1 Overview
Computer network is a computer system that links multiple computers and their external devices with independent functions in different geographical locations through communication lines, and realizes resource sharing and information transmission under the management and coordination of network operating system, network management software and network communication protocol.
2 network communication elements
Address of both parties
- ip
- Port number
Communication protocol
- Application layer: HTTP
- Presentation layer
- Session layer
- Transport layer: TCP UDP
- Network layer: IP
- data link layer
- physical layer
reflection
- How to accurately locate one or more hosts in the network? Find different hosts through IP
- How to communicate after finding the host? Different programs are distinguished by different ports
3 IP address
Corresponding java class: InetAddress
- Uniquely locate a computer on a network
- 127.0.0.1: local localhost
ip address classification
-
IPV4/ IPV6
- IPv4 consists of 32 bits and 4 bytes, with a total of 4.2 billion, 3 billion in North America and 400 million in Asia, which was exhausted in 2011
- IPV6 128 bit, 8 unsigned integers
-
Public network (Internet) / private network (LAN)
- Public network
- Private network
- ABCD class
Domain name: for the convenience of memory, websites generally bind IP addresses through domain names
Domain name -- "DNS server resolves IP --" access through IP "
4 Ports
A port represents the process of a program on a computer
-
Different processes have different port numbers! Used to distinguish software
-
Specified 0-65535
-
TCP UDP: 65535 * 2 the same protocol port cannot be the same
-
Public port 0 ~ 1023
-
HTTP: 80
-
HTTPS: 443
-
FTP: 21
-
Telent: 23
-
Program registration port: 1024 ~ 49151
-
Dynamic ~ private 49152 - 65535
View ports netstat -ano # view all ports
windows:netstat -ano | findstr "5900"
linux: netstat -ano | grep"5900"
5 TCP
client
- Link server socket
- send message
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.OutputStream;
import java.net.InetAddress;
import java.net.Socket;
import java.nio.charset.StandardCharsets;
// tcp client
public class TcpClientDemo01 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Socket socket = null;
OutputStream os = null;
try {
// 1. Know the server address and port number
InetAddress serverIP = InetAddress.getByName("127.0.0.1");
int port = 9999;
// 2 create a socket link
socket = new Socket(serverIP, port);
// 3 send information IO stream
os = socket.getOutputStream();
os.write("hello server".getBytes(StandardCharsets.UTF_8));
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}finally {
if (os!=null){
try {
os.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
if(socket!=null){
try {
socket.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
}
The server
- Establish the port of the service
- Wait for user's link accept
- Receive messages from users
import java.io.ByteArrayOutputStream;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStream;
import java.net.ServerSocket;
import java.net.Socket;
// tcp Server
public class TcpServerDemo01 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ServerSocket serverSocket = null;
Socket socket = null;
InputStream is = null;
ByteArrayOutputStream baos = null;
try {
// I have to have an address
serverSocket = new ServerSocket(9999);
while(true){
// 2 wait for the client to link
socket = serverSocket.accept();
// 3 read messages from the client
is = socket.getInputStream();
// 4 pipeline flow
baos = new ByteArrayOutputStream();
byte[] buffer = new byte[1024];
int len;
while((len=is.read(buffer))!= -1){
baos.write(buffer,0,len);
}
System.out.println(baos.toString());
}
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}finally {
// close resource
if (baos!=null){
try {
baos.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
if(is !=null){
try {
is.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
if (socket !=null){
try {
socket.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
if(serverSocket!=null){
try {
serverSocket.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
}
6 file upload
client
import java.io.*;
import java.net.InetAddress;
import java.net.Socket;
public class TcpClientDemo02 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
// 1 create a socket link
Socket socket = new Socket(InetAddress.getByName("127.0.0.1"), 9000);
// 2 create an output stream
OutputStream os = socket.getOutputStream();
// 3 read file
FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream(new File("A.jpg"));
// 4 write out the document
byte[] buffer = new byte[1024];
int len;
while ((len = fis.read(buffer)) != -1) {
os.write(buffer, 0, len);
}
// Notify the server that I'm finished
socket.shutdownOutput();
// Make sure that the server has received it before you can disconnect the link
InputStream inputStream = socket.getInputStream();
ByteArrayOutputStream baos = new ByteArrayOutputStream();
byte[] buffer2 = new byte[1024];
int len2;
while((len2=inputStream.read(buffer2))!=-1){
baos.write(buffer2,0,len2);
}
System.out.println(baos.toString());
// 5 close resources
baos.close();
inputStream.close();
fis.close();
os.close();
socket.close();
}
}
The server
import java.io.File;
import java.io.FileOutputStream;
import java.io.InputStream;
import java.io.OutputStream;
import java.net.ServerSocket;
import java.net.Socket;
import java.nio.charset.StandardCharsets;
public class TcpServerDemo02 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
// 1 create service
ServerSocket serverSocket = new ServerSocket(9000);
// 2 listen for client links,
Socket socket = serverSocket.accept(); // Blocking listening will wait for the client link
// 3 get input stream
InputStream is = socket.getInputStream();
// 4 file output
FileOutputStream fos = new FileOutputStream(new File("receive.jpg"));
byte[] buffer = new byte[1024];
int len;
while ((len = is.read(buffer)) != -1) {
fos.write(buffer, 0, len);
}
// Notification client received
OutputStream os = socket.getOutputStream();
os.write("I'm finished. You can disconnect".getBytes(StandardCharsets.UTF_8));
// 5 close resources
fos.close();
is.close();
socket.close();
serverSocket.close();
}
}
7 UDP
7.1 basic application
UDP has no concept of client and server, only sender and receiver
Sender code
import java.net.DatagramPacket;
import java.net.DatagramSocket;
import java.net.InetAddress;
public class UdpClientDemo01 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
// 1 establish a socket
DatagramSocket socket = new DatagramSocket();
// 2 a package is required
String msg = "hello server";
DatagramPacket packet = new DatagramPacket(msg.getBytes(), 0, msg.getBytes().length, InetAddress.getByName("localhost"), 9090);
// 3 send packet
socket.send(packet);
// 4 close resources
socket.close();
}
}
Receiver code
import java.net.DatagramPacket;
import java.net.DatagramSocket;
public class UdpServerDemo01 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
// Open port
DatagramSocket socket = new DatagramSocket(9090);
// Receive packet
byte[] buffer = new byte[1024];
DatagramPacket packet = new DatagramPacket(buffer, 0, buffer.length);
socket.receive(packet); // Blocking reception
// Print receive parameters
System.out.println(packet.getAddress().getHostAddress() + "--->" + new String(packet.getData(), 0, packet.getLength()));
// Close link
socket.close();
}
}
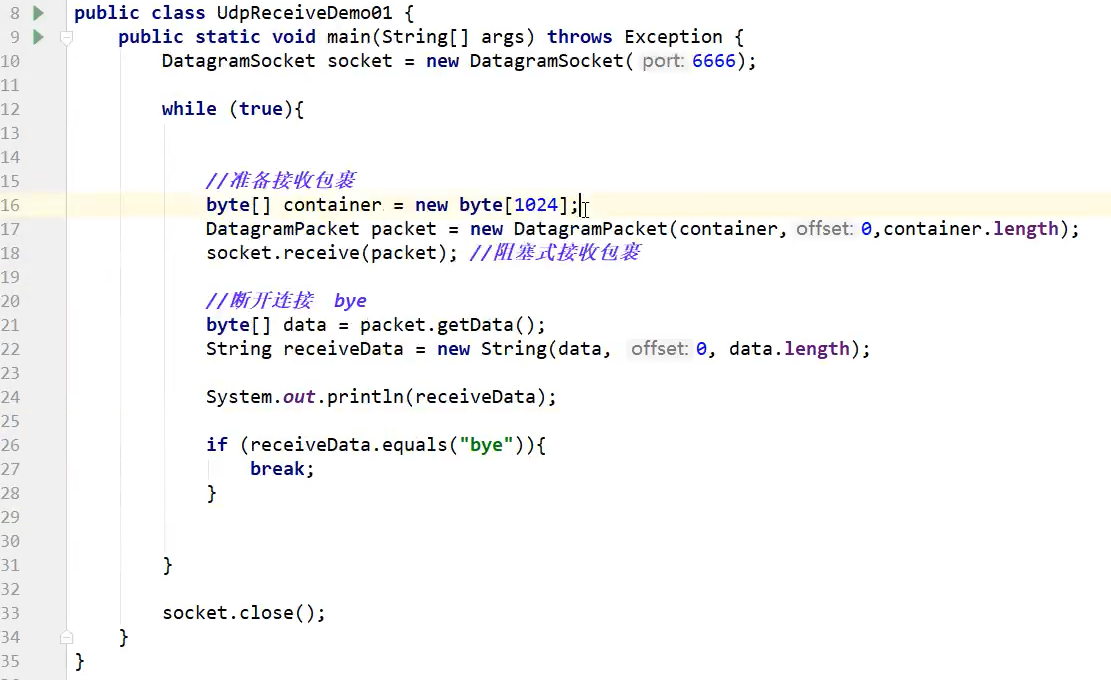
7.2 UDP chat room
Cyclic transmitter
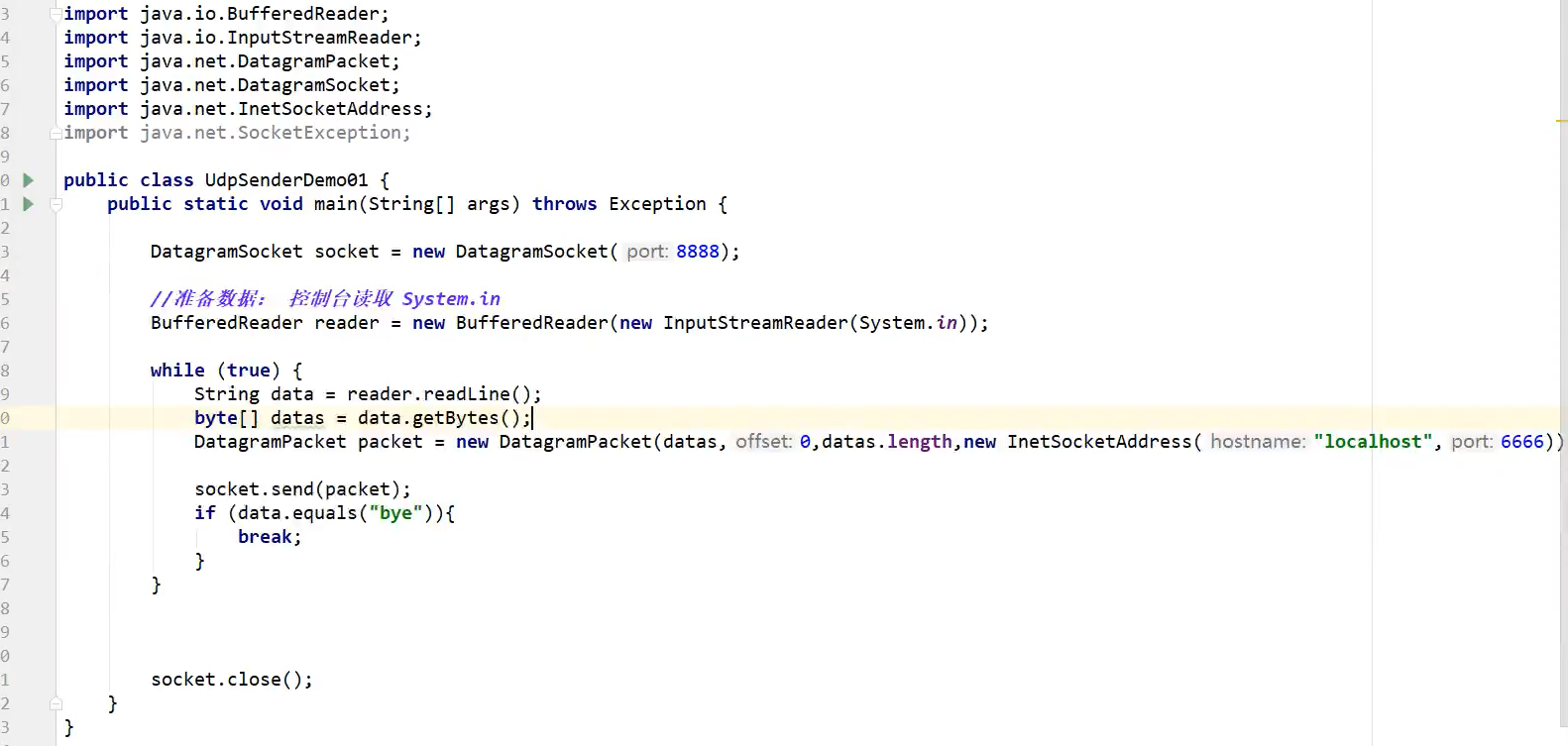
Cyclic receiver