FastDFS is an open-source lightweight distributed file system, which manages files. Its functions include file storage, file synchronization, file access (file upload, file download), etc. It solves the problems of mass storage and load balancing. FastDFS is especially suitable for online services with file as the carrier, multi picture, multi video services and so on.
First, popularize some concepts in fastDFS structure:
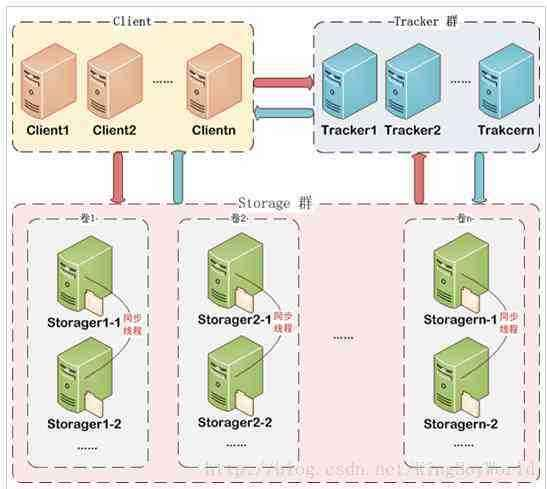
In fastDFS, it is divided into three parts: client, tracker Server and storage Server; → the client is used to initiate operations on fastDFS, such as upload and download; → the tracker Server is a deployment role (intermediary). When we initiate an operation request in client, we need tracker Server to connect us with storage Server. It is The core of load balancing; → storage Server can be understood as a warehouse, and the storage of files is storage Server. In a complete fastDFS storage structure, the maximum unit is group (or volume), which is usually used to divide file types, such as one group for picture type, one group for video type, etc., while one group contains one or more storage s. Erver. Important: storage Server is the core of file storage, but it is not the largest unit of file storage. Many beginners will be confused in this place.
One, two roles:
The FastDFS server has two roles: tracker and storage node.
① tracker
The tracker Server is the coordinator (intermediary role) of the fastDFS. During the operation of the complete fastDFS service, we will not be able to directly manage the storage Server, only the operations we initiate will operate the files in the storage Server, but the real management of the storage Server is the tracker Server - each storage Server will connect to the tracker after it is started. The server informs its own information (such as its group), and maintains a connection between the tracker Server and the storage Server. The two roles will exchange information. The tracker Server will establish a group = = > [storage Server list] mapping table in memory (the tracker Server does not need to persist any data) according to the feedback information of the storage Server.
In the fastDFS cluster, the information and data between multiple tracker servers will be synchronized, and this mechanism is not completed by the tracker servers, but by the storage Server. Because there are all tracker servers in the fastDFS service in the storage Server's configuration file, the storage Server will create a communication thread for each tracker Server. In the process of communication between the storage Server and the tracker Server, if the tracker Server returns less storage Server list information of the group than that of the local machine, the storage Server will create the tracker Server. The storage Server list information of the group that is not available on is synchronized to the tracker Server. This makes the data between each tracker Server consistent.
② storage node
storage Server is the role of storage, and storage files are managed by storage Server. Each storage Server data storage directory will have two levels of subdirectories, each level has 256 subfolders, a total of 256 * 256 = 65536 folders. When a new file is written, it will be hash ed to one of its subdirectories, and then the data of the new file will be stored in the directory as a local file.
storage Server is organized by group [or volume], even though the entire fastDFS has only one storage Server, it also has one group.
In the fastDFS cluster, taking the group as the unit can facilitate load balancing, and the tracker Server can realize the balance of access pressure within the reorganization; it can also facilitate the customization of the number of copies (i.e. backup). The number of storage servers in the same group is reduced by one, that is, the number of copies.
Data between storage servers in a group will be backed up to each other, which is done by background threads. When the client writes a file to a storage Server in the group, it will be considered that the file is written successfully, and the background thread will synchronize the file to the storage Server in the group. Note: since the storage Server data in a group is backup to each other, the capacity of storage space is determined by the storage Server with the minimum capacity in the group.
After the storage Server in the same group writes a file, it will write a binlog, which records the file name and other meta information. It is used for background synchronization. Each storage Server will record the synchronization progress to other storage servers in the group. The way to record the progress is timestamping, so as to avoid losing the synchronization progress after the machine is restarted. Progress continues to synchronize. At the same time, the synchronization progress of the storage Server will be sent to the tracker Server with metadata, so that when the client accesses the file, it can be used as a reference for the storage Server of the service selected by the tracker Server (that is, which strong Server has the file).
Illustration:
II. File Upload process
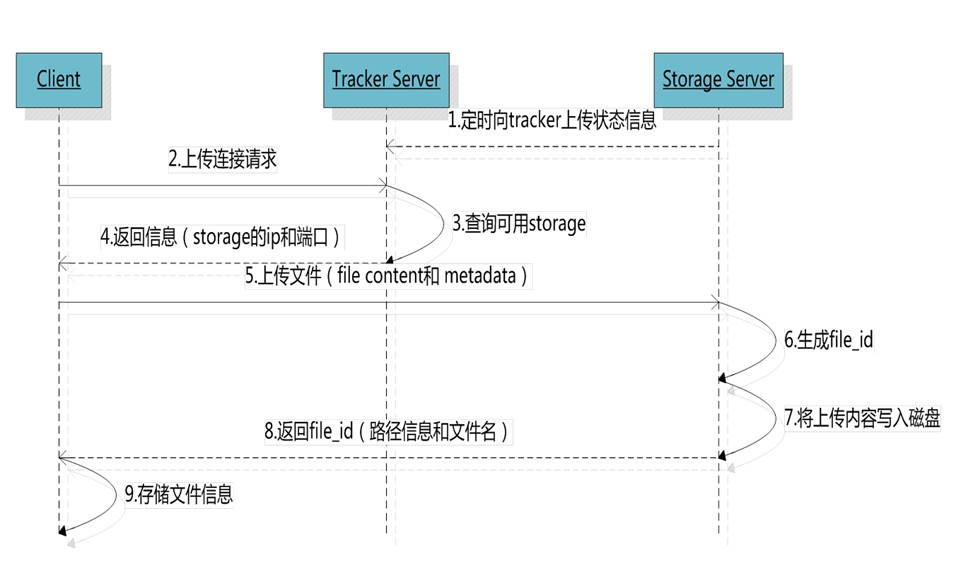
1. Select tracker Server
When there is more than one tracker Server in the cluster, since the data between the tracker servers is synchronous with each other and completely equivalent, the client can choose freely.
2. Select the storage group
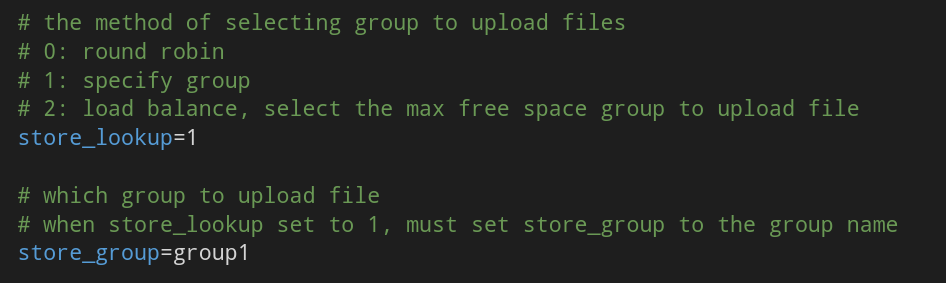
This is the two items of the tracker.conf configuration file. The store "lookup" is used to select the rules of the group. When the tracker receives the request of the upload file, it will assign a group to store the file. The following rules are supported: 1. Round robin, polling among all groups; 2. Specified group, specifying a certain group; 3. Load balance , more storage space is preferred. When store < span style = "font weight: bold;" > lookup is 2, you can specify a group through store < span style = "font weight: bold;" > group.
3. Select storage Server
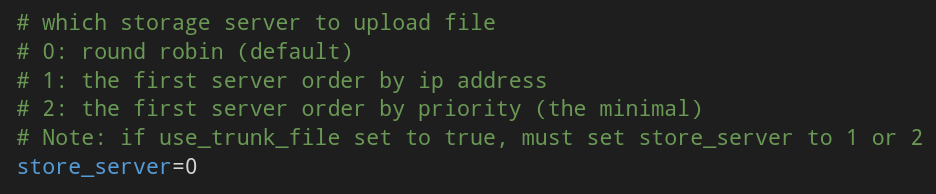
This is an item in the tracker.conf configuration file. The store [u server] is used to select the storage server rules. When a group is selected, the tracker will select a storage server in the group to give to the client. The following rules are supported: 1. Round robin, polling all storage in the group; 2. First server ordered by ip, sorting by ip; 3. First server order Ed by priority, sort by priority (priority is configured on storage).
4. Select storage path
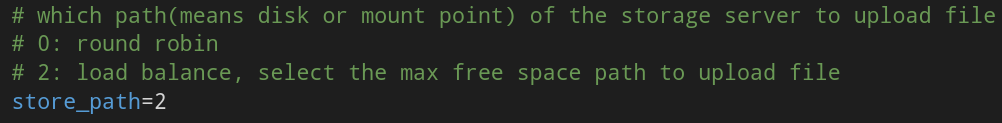
This is one of the tracker.conf configuration files. The store path is used to select the storage path rules. When the storage server is allocated, the client will send a write file request to the storage, and the storage will allocate a data storage directory for the file. The following rules are supported: 1. Round robin, polling among multiple storage directories; 2. The most remaining storage space takes precedence.
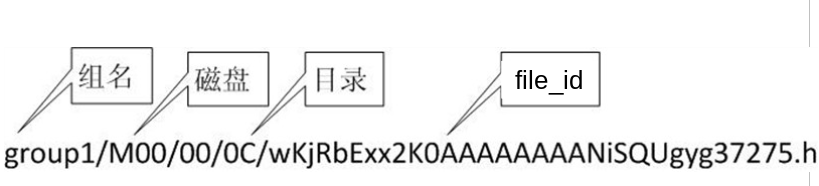
5. Select directory and generate file name
When the storage directory is selected, the storage Server generates a file ID for the file, routes the file to a secondary directory, and stores it in the subdirectory with the file ID as the file name. When a file is stored in a subdirectory, it is considered that the file is stored successfully. Next, a file name will be generated for the file. The file name is composed of group, storage directory, two-level subdirectories, fileid, and file suffix (specified by the client, mainly used to distinguish file types).
File download and Nginx module
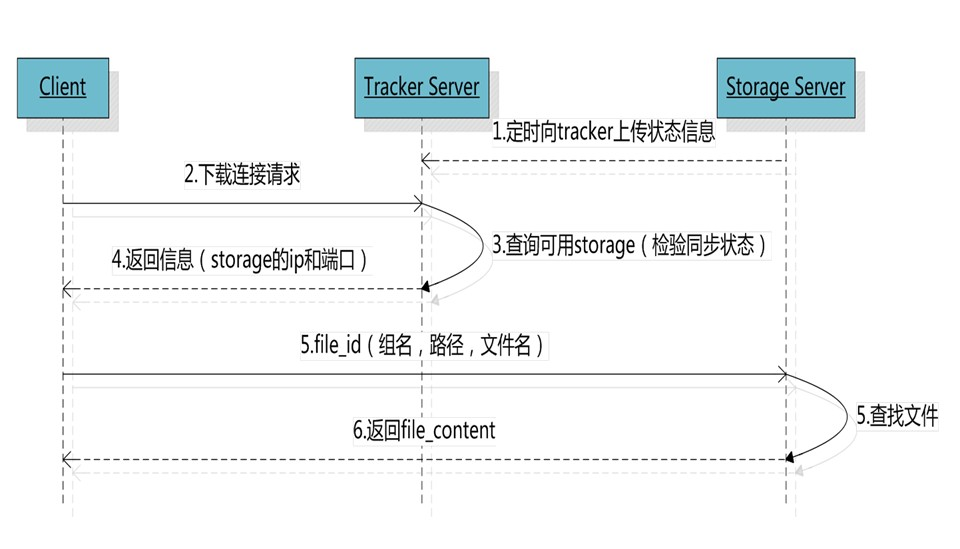
Access process:
When a client sends a download request to a tracker Server, it must bring the file name information. The tracker Server parses the group, size, creation time and other information of the file from the file name, and then selects a storage Server for the request to serve the download request.
HTTP access support:
Both the tracker Server and storage Server of FastDFS have built-in support of http protocol. The client can download files through http protocol. When the tracker receives the request, it redirects the request to the storage Server where the file is located through http redirect mechanism. In addition to the built-in http protocol, FastDFS also provides support for downloading files through apache or nginx extension module.
Nginx expansion module:
The nginx module needs to be installed in both the storage Server node and the tracker Server node.
Purpose:
1. The installation of nginx module in storage Server is combined with Http access service provided by fastdfs nginx module module, and the synchronization delay of storage Server and server in group is solved at the same time. Some students may not understand it, which is popular:
Suppose the Tracker server uploads the file to 192.168.1.80, and the file ID has returned to the client. At this time, the background will copy the file to 192.168.1.30. If the copy is not completed, the client will use the ID to retrieve the file at 192.168.1.30, and there will be an error. This fastdfs nginx module can redirect the connection to the source server to retrieve files, so as to avoid the client's errors due to the replication delay.
2. The purpose of installing nginx module on tracker Server is to reverse proxy to nginx on storage Server and load balance. At the same time, it uses NGX cache purge module to realize cache.
IV. profile details
(from XuJiaqing's blog)
1. Configuration details of tracker Server
1 # is this config file disabled 2 3 # false for enabled 4 5 # true for disabled 6 7 disabled=false 8 9 #Whether the current configuration is unavailable false available, true unavailable 10 11 12 13 # bind an address of this host 14 15 # empty for bind all addresses of this host 16 17 bind_addr= 18 19 #Whether to bind IP if there are more than one IP on a server, set which IP is available. If not, there is no limit. 20 21 22 23 # the tracker server port 24 25 port=22122 26 27 28 29 #The default port is 22122. If there is no conflict, try not to modify it. 30 31 # connect timeout in seconds 32 33 # default value is 30s 34 35 connect_timeout=30 36 37 #Connection timeout setting for socket function connect 38 39 40 41 # network timeout in seconds 42 43 # default value is 30s 44 45 network_timeout=60 46 47 #Set the network timeout in seconds. When sending or receiving data, if it still fails after the timeout, this network communication fails. 48 49 50 51 # the base path to store data and log files 52 53 base_path=/home/fdfs 54 55 #Configure to save the root directory address. This directory must exist. The subdirectory will be created automatically to save data and log files. 56 57 58 59 # max concurrent connections this server supported 60 61 max_connections=256 62 63 #Maximum number of connections supported by the server 64 65 66 67 # work thread count, should <= max_connections 68 69 # default value is 4 70 71 # since V2.00 72 73 work_threads=1 74 75 #Number of worker threads, usually set to the number of CPU s 76 77 78 79 # the method of selecting group to upload files 80 81 # 0: round robin 82 83 # 1: specify group 84 85 # 2: load balance, select the max free space group to upload file 86 87 store_lookup=2 88 89 #Upload group (volume) by: 0 poll, 1: specify, 2: load balance (select the maximum remaining space) 90 91 92 93 # which group to upload file 94 95 # when store_lookup set to 1, must set store_group to the group name 96 97 store_group=group2 98 99 #If method 1 is selected for the previous parameter, that is, group name is specified. The current parameter is used to set the specified group. If other methods are selected, the current parameter is invalid. 100 101 102 103 # which storage server to upload file 104 105 # 0: round robin (default) 106 107 # 1: the first server order by ip address 108 109 # 2: the first server order by priority (the minimal) 110 111 store_server=0 112 113 #Push method of the same group 0. Polling method, 1. Select the first server according to the ip address, 2. Sort according to the priority (the priority is set by the upload? Priority attribute in the configuration file of storeServer) 114 115 116 117 # which path(means disk or mount point) of the storage server to upload file 118 119 # 0: round robin 120 121 # 2: load balance, select the max free space path to upload file 122 123 store_path=0 124 125 #Choose which file directory to upload (there can be multiple base paths on a StoreServer) 0. Poll, 2. The maximum space left 126 127 128 129 # which storage server to download file 130 131 # 0: round robin (default) 132 133 # 1: the source storage server which the current file uploaded to 134 135 download_server=0 136 137 #Select which storeServer is the most downloaded server, 0. Poll, 1. Which is the source, which is the download 138 139 140 141 # reserved storage space for system or other applications. 142 143 # if the free(available) space of any stoarge server in 144 145 # a group <= reserved_storage_space, 146 147 # no file can be uploaded to this group. 148 149 # bytes unit can be one of follows: 150 151 ### G or g for gigabyte(GB) 152 153 ### M or m for megabyte(MB) 154 155 ### K or k for kilobyte(KB) 156 157 ### no unit for byte(B) 158 159 ### XX.XX% as ratio such as reserved_storage_space = 10% 160 161 reserved_storage_space = 10% 162 163 #The reserved space of the system is used to ensure the normal operation of the system and other applications. 164 165 166 167 #standard log level as syslog, case insensitive, value list: 168 169 ### emerg for emergency 170 171 ### alert 172 173 ### crit for critical 174 175 ### error 176 177 ### warn for warning 178 179 ### notice 180 181 ### info 182 183 ### debug 184 185 log_level=info 186 187 #log level 188 189 190 191 #unix group name to run this program, 192 193 #not set (empty) means run by the group of current user 194 195 run_by_group= 196 197 #Use that system user group to run FastDFS, which is the user group of the startup thread by default 198 199 200 201 #unix username to run this program, 202 203 #not set (empty) means run by current user 204 205 run_by_user= 206 207 #Use that system user to run FastDFS. Default to the user who started the thread 208 209 210 211 # allow_hosts can ocur more than once, host can be hostname or ip address, 212 213 # "*" means match all ip addresses, can use range like this: 10.0.1.[1-15,20] or 214 215 # host[01-08,20-25].domain.com, for example: 216 217 # allow_hosts=10.0.1.[1-15,20] 218 219 # allow_hosts=host[01-08,20-25].domain.com 220 221 allow_hosts=* 222 223 #Set the IP range that can connect to the current tracker, including client and store_server, * represents all 224 225 226 227 # sync log buff to disk every interval seconds 228 229 # default value is 10 seconds 230 231 sync_log_buff_interval = 10 232 233 #Time interval from synchronizing or refreshing logs to local hard disk, in seconds 234 235 236 237 # check storage server alive interval seconds 238 239 check_active_interval = 120 240 241 #Time interval for detecting the survival status of storage server, unit: second. This parameter is larger than the heartbeat packet sending interval of storage server, which is generally 2-3 times. 242 243 244 245 # thread stack size, should >= 64KB 246 247 # default value is 64KB 248 249 thread_stack_size = 64KB 250 251 #The thread stack size of tracker server, which should be greater than or equal to 64K 252 253 254 255 # auto adjust when the ip address of the storage server changed 256 257 # default value is true 258 259 storage_ip_changed_auto_adjust = true 260 261 #Whether the cluster adjusts automatically when the IP of storage server changes. Automatic adjustment can only be completed when the storage server process is restarted 262 263 264 265 # storage sync file max delay seconds 266 267 # default value is 86400 seconds (one day) 268 269 # since V2.00 270 271 storage_sync_file_max_delay = 86400 272 273 #The maximum delay time for synchronizing files between storage servers is 1 day by default, which can be adjusted according to the actual situation. 274 275 276 277 # the max time of storage sync a file 278 279 # default value is 300 seconds 280 281 # since V2.00 282 283 storage_sync_file_max_time = 300 284 285 #The maximum time required to synchronize a file. The default is 300 seconds, or 5 minutes 286 287 288 289 # if use a trunk file to store several small files 290 291 # default value is false 292 293 # since V3.00 294 295 use_trunk_file = false 296 297 #Whether to use the small file merge storage feature. It is off by default. When it is opened, the fragmented file can be reduced, but the server load can be increased. 298 299 300 301 # the min slot size, should <= 4KB 302 303 # default value is 256 bytes 304 305 # since V3.00 306 307 slot_min_size = 256 308 309 #The minimum number of bytes allocated for trunk file. For example, a file has only 16 bytes. According to the current setting, 256 bytes will also be allocated for trunk file. 310 311 312 313 # the max slot size, should > slot_min_size 314 315 # store the upload file to trunk file when it's size <= this value 316 317 # default value is 16MB 318 319 # since V3.00 320 321 slot_max_size = 16MB 322 323 #The maximum number of bytes allocated for the trunk file. If the file is smaller than the size, it is stored in the trunk mode. If the file size is larger than this value, it is directly saved to a file (not in the consolidated mode). 324 325 326 327 # the trunk file size, should >= 4MB 328 329 # default value is 64MB 330 331 # since V3.00 332 333 trunk_file_size = 64MB 334 335 #The size of trunk file is not recommended to be too large 336 337 338 339 # if create trunk file advancely 340 341 # default value is false 342 343 # since V3.06 344 345 trunk_create_file_advance = false 346 347 #If you want to create a trunk file in advance, only when this parameter is set to true, the following three parameters starting with trunk? Create? File will not be set. 348 349 350 351 # the time base to create trunk file 352 353 # the time format: HH:MM 354 355 # default value is 02:00 356 357 # since V3.06 358 359 trunk_create_file_time_base = 02:00 360 361 #The start time of trunk file creation, currently 2:00 a.m. 362 363 364 365 # the interval of create trunk file, unit: second 366 367 # default value is 38400 (one day) 368 369 # since V3.06 370 371 trunk_create_file_interval = 86400 372 373 #Time interval for creating trunk file in advance, 1 day by default 374 375 376 377 # the threshold to create trunk file 378 379 # when the free trunk file size less than the threshold, will create 380 381 # the trunk files 382 383 # default value is 0 384 385 # since V3.06 386 387 trunk_create_file_space_threshold = 20G 388 389 #Idle trunk size to be reached when trunk file is created in advance 390 391 #For example, if the current configuration is 20G and the idle trunk file size is 4G, only 16G trunk file will be created. 392 393 394 395 # if check trunk space occupying when loading trunk free spaces 396 397 # the occupied spaces will be ignored 398 399 # default value is false 400 401 # since V3.09 402 403 # NOTICE: set this parameter to true will slow the loading of trunk spaces 404 405 # when startup. you should set this parameter to true when neccessary. 406 407 trunk_init_check_occupying = false 408 409 #Check whether the free space is occupied during trunk file initialization 410 411 412 413 # if ignore storage_trunk.dat, reload from trunk binlog 414 415 # default value is false 416 417 # since V3.10 418 419 # set to true once for version upgrade when your version less than V3.10 420 421 trunk_init_reload_from_binlog = false 422 423 #Whether to load trunk free space information from trunk binlog unconditionally 424 425 426 427 # if use storage ID instead of IP address 428 429 # default value is false 430 431 # since V4.00 432 433 use_storage_id = false 434 435 #Whether to use serverID as storage server identity 436 437 438 439 # specify storage ids filename, can use relative or absolute path 440 441 # since V4.00 442 443 storage_ids_filename = storage_ids.conf 444 445 #Only when use storage ID is set to true can this parameter be set. For details, see conf / storage ids.conf in the source directory. 446 447 #Set group name, serverID and corresponding IP address in this file 448 449 450 451 # id type of the storage server in the filename, values are: 452 453 ## ip: the ip address of the storage server 454 455 ## id: the server id of the storage server 456 457 # this paramter is valid only when use_storage_id set to true 458 459 # default value is ip 460 461 # since V4.03 462 463 id_type_in_filename = ip 464 465 #This parameter needs to be set only when use storage ID is set to true 466 467 468 469 470 471 # if store slave file use symbol link 472 473 # default value is false 474 475 # since V4.01 476 477 store_slave_file_use_link = false 478 479 #Whether the storage slave file adopts symbol link mode 480 481 #If set to true, a slave file takes up two files: the original file and the symbolic link to it 482 483 484 485 # if rotate the error log every day 486 487 # default value is false 488 489 # since V4.02 490 491 rotate_error_log = false 492 493 #Whether to rotate the error log regularly? Currently, only one rotation per day is supported. 494 495 496 497 # rotate error log time base, time format: Hour:Minute 498 499 # Hour from 0 to 23, Minute from 0 to 59 500 501 # default value is 00:00 502 503 # since V4.02 504 505 error_log_rotate_time=00:00 506 507 #This parameter is valid when the rotate error log parameter is set to true. 508 509 510 511 # rotate error log when the log file exceeds this size 512 513 # 0 means never rotates log file by log file size 514 515 # default value is 0 516 517 # since V4.02 518 519 rotate_error_log_size = 0 520 521 #Rotation of error log by size 0 means rotation is not performed by size, otherwise rotation will occur when the error log file reaches the size. 522 523 524 525 # if use connection pool 526 527 # default value is false 528 529 # since V4.05 530 531 use_connection_pool = false 532 533 #Use connection pool or not 534 535 536 537 # connections whose the idle time exceeds this time will be closed 538 539 # unit: second 540 541 # default value is 3600 542 543 # since V4.05 544 545 connection_pool_max_idle_time = 3600 546 547 #The maximum lifetime of the connection pool link, in seconds. It is valid when use [connection] pool is set to true. 548 549 550 551 # HTTP port on this tracker server 552 553 http.server_port=8080 554 555 #http service port. By default, V4.06 does not INSTALL http service. See the INSTALL file for details. 556 557 558 559 # check storage HTTP server alive interval seconds 560 561 # <= 0 for never check 562 563 # default value is 30 564 565 http.check_alive_interval=30 566 567 #Check long link life for 30 seconds 568 569 570 571 # check storage HTTP server alive type, values are: 572 573 # tcp : connect to the storge server with HTTP port only, 574 575 # do not request and get response 576 577 # http: storage check alive url must return http status 200 578 579 # default value is tcp 580 581 http.check_alive_type=tcp 582 583 #The existing mode of long link is currently configured as tcp mode. 584 585 586 587 # check storage HTTP server alive uri/url 588 589 # NOTE: storage embed HTTP server support uri: /status.html 590 591 http.check_alive_uri=/status.html 592 593 #What identification is used for inspection
2. Details of storage Server configuration
1 #Whether this configuration file is invalid 2 3 disabled=false 4 5 #false is valid true is invalid 6 7 8 9 # group name of this storage server 10 11 group_name=group1 12 13 14 15 # One ip can be set. It is empty by default and all ip can be bound. 16 17 bind_addr= 18 19 20 21 # This configuration will take effect only after the bind ﹣ addr setting 22 23 # Whether to use the bound ip to access other servers when the local machine accesses other services as a client 24 25 client_bind=true 26 27 # storage server listening port 28 29 port=23000 30 31 #23000 by default. If there is no conflict, try not to modify it. 32 33 34 35 # Connection timeout, for the socket function connect, the default is 30 seconds 36 37 connect_timeout=30 38 39 40 41 # Network communication timeout, default is 60 seconds 42 43 network_timeout=60 44 45 46 47 # Send heartbeat interval to tracker server, 30 seconds by default 48 49 heart_beat_interval=30 50 51 52 53 # Time interval to report disk usage to tracker server, default is 60 seconds 54 55 stat_report_interval=60 56 57 58 59 # The working folder and log also exist here (this is not the address where the uploaded file is stored) 60 61 base_path=/home/yuqing/fastdfs 62 63 64 65 # Maximum connections of this traceserver 66 67 max_connections=256 68 69 70 71 # Buffer size of data sent or received, memory size consumed by work queue = buffer_size * max_connections 72 73 # It is recommended that this setting is greater than 8k, and the default is 256k. 74 75 buff_size = 256KB 76 77 78 79 # Number of threads receiving data 80 81 # Default 1 82 83 # since V4.07 84 85 accept_threads=1 86 87 88 89 # Number of worker threads, less than max_connections 90 91 # Default 4, usually set as CPU cores, with the highest efficiency 92 93 work_threads=4 94 95 96 97 # Is the disk read-write separated? true by default 98 99 disk_rw_separated = true 100 101 102 103 # Number of threads read from disk (per working folder) 104 105 # This parameter can be set to 0 for the disk read-write mode. 106 107 # The default is 1. 108 109 disk_reader_threads = 1 110 111 112 113 # Number of threads written to disk (per working folder) 114 115 # This parameter can be set to 0 for the disk read-write mode. 116 117 # The default is 1. 118 119 disk_writer_threads = 1 120 121 122 123 # When no files need to be synchronized are found, you need to wait for sync ﹣ wait ﹣ msec milliseconds to check in binlog 124 125 # Cannot be set to 0, default is 50ms 126 127 sync_wait_msec=50 128 129 130 131 # After synchronizing a file, sleep sync ﹣ interval milliseconds to continue synchronizing the next file 132 133 sync_interval=0 134 135 136 137 # Start time to allow storage synchronization 138 139 # Hour from 0 to 23, Minute from 0 to 59 140 141 sync_start_time=00:00 142 143 144 145 # The end time of the storage synchronization is allowed, that is, the storage server can only synchronize data during the period from sync start time to sync end time. 146 147 # The default is to synchronize all day 148 149 # Hour from 0 to 23, Minute from 0 to 59 150 151 sync_end_time=23:59 152 153 #The range of synchronization time is specified by start time and end time 154 155 156 157 # After synchronizing write mark file freq files, if the mark file changes, write the mark file to disk 158 159 write_mark_file_freq=500 160 161 162 163 # Number of working paths (multiple disks can be mounted), default is 1 164 165 store_path_count=1 166 167 168 169 # Working path list. If store? Path0 is not set, use base? Path storage. 170 171 # The path set must be the existing folder 172 173 # Need to configure store path count 174 175 store_path0=/home/yuqing/fastdfs 176 177 #store_path1=/home/yuqing/fastdfs2 178 179 180 181 # FastDFS stores files through a secondary directory, which is the folder data of each level directory. 182 183 # If it is set to 256, 256 * 256 = 65535 folders will be generated 184 185 # The default size of this value is 256, and the range 1-256 can be set. 186 187 subdir_count_per_path=256 188 189 190 191 # tracer server list. If there are multiple tracer servers, they will be listed in branches. 192 193 tracker_server=192.168.209.121:22122 194 195 196 197 #log level 198 199 ### emerg for emergency 200 201 ### alert 202 203 ### crit for critical 204 205 ### error 206 207 ### warn for warning 208 209 ### notice 210 211 ### info 212 213 ### debug 214 215 log_level=info 216 217 218 219 # Unix user group running this process. If it is not set, the default is the group of the current user. 220 221 run_by_group= 222 223 224 225 # The user name for running this process. If it is not set, the default is the user name of the current user. 226 227 run_by_user= 228 229 230 231 # Host ip range that can be connected to this machine, * means all servers are allowed 232 233 # Support the expression: 10.0.1.[1-15,20] or host[01-08,20-25].domain.com 234 235 allow_hosts=* 236 237 238 239 # File distributed storage strategy 240 241 # 0: polling 242 243 # 1: store randomly according to the hash result of file name 244 245 file_distribute_path_mode=0 246 247 # This configuration is valid when file? Distribute? Path? Mode = 0 248 249 250 251 # When the write file data reaches the value of file "distribute" rotate "count, rotate to another path to continue writing 252 253 # The default value of this configuration is 100 254 255 file_distribute_rotate_count=100 256 257 258 259 # Whether to call fsync landing file when writing large file 260 261 # 0: never call 262 263 # Other values: call fsync once for every bytes written 264 265 # The default is 0. 266 267 fsync_after_written_bytes=0 268 269 270 271 # The interval between landing the logs in the cache to the disk, which is 10 seconds by default 272 273 sync_log_buff_interval=10 274 275 276 277 # The interval between landing the binlog in the cache to the disk, which is 10 seconds by default 278 279 sync_binlog_buff_interval=10 280 281 282 283 # The interval between landing the status data in the storage server cache to the disk, which is 10 seconds by default 284 285 sync_stat_file_interval=300 286 287 288 289 # Thread stack size, 64k by default, not recommended less than 64k, 512k by default 290 291 thread_stack_size=512KB 292 293 294 295 # Corresponding to the configuration when store_server= 2 in tracker.conf, this storage server serves as the target server, and the priority of uploading files can be negative. The lower the value, the higher the priority. 296 297 # Description of the store? Server parameter in tracker.conf: 298 299 # Rules for selecting server for uploading files: 300 301 # 0: Poll (default) 302 303 # 1: server s ranked first by IP 304 305 # 2: sort by priority, the smallest server 306 307 upload_priority=10 308 309 310 311 # Network card alias. You can see many local network card aliases with ifconfig-a, such as eth0,eth0:0, etc. 312 313 # Multiple network card aliases are separated by commas. The default value is blank. The system automatically selects them. 314 315 if_alias_prefix= 316 317 318 319 # Check whether duplicate files are checked. If it is set to true, use FastDHT to store the file index. 320 321 # 1 or yes: need to check 322 323 # 0 or no: no check required 324 325 # The default value is 0 326 327 check_file_duplicate=0 328 329 330 331 # The file signature form, hash or md5, is used for file de duplication. The default is hash. 332 333 file_signature_method=hash 334 335 336 337 # The namespace where the file index is stored (valid when check file duplicate = 1) 338 339 key_namespace=FastDFS 340 341 342 343 # Whether to use long connection with FastDHT 344 345 # 0 for short link, 1 for long link 346 347 # The default value is 0 348 349 keep_alive=0 350 351 352 353 # have access to#include filename to load the list of FastDHT servers. Filename can be a relative path (based on base path) 354 355 # Valid when check file duplicate = 1 356 357 358 359 # See FastDHT installation instructions for more information 360 361 ##include /home/yuqing/fastdht/conf/fdht_servers.conf 362 363 364 365 # Record access log or not 366 367 use_access_log = false 368 369 370 371 # Whether to rotate access logs regularly? Currently, only one rotation per day is supported. 372 373 rotate_access_log = false 374 375 376 377 # If the log is accessed according to the rotation of the sky, the specific time when the new error log file is generated 378 379 # Hour from 0 to 23, Minute from 0 to 59 380 381 access_log_rotate_time=00:00 382 383 384 385 # Whether to rotate the error log on a regular basis? Currently, rotation is only supported once a day. 386 387 rotate_error_log = false 388 389 390 391 # If the error log is rotated according to the sky, the specific time when the new error log file is generated 392 393 # Hour from 0 to 23, Minute from 0 to 59 394 395 error_log_rotate_time=00:00 396 397 398 399 # Whether to generate a new access log file when the error access file reaches a certain size 400 401 # 0 is not sensitive to log file size 402 403 rotate_access_log_size = 0 404 405 406 407 # Whether to generate a new error log file when the error log file reaches a certain size 408 409 # 0 is not sensitive to log file size 410 411 rotate_error_log_size = 0 412 413 414 415 # Log file save date 416 417 # 0 means permanent save, do not delete 418 419 # The default is 0. 420 421 log_file_keep_days = 0 422 423 424 425 # if skip the invalid record when sync file 426 427 # default value is false 428 429 # since V4.02 430 431 file_sync_skip_invalid_record=false 432 433 434 435 # Use connection pool or not 436 437 use_connection_pool = false 438 439 440 441 # Connection idle timeout. If the connection is idle for more than this configuration, close the connection times, in seconds. 442 443 connection_pool_max_idle_time = 3600 444 445 # The domain name of the http access method of the storage server. If the domain name is empty, only ip access can be used. 446 447 http.domain_name= 448 449 450 451 # HTTP port 452 453 http.server_port=8888
3. Details of the client's configuration file
1 # Connection timeout 2 3 # Default 30 seconds 4 5 connect_timeout=30 6 7 8 9 # Network timeout 10 11 # default value is 30s 12 13 network_timeout=60 14 15 16 17 # Working folder, log exists here 18 19 base_path=/home/yuqing/fastdfs 20 21 22 23 # tracer server list. If there are multiple tracer servers, they will be listed in branches. 24 25 tracker_server=192.168.0.197:22122 26 27 28 29 #log level 30 31 ### emerg for emergency 32 33 ### alert 34 35 ### crit for critical 36 37 ### error 38 39 ### warn for warning 40 41 ### notice 42 43 ### info 44 45 ### debug 46 47 log_level=info 48 49 50 51 # Use connection pool or not 52 53 use_connection_pool = false 54 55 56 57 # Connection idle timeout. If the connection is idle for more than this configuration, close the connection times, in seconds. 58 59 connection_pool_max_idle_time = 3600 60 61 62 63 # Whether to read the parameter of fastdfs from tracer server, default to false 64 65 load_fdfs_parameters_from_tracker=false 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 # Use storage id to replace ip, default to false 74 75 # The meaning of this parameter is the same as that of tracker.conf 76 77 # This configuration only takes effect when load ﹣ FDFS ﹣ parameters ﹣ from ﹣ tracker = false 78 79 # This configuration defaults to false 80 81 use_storage_id = false 82 83 84 85 # Specifies the file name of the storage id, allowing absolute paths 86 87 # The meaning of this parameter is the same as that of tracker.conf 88 89 # This configuration only takes effect when load ﹣ FDFS ﹣ parameters ﹣ from ﹣ tracker = false 90 91 storage_ids_filename = storage_ids.conf 92 93 94 95 96 97 #HTTP settings 98 99 http.tracker_server_port=8080 100 101 102 103 #Introduce HTTP related configuration 104 105 ##include http.conf
V. summary
fastDFS is built for clusters, and single machine fastDFS is of little significance, because the significance of fastDFS lies in its distributed file system. If you want to play with fastDFS, it is not enough to only master fastDFS.