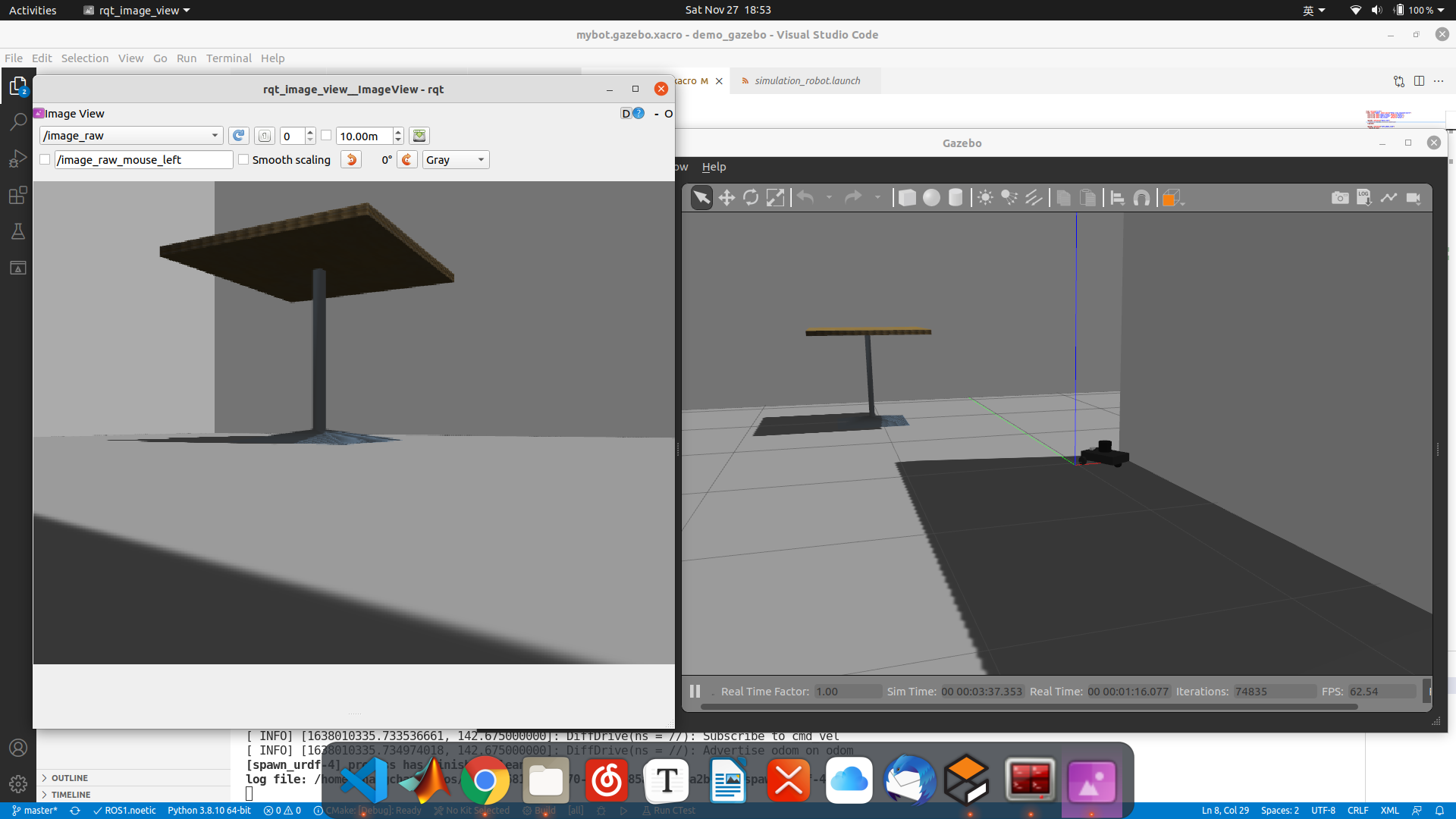
Gazebo robot simulation learning notes
1, Experimental preparation
-
Refer to the video tutorial: 70 minute quick start Gazebo robot simulation.
-
Experimental function Pack:
git clone https://gitee.com/bingda-robot/bingda_tutorials
- Some third-party feature packs
2, world model building
1) Install the official model library of Gazebo
git clone https://gitee.com/bingda-robot/gazebo_models
After the clone is finished, find / home/.gazebo. There is a model in it. You need to put the downloaded file in it.
Possible problems in this step: sometimes Gazebo cannot pop up the file manager. At this time, minimize it and open it again. But I didn't find this problem when I installed Ubuntu 20.04 and noetic on the physical machine. I guess it may be related to the virtual machine.
2) Self built model
- Click Edit - > building editor in the title bar. You can select maps on the left. Click file to save and exit
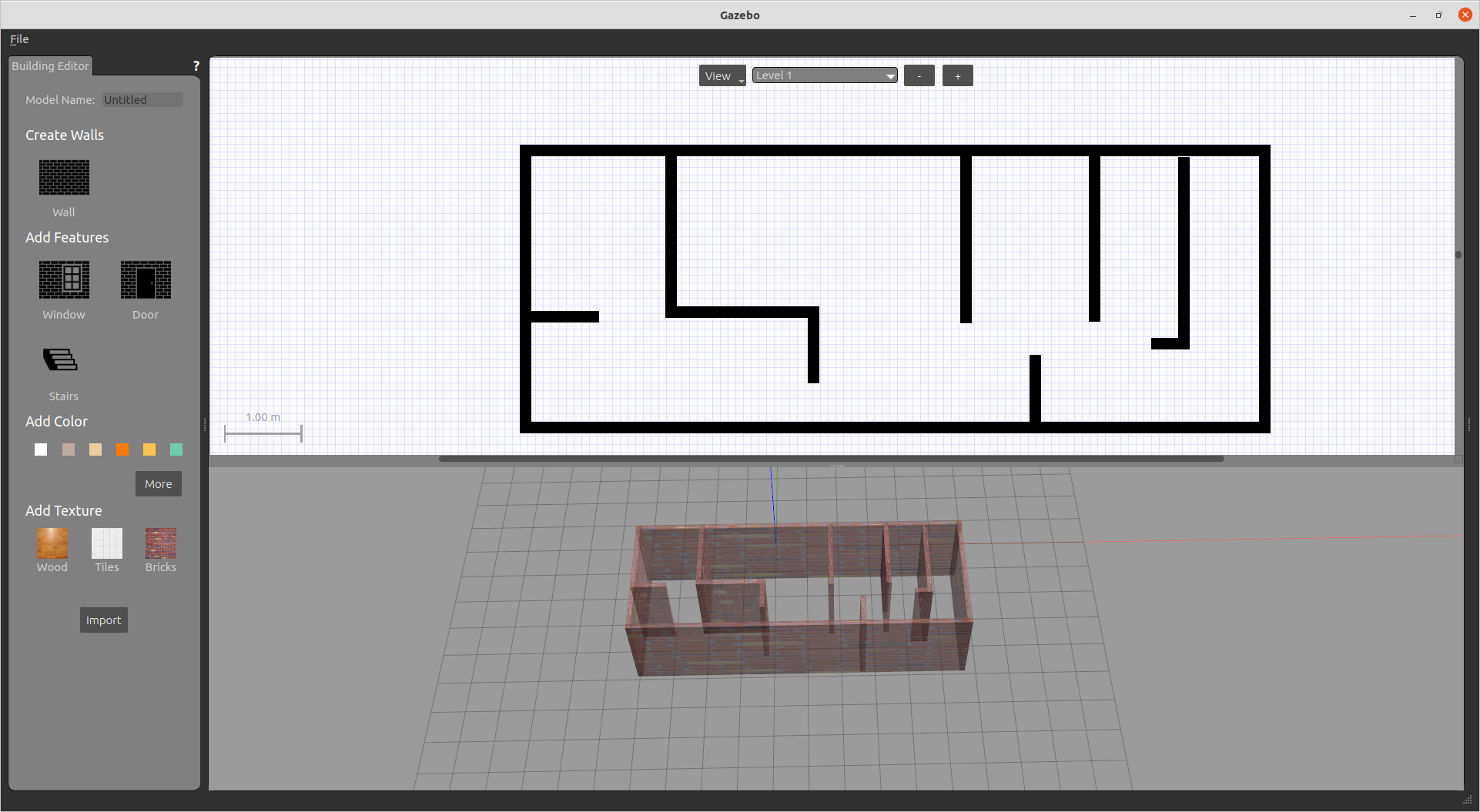
- After exiting, you can see your model in the world. You can add some small objects and save the world
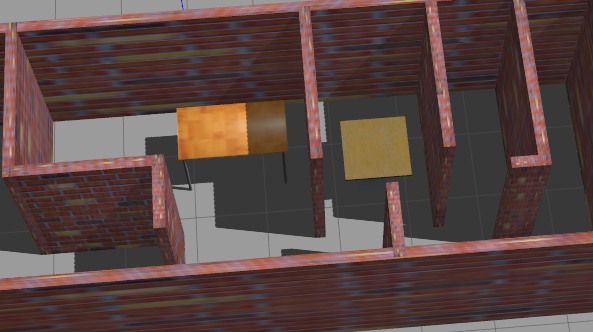
- When using, put it into the world folder in the function package, and modify the launch file.
<launch>
<include file="$(find gazebo_ros)/launch/empty_world.launch">
<!-- My file name is myroom,So modify the following line -->
<arg name="world_name" value="$(find bingda_tutorials)/world/myroom"/>
<arg name="paused" value="false"/>
<arg name="use_sim_time" value="true"/>
<arg name="gui" value="true"/>
<arg name="headless" value="false"/>
<arg name="debug" value="false"/>
</include>
</launch>
3, Robot model building
Introduction to URDF file
- Introduction to ROS official website
- Label of URDF , commonly used are robot, link and joint
- Example
<?xml version="1.0"?>
<robot name="mybot">
<!-- Start label -->
<link name="base_footprint"/>
<!-- ROS In fact, it is an "empty" coordinate without inertia, vision, etc
ROS In, base_link It refers to the coordinates of the robot body, and base_footprint refer to base_link Projection of -->
<joint name="base_joint" type="fixed">
<parent link="base_footprint"/>
<child link="base_link"/>
<origin rpy="0 0 0" xyz="0 0 0"/>
</joint>
<link name="base_link">
<!-- Inertial parameters -->
<inertial>
<origin xyz="0 0 0" rpy="0 0 0"/>
<mass value="0.1"/>
<inertia ixx="0.0001" ixy="0" ixz="0" iyy="0.0001" iyz="0" izz="0.001" />
</inertial>
<!-- Visual parameters -->
<visual>
<geometry>
<box size="0.25 0.16 0.05"/>
</geometry>
<origin rpy="0 0 0" xyz="0 0 0"/>
<material name="blue">
<color rgba="0 0 0.8 1"/>
</material>
</visual>
<!-- Collision parameters -->
<!-- The general setting is the same as the vision, so that the naked eye can see whether there is a collision -->
<collision>
<origin xyz="0 0 0" rpy="0 0 0"/>
<geometry>
<box size="0.25 0.16 0.05"/>
</geometry>
</collision>
</link>
<link name="right_wheel_link">
<inertial>
<origin xyz="0 0 0" rpy="0 0 0"/>
<mass value="0.1"/>
<inertia ixx="0.0001" ixy="0" ixz="0" iyy="0.0001" iyz="0" izz="0.0001" />
</inertial>
<visual>
<geometry>
<cylinder length="0.02" radius="0.025"/>
</geometry>
<material name="black">
<color rgba="0 0 0 1"/>
</material>
</visual>
<collision>
<origin xyz="0 0 0" rpy="0 0 0"/>
<geometry>
<cylinder length="0.02" radius="0.025"/>
</geometry>
</collision>
</link>
<joint name="right_wheel_joint" type="continuous">
<axis xyz="0 0 -1"/>
<parent link="base_link"/>
<!-- Body↑And wheels↓connect -->
<child link="right_wheel_link"/>
<origin rpy="1.5707 0 0" xyz=" 0.1 -0.09 -0.03"/>
</joint>
<link name="left_wheel_link">
<inertial>
<origin xyz="0 0 0" rpy="0 0 0"/>
<mass value="0.1"/>
<inertia ixx="0.0001" ixy="0" ixz="0" iyy="0.0001" iyz="0" izz="0.0001" />
</inertial>
<visual>
<geometry>
<cylinder length="0.02" radius="0.025"/>
</geometry>
<material name="black">
<color rgba="0 0 0 1"/>
</material>
</visual>
<collision>
<origin xyz="0 0 0" rpy="0 0 0"/>
<geometry>
<cylinder length="0.02" radius="0.025"/>
</geometry>
</collision>
</link>
<joint name="left_wheel_joint" type="continuous">
<axis xyz="0 0 -1"/>
<parent link="base_link"/>
<child link="left_wheel_link"/>
<origin rpy="1.5707 0 0" xyz="0.1 0.09 -0.03"/>
</joint>
<link name="ball_wheel_link">
<inertial>
<origin xyz="0 0 0" rpy="0 0 0"/>
<mass value="0.1"/>
<inertia ixx="0" ixy="0" ixz="0" iyy="0" iyz="0" izz="0" />
</inertial>
<visual>
<geometry>
<sphere radius="0.025"/>
</geometry>
<material name="black">
<color rgba="0 0 0 1"/>
</material>
</visual>
<collision>
<origin xyz="0 0 0" rpy="0 0 0"/>
<geometry>
<sphere radius="0.025"/>
</geometry>
</collision>
</link>
<joint name="ball_wheel_joint" type="fixed">
<axis xyz="0 0 1"/>
<parent link="base_link"/>
<child link="ball_wheel_link"/>
<origin rpy="0 0 0" xyz="-0.10 0 -0.03"/>
</joint>
</robot>
-
You can run check_urdf to check
-
First, cd to the directory where urdf is stored
check_urdf yoururdf.urdf
-
You may be prompted that the command cannot be found here. Just install the tool
sudo apt install liburdfdom-tools
-
After successful operation, the link condition should be displayed
-
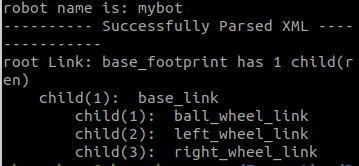
-
It can also be used with the launch file, and the following instructions are used to observe in rviz
roslaunch bingda_tutorials display_robot.launch
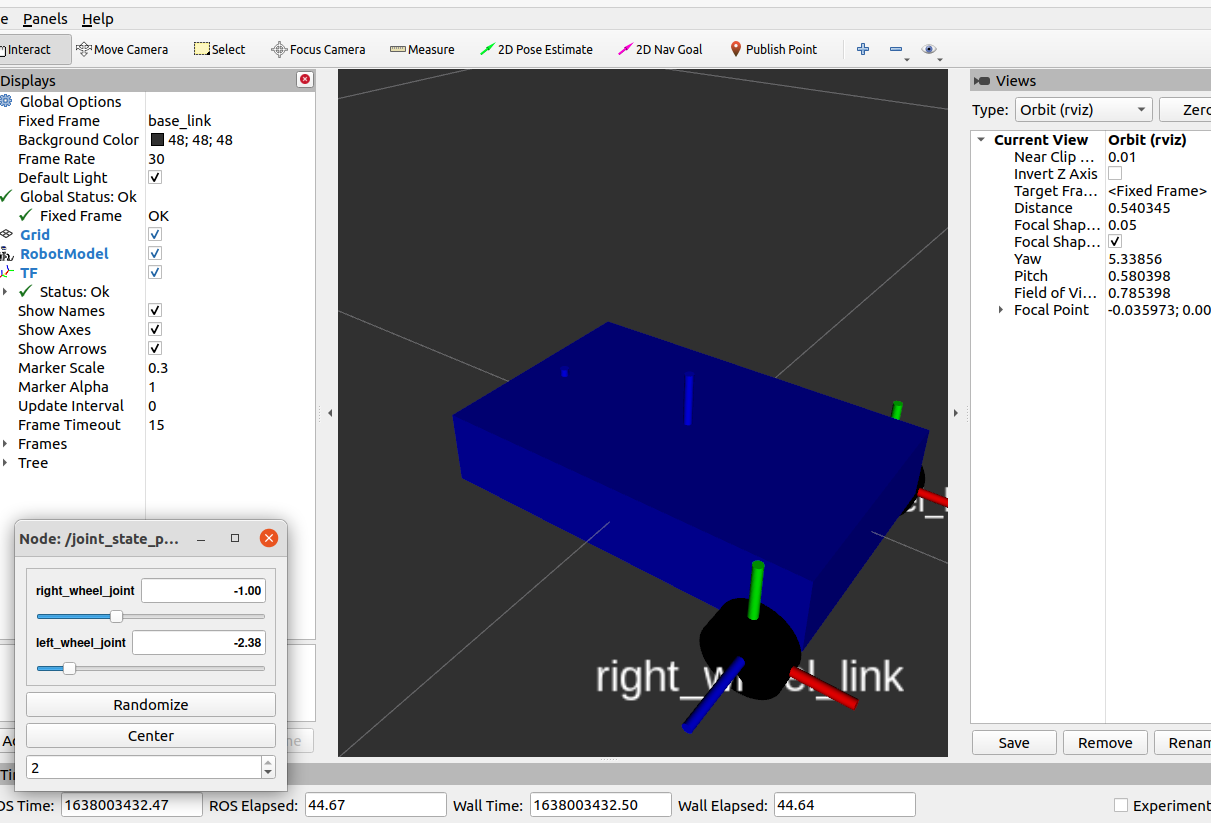
-
Similarly, the launch file is also required for startup in gazebo
<launch> <include file="$(find bingda_tutorials)/launch/gazebo_world.launch"/> <!--Start our world first--> <node name="spawn_model" pkg="gazebo_ros" type="spawn_model" args="-file $(find bingda_tutorials)/urdf/mybot.urdf -urdf -model robot_description" output="screen" /> </launch>4, Sensor and actuator installation
xacro file introduction
-
xacro file is a supplement and perfection of urdf file
-
The main differences between the xacro file of the example and the urdf file are as follows
- Install some sensors
<!-- imu sensor --> <link name="imu"> <visual> <geometry> <box size="0.01 0.01 0.01"/> </geometry> <material name="white"> <color rgba="1 1 1 1"/> </material> </visual> </link> <joint name="imu_joint" type="fixed"> <parent link="base_link"/> <child link="imu"/> <origin xyz="0.08 0 0.025"/> </joint> <!-- camera --> <link name="base_camera_link"> <visual> <geometry> <box size="0.02 0.03 0.03"/> </geometry> <material name="white"> <color rgba="1 1 1 1"/> </material> </visual> </link> <joint name="camera_joint" type="fixed"> <parent link="base_link"/> <child link="base_camera_link"/> <origin xyz="0.1 0 0.025"/> </joint> <!-- laser lidar --> <link name="base_laser_link"> <visual> <geometry> <cylinder length="0.06" radius="0.04"/> </geometry> <material name="white"> <color rgba="1 1 1 1"/> </material> </visual> </link> <joint name="laser_joint" type="fixed"> <parent link="base_link"/> <child link="base_laser_link"/> <origin xyz="0 0.0 0.06"/> </joint>- Reference xacro files, such as C's h file
<robot name="mybot" xmlns:xacro="http://ros.org/wiki/xacro"> <xacro:include filename="$(find bingda_tutorials)/urdf/mybot.gazebo.xacro" /> -
It is better to separate the model xacro file from the simulation related file, which can improve the reusability of our code
-
xacro file about gazebo simulation
Tutorial: Using a URDF in Gazebo This link explains the usage and meaning of tags in detail
Tutorial: Using Gazebo plugins with ROS The sensor and radar shall be inserted in the way of plugin
<?xml version="1.0"?> <robot name="mybot" xmlns:xacro="http://ros.org/wiki/xacro"> <xacro:arg name="laser_visual" default="false"/> <xacro:arg name="camera_visual" default="false"/> <xacro:arg name="imu_visual" default="false"/> <gazebo reference="base_link"> <material>Gazebo/DarkGrey</material> </gazebo> <gazebo reference="left_wheel_link"> <mu1>0.5</mu1> <mu2>0.5</mu2> <kp>500000.0</kp> <kd>10.0</kd> <minDepth>0.001</minDepth> <maxVel>1.0</maxVel> <fdir1>1 0 0</fdir1> <material>Gazebo/DarkGrey</material> </gazebo> <gazebo reference="right_wheel_link"> <mu1>0.5</mu1> <mu2>0.5</mu2> <kp>500000.0</kp> <kd>10.0</kd> <minDepth>0.001</minDepth> <maxVel>1.0</maxVel> <fdir1>1 0 0</fdir1> <material>Gazebo/FlatBlack</material> </gazebo> <gazebo reference="ball_wheel_link"> <mu1>0.1</mu1> <mu2>0.1</mu2> <kp>500000.0</kp> <kd>100.0</kd> <minDepth>0.001</minDepth> <maxVel>1.0</maxVel> <material>Gazebo/FlatBlack</material> </gazebo> <gazebo reference="imu"> <sensor type="imu" name="imu"> <always_on>true</always_on> <visualize>$(arg imu_visual)</visualize> </sensor> <material>Gazebo/FlatBlack</material> </gazebo> <!-- Speed controller --> <gazebo> <plugin name="mybot_controller" filename="libgazebo_ros_diff_drive.so"> <commandTopic>cmd_vel</commandTopic> <odometryTopic>odom</odometryTopic> <odometryFrame>odom</odometryFrame> <odometrySource>world</odometrySource> <publishOdomTF>true</publishOdomTF> <robotBaseFrame>base_footprint</robotBaseFrame> <publishWheelTF>false</publishWheelTF> <publishTf>true</publishTf> <publishWheelJointState>true</publishWheelJointState> <legacyMode>false</legacyMode> <updateRate>30</updateRate> <leftJoint>left_wheel_joint</leftJoint> <rightJoint>right_wheel_joint</rightJoint> <wheelSeparation>0.180</wheelSeparation> <wheelDiameter>0.05</wheelDiameter> <wheelAcceleration>10</wheelAcceleration> <wheelTorque>100</wheelTorque> <rosDebugLevel>na</rosDebugLevel> </plugin> </gazebo> <gazebo> <plugin name="imu_plugin" filename="libgazebo_ros_imu.so"> <alwaysOn>true</alwaysOn> <bodyName>imu</bodyName> <frameName>imu</frameName> <topicName>imu</topicName> <serviceName>imu_service</serviceName> <gaussianNoise>0.0</gaussianNoise> <updateRate>0</updateRate> <imu> <noise> <type>gaussian</type> <rate> <mean>0.0</mean> <stddev>2e-4</stddev> <bias_mean>0.0000075</bias_mean> <bias_stddev>0.0000008</bias_stddev> </rate> <accel> <mean>0.0</mean> <stddev>1.7e-2</stddev> <bias_mean>0.1</bias_mean> <bias_stddev>0.001</bias_stddev> </accel> </noise> </imu> </plugin> </gazebo> <gazebo reference="base_laser_link"> <material>Gazebo/FlatBlack</material> <sensor type="ray" name="rplidar_sensor"> <pose>0 0 0 0 0 0</pose> <visualize>$(arg laser_visual)</visualize> <update_rate>7</update_rate> <ray> <scan> <horizontal> <samples>720</samples> <resolution>0.5</resolution> <min_angle>0.0</min_angle> <max_angle>6.28319</max_angle> </horizontal> </scan> <range> <min>0.120</min> <max>12.0</max> <resolution>0.015</resolution> </range> <noise> <type>gaussian</type> <mean>0.0</mean> <stddev>0.01</stddev> </noise> </ray> <plugin name="gazebo_ros_rplidar_controller" filename="libgazebo_ros_laser.so"> <topicName>scan</topicName> <frameName>base_laser_link</frameName> </plugin> </sensor> </gazebo> <gazebo reference="base_camera_link"> <sensor type="camera" name="csi Camera"> <always_on>true</always_on> <visualize>$(arg camera_visual)</visualize> <camera> <horizontal_fov>1.085595</horizontal_fov> <image> <width>640</width> <height>480</height> <format>R8G8B8</format> </image> <clip> <near>0.03</near> <far>100</far> </clip> </camera> <plugin name="camera_controller" filename="libgazebo_ros_camera.so"> <alwaysOn>true</alwaysOn> <updateRate>30.0</updateRate> <cameraName>/</cameraName> <frameName>base_camera_link</frameName> <imageTopicName>image_raw</imageTopicName> <cameraInfoTopicName>camera_info</cameraInfoTopicName> <hackBaseline>0.07</hackBaseline> <distortionK1>0.0</distortionK1> <distortionK2>0.0</distortionK2> <distortionK3>0.0</distortionK3> <distortionT1>0.0</distortionT1> <distortionT2>0.0</distortionT2> </plugin> </sensor> </gazebo> </robot> -
Startup file
<launch> <arg name="x_pos" default="0.0"/> <arg name="y_pos" default="0.0"/> <arg name="z_pos" default="0.0"/> <param name="/use_sim_time" value="true" /> <!-- Start the environment first--> <include file="$(find bingda_tutorials)/launch/gazebo_world.launch"/> <!--Start the robot description and generate the robot--> <param name="robot_description" command="$(find xacro)/xacro --inorder $(find bingda_tutorials)/urdf/mybot.xacro" /> <node pkg="gazebo_ros" type="spawn_model" name="spawn_urdf" args="-urdf -model mybot.xacro -x $(arg x_pos) -y $(arg y_pos) -z $(arg z_pos) -param robot_description" /> <!--Start a controller--> <node name="robot_state_publisher" pkg="robot_state_publisher" type="robot_state_publisher" /> </launch>
-
-
After starting the launch file, we can use the following instructions to view the topic
rostopic list rostopic info
-
Finally, start the keyboard control node to control the movement of the trolley