1. Create required tables and insert data
#Create Data Table
mysql> create table fruits ( f_id char(10) not null, s_id int not null, f_name char(255) not null, f_price decimal(8,2) not null, primary key(f_id) );
#insert data
mysql> insert into fruits(f_id,s_id,f_name,f_price)
-> values('a1',101,'apple','5.2'),
-> ('b1',101,'blackberry','10.2'),
-> ('bs1',102,'orange','11.2'),
-> ('bs2',105,'melon','8.2'),
-> ('t1',102,'banana','10.3'),
-> ('t2',102,'grape','5.3'),
-> ('o2',103,'coconut','9.2'),
-> ('c0',101,'cherry','3.2'),
-> ('a2',103,'apricot','2.2'),
-> ('l2',104,'lemon','6.4'),
-> ('b2',104,'berry','7.6'),
-> ('m1',106,'mango','15.7'),
-> ('m2',105,'xbabay','2.6'),
-> ('t4',107,'xbababa','2.6'),
-> ('m3',105,'xxtt','11.6'),
-> ('b5',107,'xxxx','3.6');
#Create a second table
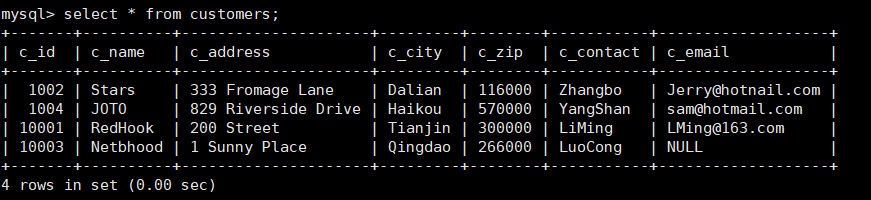
mysql> create table customers(
-> c_id int not null auto_increment,
-> c_name char(50) not null,
-> c_address char(50) null,
-> c_city char(50) null,
-> c_zip char(50) null,
-> c_contact char(50) null,
-> c_email char(50) null,
-> primary key(c_id)
-> );
#Second table inserts data
mysql> insert into customers(c_id,c_name,c_address,c_city,c_zip,c_contact,c_email)
-> values(10001,'RedHook','200 Street','Tianjin','300000','LiMing','LMing@163.com'),
-> (1002,'Stars','333 Fromage Lane','Dalian','116000','Zhangbo','Jerry@hotnail.com'),
-> (10003,'Netbhood','1 Sunny Place','Qingdao','266000','LuoCong',NULL),
-> (1004,'JOTO','829 Riverside Drive','Haikou','570000','YangShan','sam@hotmail.com');2. View all data for both tables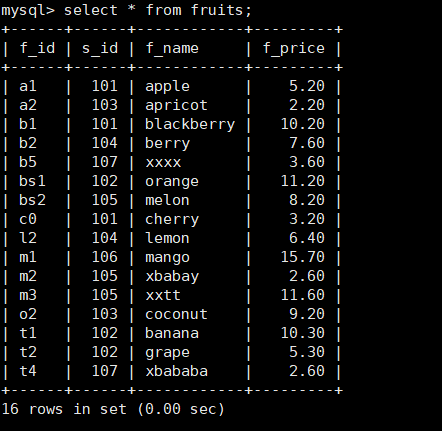
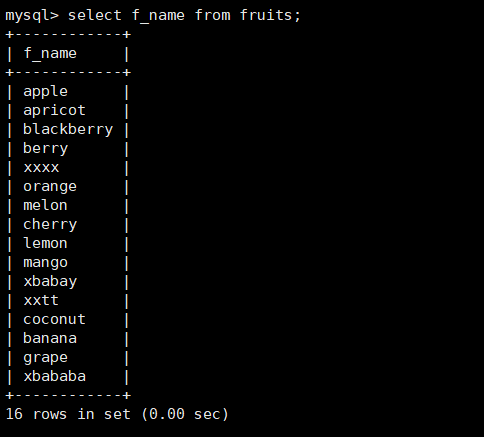
3. Query data for f_name column in fruits table
mysql> select f_name from fruits;
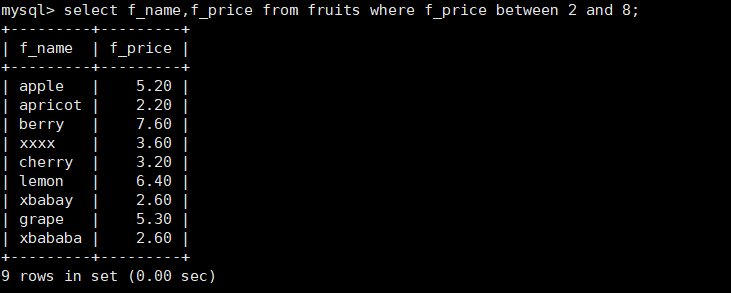
4. Query fruits table for data in columns f_name and f_price
mysql> select f_name,f_price from fruits;
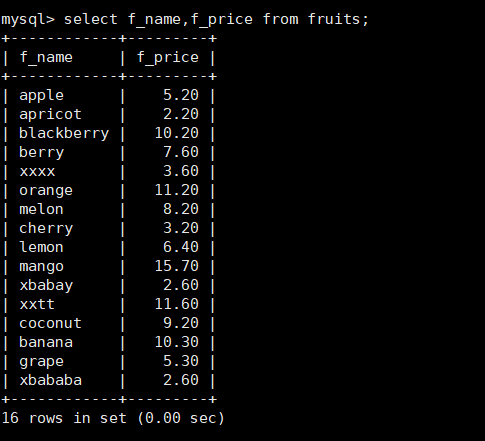
5. Query the columns of f_name and f_price in the fruits table, and the value of f_price is equal to 5.2
mysql> select f_name,f_price from fruits where f_price=5.2;
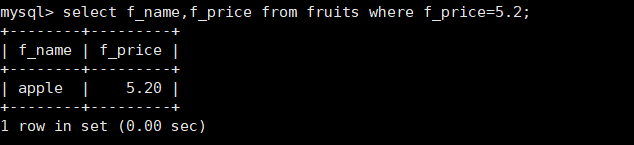
6. Query the columns of f_name and f_price in the fruits table, and the value of f_price is greater than or equal to 10
mysql> select f_name,f_price from fruits where f_price >= 10;
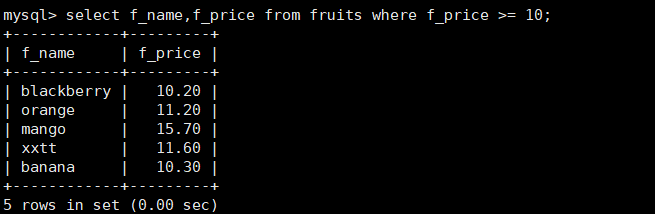
7. Query the columns of f_name and f_price in the fruits table, and the value of f_price is between 2 and 8
mysql> select f_name,f_price from fruits where f_price between 2 and 8;
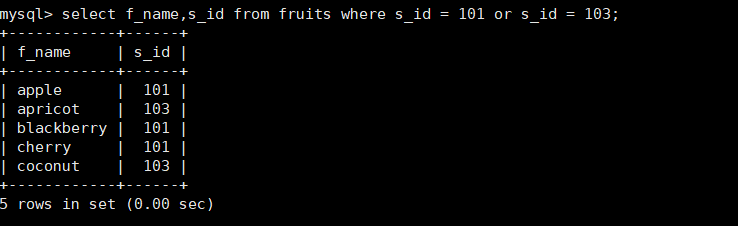
8. Query the f_name and s_id columns in the fruits table, and the value of s_id is 101 or 103
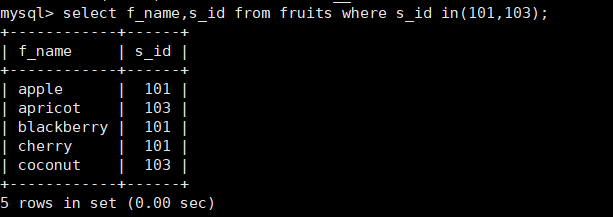
Different methods, the results are the same
Query method one:
mysql> select f_name,s_id from fruits where s_id = 101 or s_id = 103;
Query method two:
mysql> select f_name,s_id from fruits where s_id in(101,103);
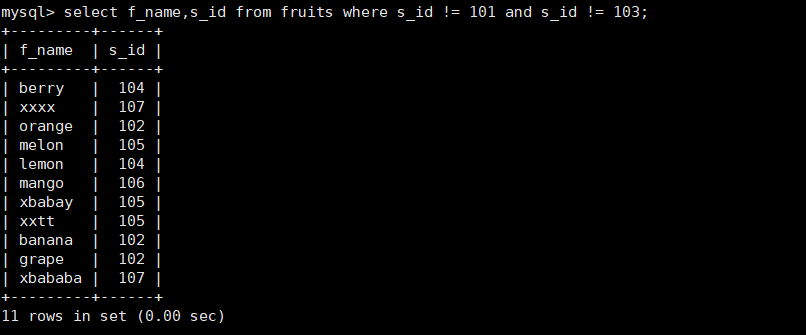
9. Query the f_name and s_id columns in the fruits table, and the value of s_id is not 101 or 103
Query Method One
mysql> select f_name,s_id from fruits where s_id != 101 and s_id != 103;
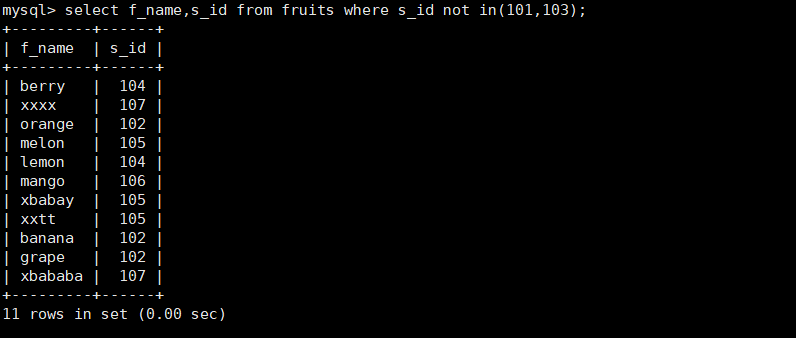
Query Method Two
mysql> select f_name,s_id from fruits where s_id not in(101,103);
10. Use of Fuzzy Query'%'and''
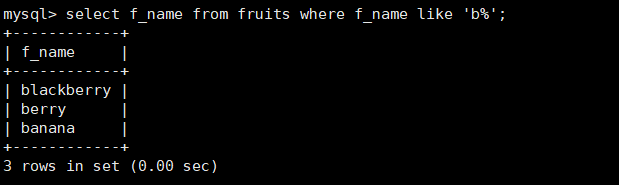
#Query the f_name column in the fruits table, and the value starts with "b" mysql> select f_name from fruits where f_name like 'b%';
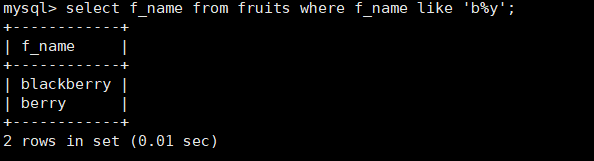
#Query the f_name column in the fruits table, and the value starts with "b" and ends with "y" mysql> select f_name from fruits where f_name like 'b%y';
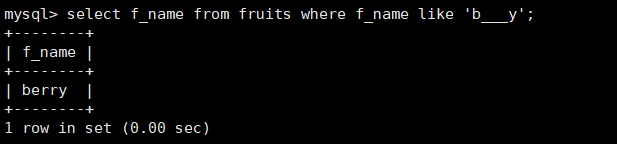
#Query the f_name column in the fruits table, starting with "b" and ending with "y", with three characters between B and Y mysql> select f_name from fruits where f_name like 'b___y';
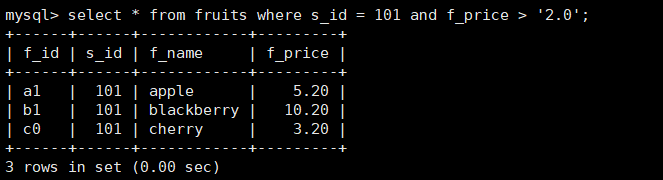
11. Query fruits table for rows with s_id value 101 and f_price value greater than 2.0
mysql> select * from fruits where s_id = 101 and f_price > '2.0';
12. Query fruits table for s_id values of 101 or 103 and f_price column values greater than 5
mysql> select * from fruits where s_id in(101,103) and f_price > 5;
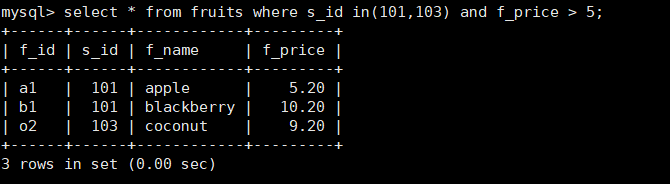
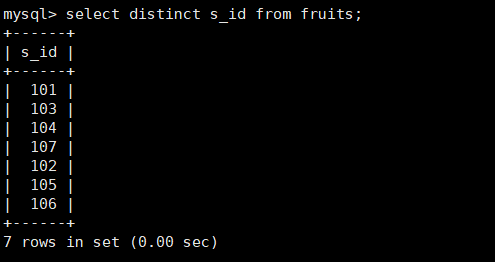
13. Query the s_id column in the fruits table and remove duplicate values
mysql> select distinct s_id from fruits;
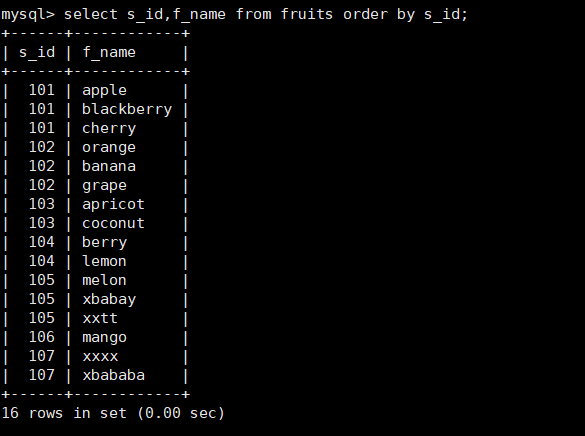
14. Query the s_id and f_name columns in the fruits table and sort the results by s_id
mysql> select s_id,f_name from fruits order by s_id;
15. Query the f_name and f_price columns in the fruits table and sort them by the f_name and f_price columns
mysql> select f_name,f_price from fruits order by f_name,f_price;
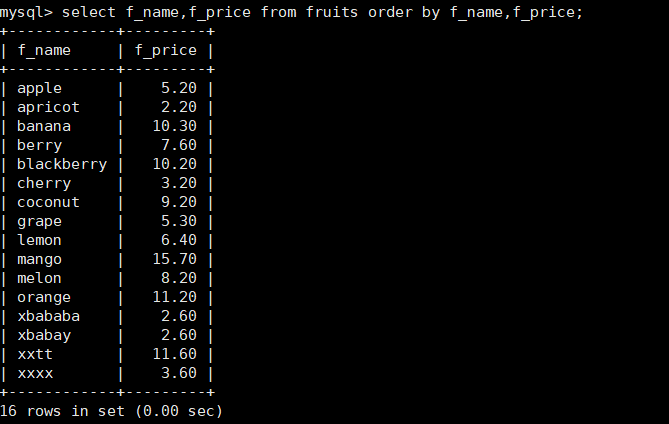
Note: Multi-field sorting, if the first sorted field is the same, will depend on the second field sorting, and so on. If the first field is different, it will be sorted directly by the first paragraph.
16. Query the f_price column in the fruits table and sort the results in descending order
#The default is asc ending sort, which can be changed to descending by the keyword DESC mysql> select f_price from fruits order by f_price desc;
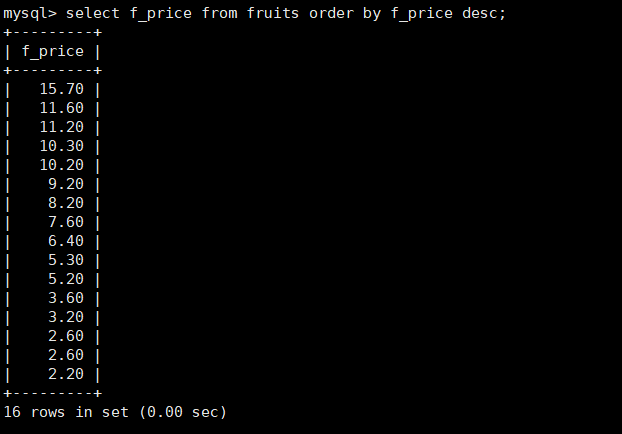
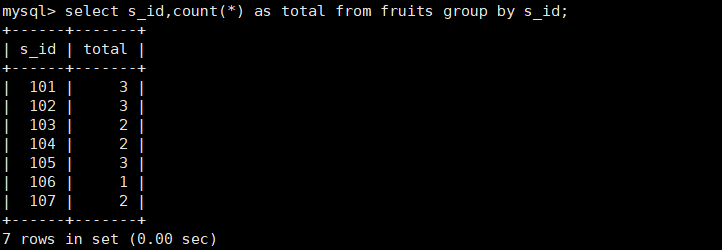
17. Query the number of occurrences of different values of s_id column in fruits and display them in groups
#The count(*) function is called to count the number of times, aliased by as, and grouped by group by mysql> select s_id,count(*) as total from fruits group by s_id;
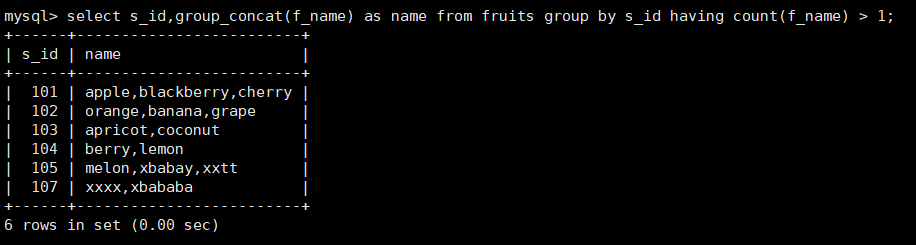
18. Query all values of the f_name column corresponding to each of the same s_id s in the fruits table. The value of f_name is displayed in one row and has a value of more than one
mysql> select s_id,group_concat(f_name) as name from fruits group by s_id having count(f_name) > 1;
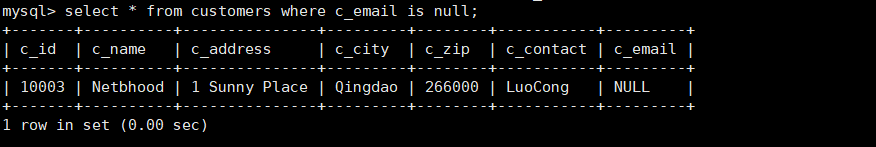
19. Query for rows with null values in the c_email column of the customers table
mysql> select * from customers where c_email is null;