Eureka can maintain the status of various Spring boot microservices. The microservice end is registered with Eureka service end. Service consumers can obtain various service addresses from Eureka. There are not many specific details. There are already many online addresses.
In order to register and discover Eureka's services, we need to prepare to launch two Spring boot projects
Eureka server building
pom.xml
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.cloud</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-cloud-starter-config</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.cloud</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-cloud-starter-netflix-eureka-server</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-test</artifactId>
<scope>test</scope>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
<dependencyManagement>
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.cloud</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-cloud-dependencies</artifactId>
<version>${spring-cloud.version}</version>
<type>pom</type>
<scope>import</scope>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
</dependencyManagement>application.yml
server:
port: 8761
eureka:
instance:
hostname: localhost
client:
registerWithEureka: false #The server does not actively register and discover
fetchRegistry: false
serviceUrl:
defaultZone: http://${eureka.instance.hostname}:${server.port}/eureka/The startup class adds the annotation @ EnableEurekaServer, indicating that it is the Eureka server
package com.example.eurka.eurkaserver;
import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication;
import org.springframework.cloud.netflix.eureka.server.EnableEurekaServer;
@EnableEurekaServer
@SpringBootApplication
public class EurkaServerApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(EurkaServerApplication.class, args);
}
}
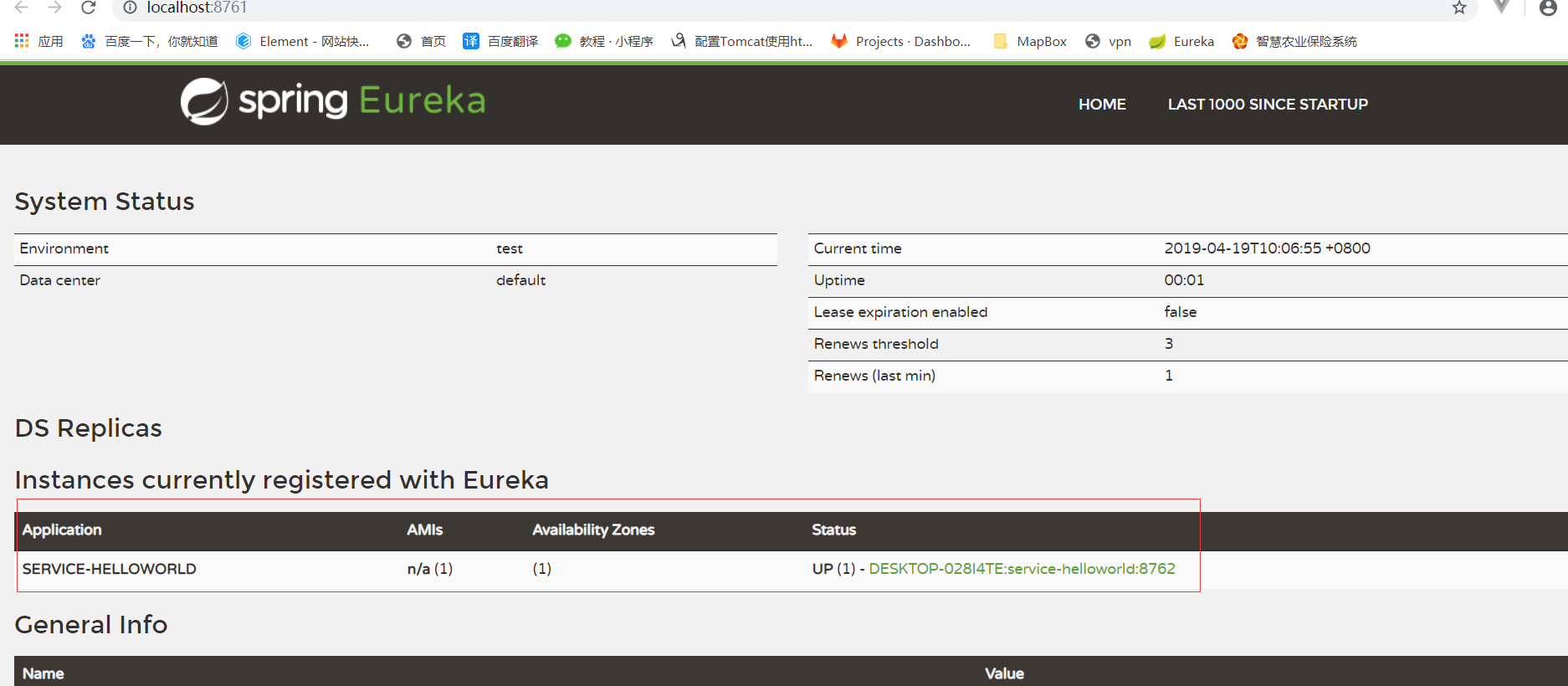
Visit http://localhost:8761/ , you can see that the Eureka server has started

Eureka client building
pom.xml
<dependencies>
<!--No addition web Will close-->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.cloud</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-cloud-starter-config</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.cloud</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-cloud-starter-netflix-eureka-client</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-test</artifactId>
<scope>test</scope>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
<build>
<plugins>
<plugin>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-maven-plugin</artifactId>
</plugin>
</plugins>
</build>
<dependencyManagement>
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.cloud</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-cloud-dependencies</artifactId>
<version>Finchley.RELEASE</version>
<type>pom</type>
<scope>import</scope>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
</dependencyManagement>application.properties
#eureka server address eureka.client.serviceUrl.defaultZone=http://localhost:8761/eureka/ server.port= 8762 #Service name spring.application.name= service-helloworld
Start class add client annotation @ EnableEurekaClient
package com.example.eurekaclient;
import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication;
import org.springframework.cloud.netflix.eureka.EnableEurekaClient;
@EnableEurekaClient
@SpringBootApplication
public class EurekaClientApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(EurekaClientApplication.class, args);
}
}
Create a new Controller
package com.example.eurekaclient.controller;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Value;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.GetMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
@RestController
public class TestController {
@Value("${server.port}")
String serverPort;
@GetMapping("/test")
public String test() {
return "The port number of the calling service is:" + serverPort;
}
}
After startup, open http://localhost:8761/ , you can see the configuration name and port number of the client