AJAX front-end transmission of arrays and java back-end reception (back-end reception of array type data sent by the front-end) are two solutions
In the first method, the front-end converts the array into json format data through JSON.stringify() method, and the back-end converts the received json data into an array.
function search() {
var equiNames = JSON.stringify($("#equiNames").val());
var startDate = $('#daterange-btn span').text().substring(0, 10);
var endDate = $('#daterange-btn span').text().substring(13);
$.ajax({
url : "dataAcquisition/report",
type : "post",
dataType : "json",
data : {
"equiNames" : equiNames,
"startDate" : startDate,
"endDate" : endDate
},
success : function(result) {
......
}
}
});
}
@RequestMapping("/report")
public void report(String equiNames, String startDate, String endDate, HttpServletRequest request,
HttpServletResponse response) throws ExecutionException, InterruptedException, IOException, ParseException {
//Converting received json data into arrays
List<String> equiNameList = new Gson().fromJson(equiNames, new TypeToken<List<String>>() {
}.getType());
List<DataAcquisitionVo> resultList = dataAcquisitionService.report(equiNameList, startDate, endDate);
response.setContentType("application/json; charset=UTF-8");
response.getWriter().write(new Gson().toJson(resultList));
}
In the second method, the front end passes the array */ directly by setting the traditional attribute to true, while the background receives the object.
function search() {
var equiNames = JSON.stringify($("#equiNames").val());
var startDate = $('#daterange-btn span').text().substring(0, 10);
var endDate = $('#daterange-btn span').text().substring(13);
$.ajax({
url : "dataAcquisition/report",
type : "post",
dataType : "json",
traditional : true,//Serialize data in a traditional way
data : {
"equiNames" : equiNames,
"startDate" : startDate,
"endDate" : endDate
},
success : function(result) {
......
}
}
});
}
object
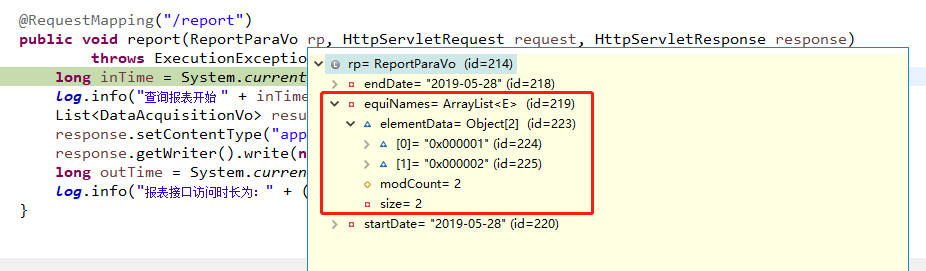
@RequestMapping("/report")
public void report(ReportParaVo rp, HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response)
throws ExecutionException, InterruptedException, IOException, ParseException {
List<DataAcquisitionVo> resultList = dataAcquisitionService.report(rp);
response.setContentType("application/json; charset=UTF-8");
response.getWriter().write(new Gson().toJson(resultList));
}
import java.util.List;
public class ReportParaVo {
private List<String> equiNames;
private String startDate;
private String endDate;
public List<String> getEquiNames() {
return equiNames;
}
public void setEquiNames(List<String> equiNames) {
this.equiNames = equiNames;
}
public String getStartDate() {
return startDate;
}
public void setStartDate(String startDate) {
this.startDate = startDate;
}
public String getEndDate() {
return endDate;
}
public void setEndDate(String endDate) {
this.endDate = endDate;
}
}
The second method works as shown in the figure.