Browser's optimization strategy for reflow (rearrangement) and redraw

If you only read the "sensitive" attribute and do not change the geometry of the node, only style calculation will be performed during js execution, and the layout will not be forced.
testing environment
Chrome version 96.0.4664.45 (official version) (64 bit)
Test code
Click to view the code<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8" />
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge" />
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0" />
<title>Document</title>
</head>
<body>
<div id="div">
<div></div>
</div>
<button>Click test</button>
<script>
const div = document.getElementById('div');
const btn = document.querySelector('button');
btn.onclick = () => {
// do something
};
</script>
</body>
</html>
When setting the style of a node, the browser handles a variety of situations
Only observe the browser processing near the btn click event in the code
The browser does nothing during js execution
After js is executed, style calculation, updating hierarchical tree, drawing and composition are performed
Test situation
There is no code in the click event
btn.onclick = () => {
// do something
};
Set the properties of irrelevant element geometry (position, size, etc.)
btn.onclick = () => {
div.style.color = 'red';
};
Set the attributes of irrelevant element geometry (position, size, etc.) and read some style attributes of the element
btn.onclick = () => {
div.style.color = 'red';
const { color, width, height } = div.style;
}
performance record
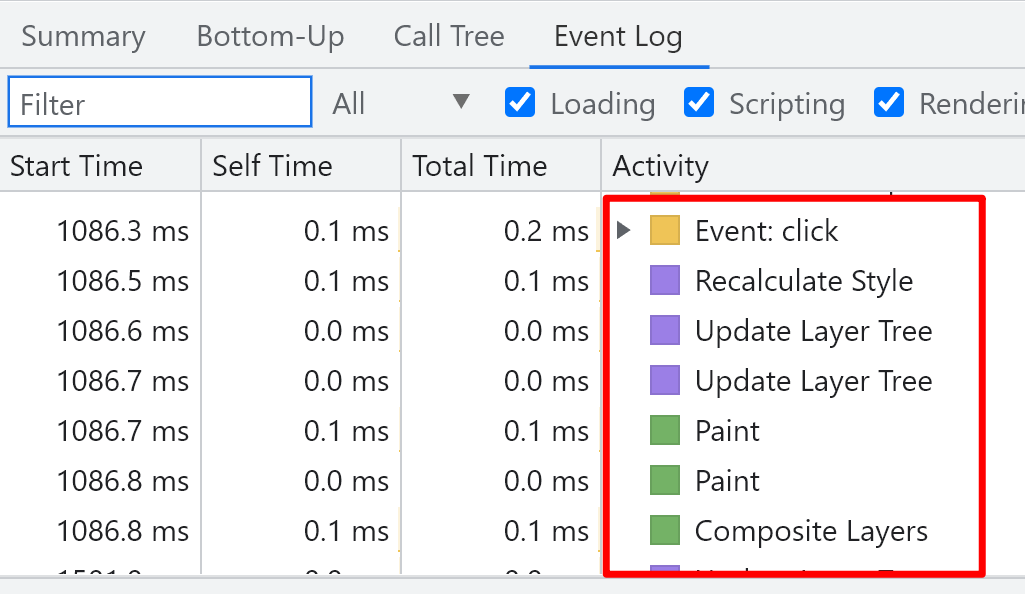
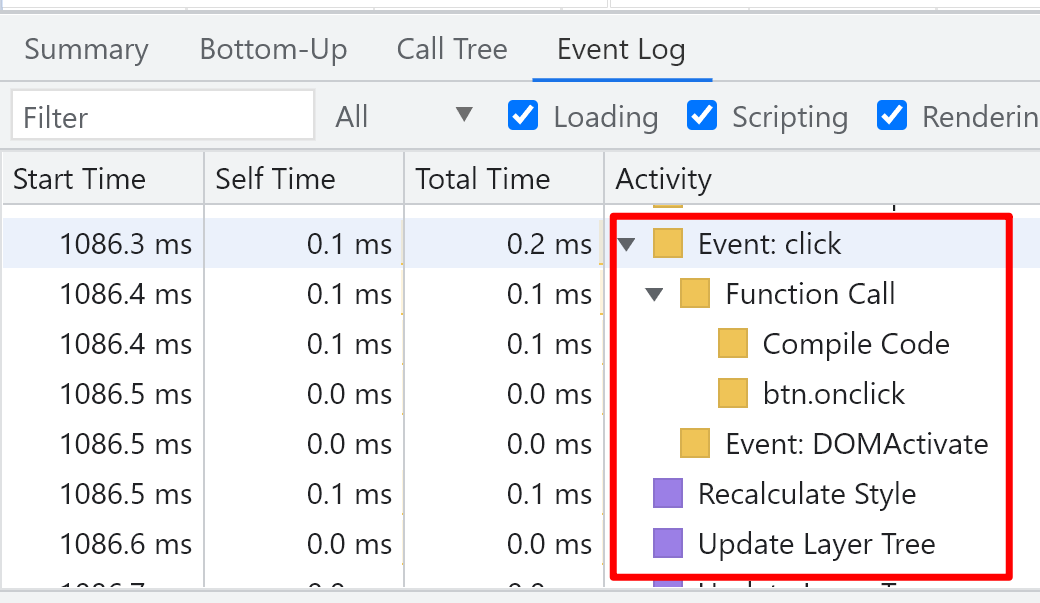
After js is executed, style calculation, layout, updating hierarchical tree, drawing and composition are carried out
One more layout step than the previous one
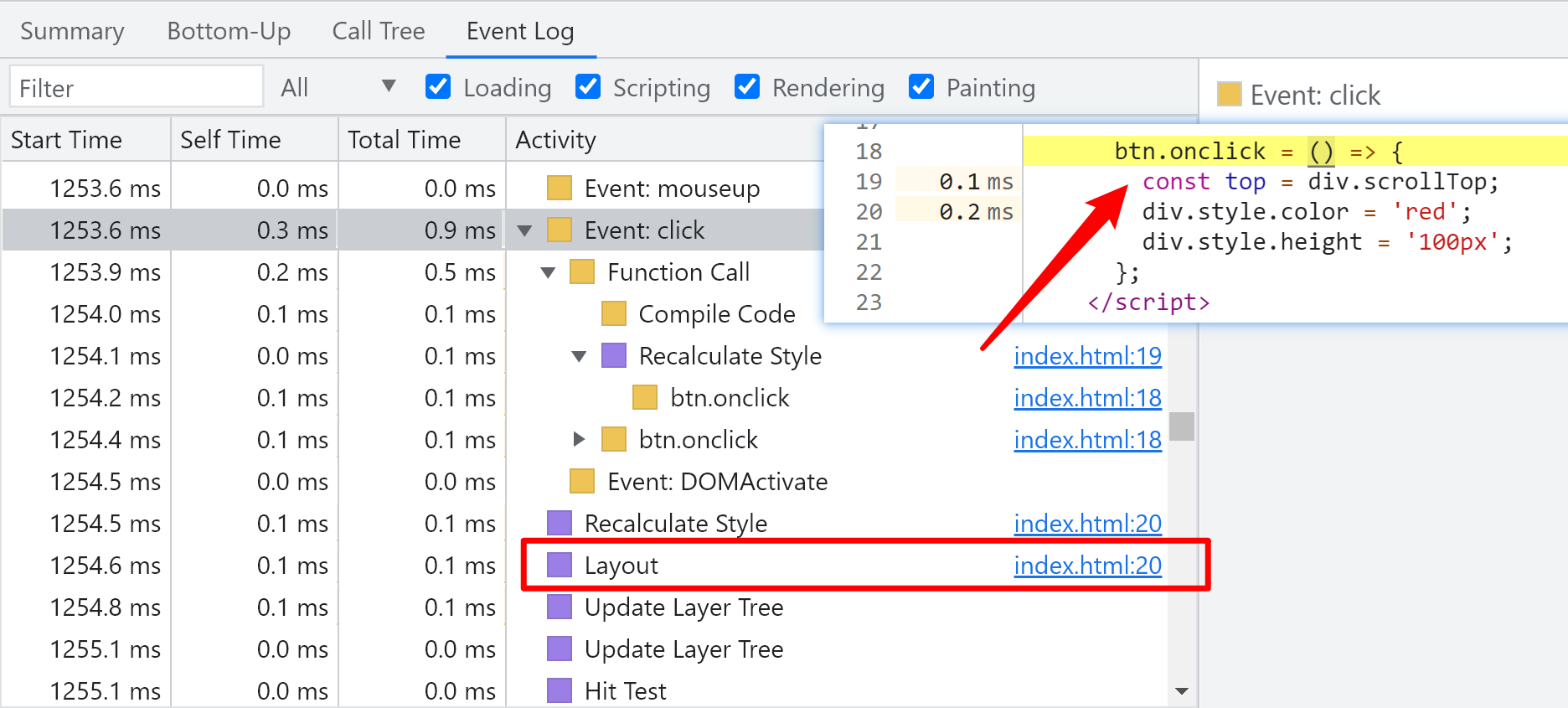
Test situation
Set attributes about the geometry of the element (position, size, etc.)
btn.onclick = () => {
div.style.height = '100px';
}
Set attributes about the element's geometry (position, size, etc.) and read the element's non "sensitive" style attributes
btn.onclick = () => {
div.style.height = '100px';
const { color, width, height } = div.style;
}
performance record
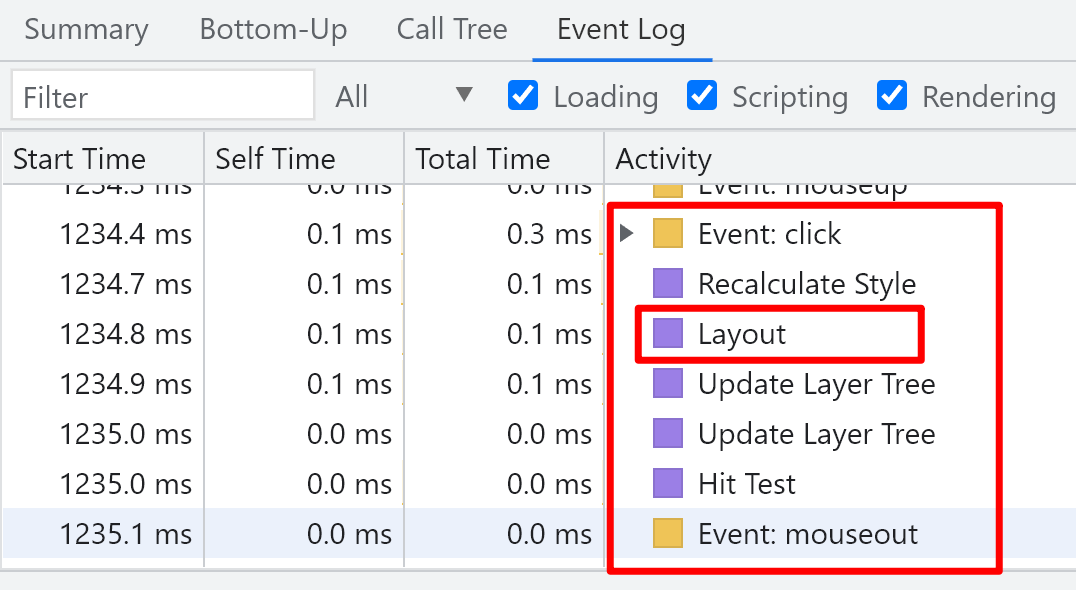
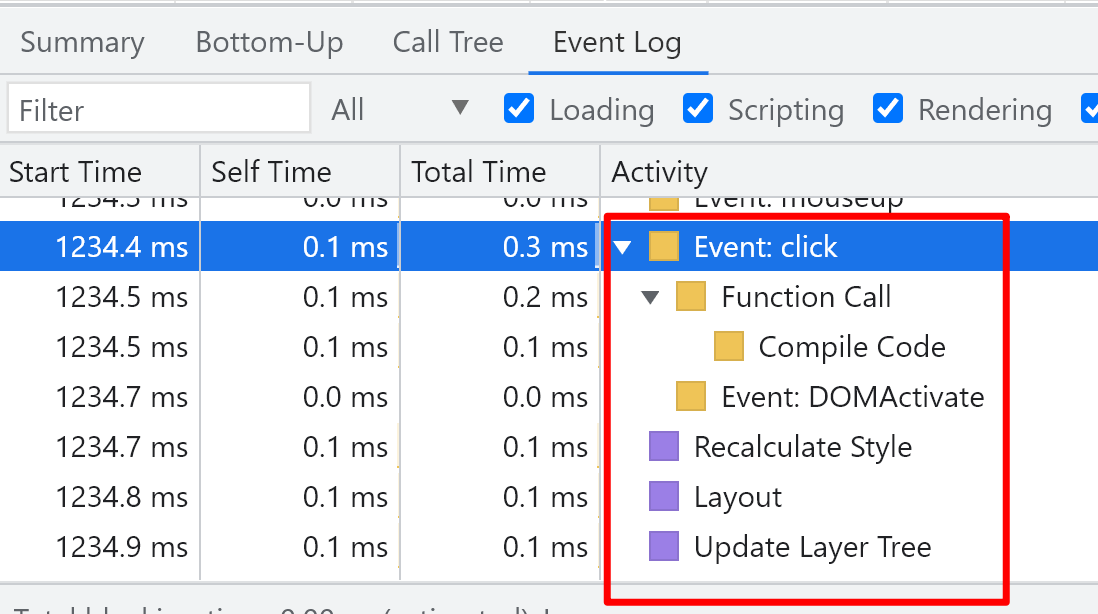
The browser performs style calculation during js execution
After style calculation, if there are new style settings, they are placed in the render optimization queue
Read sensitive attribute
btn.onclick = () => {
const top = div.scrollTop,
width = div.clientWidth;
};
performance record
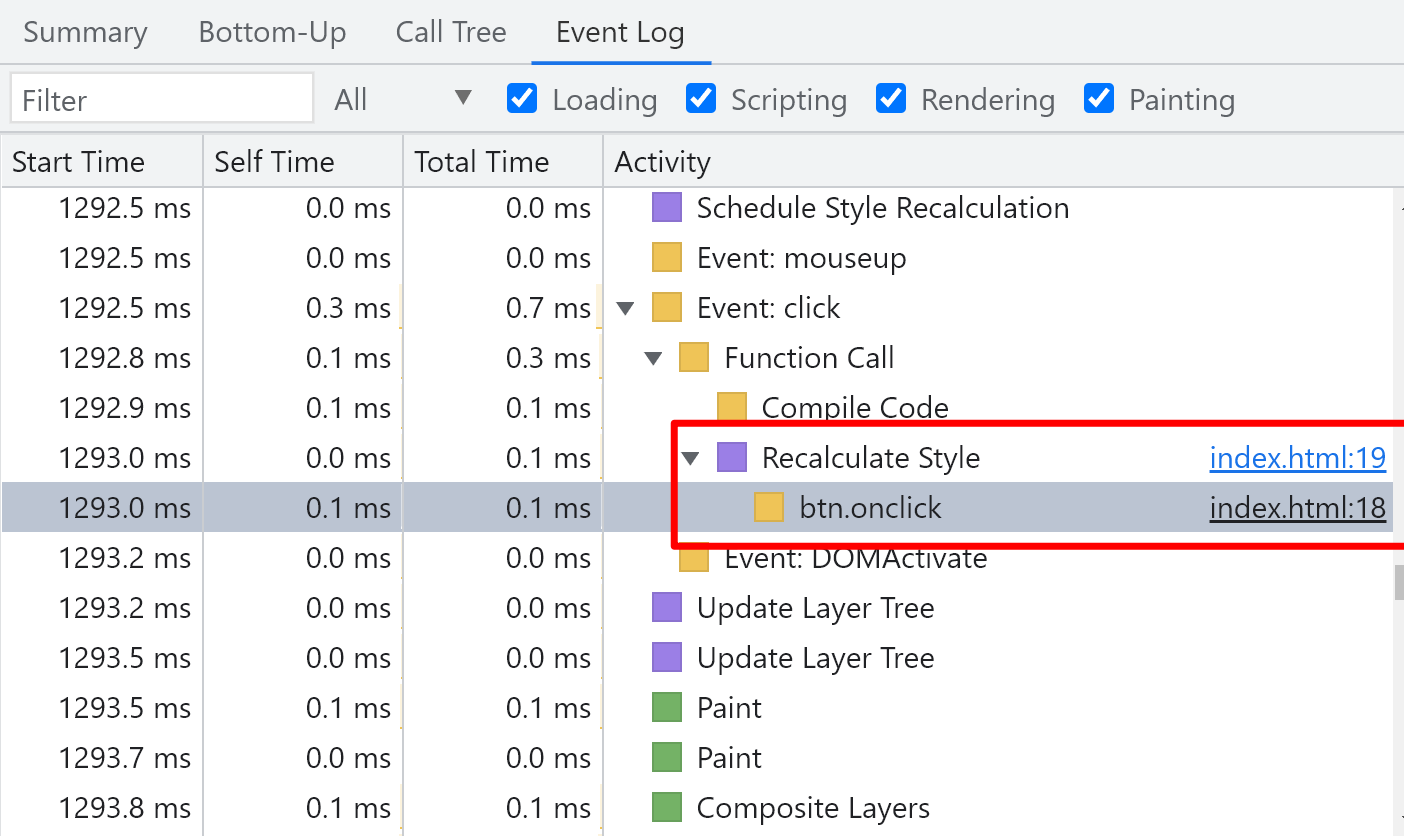
After reading the sensitive attribute, set the style independent of the geometric position of the node
btn.onclick = () => {
const top = div.scrollTop;
div.style.color = 'red';
div.style.backgroundColor = 'blue';
};
performance record
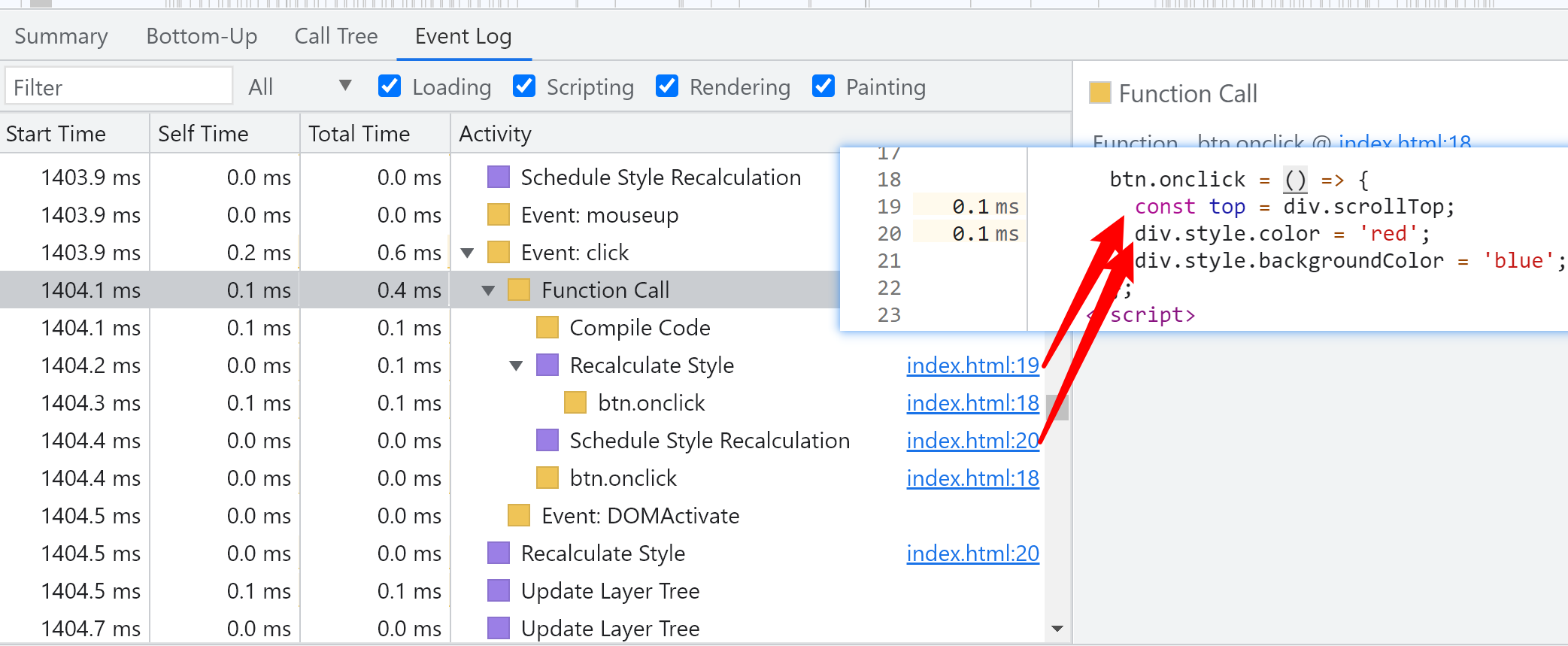
After reading the sensitive attribute, set the style about the geometric position of the node
btn.onclick = () => {
const top = div.scrollTop;
div.style.color = 'red';
div.style.height = '100px';
};
performance record
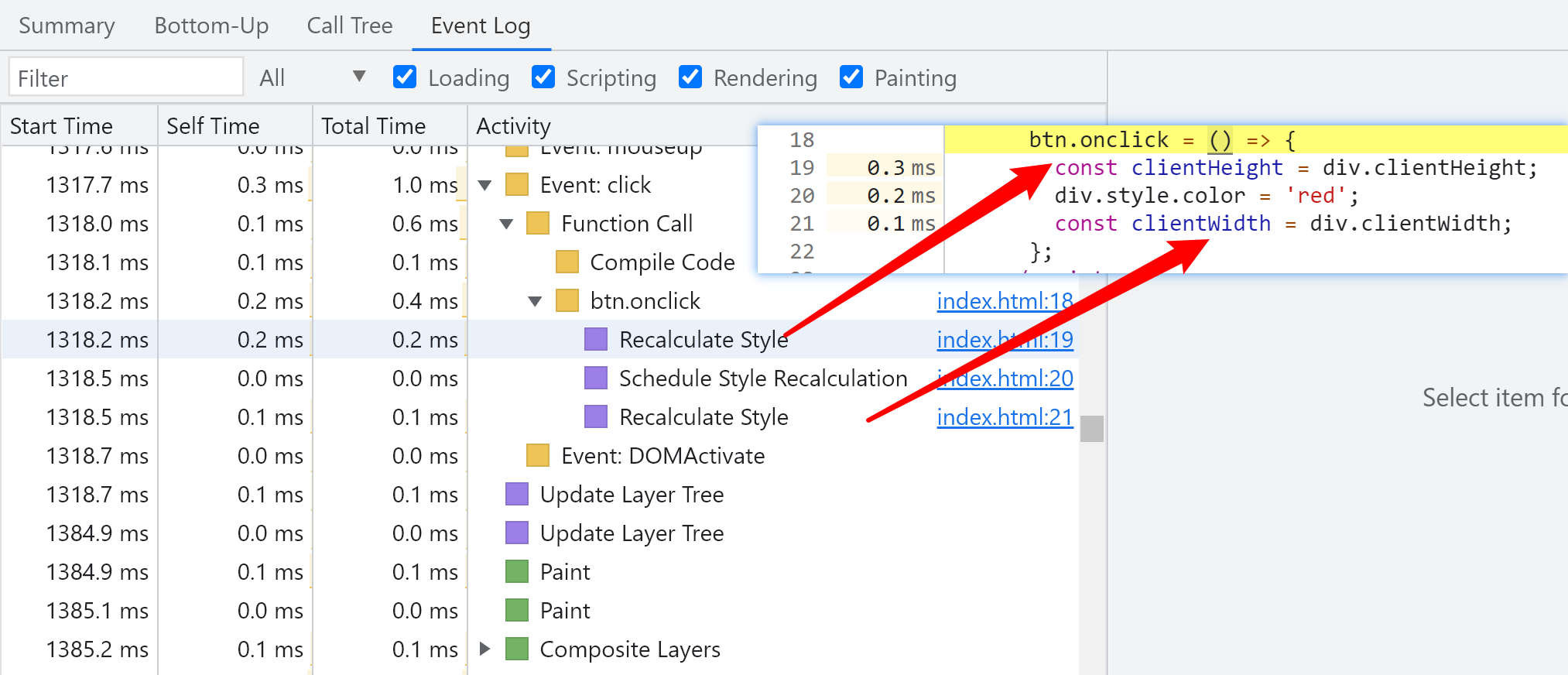
After reading the sensitive attribute, set the style independent of the geometric position of the node, and then read the sensitive attribute again
The browser performs style calculations twice
btn.onclick = () => {
const clientHeight = div.clientHeight;
div.style.color = 'red';
const clientWidth = div.clientWidth;
};
performane record
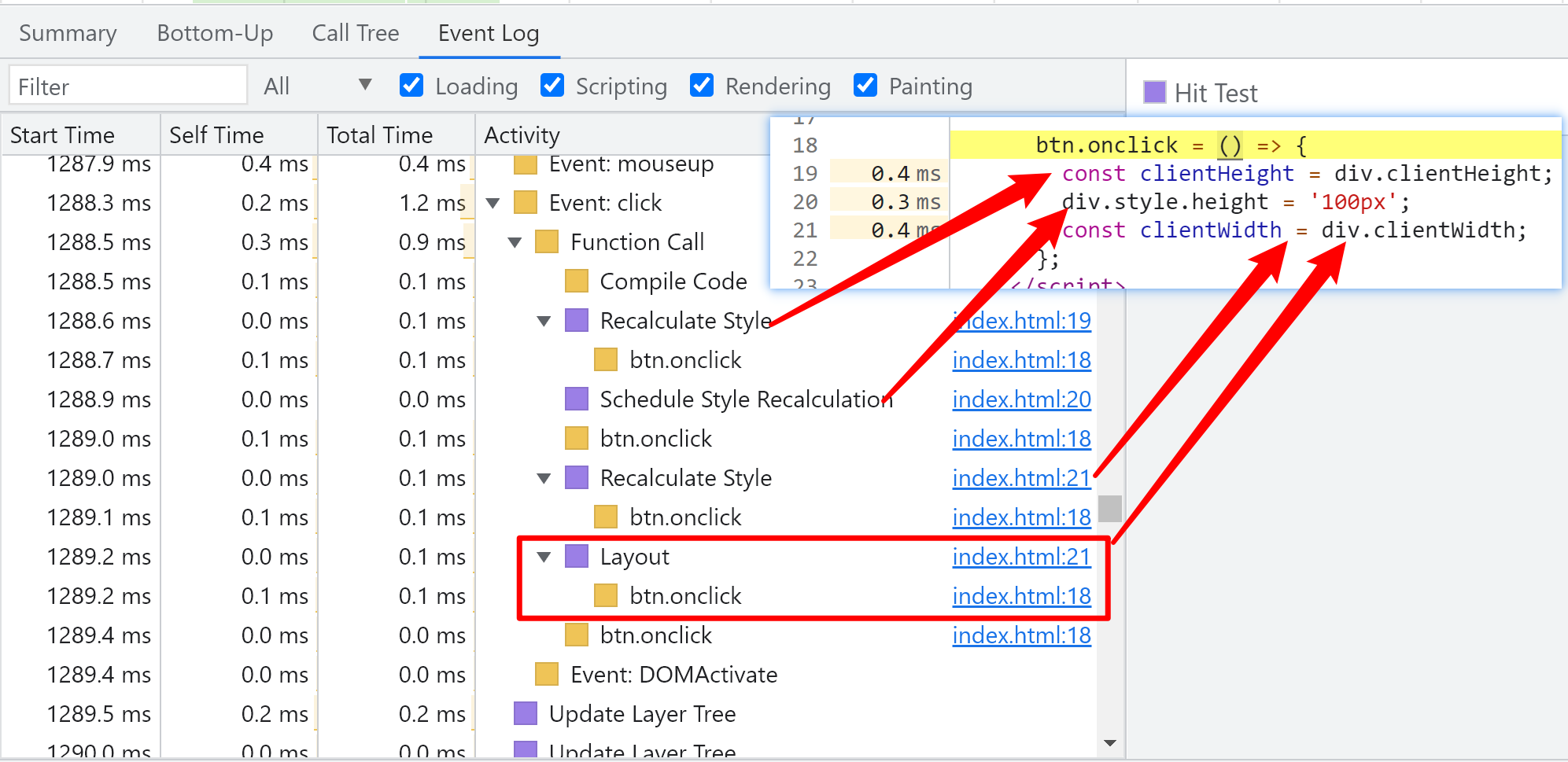
After reading the sensitive attribute and styling the geometric position of the node, read the sensitive attribute again
The browser will perform style calculation twice during js execution and force synchronization of layout.
btn.onclick = () => {
const clientHeight = div.clientHeight;
div.style.height = '100px';
const clientWidth = div.clientWidth;
};
performane record
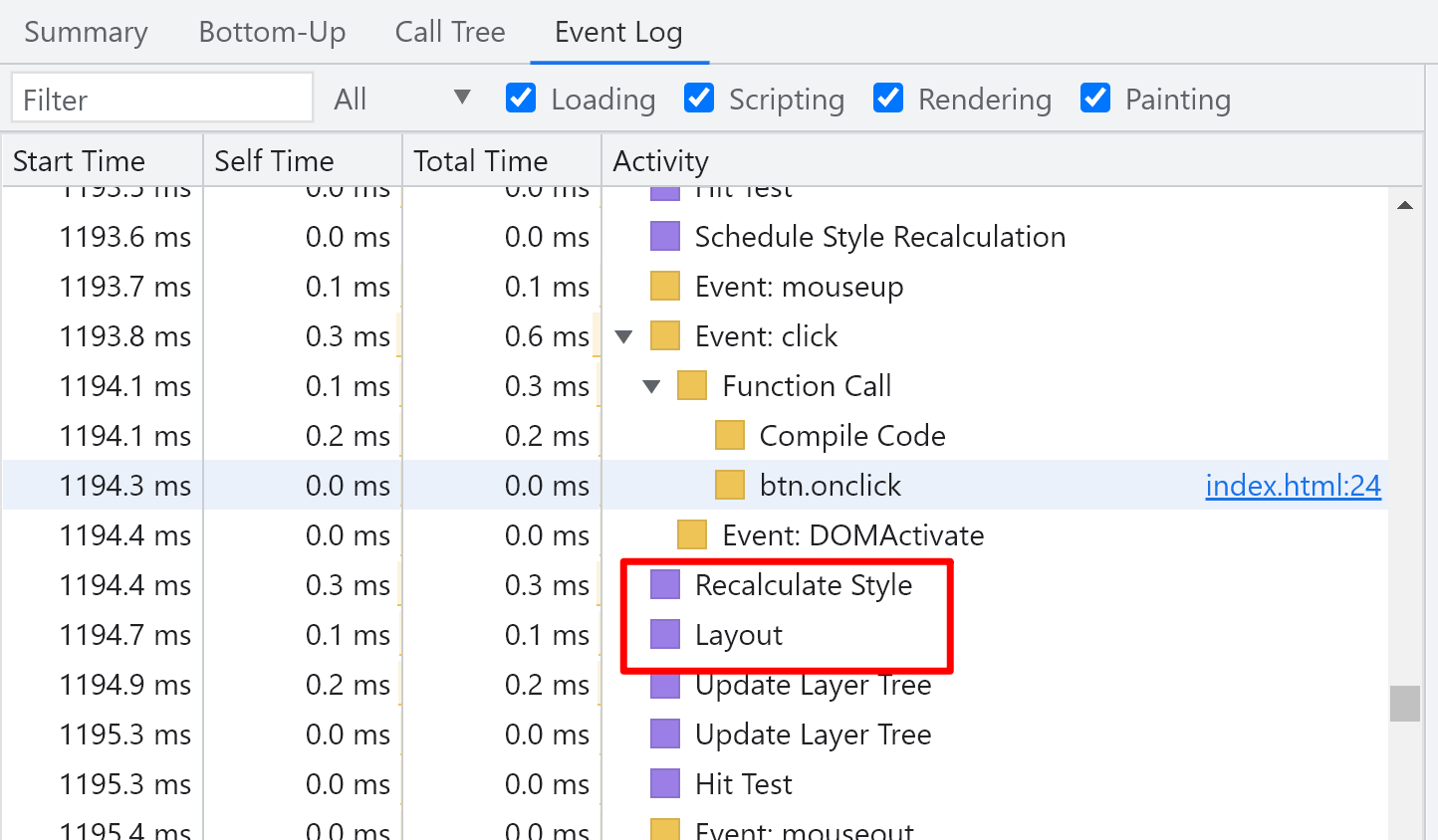
Browser processing operations related to the class of the node
The browser does nothing during js execution. So this is what the Internet says to use class style to reduce the operation of node style?
.style {
color: red;
height: 100px;
}
btn.onclick = () => {
const className = div.className;
div.className = `style`;
// Or the following code
/*
div.classList.add('style');
const className = div.classList.toString();
*/
};
performance record
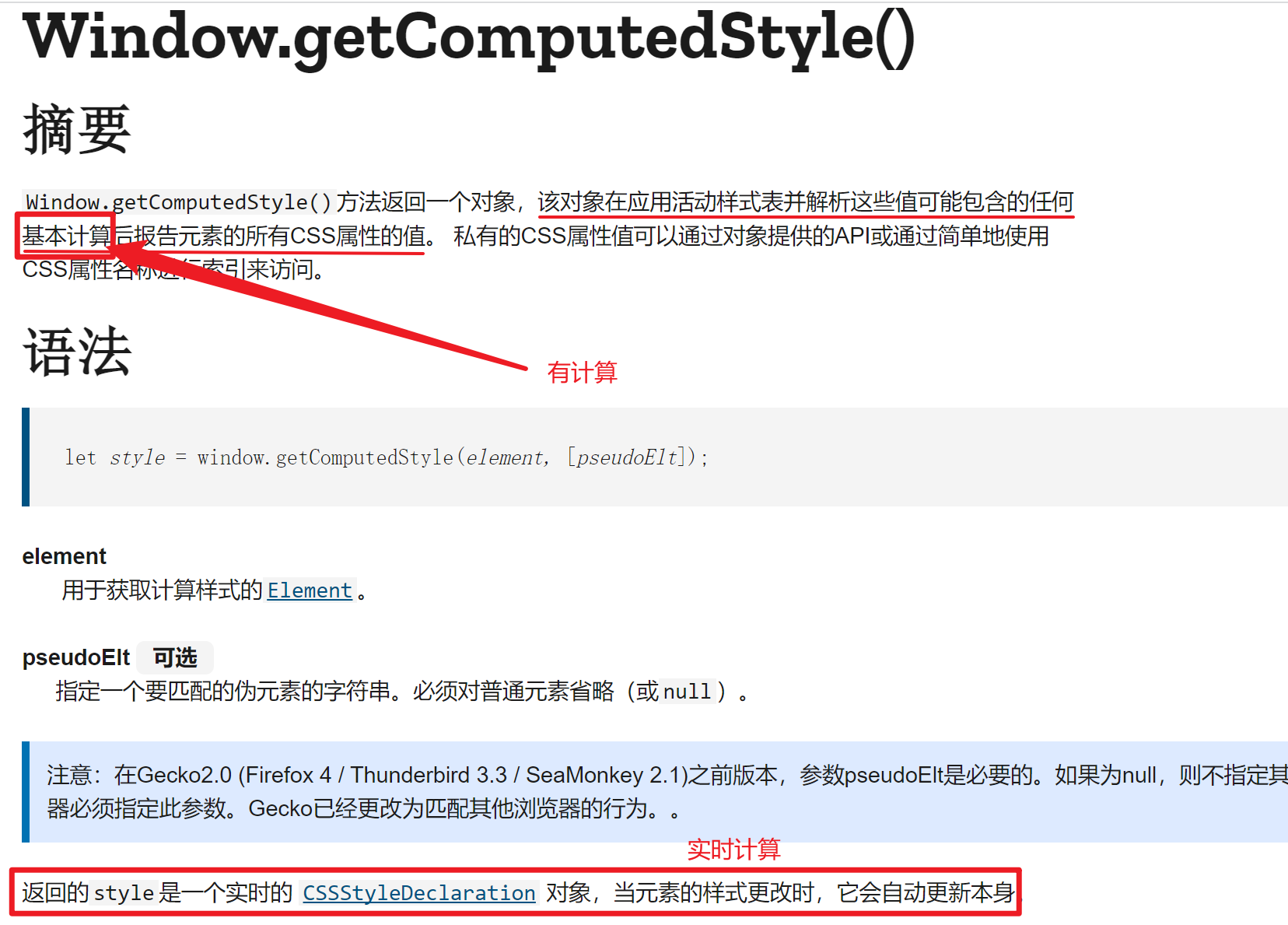
About window.getComputedStyle()
conclusion
- It is recommended on the Internet to use class and less style operation dom, which can reduce some browser operations (style calculation, forced synchronization layout, etc.) and reduce performance consumption
- When operating style on the Internet, read and write are separated. Read before write can also reduce the performance consumption of some style calculations
- Don't use window.getComputedStyle() to get the style
source
https://www.phpied.com/rendering-repaint-reflowrelayout-restyle/
https://dl.acm.org/doi/10.1145/1772690.1772741
https://developer.mozilla.org/zh-CN/docs/Web/API/Window/getComputedStyle