friend keyword
There is a friend keyword in c++, which allows the modified object to break through the encapsulation feature of the class, so that it can access the private object of the class.
Simply put, it is:
-
If you declare func() as your friend in class A, func() can use all the member variables of class A, regardless of where it is defined.
-
If you declare that Class B is your friend in Class A, then the method in Class B can access all the member variables of Class A.
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
class A {
public:
A() {
password = 1111;
birthday = 808;
}
~A() { }
friend int func(A a); // To c++, int func (A) is my friend, so it can use everything I have.
friend class B; // To c++, class B is my friend, so it can use everything I have.
private:
int password;
int birthday;
};
int func(A a) {
cout << a.password << " and " << a.birthday << endl; //Can access
a.password = 1; //It can even be modified.
cout << a.password << endl;
return 0;
}
class B {
public:
B() { }
~B() { }
// Because Class B has been declared as its friend in Class A, methods in Class B can access private variables in Class A.
void show(A a) {
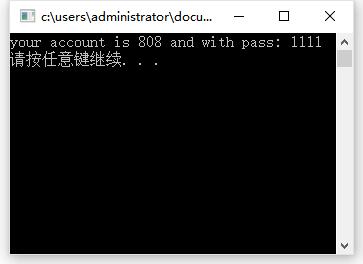
cout << "your account is " << a.account << " and with pass: " << a.password << endl;
}
private:
};
int main() {
A a;
func(a);
B b;
b.show(a);
system("pause");
}- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
Using friend Overload or > Operation
With this, we can overload the operation of or
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
class A {
public:
A() {
password = 1111;
account = 808;
}
~A() { }
friend ostream& operator << (ostream &os , A a);
private:
int password;
int account;
};
ostream& operator << (ostream &os , A a) {
os << "your account is " << a.account << " and with pass: " << a.password << endl;
return os;
}
int main() {
A a;
cout << a;
system("pause");
}- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
Results: