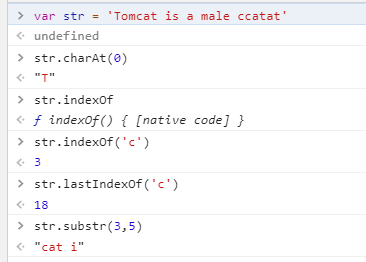
- Charat (subscript of character): return character
- indexOf (character): returns the first position of a character
- lastIndexOf (character): returns the last occurrence of a character
- substr (character subscript 3, length len of the obtained string): returns a string from subscript 3 to length len
- substring (character subscript, total length of the string): from the following table of characters, output to the total length position
- Replace (string to replace, string to replace)
- toUpperCase(), lowercase to uppercase
- toLowerCase(), uppercase string converted to lowercase
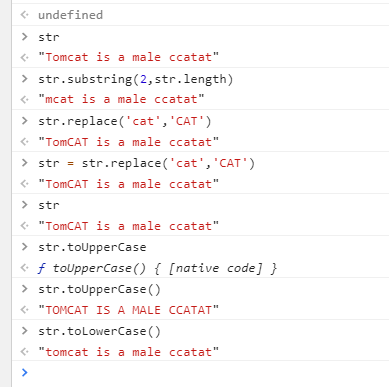
var str = 'Tomcat is a male ccatat'; do{ str = str.replace('cat',''); }while(str.indexOf('cat')!=-1); //Results: "Tom is a male"
Array method
- There are two ways to create an array
/* 1.var arr = new Array(); 2.var arr = [data1,data2,data3] */ var arr = new Array(); arr[0] = 'css' arr[1] = 'html' arr[2] = 'js' var lan = ['html','css','javaScript']
- len(): get the length of the array
- push (one or more data): add data at the end of the array
- pop(): delete the data at the end of the array
- shift(): delete the first data of the array
- Splice (starting position, quantity to be deleted or inserted, data to be deleted or inserted)

3, Functions and objects
Function, function expression
- Function function name (parameter list) {function body consists of one or more statements}
//Methods that use functions as events var hello = function () { doucument.write('hello word'); } hello();
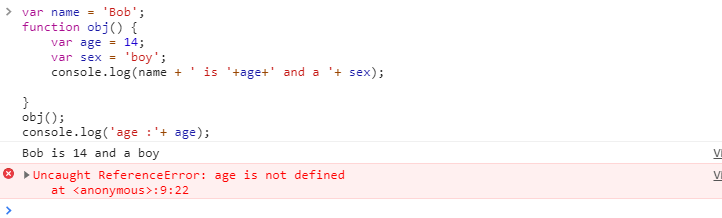
Variable scope
- Variables created within a function are local variables and can only be used within a function
- Global variables are created outside the function, and can be used anywhere in the current script
var name = 'Bob'; function obj() { var age = 14; var sex = 'boy'; console.log(name + ' is '+age+' and a '+ sex); } obj(); console.log('age :'+ age);
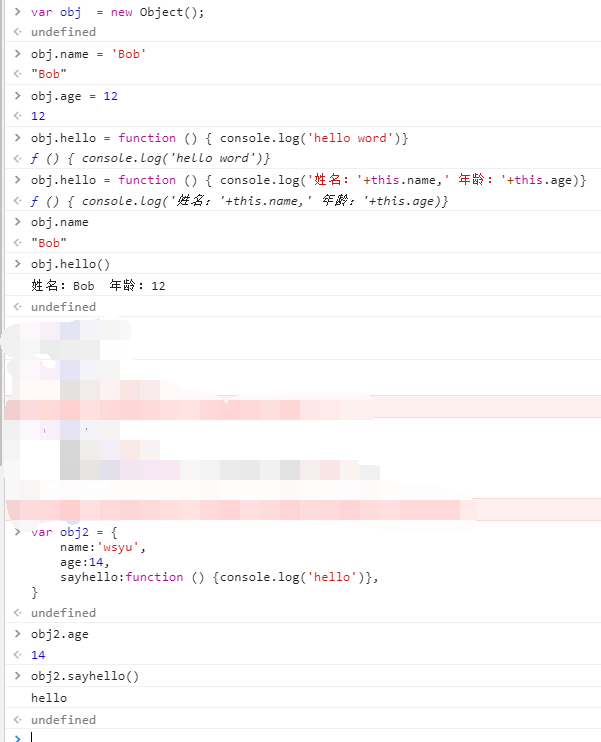
Object & object creation and view
- Object oriented is a kind of thought of transformation
- All objects in js
- Creating objects based on prototypes
- Objects (properties and methods)
- Carrier of attribute: variable
- Method carrier: function
- Object created in view
var obj2 = { name:'wsyu', age:14, sayhello:function () {console.log('hello')}, }
4, Process control
- Conditional judgement
- switch: multi branch judgment
- while,do~while
- for cycle
- for – in loop: traversing objects or arrays
- There is no detailed introduction to this process control, because there is a basis of c, this should not have too big a problem
- The only difference is to traverse the object
-
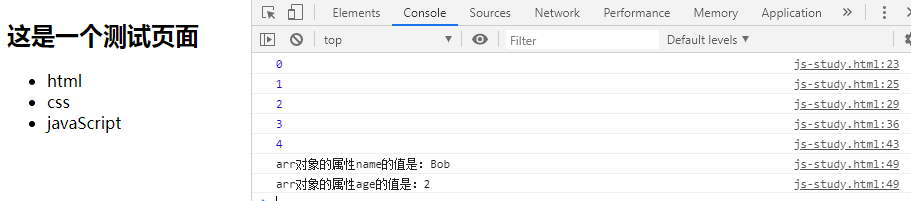
for (placeholder in object) {object [placeholder]}
- Placeholders are replaced by object properties or array elements
- Data output must use '[]' instead of ',' operator
<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title>Document</title> </head> <body> <script> var arr = { name:'Bob', age:2, // sayhello:function () { // console.log(name+' is '+age+'year old'); // }, }; for(var i = 0; i < 6; i++) { var t = i; switch (t) { case 0: if(t==0) console.log(t);break; case 1: if(t==1) console.log(t); else console.log('not 1'); break; case 2: if(t==2) console.log(t); else if(t == 3) console.log(t+'=2 At that time, t+1=3'); else console.log('hello'); break; case 3: //Entry detection while(t==3) { console.log(t); break; } break; case 4: //Export inspection do{ console.log(t); t++; }while(t==4); break; case 5: for(p in arr){ console.log('arr Object properties'+p+'The value is:'+arr[p]); } break; } } </script> <h2 id="header"> //This is a test page </h2> <ul class="list"> <li>html</li> <li>css</li> <li>javaScript</li> </ul> </body> </html>
5, DOM operation
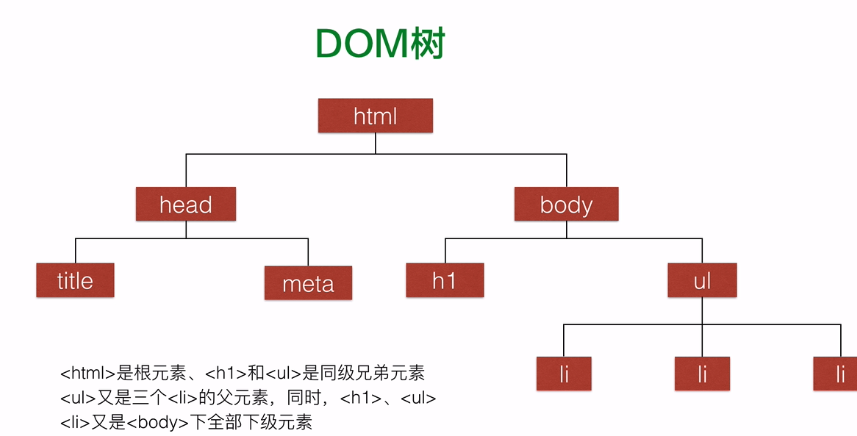
DOM tree
- [document object model] the relationship between elements and themselves in HTML documents
- Each level of element label can be represented in the form of tree
onload & onclick
- window.onload(): executed after all elements of the page are loaded
- document.onclick(): mouse click trigger
<script> window.onload = function () { window.alert('I am window object'); document.onclick = function () { window.alert('I am document object'); } } </script>
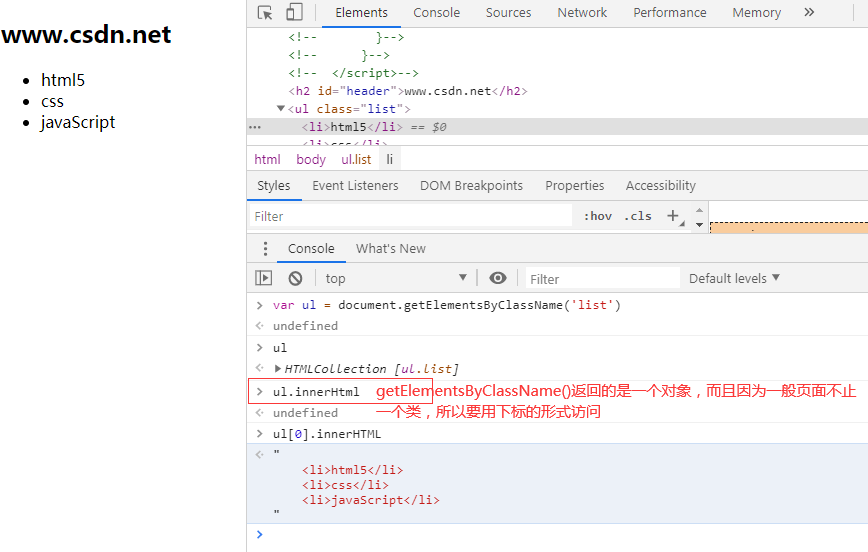
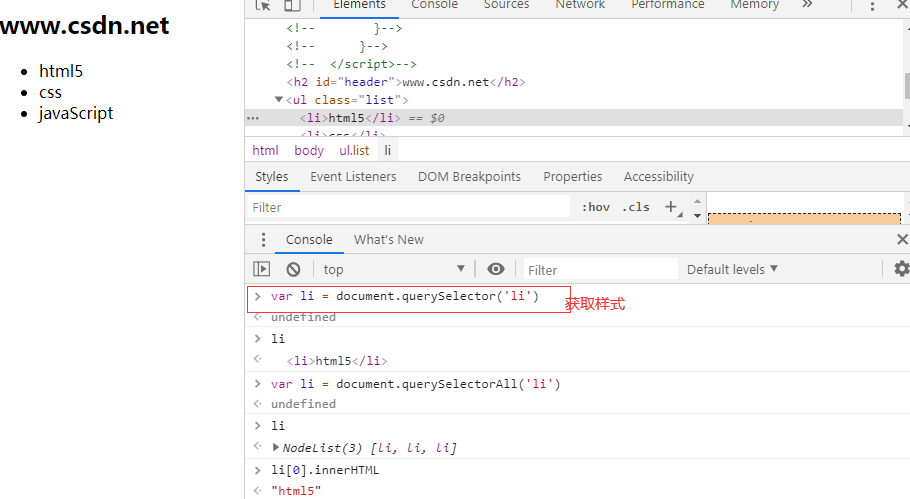
Four common methods of selecting page elements
- Tag: document.getelementsbytagname (tag name)
- id:document.getElementById (id property value)
- Class class: document.getelementsbyclassname (class name)
- querySelector: document.querySelector (Style Selector)
- qureySelectorAll: document.querySelectorAll (Style Selector)


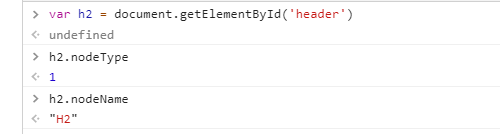
Node attribute: type, name, value
- Node type
- nodeName (element node): nodeValue = 1
- nodeName (attribute node): nodeValue = 2
- nodeName (text node): nodeValue = 3
Relationship between nodes
- Parent node: parentNode
- Child node: childNode
- Previous sibling: previousSibling
- Next sibling: nextSibling
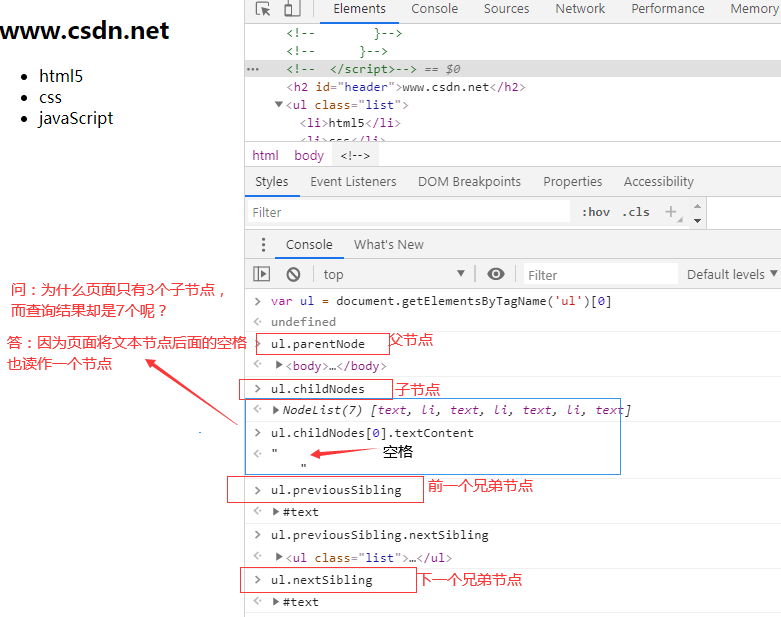
Add, delete, modify and query attribute nodes
//". operator //Get properties of h2 var h2 = document.getElementById('header') //result: <h2 id="header">www.csdn.net</h2> h2.id // result: "header" //Add a property h2.className = 'red' //Set property values and colors h2.className = 'blue' h2.style.color = 'blue' //Method of element //Query label properties h2.getAttribute('id') //result: "header" h2.getAttribute('style') //result: "color: blue;" h2.getAttribute('class') //result: "blue" //Set label properties h2.setAttribute('class','green') //result: undefined h2.getAttribute('class') //result: "green" h2.setAttribute('style','color:green') //result: undefined h2.getAttribute('style') //result: "color:green" //Delete attribute h2.removeAttribute('class') //result: undefined h2.getAttribute('class') //result: null //attributes attribute of element h2.attributes//Returned a key value pair (object) //result: NamedNodeMap {0: id, 1: style, id: id, style: style, length: 2} h2.attributes['style'] //result: style="color:green" //Delete style attribute h2.attributes.removeNamedItem('style') //result: style="color:green"
Addition, deletion, modification and query of element nodes
- Create element node: createElement (tag name)
- Create text node: creareTextNode (text content)
- Insert node to end of parent element: appendChild (node)
- Add to specified location: insertBefor (node to insert, location to insert)
//Create element node var li = document.createElement('li') //Create text node var txt = document.createTextNode('jQuery') //Insert text node into element node li.appendChild(txt) //Parent element node found var ul = document.getElementsByClassName('list')[0] //Insert parent element node ul.append(li) //Insert to specified location ul.insertBefore(li,ul.childNodes[5]) //Delete child nodes ul.removeChild(li)
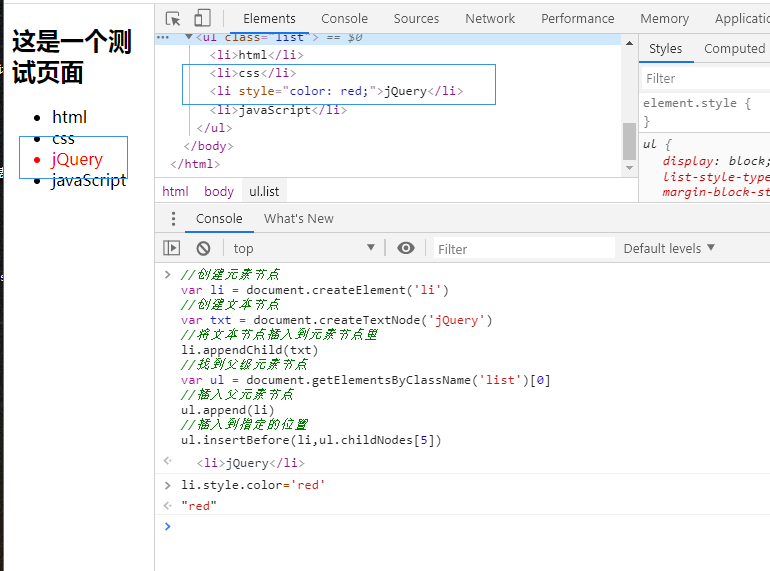
Six, events
Three methods of binding events to objects
- Events are added directly to the element
- Add event to object
- Add events as methods to objects
I don't know how to describe it in words, so I'll go straight to the code
<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0"> <meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="ie=edge"> <title>Document</title> </head> <body> <script> window.onload = function () { var li = document.getElementsByTagName('li')[0]; li.onclick = function () { console.log('li Clicked~~Hey hey hey'); }; var h2 = document.getElementsByTagName('h2')[0]; //Add the event as a method to the object, method name: addEventListener var show = function () { console.log('I'm the monitor'); }; h2.addEventListener('click',show,false) } </script> <h2 id="header" > //This is a test page </h2> <ul class="list"> <li>html</li> <li>css</li> <li onclick="console.log('js Clicked')"> <!-- There is no separation between the form and the behavior structure--> javaScript </li> </ul> </body> </html>
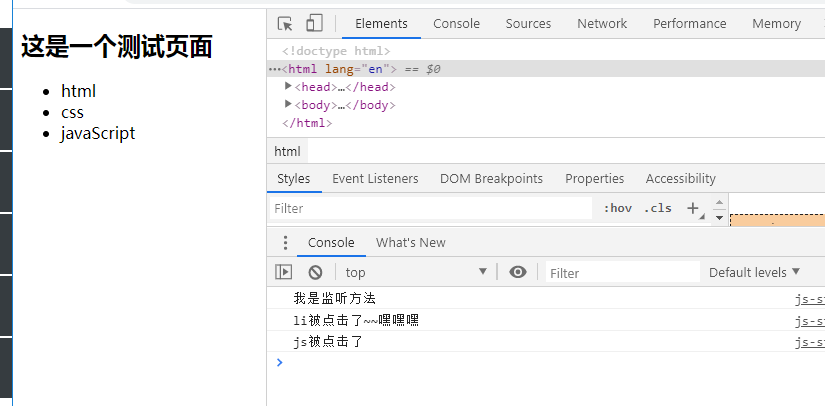
Event bubbling and interception
- I didn't understand the bubble time. I didn't understand the meaning of the video explanation, so it was a bit confusing
- If there's a big problem, please give me a link to learn as a rookie. Thank you

