Input a list and output the reciprocal k node in the list.
Idea 1:
Require the reciprocal K node, then we must first think of the length of the list len, after the length len, the reciprocal K node is the head node to traverse len-k nodes backwards.
1) Reference to p1 pointer node
2) traversing len-k nodes after p1 image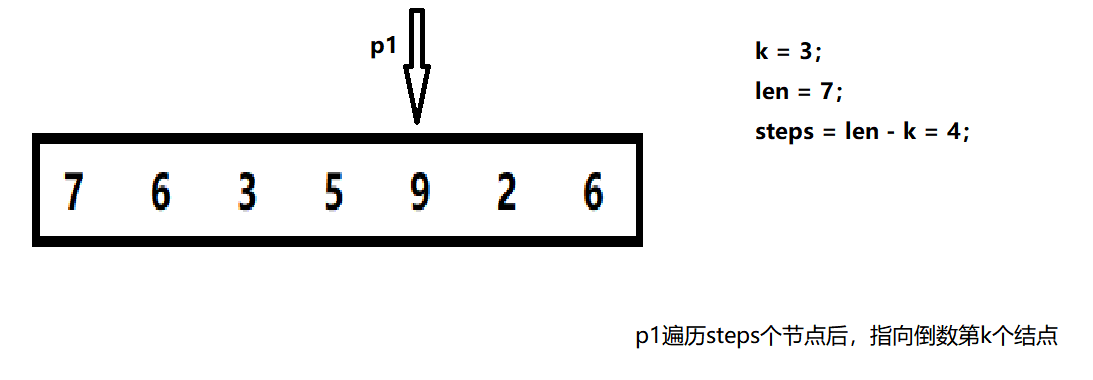
public class FindKthToTail { //Find the penultimate k node in the list //1. Find the length len of the list //2. Create a new reference to head //3.head traverses len-k nodes to get the reciprocal K node public static Node FindKthToTail(Node head,int k){ int len = getLength(head); if(len < k){ return null; } int steps = len-k; Node result = head; for(int i = 0;i<steps;i++){ result = result.next; } return result; } public static int getLength(Node head){ int len = 0; for(Node cur = head;cur != null;cur = cur.next){ len++; } return len; }
Train of thought two:
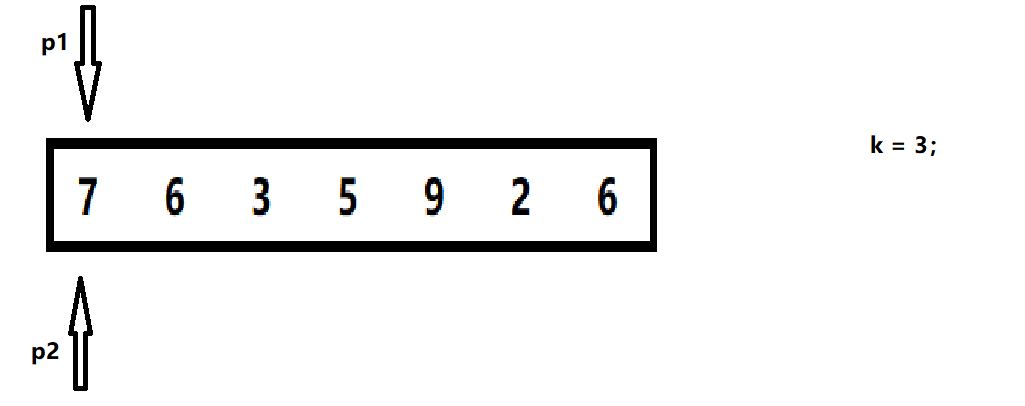
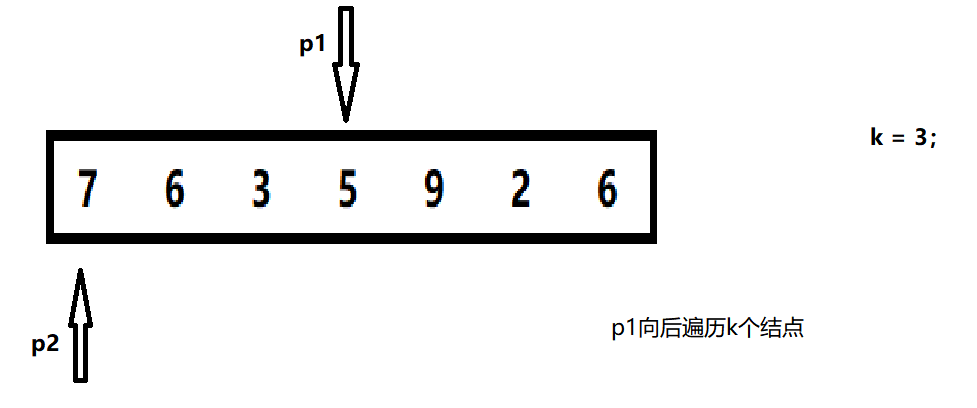
1. Create two nodes so that the first reference traverses k, then the second one traverses back together.
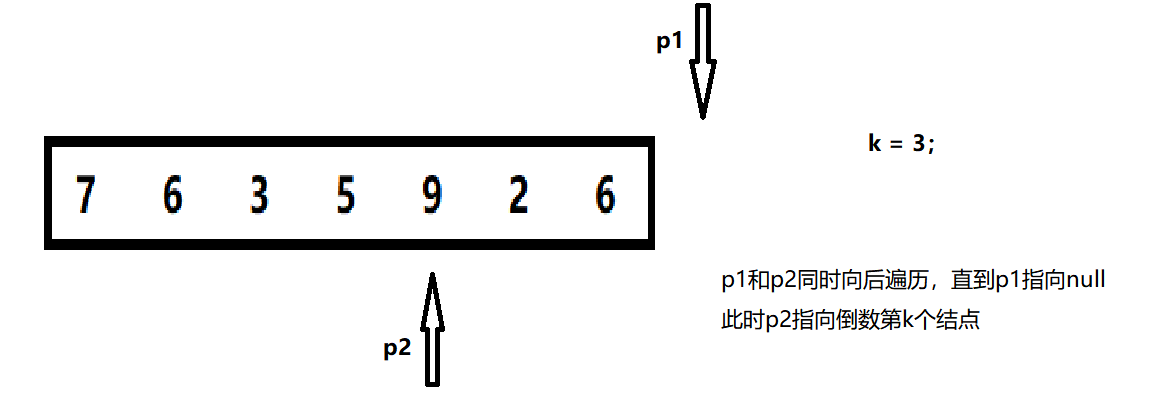
2. When the first reference is empty, the second refers to the penultimate k node
public class FindKthToTail { //Find the penultimate k node in the list //1. Create two nodes so that the first reference traverses k, then the second one traverses back together. //2. When the first reference is empty, the second refers to the penultimate k node public static Node findKthToTail(Node head,int k){ Node p1 = head; Node p2 = head; for(int i = 0;i<k;i++){ if(p1 == null){ return null; } p1 = p1.next; } while(p1 != null){ p1 = p1.next; p2 = p2.next; } return p2; } public static void main(String[] args) { Node head = new Node(1); head.next = new Node(3); head.next.next = new Node(4); head.next.next.next = new Node(9); head.next.next.next.next = new Node(12); System.out.println(findKthToTail(head,2).val); } }