Write algorithm to judge whether an undirected graph is a tree.
[analysis]
The condition for a undirected graph G to be a tree is: G must be a connected graph without a loop or a connected graph with n-1 edges. Here we use the latter as the judging condition. For example, the following figure shows:
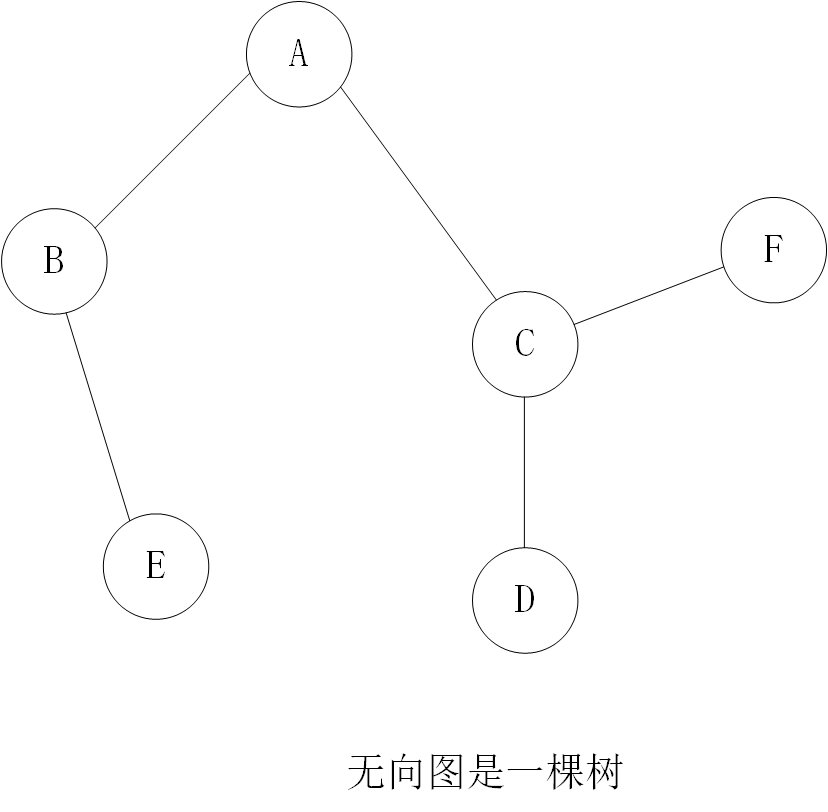
The undirected graph above is a tree with six vertices and five edges.
code:
#include<stdlib.h>
#include<stdio.h>
#include<malloc.h>
#include<string.h>
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
/*Adjacency table type definition of Graphs*/
typedef char VertexType[4];
typedef char InfoPtr;
typedef int VRType;
#define MAXSIZE 100 / * maximum number of vertices*/
typedef enum { DG, DN, UG, UN }GraphKind; /*Types of graphs: directed graph, directed net, undirected graph and undirected net*/
typedef struct ArcNode /*Type definition of edge node*/
{
int adjvex; /*The position of the vertex pointed by the arc*/
InfoPtr *info; /*Arc related information*/
struct ArcNode *nextarc; /*Indicates the next vertex adjacent to that vertex*/
}ArcNode;
typedef struct VNode /*Type definition of head node*/
{
VertexType data; /*Used to store vertices*/
ArcNode *firstarc; /*Indicates the first vertex adjacent to the vertex*/
}VNode, AdjList[MAXSIZE];
typedef struct /*Type definition of graph*/
{
AdjList vertex;
int vexnum, arcnum; /*The number of vertices and arcs in a graph*/
GraphKind kind; /*Types of Graphs*/
}AdjGraph;
int LocateVertex(AdjGraph G, VertexType v);
void CreateGraph(AdjGraph *G);
void DisplayGraph(AdjGraph G);
void DestroyGraph(AdjGraph *G);
void DFS(AdjGraph *G, int v, int *vNum, int *eNum, int visited[]);
int LocateVertex(AdjGraph G, VertexType v)
//Return to the corresponding position of vertices in the graph
{
int i;
for (i = 0; i < G.vexnum; i++)
if (strcmp(G.vertex[i].data, v) == 0)
return i;
return -1;
}
void CreateGraph(AdjGraph *G)
//Using adjacency table storage structure to create undirected graph G
{
int i, j, k;
VertexType v1, v2; //Define two vertices v1 and v2
ArcNode *p;
cout << "Please enter the number of vertices and edges of the graph: ";
cin >> (*G).vexnum >> (*G).arcnum;
cout << "Please input" << G->vexnum << "Value of vertices:" << endl;
for (i = 0; i < G->vexnum; i++) //Store vertex in head node
{
cin >> G->vertex[i].data;
G->vertex[i].firstarc = NULL; //Leave associated vertices empty
}
cout << "Please input the end of arc head:" << endl;
for (k = 0; k < G->arcnum; k++) //Set up side chain list
{
cin >> v1 >> v2;
i = LocateVertex(*G, v1);/*Determine the number corresponding to v1*/
j = LocateVertex(*G, v2);/*Determine the number corresponding to v2*/
//j creates an adjacency table for arc head i and arc tail
p = (ArcNode*)malloc(sizeof(ArcNode));
p->adjvex = j;
p->info = NULL;
p->nextarc = G->vertex[i].firstarc;
G->vertex[i].firstarc = p;
//i creates an adjacency table for arc head j and arc tail
p = (ArcNode*)malloc(sizeof(ArcNode));
p->adjvex = i;
p->info = NULL;
p->nextarc = G->vertex[j].firstarc;
G->vertex[j].firstarc = p;
}
(*G).kind = UG;
}
void DestroyGraph(AdjGraph *G)
//Destroy undirected graph G
{
int i;
ArcNode *p, *q;
for (i = 0; i < (*G).vexnum; i++) //Release edge table node in graph
{
p = G->vertex[i].firstarc;//p points to the first node of the edge table
if (p != NULL) //If the edge table is not empty, the nodes of the edge table are released
{
q = p->nextarc;
free(p);
p = q;
}
}
(*G).vexnum = 0; //Set the number of vertices to 0
(*G).arcnum = 0; //Set the number of sides to 0
}
void DisplayGraph(AdjGraph G)
//Adjacency matrix G of output graph
{
int i;
ArcNode *p;
cout << G.vexnum << "Apex:" << endl;
for (i = 0; i < G.vexnum; i++)
cout << G.vertex[i].data << " ";
cout << endl << G.arcnum << "Strip edge:" << endl;
for (i = 0; i < G.vexnum; i++)
{
p = G.vertex[i].firstarc;
while (p)
{
cout << G.vertex[i].data << "→" << G.vertex[p->adjvex].data << " ";
p = p->nextarc;
}
cout << endl;
}
}
int IsTree(AdjGraph *G)
{
int vNum = 0, eNum = 0, i, visited[MAXSIZE];
for (i = 0; i < G->vexnum; i++)
visited[i] = 0;
DFS(G, 0, &vNum, &eNum, visited);
if (vNum == G->vexnum && eNum == 2 * (G->vexnum - 1))
return 1;
else
return 0;
}
void DFS(AdjGraph *G, int v, int *vNum, int *eNum, int visited[])
{
ArcNode *p;
visited[v] = 1;
(*vNum)++;
p = G->vertex[v].firstarc;
while (p != NULL)
{
(*eNum)++;
if (visited[p->adjvex] == 0)
DFS(G, p->adjvex, vNum, eNum, visited);
p = p->nextarc;
}
}
void main()
{
AdjGraph G;
cout << "Using adjacency table to create undirected graph G: " << endl;
CreateGraph(&G);
cout << "Output undirected graph G Adjacency table of:" << endl;
DisplayGraph(G);
if (IsTree(&G))
cout << "Undirected graph G It's a tree.!" << endl;
else
cout << "Undirected graph G Not a tree!" << endl;
DestroyGraph(&G);
system("pause");
}
Result:
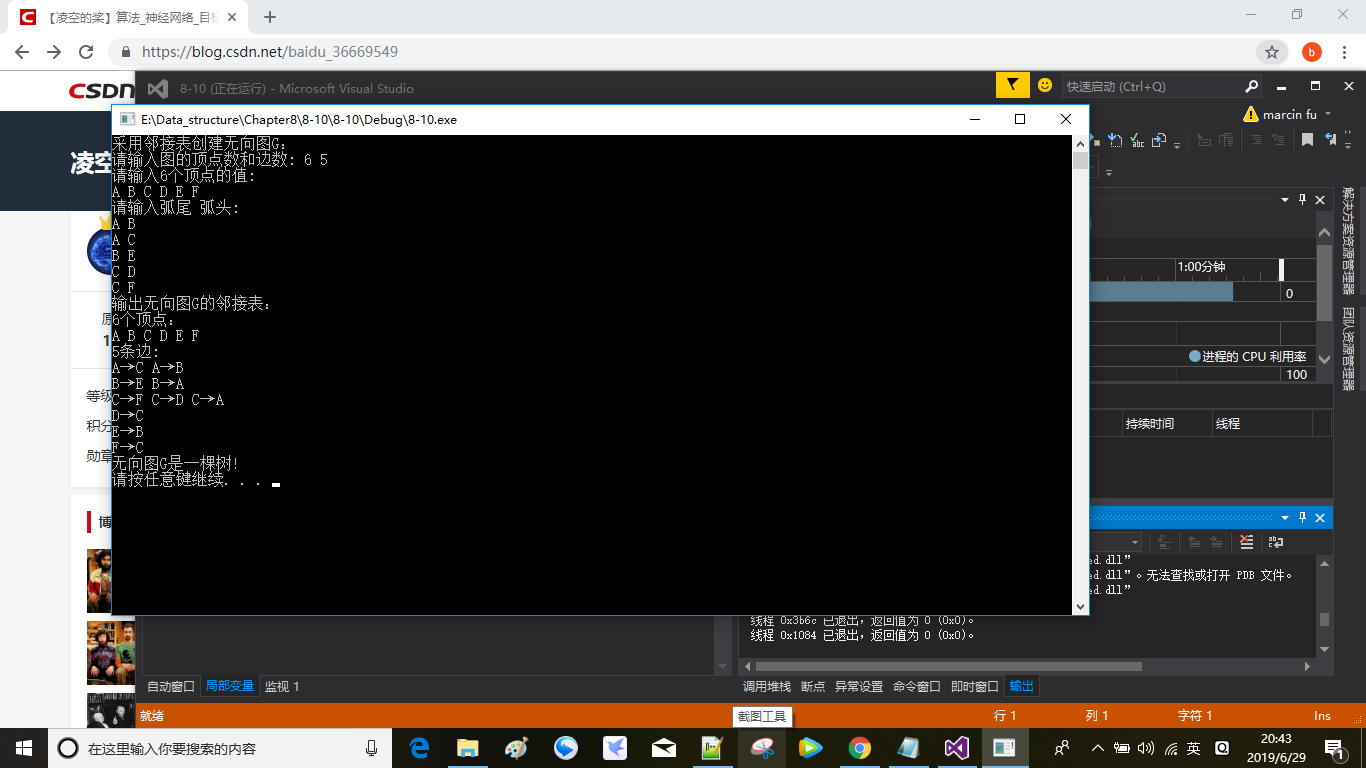
Use adjacency table to create undirected graph G: Please enter the number of vertices and edges of the graph: 6 5 Enter values for 6 vertices: A B C D E F Please enter the tail arc head: A B A C B E C D C F Output adjacency table of undirected graph G: 6 vertices: A B C D E F The 5 side: A→C A→B B→E B→A C→F C→D C→A D→C E→B F→C Undirected graph G is a tree!