★ experimental task
In the final exam of the first grade of primary school, the teacher gave a question: give a row of numbers, select several consecutive numbers, and calculate their sum. The sum of these numbers is required to meet the conditions of a and b. Quickly count out the number of subsequences of students, you can get full marks! After Xiaoming went home, he asked his cousin, mcginn, who was studying as a graduate student. mcginn wrote a piece of code and solved the problem quickly and efficiently. Since then, Xiaoming is determined to become a code farmer!
★ data input
Enter a n n for the number of numbers, and a and B (|a|, |b| < = 100000) enter an array of nums [], (|nums [i] | < = 100000) for the number
★ data output
There are several kinds of continuous subsequences that output a number to indicate that the condition is satisfied
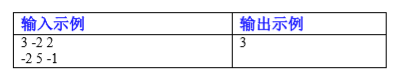
Note: statistical results do not include empty sequences
★ data range
80% of points, n < = 1000, the remaining 20%, n < = 100000
Code 1:
#include <iostream> #include <stdio.h> #include <string.h> #include <algorithm> #include <math.h> #include <stdlib.h> #include <vector> #include <queue> using namespace std; class Search { public: int mergeSort(vector<long>& sum, int left, int right, int lo, int hi) { if(hi-lo <= 1) return 0; int mid = (lo+hi)/2, m = mid, n = mid, count =0; count = mergeSort(sum,left,right,lo,mid) + mergeSort(sum,left,right,mid,hi); for(int i =lo; i< mid; i++) { while(m < hi && sum[m] - sum[i] < left) m++; while(n < hi && sum[n] - sum[i] <= right) n++; count += n - m; } inplace_merge(sum.begin()+lo, sum.begin()+mid, sum.begin()+hi); return count; } int countRangeSum(vector<int>& nums, int left, int right) { int len = nums.size(); vector<long> sum(len + 1, 0); for(int i =0; i< len; i++) sum[i+1] = sum[i]+nums[i]; return mergeSort(sum, left, right, 0, len+1); } }s; int main(){ int n,a,b,i; scanf("%d %d %d",&n,&a,&b); vector<int> nums(n,0); for(i=0;i<n;i++){ scanf("%d",&nums[i]); } int count=s.countRangeSum(nums,a,b); printf("%d",count); return 0; }