1. Common built-in objects
The so-called built-in objects are some objects provided by ECMAScript. We know that all objects have corresponding properties and methods.
1.1 Array
1.1.1 array creation method
Create in a literal way (recommended).
var colors = ['red','color','yellow'];
Use the constructor (later on) to create, and use the new keyword to create objects for the constructor.
var colors2 = new Array();
1.1.2 array assignment
var arr = []; //One by one assignment by subscript arr[0] = 123; arr[1] = 'Ha ha ha'; arr[2] = 'Hey hey hey'
1.1.3 common methods of array
(1) concat(): array merging
var north = ['Beijing','Shandong','Tianjin']; var south = ['Dongguan','Shenzhen','Shanghai']; var newCity = north.concat(south); console.log(newCity)
(2) join(): connect the elements in the array with the specified string, which will form a new string
var score = [98,78,76,100,0]; var str = score.join('|'); console.log(str);//98|78|76|100|0
(3) toString(): convert array to string
var score = [98,78,76,100,0]; //toString() Convert directly to a string using commas between each element var str = score.toString(); console.log(str);//98,78,76,100,0
(4) slice(start,end): returns a segment of the array, left closed and right open
var arr = ['Zhang San','Li Si','Wang Wen','Zhao Liu']; var newArr = arr.slice(1,3); console.log(newArr);//["Li Si", "Wang Wen"]
(5) pop(): delete the last element of the array and return the deleted element
var arr = ['Zhang San','Li Si','Wang Wen','Zhao Liu']; var item = arr.pop(); console.log(arr);//["Zhang San", "Li Si","Wang Wen"] console.log(item);//Zhao Liu
(6) push(): add one or more elements to the end of the array and return the new length
var arr = ['Zhang San','Li Si','Wang Wen','Zhao Liu']; var newLength= arr.push('Little horse elder brother');//Multiple can be added, separated by commas console.log(newLength);//5 console.log(arr);//["Zhang San", "Li Si","Wang Wen","Zhao Liu","Little horse elder brother"]
(7) reverse(): flip array
var names = ['alex','xiaoma','tanhuang','angle']; //4.Inverted array names.reverse(); console.log(names);
(8) sort(): sort an array
var names = ['alex','xiaoma','tanhuang','abngel']; names.sort(); console.log(names);// ["alex", "angle", "tanhuang", "xiaoma"]
(9) isArray(): judge whether it is an array
Boolean type value = array.isarray (detected value);
(10) shift(): delete and return the first element of the array
var arr = ['Zhang San','Li Si','Wang Wen','Zhao Liu']; var a = arr.shift(); console.log(a); //Zhang San console.log(arr); //['Li Si','Wang Wen','Zhao Liu']
(11) unshift(): adds one or more elements to the beginning of the array and returns the new length
var arr = ['Zhang San','Li Si','Wang Wen','Zhao Liu']; var a = arr.unshift('Wang Wu'); console.log(a); //5 console.log(arr); //['Wang Wu','Zhang San','Li Si','Wang Wen','Zhao Liu']
1.2 common methods of String
String method:
(1) chartAt(): returns the character of the location of the specified index
var str = 'alex'; var charset = str.charAt(1); console.log(charset);//l
(2) concat(): returns the string value, indicating the splicing of two or more strings
var str1 = 'al'; var str2 = 'ex'; console.log(str1.concat(str2,str2));//alexex
(3) replace(a,b): replace string a with string B
var a = '1234567755'; var newStr = a.replace("4567","****"); console.log(newStr);//123****755
(4) indexof(): find the subscript of the character. If the subscript of the returned string is found, return - 1. Same usage as the seal () method
var str = 'alex'; console.log(str.indexOf('e'));//2 console.log(str.indexOf('p'));//-1
(5) slice(start, end): extract a part of a string and return a new string. Left closed right split string
var str = 'Little horse elder brother'; console.log(str.slice(1,2));//Horse
(6) split('a',1): splits the string with string a and returns a new array. If the second parameter is not written, the whole array is returned. If the number is defined, the maximum length of the array is returned
var str = 'My God?,a Right?,What are you talking about?a Ha ha ha'; console.log(str.split('a'));//["My God?,", "Right?,What are you talking about?", "Ha ha ha"]
(7) substr(start,length): returns the characters in a string from the specified position to the specified number of characters
var str = 'My God?,a Right?,What are you talking about?a Ha ha ha'; console.log(str.substr(0,4));//My God?
(8) toLowerCase(): lower case
var str = 'XIAOMAGE'; console.log(str.toLowerCase());//xiaomage
(9) toUpperCase(): capitalize
var str = 'xiaomage'; console.log(str.toUpperCase());
(10) substring(indexStart,indexEnd): extract the characters that the string mediates between two specified subscripts.
If indexStart equals indexEnd, substring returns an empty string.
If you omit indexEnd, substring extracts the character all the way to the end of the string.
If any parameter is less than 0 or is NaN, it is treated as 0.
If any parameter is greater than stringName.length, it is treated as stringName.length.
If indexStart is greater than indexEnd, the execution effect of substring is the same as two parameters swapped
(11) trim(): remove the white space on both sides of the string
The main application is user login registration, because the user input content cannot be predicted, and the space may be entered, so the input result can remove the blank.
var str = ' xhh '; console.log(str); console.log(str.trim());
1.3 Date object
There is only one way to create a date object, using the new keyword.
//Created a date object var myDate = new Date();

//Create date object var myDate=new Date(); //Get a day of the month console.log(myDate.getDate()); //Return to local time console.log(myDate().toLocalString());//2018/5/27 10 p.m.:36:23
Note: the above getxxx methods are all for obtaining time. If you want to set time and use setxxx, please refer to the link: https://www.runoob.com/jsref/jsref-obj-date.html
1.4 Math built in objects
Common built-in objects:
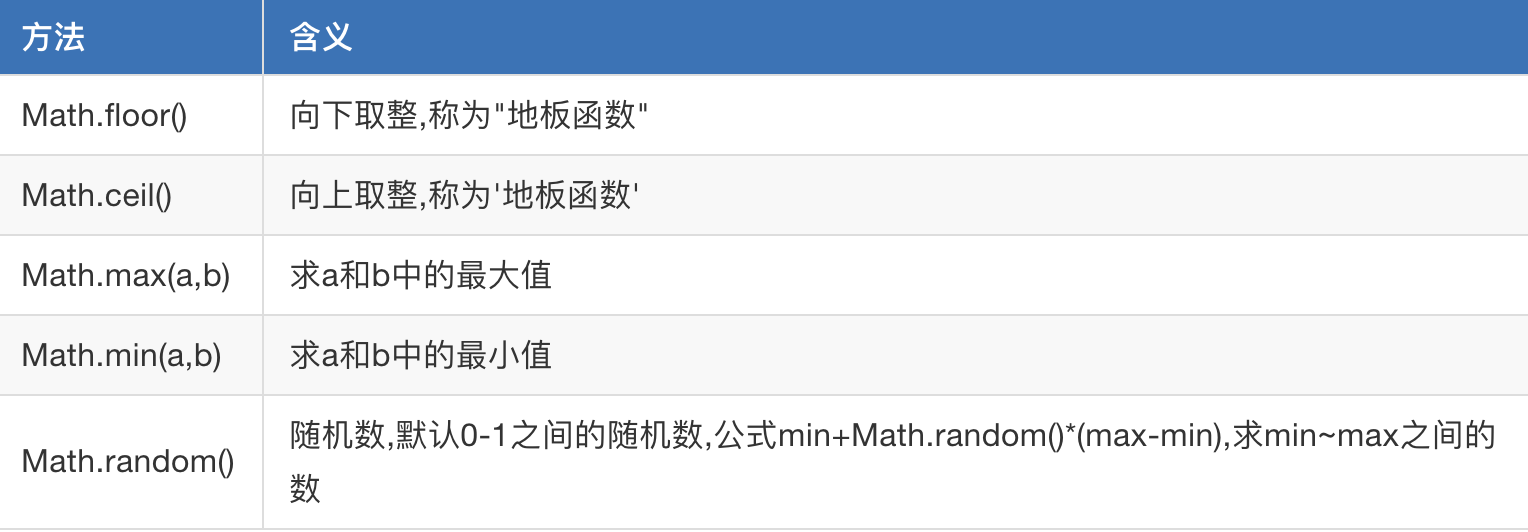
(1) Math.ceil() rounded up
var x = 1.234; //Ceiling function is greater than or equal to x,And the nearest integer to it is 2 var a = Math.ceil(x); console.log(a);//2
(2) Math.floor(): round down
var x = 1.234; // Less than or equal to x,And the nearest integer 1 var b = Math.floor(x); console.log(b);//1
(3) find the maximum and minimum of two numbers
//Find the maximum and minimum of two numbers console.log(Math.max(2,5));//5 console.log(Math.min(2,5));//2
(4) random number: Math.random()
var ran = Math.random(); console.log(ran); //[0,1)
2. function
Function: encapsulate some statements, and then execute them in the form of calls.
Function function: write a large number of repeated statements in the function. When you need these statements in the future, you can call the function directly to avoid repeated work.
Simplify programming and modularize programming.
console.log("hello world");
sayHello(); //Calling function
//Define function:
function sayHello(){
console.log("hello");
console.log("hello world");
}
2.1 definition of function
Syntax of function definition:
Function function name (){
}
Explain as follows:
Function: is a keyword. Chinese is "function", "function".
Function name: the naming rules are the same as the variable naming rules. It can only be letters, numbers, underscores, dollar symbols, and cannot start with a number.
Parameter: there are a pair of brackets at the back, which are used to put parameters.
Inside the braces are the statements of this function.
2.2 function call
Syntax of function call:
Function name ();
2.2.1 parameter of function: formal parameter and actual parameter
The parameters of a function include parameters and arguments
Note: the number of actual parameters and formal parameters should be the same.
Example:
sum(3,4); sum("3",4); sum("Hello","World"); //Functions: summing function sum(a, b) { console.log(a + b); }
2.2.2 return value of function
Example:
console.log(sum(3, 4)); //Functions: summing function sum(a, b) { return a + b; }