1. ffmpeg video decoding I
2. ffmpeg video decoding II
3. ffmpeg audio decoding I
preface
The video decoding process has been introduced earlier. This article starts audio decoding at the beginning. There are also two articles, one is parsed by parser, and the other is processed according to the conventional process.
Some basic knowledge
-
sample_rate:
That is, the sampling frequency defines the number of samples extracted from continuous signals and composed of discrete signals per second, which is expressed in Hertz (Hz). The reciprocal of sampling frequency is the sampling period or sampling time, which is the time interval between samples. Generally speaking, sampling frequency refers to how many signal samples the computer collects per second.
-
Number of samples (frame_size):
The size of a frame of audio.
-
Sampling format (sample_fmt):
Storage format of audio sample.
You can use 8-bit unsigned integers, 16 bit signed integers, 32-bit signed integers, and single precision floating-point numbers. Double precision floating-point numbers represent a sample. However, 24 bit signed integers are not used because these different formats use the native C type, which has no 24 bit length.
We can use the following command to view the formats supported by ffmpeg:
ffplay -sample_fmts
Of course, you can also view the source code. Here, the source code of the structure of SampleFmtInfo (including information about AVSampleFormat conversion) is posted:
static const SampleFmtInfo sample_fmt_info[AV_SAMPLE_FMT_NB] = { [AV_SAMPLE_FMT_U8] = { .name = "u8", .bits = 8, .planar = 0, .altform = AV_SAMPLE_FMT_U8P }, [AV_SAMPLE_FMT_S16] = { .name = "s16", .bits = 16, .planar = 0, .altform = AV_SAMPLE_FMT_S16P }, [AV_SAMPLE_FMT_S32] = { .name = "s32", .bits = 32, .planar = 0, .altform = AV_SAMPLE_FMT_S32P }, [AV_SAMPLE_FMT_S64] = { .name = "s64", .bits = 64, .planar = 0, .altform = AV_SAMPLE_FMT_S64P }, [AV_SAMPLE_FMT_FLT] = { .name = "flt", .bits = 32, .planar = 0, .altform = AV_SAMPLE_FMT_FLTP }, [AV_SAMPLE_FMT_DBL] = { .name = "dbl", .bits = 64, .planar = 0, .altform = AV_SAMPLE_FMT_DBLP }, [AV_SAMPLE_FMT_U8P] = { .name = "u8p", .bits = 8, .planar = 1, .altform = AV_SAMPLE_FMT_U8 }, [AV_SAMPLE_FMT_S16P] = { .name = "s16p", .bits = 16, .planar = 1, .altform = AV_SAMPLE_FMT_S16 }, [AV_SAMPLE_FMT_S32P] = { .name = "s32p", .bits = 32, .planar = 1, .altform = AV_SAMPLE_FMT_S32 }, [AV_SAMPLE_FMT_S64P] = { .name = "s64p", .bits = 64, .planar = 1, .altform = AV_SAMPLE_FMT_S64 }, [AV_SAMPLE_FMT_FLTP] = { .name = "fltp", .bits = 32, .planar = 1, .altform = AV_SAMPLE_FMT_FLT }, [AV_SAMPLE_FMT_DBLP] = { .name = "dblp", .bits = 64, .planar = 1, .altform = AV_SAMPLE_FMT_DBL }, };Where name is the format name, bits is the number of bits occupied in the computer, plannar is the file storage method, and altform is the corresponding name of the obtained file according to different storage methods (for example, u8 is the format of plannar=0, which is u8p when converted to plannar=1).
Sample has two types of storage methods: planar and packed. In planar, each channel occupies a storage plane alone; In packed, the sample interleaving of all channels is stored in the same plane.
-
Channel information:
Channels is the number of audio channels 1 2 3 4 5
channel_layout is an audio channel format type, such as single channel, dual channelFor mono sound files, the sampling data is an eight bit short integer (short int 00H-FFH);
For two channel stereo sound files, each sampling data is a 16 bit integer (int), and the high eight bits (left channel) and low eight bits (right channel) represent two channels respectively.
If it is a stereo, the sampling is double, and the file is almost twice as large.
Audio information
If audio, sample: fltp; Sampling rate: 44100; Channel: 2.
av_get_bytes_per_sample(fltp) == 4;
-
AAC (nb_samples and frame_size = 1024)
Then you can get the size of one frame of audio:
4 * 2 * 1024 = 8192 (bytes)
The playback time of a frame is
1024*1000000/44100= 46.43ms -
MP3 (nb_samples and frame_size = 1152)
Then you can get the size of one frame of audio:
4 * 2 * 1152 = 9216 (bytes)
The playback time of a frame is
1152*1000000/44100= 52.24ms
flow chart
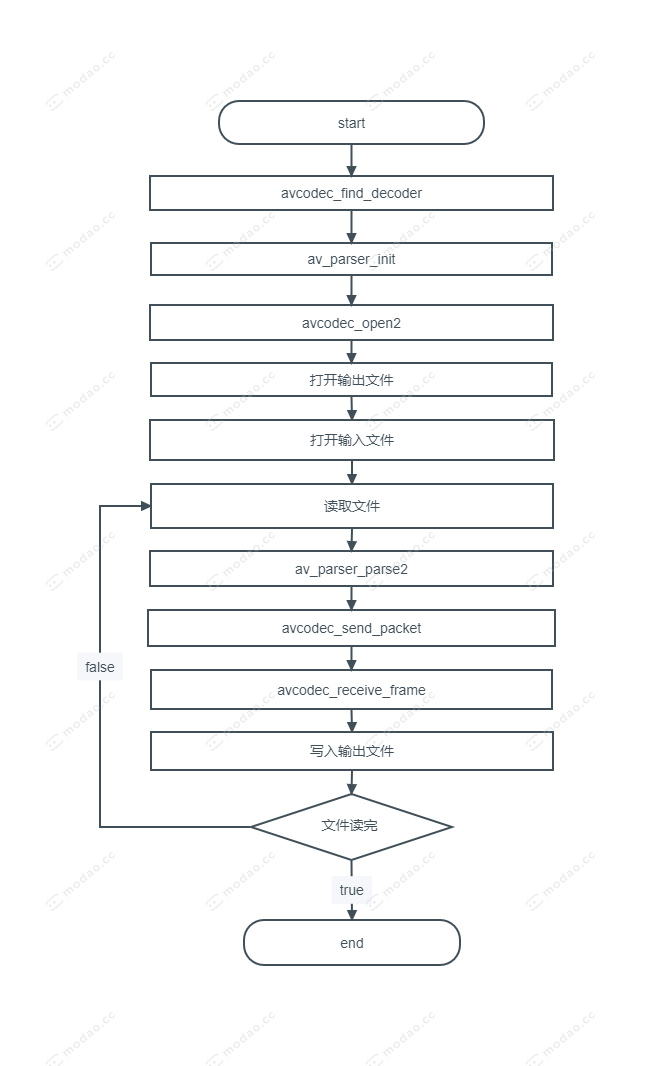
The code flow is shown in the flow chart. Let's explain the functions of some of them.
- av_parser_init
This is a parser. We instantiate this parser according to the decoder and use it later when parsing data. - av_parser_parse2
The original data we get from the input file (not applicable to the api of ffmpeg) cannot be used directly. At this time, we need to parse the original data using the parser instantiated above, divide the data into frames, and prepare for decoding the data later. - avcodec_send_packet
Send the parsed data we just got to the decoder for decoding. - avcodec_receive_frame
Get the decoded data.
Source code
#pragma once
#define __STDC_CONSTANT_MACROS
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS
extern "C"
{
#include "libavcodec/avcodec.h"
}
//Buffer size (CACHE 5 frames of data)
#define AUDIO_INBUF_SIZE 40960
/*
name depth
u8 8
s16 16
s32 32
flt 32
dbl 64
u8p 8
s16p 16
s32p 32
fltp 32
dblp 64
s64 64
s64p 64
//The audio file format decoded by this code is as follows:
//AAC File (1024 bytes per frame), dual channel (2), FLTP (32 bits, 4 bytes)
//AAC File frame_size and Nb_ The size of samples is 1024
//Byte size of one frame of audio
//1024*2*4=8192 byte
*/
#define AUDIO_REFILL_THRESH 8192
using namespace std;
#define INPUT_FILE_NAME "lh_online.aac"
#define OUTPUT_FILE_NAME "lh_online.pcm"
static int get_format_from_sample_fmt(const char** fmt,
enum AVSampleFormat sample_fmt)
{
int i;
struct sample_fmt_entry {
enum AVSampleFormat sample_fmt; const char* fmt_be, * fmt_le;
} sample_fmt_entries[] = {
{ AV_SAMPLE_FMT_U8, "u8", "u8" },
{ AV_SAMPLE_FMT_S16, "s16be", "s16le" },
{ AV_SAMPLE_FMT_S32, "s32be", "s32le" },
{ AV_SAMPLE_FMT_FLT, "f32be", "f32le" },
{ AV_SAMPLE_FMT_DBL, "f64be", "f64le" },
};
*fmt = NULL;
for (i = 0; i < FF_ARRAY_ELEMS(sample_fmt_entries); i++) {
struct sample_fmt_entry* entry = &sample_fmt_entries[i];
if (sample_fmt == entry->sample_fmt) {
*fmt = AV_NE(entry->fmt_be, entry->fmt_le);
return 0;
}
}
av_log(NULL, AV_LOG_ERROR, "sample format %s is not supported as output format\n", av_get_sample_fmt_name(sample_fmt));
return -1;
}
static void decode(AVCodecContext* dec_ctx, AVFrame* frame, AVPacket* pkt,
FILE* ofile)
{
int i, ch;
int ret, data_size;
ret = avcodec_send_packet(dec_ctx, pkt);
if (ret < 0) {
av_log(NULL, AV_LOG_ERROR, "Error sending packet to decoder.\n");
exit(1);
}
while (ret >= 0) {
ret = avcodec_receive_frame(dec_ctx, frame);
if (ret == AVERROR(EAGAIN) || ret == AVERROR_EOF)
return;
else if (ret < 0) {
av_log(NULL, AV_LOG_ERROR, "Error sending a packet for decoding.\n");
exit(1);
}
printf("frame_number: %d \n", dec_ctx->frame_number);
//Get the size of each channel in each sampling point
data_size = av_get_bytes_per_sample(dec_ctx->sample_fmt);
if (data_size < 0) {
av_log(NULL, AV_LOG_ERROR, "Failed to calculate data size.\n");
exit(1);
}
//Traverse sampling points
for (i = 0; i < frame->nb_samples; i++) {
//Traversal channel
for (ch = 0; ch < dec_ctx->channels; ch++) {
fwrite(frame->data[ch] + data_size * i, 1, data_size, ofile);
}
}
}
}
int main(int argc, char* argv[])
{
const AVCodec* codec;
AVCodecParserContext* parser;
AVCodecContext* c = NULL;
FILE* ifile, * ofile;
AVFrame* frame;
AVPacket* pkt;
uint8_t inbuf[AUDIO_INBUF_SIZE + AV_INPUT_BUFFER_PADDING_SIZE];
uint8_t* data;
size_t data_size;
int ret,len;
enum AVSampleFormat sfmt;
const char* fmt;
//Initialize inbuf numeric defaults
memset(inbuf + AUDIO_INBUF_SIZE, 0, AV_INPUT_BUFFER_PADDING_SIZE);
//Get decoder (the file to be read here is AAC, so)
codec = avcodec_find_decoder(AV_CODEC_ID_AAC);
if (!codec) {
av_log(NULL, AV_LOG_ERROR, "Codec not found.\n");
exit(1);
}
//Register parser
parser = av_parser_init(codec->id);
if (!parser) {
av_log(NULL, AV_LOG_ERROR, "parser not found.\n");
exit(1);
}
//Assign parser context
c = avcodec_alloc_context3(codec);
if (!c) {
av_log(NULL, AV_LOG_ERROR, "Could not allocate video codec context.\n");
exit(1);
}
//Open decoder
if (avcodec_open2(c, codec, NULL) < 0) {
av_log(NULL, AV_LOG_ERROR, "Could not open codec.\n");
exit(1);
}
//Allocate AVPacket
pkt = av_packet_alloc();
if (!pkt) {
exit(1);
}
//Assign AVFrame
frame = av_frame_alloc();
if (!frame) {
exit(1);
}
//Open input file
ifile = fopen(INPUT_FILE_NAME, "rb");
if (!ifile) {
av_log(NULL, AV_LOG_ERROR, "Could not open \s.\n", INPUT_FILE_NAME);
exit(1);
}
//Open input file
ofile = fopen(OUTPUT_FILE_NAME, "wb+");
if (!ofile) {
av_log(NULL, AV_LOG_ERROR, "Could not open \s.\n", OUTPUT_FILE_NAME);
exit(1);
}
//Read data from the input stream ifile into the array pointed to by inbuf
data = inbuf;
data_size = fread(inbuf, 1, AUDIO_INBUF_SIZE, ifile);
while (data_size > 0) {
//Use the registered parser to divide the data into frames
ret = av_parser_parse2(parser, c, &pkt->data, &pkt->size,
data, data_size,
AV_NOPTS_VALUE, AV_NOPTS_VALUE, 0);
if (ret < 0) {
fprintf(stderr, "Error while parsing\n");
exit(1);
}
//Reset data location according to usage
data += ret;
data_size -= ret;
//Send to decode
if (pkt->size)
decode(c, frame, pkt, ofile);
//Judge whether the remaining data in the buffer is less than the size of one frame of audio
//If less than, continue to read from the file, and then send it to decoding
if (data_size < AUDIO_REFILL_THRESH) {
memmove(inbuf, data, data_size);
data = inbuf;
len = fread(data + data_size, 1,
AUDIO_INBUF_SIZE - data_size, ifile);
if (len > 0)
data_size += len;
}
}
//flush decoder
decode(c, frame, NULL, ofile);
//At this point, the decoding is finished. We will use ffplay to play the audio later
//The decoded pcm data does not have these basic data. We need to obtain them from metadata
//Print basic information
//Channels
printf("channels: %d \n", c->channels);
//sampling rate
printf("sample_rate: %d \n", c->sample_rate);
//Bytes occupied by one frame of audio are sold on a commission basis
printf("buffer: %d \n", av_samples_get_buffer_size(NULL, c->channels, c->frame_size, c->sample_fmt, 1));
//Sampling format
sfmt = c->sample_fmt;
printf("sample_fmt: %s \n", av_get_sample_fmt_name(sfmt));
//If it is planar, convert it to packed format
if (av_sample_fmt_is_planar(sfmt)) {
const char* packed = av_get_sample_fmt_name(sfmt);
sfmt = av_get_packed_sample_fmt(sfmt);
}
if (get_format_from_sample_fmt(&fmt, sfmt) < 0) {
av_log(NULL, AV_LOG_ERROR, "Could not get forma \s.\n", av_get_sample_fmt_name(sfmt));
exit(1);
}
//Print playback command
printf("Play the output audio file with the command:\n"
"ffplay -f %s -ac %d -ar %d %s\n",
fmt, c->channels, c->sample_rate,OUTPUT_FILE_NAME);
//Resource release
fclose(ifile);
fclose(ofile);
av_parser_close(parser);
avcodec_free_context(&c);
av_frame_free(&frame);
av_packet_free(&pkt);
return 0;
}
This example demonstrates a process of decoding aac files into pcm files.
The printing information is as follows:
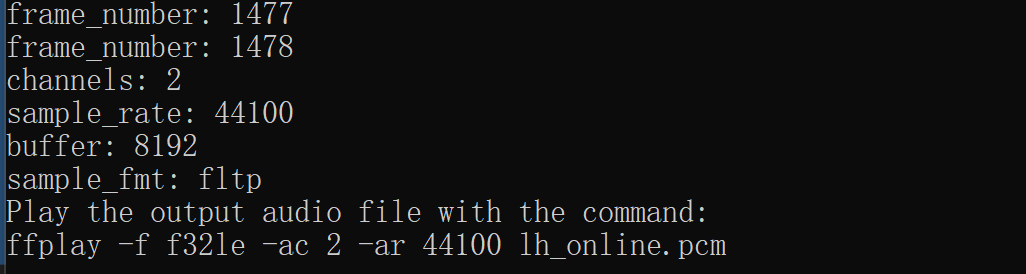
It can be seen that the file to be decoded is a file with 2 channels, sampling rate of 44100HZ and sampling format of fltp, with a total of 1478 frames.
Next, use the command to play the decoded audio:
ffplay -f f32le -ac 2 -ar 44100 lh_online.pcm
result:
At this time, you should be able to hear the audio sound, and you're done.
So far, the way to decode audio based on parser parser is over.
The next article, like the video, will talk about a purely API based approach, which should be much more convenient than this.