General Mapper notes
Build development environment (spring boot)
Database table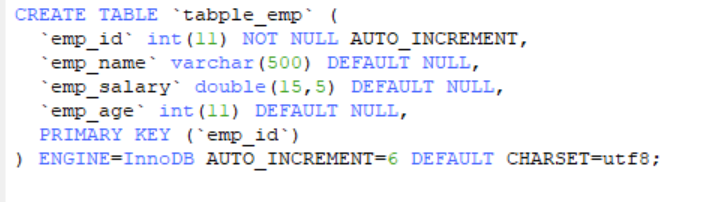
Import dependency
<dependency> <groupId>tk.mybatis</groupId> <artifactId>mapper</artifactId> <version>4.0.4</version> </dependency>
To configure
server: port: 8088 #jdbc configuration spring: datasource: driver-class-name: com.mysql.jdbc.Driver url: jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/mybatis?useUnicode=true&characterEncoding=utf8 username: root password: 123456
Entity class
package com.wang.pojo; import javax.persistence.*; @Table(name="tabple_emp") public class Employee { private Integer empId;//emp_id private String empName;//emp_name private Double empSalary;//emp_salary_apple private Integer empAge;//emp_age public Employee() { } public Employee(Integer empId, String empName, Double empSalary, Integer empAge) { super(); this.empId = empId; this.empName = empName; this.empSalary = empSalary; this.empAge = empAge; } @Override public String toString() { return "Employee [empId=" + empId + ", empName=" + empName + ", empSalary=" + empSalary + ", empAge=" + empAge + "]"; } public Integer getEmpId() { return empId; } public void setEmpId(Integer empId) { this.empId = empId; } public String getEmpName() { return empName; } public void setEmpName(String empName) { this.empName = empName; } public Double getEmpSalary() { return empSalary; } public void setEmpSalary(Double empSalary) { this.empSalary = empSalary; } public Integer getEmpAge() { return empAge; } public void setEmpAge(Integer empAge) { this.empAge = empAge; } }
dao interface
package com.wang.dao; import com.wang.pojo.Employee; import org.springframework.stereotype.Repository; import tk.mybatis.mapper.common.Mapper; @Repository public interface EmpLoyeeDao extends Mapper<Employee> { }
service
package com.wang.service; import com.wang.dao.EmpLoyeeDao; import com.wang.pojo.Employee; import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired; import org.springframework.stereotype.Service; @Service public class EmployeeService { @Autowired private EmpLoyeeDao empLoyeeDao; public Employee getOne(Employee employeeQueryCondition) { return empLoyeeDao.selectOne(employeeQueryCondition); } }
Test class
package mapper.test; import com.wang.Application; import com.wang.pojo.Employee; import com.wang.service.EmployeeService; import org.junit.Test; import org.junit.runner.RunWith; import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired; import org.springframework.boot.test.context.SpringBootTest; import org.springframework.test.context.junit4.SpringJUnit4ClassRunner; @RunWith(SpringJUnit4ClassRunner.class) @SpringBootTest(classes = Application.class) public class Test1 { @Autowired private EmployeeService employeeService; @Test public void testSelectOne() { //1. Create entity class to encapsulate query criteria Employee employee = new Employee(null,"bob",null,null); //2. Execute query Employee result = employeeService.getOne(employee); System.out.println(result); } }
Common annotations
@Table annotation
Function: establish correspondence between entity class and database table.
Default rule: the first letter of entity class name is lowercase as the table name. Employee class → employee table.
Usage: specify the Table name of the target database Table in the name attribute of the @ Table annotation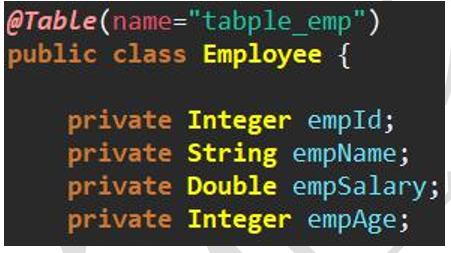
@Column annotation
Function: establish correspondence between entity class fields and database table fields.
Default rule:
- Entity field: hump naming
- Database table fields: use "" to distinguish words
Usage: specify the field name of the target field in the name attribute of the @ Column annotation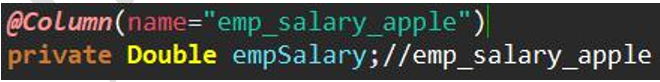 @Id annotation
@Id annotation
When general Mapper executes the xxxByPrimaryKey(key) method, there are two situations.
Case 1: the @ Id annotation is not used to explicitly specify the primary key field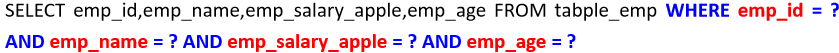
The reason why the above WHERE clause is generated is that the general Mapper takes all the fields in the entity class together as the union primary key.
Case 2: use @ Id primary key to explicitly mark entity class fields corresponding to primary key fields in database tables.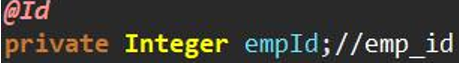
@Generated value annotation
Function: let the general Mapper write back the primary key value automatically generated by the database to the entity class object after the insert operation.
Add primary key usage: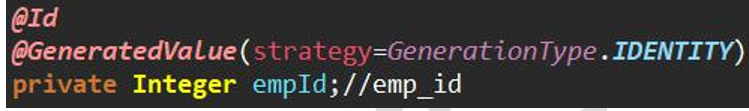
@Transient primary key
Used to mark entity class fields that do not correspond to database table fields.

common method
selectOne method
General Mapper automatically generates SQL statements for us
Entity class encapsulates the rules of WHERE clause generated by query condition
- Generate a WHERE clause with a non empty value
- Use "=" for comparison in conditional expressions
An entity class result must be returned. If there are multiple results, an exception will be thrown
xxxByPrimaryKey method
You need to use the @ Id primary key to clearly mark the entity class fields corresponding to the database table primary key fields, otherwise the general Mapper will use all entity class fields as the union primary key.
xxxSelective method
If the non primary key field is null, it will not be added to the SQL statement.
QBC query
concept
QueryByCriteria
Criteria is the plural form of criteria. Rules, standards, rules. Equivalent to query condition in SQL statement.
QBC query is a modular encapsulation of query conditions through Java objects.
Code example
@Test public void testSelectByExample() { //Objective: where (EMP < salary >? And EMP < age >) or (EMP < salary <? And EMP < age >?) //1. Create Example object Example example = new Example(Employee.class); //*********************** //i. Set sorting information example.orderBy("empSalary").asc().orderBy("empAge").desc(); //ii. Set "de duplication" example.setDistinct(true); //iii. set select field example.selectProperties("empName","empSalary"); //*********************** //2. Create Criteria object through Example object Example.Criteria criteria01 = example.createCriteria(); Example.Criteria criteria02 = example.createCriteria(); //3. Set query Criteria in two Criteria objects //Property parameter: property name of entity class //Value parameter: attribute value of entity class criteria01.andGreaterThan("empSalary", 3000) .andLessThan("empAge", 25); criteria02.andLessThan("empSalary", 5000) .andGreaterThan("empAge", 30); //4. Use OR keyword to assemble two Criteria objects example.or(criteria02); //5. Execute query List<Employee> empList = employeeService.getEmpListByExample(example); for (Employee employee : empList) { System.out.println(employee); } }

