1. Calculate the following integrals with the trapezoidal method of variable step size to make the accuracy reach 10-4.
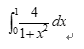
Requirement:
(1) the information of the accuracy ε and the end points a and b of the interval are input from the keyboard terminal;
(2) print out the calculation results of each step.
Source code:
#include<iostream>
#include<cmath>
using namespace std;
int main(){
double x,a,s,b,e,h,T1,T2;
cout<<"Please enter the range endpoint a,b And precision e:"<<endl;
cin>>a>>b>>e;
cout<<endl;
h = b-a;
T1 = (h/2)*(4/(1+pow(a,2))+4/(1+(pow(b,2))));
int count=0;
cout<<"K "<<" T1 "<<" T2 "<<endl;
do{
if(count!=0){
h = h/2;
T1 = T2;
}
count++;
s = 0;
x = a + h/2;
do{
s = s + (4/(1+pow(x,2)));
x = x + h;
}while(x<b);
T2 = (T1/2)+h*s/2;
printf("%d: %.6lf %.6lf\n",count,T1,T2);
}while(abs(T2-T1)>=e);
cout<<endl;
printf("The final results are as follows:%.4lf",T2);
return 0;
}
2. Calculate the following integral values with the longberg algorithm to achieve the accuracy of 10-4.
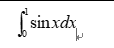
Requirement:
(1) draw the implementation block diagram of longberg algorithm;
(2) the information of the accuracy ε and the end points a and b of the interval are input from the keyboard terminal;
(3) print out the calculation results of trapezoid sequence, Simpson sequence, Cotes sequence and longberg sequence according to the calculation sequence of longberg algorithm, as shown below;
|
k |
Interval equiscore n=2k |
Trapezoidal sequence T2k |
Simpson sequence S2k-1 |
Cotes sequence C2k-2 |
Longberg sequence R2k-3 |
|
0 |
1 |
T1 |
|
|
|
|
1 |
2 |
T2 |
S1 |
|
|
|
2 |
4 |
T4 |
S2 |
C1 |
|
|
3 |
8 |
T8 |
S4 |
C2 |
R1 |
|
4 |
16 |
T16 |
S8 |
C4 |
R2 |
|
5 |
32 |
T32 |
S16 |
C8 |
R4 |
(4) output the integration approximate value that meets the accuracy requirements finally.
Algorithm block diagram
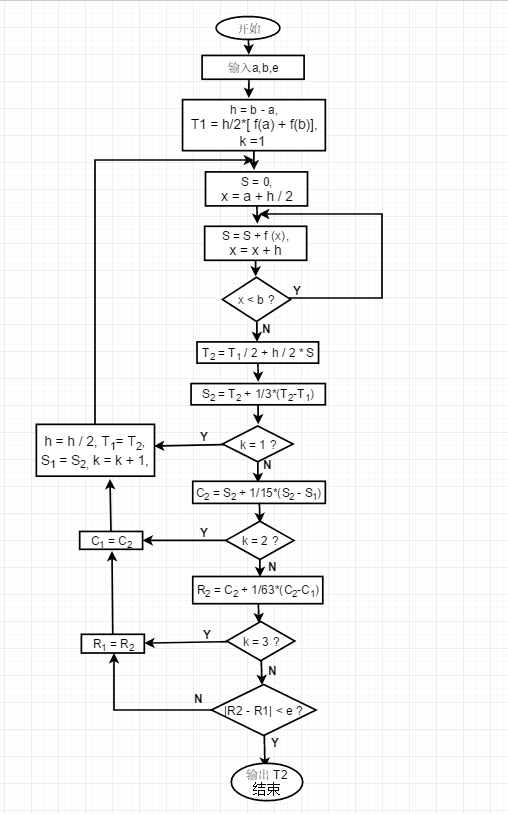
#include<iostream>
#include<cmath>
using namespace std;
int main(){
double x,a,s,b,e,h,T1,T2;
cin>>a>>b>>e;
double q[7][7];
double T[100] = {0};
h = b-a;
int d=0;
int i,j;
for(i=0;i<7;i++){
for(j=0;j<7;j++){
if(j == 0){
q[i][j] = pow(2,i);
}
else{
q[i][j] = 0;
}
}
}
T1 = (h/2)*(sin(b)+sin(a));
int count=-1,k=0;
do{
if(count!=-1){
h = h/2;
T1 = T2;
}
count = pow(2,k);
k++;
s = 0;
x = a + h/2;
do{
s = s + sin(x);
x = x + h;
}while(x<b);
T2 = (T1/2)+h*s/2;
T[count] = T1;
q[d++][1] = T[count];
}while(abs(T2-T1)>=e);
cout<<endl;
double S[100] = {0};
double C[100] = {0};
double R[100] = {0};
d = 1;
for(int i=1;i<=count/2;i=i*2){
S[i] = (4.00/3)*T[2*i]-(1.00/3)*T[i];
q[d++][2] = S[i];
}
cout<<endl;
d = 2;
for(int i=1;i<=count/4;i=i*2){
C[i] = (16.00/15)*S[2*i]-(1.00/15)*S[i];
q[d++][3] = C[i];
}
cout<<endl;
d = 3;
for(int i=1;i<=count/8;i=i*2){
R[i] = (64.00/63)*C[2*i]-(1.00/63)*C[i];
q[d++][4] = R[i];
}
cout<<"n"<<" Trapezoidal sequence "<<" Simpson sequence "<<" Cortez sequence "<<" Longberg sequence "<<endl;
for(i=0;i<6;i++){
for(j=0;j<5;j++){
if(q[i][j] == 0){
printf(" ");
}
else{
if(j==0){
printf("%.0lf ",q[i][j]);
if(q[i][j]<=8) printf(" ");
}
else{
printf("%.8lf ",q[i][j]);
}
}
}
printf("\n");
}
printf("\n The final results are as follows: %.4lf",q[3][4]);
return 0;
}