1. Verification codes are implemented by the back end.
2. What is Vue.js
At present, three popular front-end frameworks are Vue.js, React.js and Angular.js.
Benefits of front-end frameworks: Reducing unnecessary operations, two-way data binding concepts
3. Differences between frameworks and libraries (which can be called plug-ins):
Framework is a set of solutions; libraries can be seen as plug-ins that provide functionality
4. Diagram of the relationship between MVC and MVVM
MVC Framework: (Note that App.js in the figure is the content of the back end)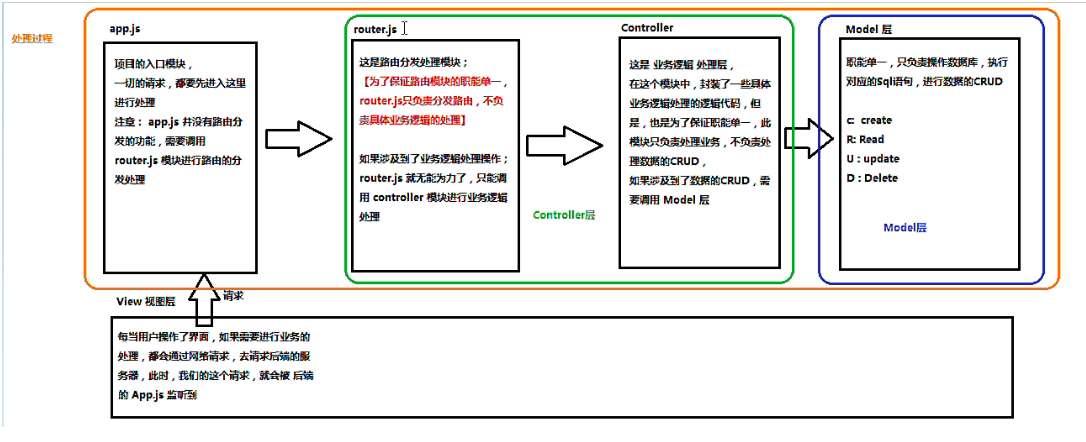
MVVM framework (is the hierarchical development idea of front-end view layer, which divides each page into M, V and VM, in which VM is the core of MVVM idea, because VM layer is the dispatcher between M and V):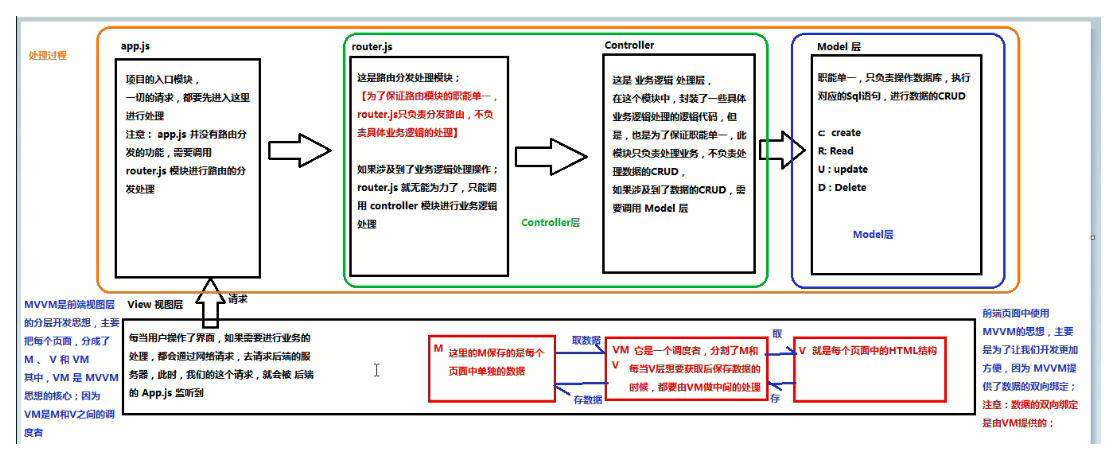
5. Correspondence between Vue Basic Code and MVVM
V: In the label, what can be displayed on the page
Contents defined by VM: new Vue ({xxxx})
M: Store data for each page
new Vue({xxx}) returns an instance object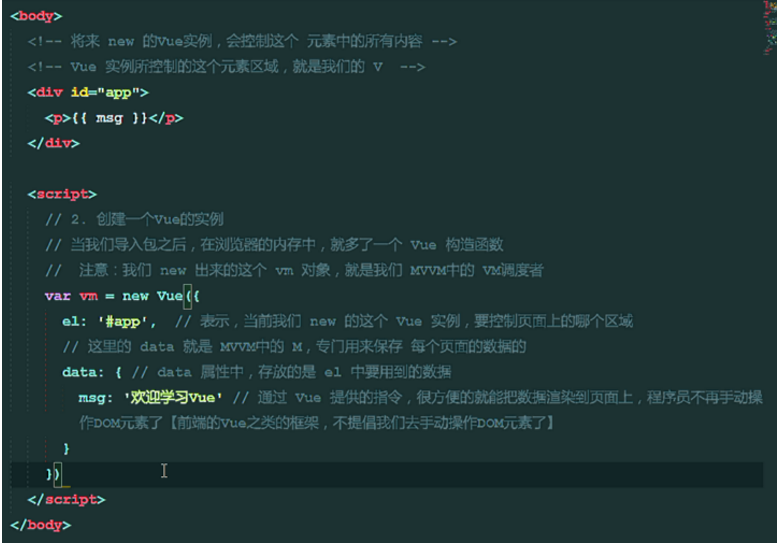
6. Explain the basic usage of V-cloak, v-text and v-html.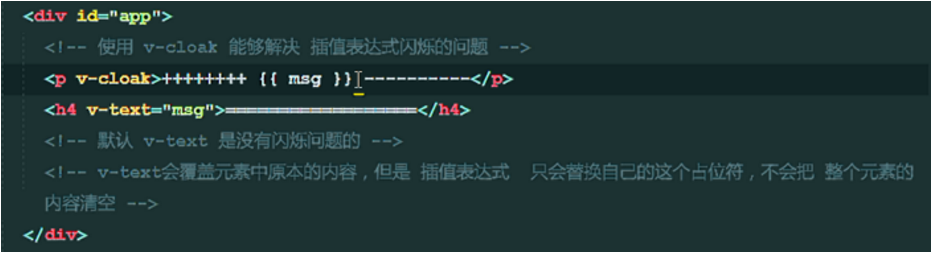

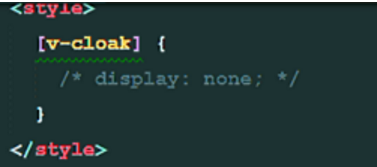
v-html: will display < H 1 > </h 1 >'(html tag) as normal, rather than output as a string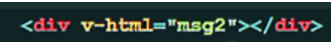
7. v-bind Instruction Learning
mytitle is a variable in the code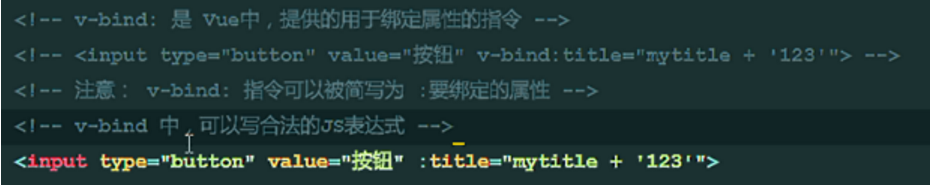
8. Define events in Vue using v-on instructions
DOM operation: document.getelementById("xx"). onclick = function(){xxx}
Vue:v-on:click = "xxx"
Method Writing Method (Method is an object)
Mouse Coverage: v-on:mouseover= "xxx"
9. Effectiveness Production of Racing Horse Lamp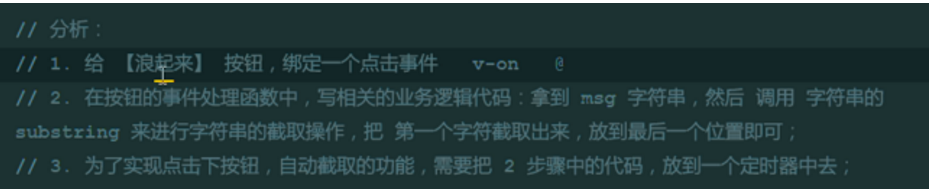

<template>
<div>
<!--Horse Lantern Effect
//The substring is used to intercept the string, and the first string is intercepted and placed in the last position.
//Click on the button, use the timer to intercept automatically, 0.5s once
-->
<button @click="show">start</button>
<button @click="shop">Stop it</button>
<h4>{{text}}</h4>
</div>
</template>
<script>
export default {
//Note that using data data in this {} requires this to point to.
//Explain that the data data data is inside this {}
name: 'day_one',
data(){
return{
text:'Multilingual Real-time Online Translation_Baidu Translate',
intervalId:null //Define the timer ID on data
}
},
methods:{
show(){
if (this.intervalId !== null){
return 0;
}
//=> To solve the problem of this pointing; to make the internal and external this pointing consistent
this.intervalId = setInterval(()=>{
//start: intercepts the first string
var start = this.text.substring(0,1);
//start: Intercept the remaining strings
var end = this.text.substring(1);
//Connect two strings together
this.text = end + start;
}
,500)
},
shop(){
clearInterval(this.intervalId);
//After clearing the timer, return this. intervarId = 6
//So in order to turn on the timer next time, set intervalId manually to null
this.intervalId = null;
}
}
}
</script>
10. Event modifiers
(1) @. click.shop: Prevent event bubbles (from inside to outside)
(2) @. click.prevent: Prevent default behavior
(3) @. click.capture: capture mechanism (from outside to inside)
(4) @. click.self: When you click on your button, it will trigger. It will not trigger passively because of bubbles or capture.
(5) @. click.once: Events are triggered only once
(6) @. click.prevent.once: the default behavior is blocked when the first click is clicked, but not when the next click is clicked;.Prevent and. once have no orderly difference
11. v-model (unique) implements bidirectional data binding of form elements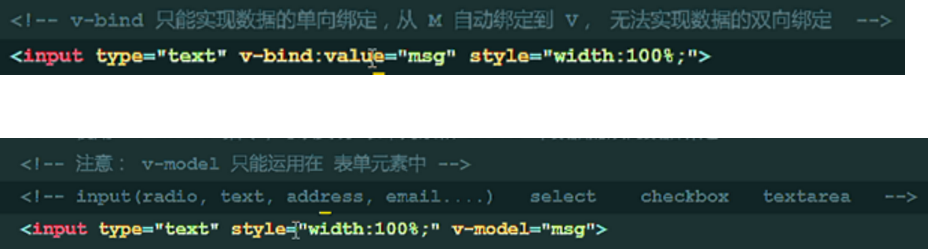
The Case of v-model Implementing Calculator
<template>
<!--v-model A Case Study of Implementing a Calculator-->
<div>
<input type="text" v-model="n1">
<select v-model="opt">
<option value="+">+</option>
<option value="-">-</option>
<option value="*">*</option>
<option value="/">/</option>
</select>
<input type="text" v-model="n2">
<button @click="calc">=</button>
<input type="text" v-model="result">
</div>
</template>
<script>
export default {
data(){
return{
n1:0,
n2:0,
result:0,
opt:'+'
}
},
methods:{
//Method 1:
calc() {
// switch (this.opt) {
// case '+' :
// this.result = parseInt(this.n1) + parseInt(this.n2);
// break;
// case '-' :
// this.result = parseInt(this.n1) - parseInt(this.n2);
// break;
// case '*' :
// this.result = parseInt(this.n1) * parseInt(this.n2);
// break;
// case '/' :
// this.result = parseInt(this.n1) / parseInt(this.n2);
// break;
// }
//Method 2 (not recommended for project development):
eval() Function calculates a string and executes its JavaScript Code.
var codeStr = parseInt(this.n1) + this.opt + parseInt(this.n2);
this.result = eval(codeStr)
}
}
}
</script>
12. vue sets class style through attribute binding to element (4-minute method)
class="[]/{}/ Write attribute names directly"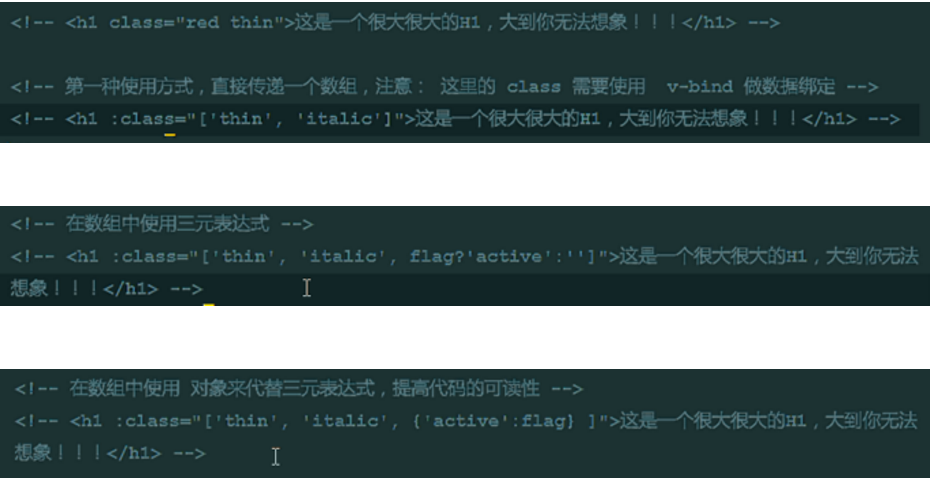
However, attributes within an object but "-" need to be caused by'(quotation marks).
13. In vue, style is bound to elements by attribute binding (three ways)
style="{xxx}"; when multiple objects are needed, arrays []
Four Ways of v-for Instruction
// item; represents an item of the list array, using v-for to loop each item
Circulating ordinary arrays: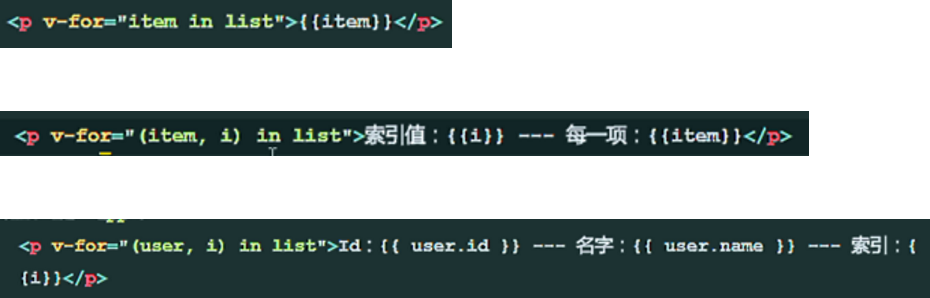
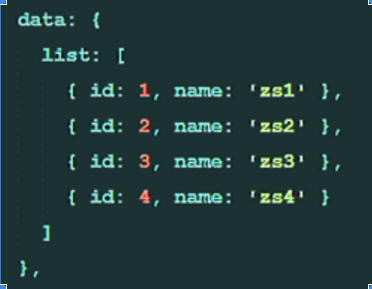
Traversing objects: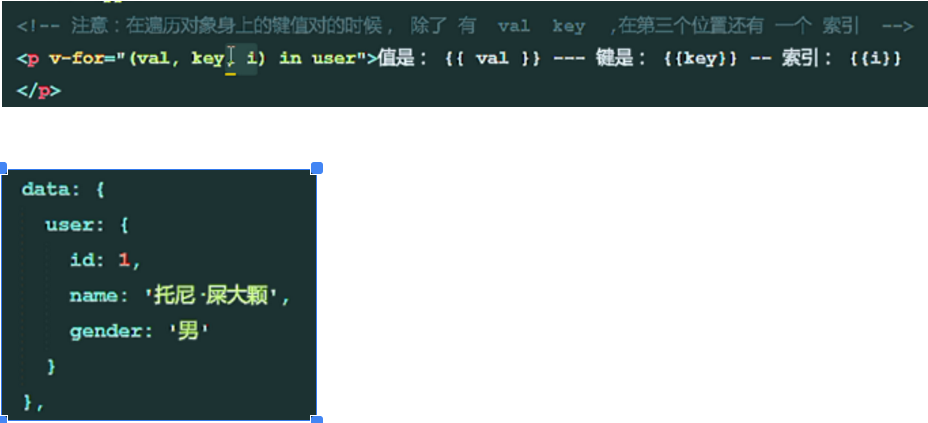
count: No need to define in data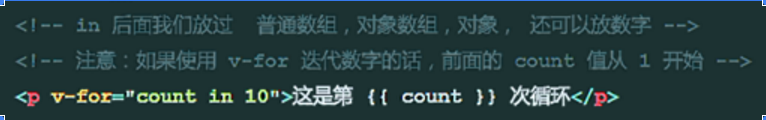
(2) Notes on the use of key in v-for
Key: guarantees the uniqueness of the data (for example, if the key attribute is not defined, when the input of id=5 is checked, a data is inserted before the input, and the selected content checks the input of id=4 (that is, the content of the current index is 5)).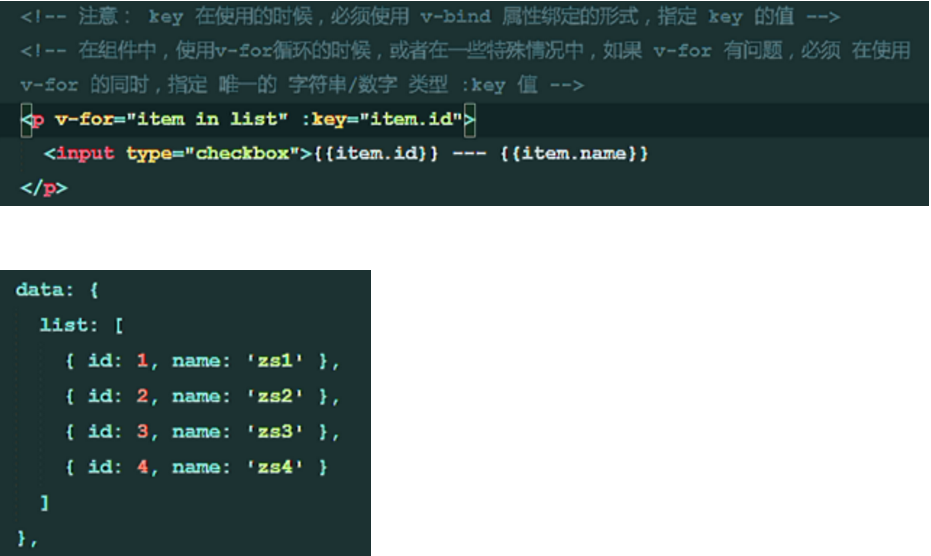
15. Use and Characteristics of v-if and v-show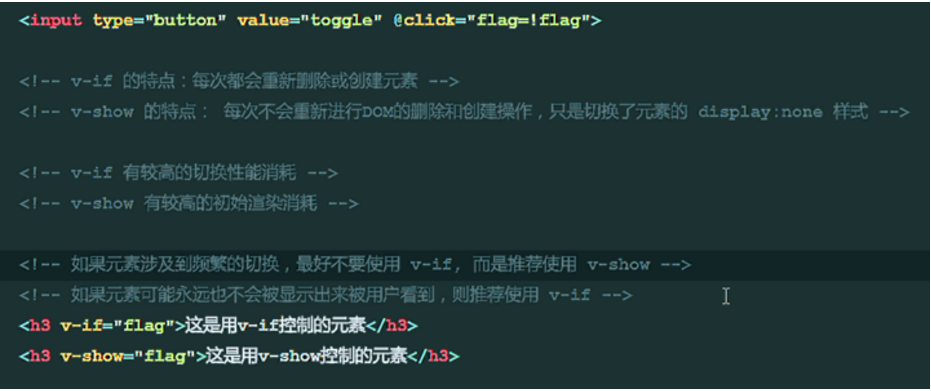
16. Summary of day1:
(1) Don't add id to body