catalogue
2.3. Initialization of variables
3. Syntax extension of variables
3.2 declaring multiple variables
3.3 special cases of declared variables
4. Naming specification of variables
Objectives:
Be able to tell the main role of variables
Be able to write out the initialization of variables
Be able to say the naming convention of variables
Can draw how variables are stored in memory
Be able to write cases of exchanging variables
1. Variable overview
1.1 what are variables
Vernacular: a variable is a box of things.
Popular: variables are containers for storing data. We obtain data through variable names, and even data can be modified.
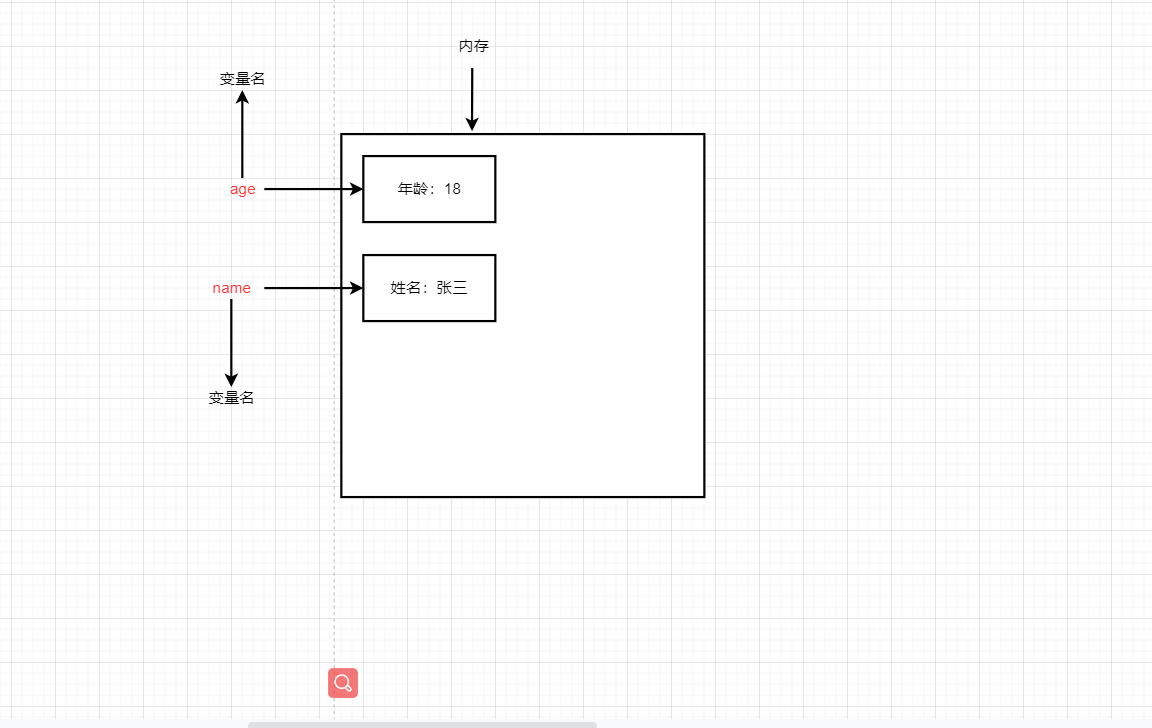
1.2 storage of variables in memory
Essence: a variable is a piece of space applied by a program in memory for storing data.
2. Use of variables
The use of variables is divided into two parts: 1. Declare variables 2. Assignment
2.1 declare case variables
//Declare variable var age;//Declare a variable named age
var Is a JS keyword used to declare a variable (the meaning of variable variable). After using this keyword to declare a variable, the computer will automatically allocate memory space for the variable, which does not need to be managed by the programmer
age is the variable name defined by the programmer. We need to access the allocated space in memory through the variable name.
2.2. Assignment
age = 10;//Assign a value of 10 to this variable
=It is used to assign the value on the right to the variable space on the left, which represents the meaning of assignment
The variable value is the value that the programmer saves in the variable space
2.3. Initialization of variables
var age = 10;//The declared variable is also assigned a value of 10
Declaring and assigning a variable is called variable initialization.
Case: use of variables:
1. An input box pops up, prompting the user to enter the name
2. A dialog box pops up to output the name just entered by the user.
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Title</title>
</head>
<body>
<script>
//1. The user enters the name and stores it in the name of myname
var myname = prompt('Please enter your name')
//2. Output the user name
alert(myname)
</script>
</body>
</html>Feel it.
3. Syntax extension of variables
3.1 updating variables
After a variable is re assigned, its source value will be overwritten, and the variable value will be subject to the last assigned value.
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Title</title>
</head>
<body>
<script>
var myname = 'Zhang San';
console.log(myname);
myname = 'Li Si';
console.log(myname);
</script>
</body>
</html>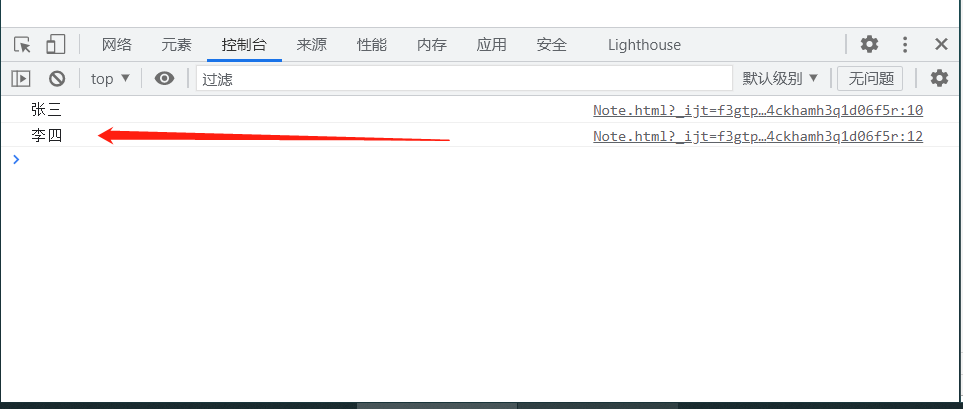
Update the variable, subject to the last assignment.
3.2 declaring multiple variables
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Title</title>
</head>
<body>
<script>
//1. Declare variables
// var age = 18;
// var address = 'Heilongjiang';
// var sal = 2000;
//Declare multiple variables
var age =18,
address = 'Heilongjiang',
sal = 2000;
</script>
</body>
</html>3.3 special cases of declared variables
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Title</title>
</head>
<body>
<script>
//3.3 special cases of declared variables
//1. Only declare not to copy, the result is? The program doesn't know what's inside, so the result is undefined
var sex;
console.log(sex);
//2. If a variable is used directly without declaration or assignment, an error will be reported
console.log(tel);
//3. Do not declare direct assignment (yes, but not recommended)
qq = 924;
console.log(qq);
</script>
</body>
</html>4. Naming specification of variables
It consists of characters (A-Za-z), numbers (0-9), underscores (), and dollar symbols ($), such as usrAge,num01,name
Strictly case sensitive: var App and var App are two variables
Cannot start with a number, 18age is wrong
Cannot be a keyword, reserved word, such as var for while
Variable names must be meaningful. MMD BBD nl -------> age
Follow the hump naming method, the first letter is lowercase, and the first character of the following word needs to be capitalized myFirstName
Case: exchange variables
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Title</title>
</head>
<body>
<script>
//1. We need a temporary variable
//2. Give our apple1 to our temporary variable temp
//3. Give apple2 to apple1
//4. Give the value in the temporary variable to apple2
var temp;
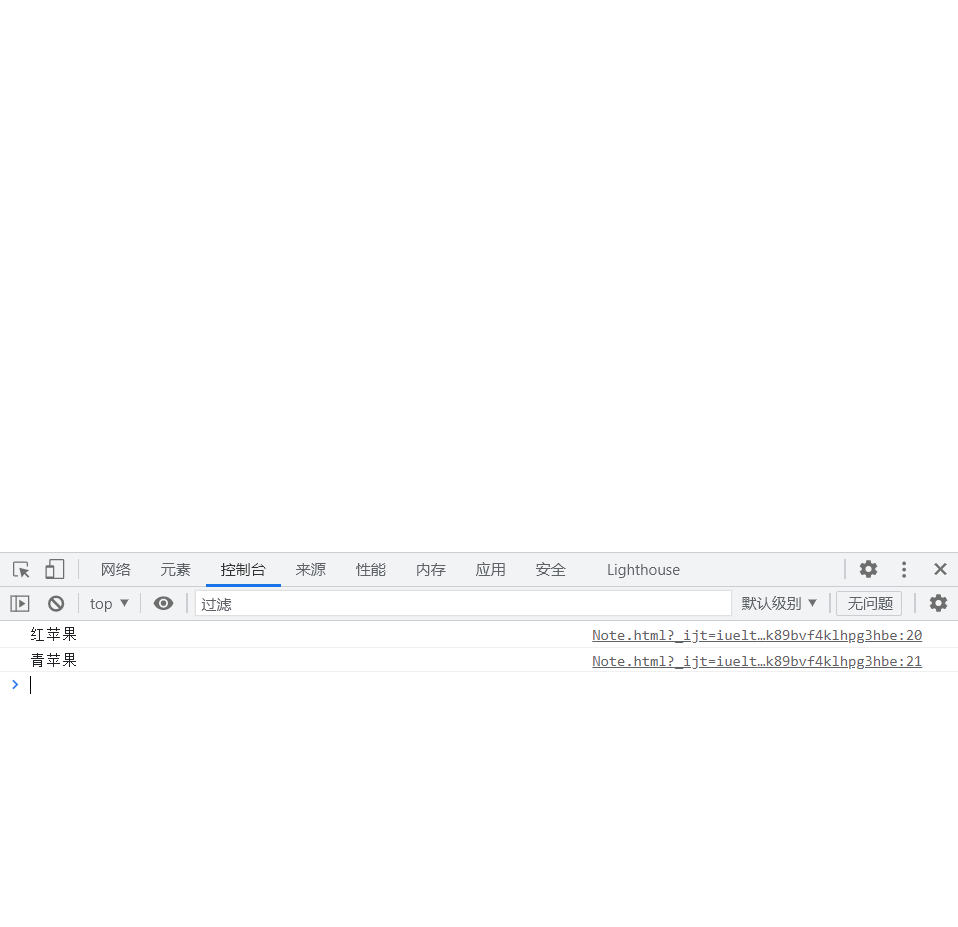
var apple1 ='green apple';
var apple2 = 'Red apple';
//Give the right to the left
temp = apple1;
apple1 = apple2;
apple2 = temp;
console.log(apple1);
console.log(apple2);
</script>
</body>
</html>Output it and see that the exchange has been completed
5. Summary:
Why do I need variables? Because we need to save some data, we need variables.
What are variables? A variable is a container for storing data, which is convenient for us to use in the future
What is the nature of variables? A variable is a space in memory that is used to store data.
How are variables used? When we use variables, we must declare variables and then assign values
The essence of declaring variables is to apply for memory space.
What is variable initialization? Declaring variables and assigning values is called variable initialization
What are the naming conventions for variables? The variable name shall be standardized as far as possible. See the meaning of name ------------ hump naming method
Distinguish which variables are illegal