Getting started with Git
What is Git?
Git is the most advanced distributed version control system in the world. Git records modification rather than content, mainly including workspace, staging area, local warehouse and remote warehouse. Its general workflow is as follows.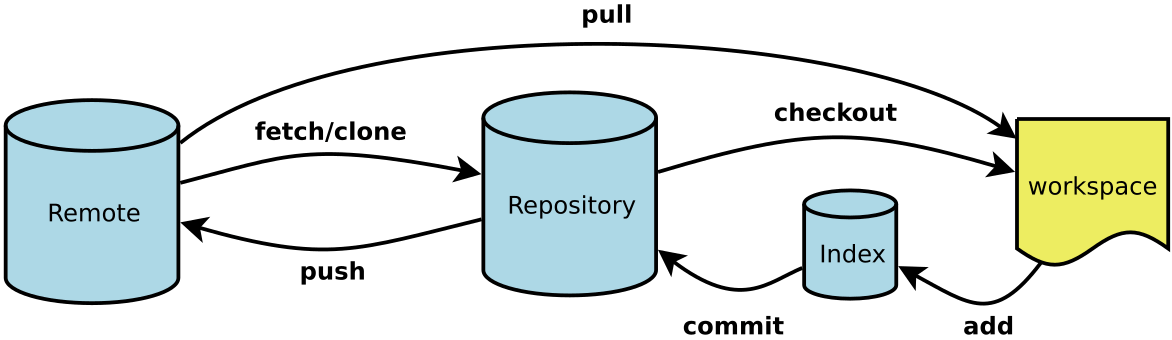
Create version library information and configure user information
# First go to the folder you want to use as the version Library mkdir LearnGit cd LearnGit # Configure user information git config --global user.name "your name" git config --global user.email "your email" # Version library initialization git init
Submit modification process
# Add management files or put changes in staging area git add <file1> <file2> # Put all changes in staging area git add . # Submit all changes in staging area to warehouse git commit -m "modify message"
View operation
# View the difference between the modified version and the latest submitted version git diff HEAD -- <file> # View file modification status git status # View all modification submission history, with--oneline Parameters are displayed in one line.--graph More intuitive display for linked list git log --oneline --graph # View all actions git reflog
Revocation
# If the modification has been added to the staging area, you want to undo the modification made again in the staging area and return to the workspace. git reset HEAD <file> # Discard workspace changes and roll back versions to the latest submitted version git checkout -- <file>
Version rollback
# Back to previous version git reset --hard HEAD # Fallback to specified version git reset --hard <commit_id>
Branching operation
# Create branch git checkout <branch name> # Switch branches after creation git checkout <branch name> # Create and switch branches git checkout -b <branch name> # View branch git branch # You need to switch to the branch to be merged for merging git merge --no--ff -m "merge info" <branch name> # Delete branch git branch -d <branch name> # Force branch deletion git branch -D <branch name>
Storage work area
# Store the workspace, modify the previous bug s and so on. git stash # Display storage area content git stash list # Take out the contents of the storage area. After taking out, the contents of the storage area still need to be manually deleted by git stash drop. git stash apply # Pop up the contents of the storage area, remove the contents of the storage area at the same time git stash pop
Remote warehouse
# git mainly complies with ssh communication protocol, and first generates public key and private key files. ssh-keygen -t rsa -C "your email" # Copy the contents of the id_rsa.pub file in the. ssh folder to the ssh settings in your github account. # Remote Association after creating a new management library git remote add origin git@github.com:JsutCheng/learngit.git # Push all content of branch for the first time git push -u origin <branch name> # Every push after that git push origin <branch name> # Push conflict grab latest commit modify commit again after conflict git pull # Clone Management Library git clone git@github.com:JsutCheng/learngit.git