The last one is mainly about opening http basic authentication. From a security point of view, based on base64 encoding, it is easy to be cracked after being caught, and it is very unsafe in the public network. This article discusses how to open https in eureka server and eureka client.
Public Dependent pom Files
<parent>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-parent</artifactId>
<version>2.0.3.RELEASE</version>
<relativePath/>
</parent>
<properties>
<project.build.sourceEncoding>UTF-8</project.build.sourceEncoding>
<project.reporting.outputEncoding>UTF-8</project.reporting.outputEncoding>
<java.version>1.8</java.version>
<spring-cloud.version>Finchley.RELEASE</spring-cloud.version>
</properties>
<dependencyManagement>
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.cloud</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-cloud-dependencies</artifactId>
<version>${spring-cloud.version}</version>
<type>pom</type>
<scope>import</scope>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
</dependencyManagement>
1. Ereka server project
1.1. Ereka server project pom:
<!--Plus the public dependence on the header of the article-->
<dependencies> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.cloud</groupId> <artifactId>spring-cloud-starter-netflix-eureka-server</artifactId> </dependency> </dependencies> <build> <plugins> <plugin> <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-maven-plugin</artifactId> </plugin> </plugins> </build>
1.2. Ereka server project startup class:
import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication; import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication; import org.springframework.cloud.netflix.eureka.server.EnableEurekaServer; @SpringBootApplication @EnableEurekaServer public class EurekaServerApplication { public static void main(String[] args) { SpringApplication.run(EurekaServerApplication.class, args); } }
1.3. Generating Certificates
a. Generate the certificate of server project and execute the following instructions using command line tools:
keytool -genkeypair -alias server -storetype PKCS12 -keyalg RSA -keysize 2048 -keystore server.p12 -validity 3650 Enter the keystore password: Enter a new password again: What is your name and last name? [Unknown]: spring What is the name of your organization? [Unknown]: spring What is the name of your organization? [Unknown]: spring What is the name of your city or district? [Unknown]: spring What is the name of your province / city / autonomous region? [Unknown]: spring What is the double letter country / territory code of this unit? [Unknown]: spring Is CN=spring, OU=spring, O=spring, L=spring, ST=spring, C=spring correct? [no]: y
b. Generate client Engineering Certificate in the same way and execute the following instructions:
keytool -genkeypair -alias client -storetype PKCS12 -keyalg RSA -keysize 2048 -keystore client.p12 -validity 3650
//. You also need to set a password to answer the questions above.
c. Export two p12 certificates and execute instructions:
keytool -export -alias server -file server.crt --keystore server.p12 Enter the keystore password: The password here is the password set when the server certificate is generated Certificates stored in file <server.crt>.
keytool -export -alias client -file client.crt --keystore client.p12 Enter the keystore password: The password here is the password set when the client certificate is generated Certificates stored in file <client.crt>.
d. Import the server.crt file into the client.p12 certificate, so that the client side trusts the server's certificate, and execute the following instructions
keytool -import -alias server -file server.crt -keystore client.p12 Enter the keystore password: The password here is to generate the client certificate password. The password error will prompt the following information: [Message prompted when password error: keytool error: java.io.IOException: keystore password was incorrect]
Owner: CN=spring, OU=spring, O=spring, L=spring, ST=spring, C=spring Publisher: CN=spring, OU=spring, O=spring, L=spring, ST=spring, C=spring Serial number: 2b87a269 The validity period is Fri Oct 04 20:11:07 CST 2019 to Mon Oct 01 20:11:07 CST 2029. Certificate Fingerprint: MD5: EF:A3:6B:32:DE:8F:E4:34:46:E6:0D:48:B9:8F:B8:7E SHA1: AE:42:78:14:D8:6B:B2:E9:46:F4:76:E8:D9:D0:51:E0:3A:E6:C9:2E SHA256: 54:6D:93:7E:B3:D3:C4:49:87:84:9D:46:66:B1:B8:1B:95:5B:DC:05:9A:8A:A4:DF:43:E4:A7:A7:4A:81:F7:B0 Signature algorithm name: SHA256withRSA Principal Public Key Algorithms: 2048-bit RSA Key Version: 3 Extension: #1: ObjectId: 2.5.29.14 Criticality=false SubjectKeyIdentifier [ KeyIdentifier [ 0000: 6C 1A E4 01 EB 84 0B C2 90 97 81 3D DB 0D C3 F1 l..........=.... 0010: 4A FB 2A F4 J.*. ] ] Do you trust this certificate? [No]:y Certificates have been added to the keystore
e. Import client.crt file into server.p12 file to make server service trust client's certificate. Execute the following instructions:
keytool -import -alias client -file client.crt -keystore server.p12
Enter the keystore password: The password here is to generate the server certificate password
Owner: CN=cloud, OU=cloud, O=cloud, L=cloud, ST=cloud, C=cloud
Publisher: CN=cloud, OU=cloud, O=cloud, L=cloud, ST=cloud, C=cloud
Sequence number: 6ea2a01
The validity period is Fri Oct 04 20:27:38 CST 2019 to Mon Oct 01 20:27:38 CST 2029.
Certificate Fingerprint:
MD5: E9:22:2C:8D:C4:08:27:AD:02:75:93:31:C2:17:35:8E
SHA1: BB:B0:9A:3A:98:43:5E:02:FC:8A:BC:85:33:DD:82:4A:4E:DF:3A:5C
SHA256: 20:96:61:27:D1:CA:55:E5:B6:0E:41:CA:BC:84:F8:8F:1F:D8:25:87:10:50:90:E3:BC:12:39:35:74:16:4A:B3
Signature algorithm name: SHA256withRSA
Principal Public Key Algorithms: 2048-bit RSA Key
Version: 3
Extension:
#1: ObjectId: 2.5.29.14 Criticality=false
SubjectKeyIdentifier [
KeyIdentifier [
0000: 91 E6 46 EF 4C 9E 88 B1 2F 63 12 4B 39 53 9D 32 ..F.L.../c.K9S.2
0010: EF 0F 42 F9 ..B.
]
]
Do you trust this certificate? [No]:y
Certificates have been added to the keystore
1.4. Place the generated server.p12, server.crt and client.crt files in the resources directory of the eureka server project.
1.5. Add Ereka server project-related resources configuration file
application-https.yml:
server: port: 8766 ssl: enabled: true key-store: classpath:server.p12 key-store-password: hello2019 #Password set when generating server certificate key-store-type: PKCS12 key-alias: server eureka: instance: hostname: localhost securePort: ${server.port} securePortEnabled: true nonSecurePortEnabled: false homePageUrl: https://${eureka.instance.hostname}:${server.port}/ statusPageUrl: https://${eureka.instance.hostname}:${server.port}/ client: registerWithEureka: false fetchRegistry: false serviceUrl: defaultZone: https://${eureka.instance.hostname}:${server.port}/eureka/ server: waitTimeInMsWhenSyncEmpty: 0 enableSelfPreservation: false
application.yml:
spring:
profiles:
active: https
1.6. Start the eureka server project and execute the instructions:
mvn spring-boot:run -Dspring.profiles.active=https
Access: https://localhost:8766
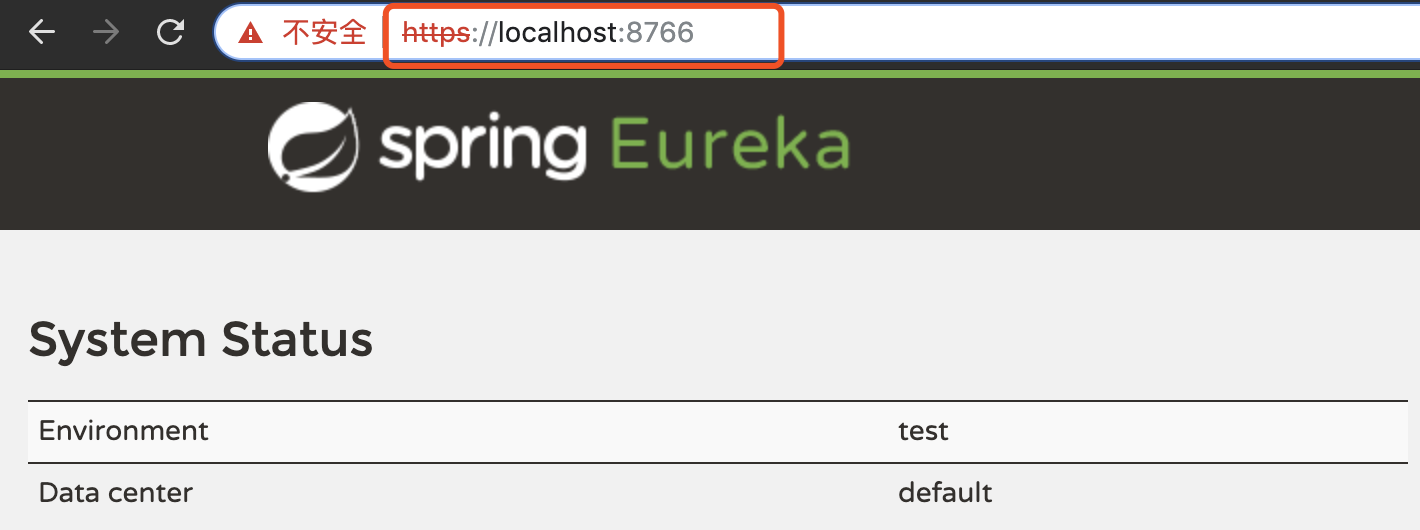
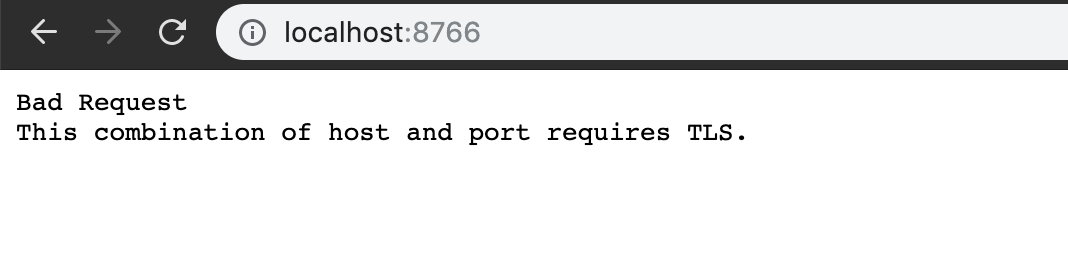
As you can see, https is actually used, so try visiting: http://localhost:8766
2. Ereka Client Project
2.1. client project pom file:
<!--Plus the public dependence on the header of the article-->
<dependencies> <dependency> <groupId>org.apache.httpcomponents</groupId> <artifactId>httpclient</artifactId> <version>4.5.5</version> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.cloud</groupId> <artifactId>spring-cloud-starter-netflix-eureka-client</artifactId> </dependency> </dependencies> <build> <plugins> <plugin> <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-maven-plugin</artifactId> </plugin> </plugins> </build>
2.2. client Project Startup Class:
import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication; import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication; import org.springframework.cloud.netflix.eureka.EnableEurekaClient; @SpringBootApplication @EnableEurekaClient public class EurekaClientApplication { public static void main(String[] args) { SpringApplication.run(EurekaClientApplication.class, args); } }
2.2. client Engineering resources Configuration File
First, the client.crt, client.p12 and server.crt files are placed in the resources directory of the client project.
application.yml:
spring:
profiles:
active: https
application-https.yml:
server: port: 8081 spring: application: name: client1 eureka: client: securePortEnabled: true ssl: key-store: client.p12 key-store-password: hello2020 serviceUrl: defaultZone: https://localhost:8766/eureka/
There is no https enabled for the entire application instance, just the https configuration for accessing eureka server, the two properties of eureka.client.ssl.key-store and eureka.client.ssl.key-store-password are customized, and the sslContext configuration for client accessing server is specified. DiscoveryClient. DiscoveryClient Optional Args need to be specified in the code:
import com.netflix.discovery.DiscoveryClient; import com.netflix.discovery.shared.transport.jersey.EurekaJerseyClientImpl; import org.apache.http.ssl.SSLContextBuilder; import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Value; import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean; import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration; import org.springframework.context.annotation.Profile; import javax.net.ssl.SSLContext; import java.io.IOException; import java.security.KeyManagementException; import java.security.KeyStoreException; import java.security.NoSuchAlgorithmException; import java.security.cert.CertificateException; /** * Specify sslContext configuration for client access server */ @Profile({"https"}) @Configuration public class EurekaHttpsClientConfig { @Value("${eureka.client.ssl.key-store}") String keyStoreFileName; @Value("${eureka.client.ssl.key-store-password}") String keyStorePassword; @Bean public DiscoveryClient.DiscoveryClientOptionalArgs discoveryClientOptionalArgs() throws CertificateException, NoSuchAlgorithmException, KeyStoreException, IOException, KeyManagementException { EurekaJerseyClientImpl.EurekaJerseyClientBuilder builder = new EurekaJerseyClientImpl.EurekaJerseyClientBuilder(); builder.withClientName("eureka-https-client"); SSLContext sslContext = new SSLContextBuilder() .loadTrustMaterial( this.getClass().getClassLoader().getResource(keyStoreFileName),keyStorePassword.toCharArray() ) .build(); builder.withCustomSSL(sslContext); builder.withMaxTotalConnections(10); builder.withMaxConnectionsPerHost(10); DiscoveryClient.DiscoveryClientOptionalArgs args = new DiscoveryClient.DiscoveryClientOptionalArgs(); args.setEurekaJerseyClient(builder.build()); return args; } }
2.3. Execute instructions to start client project:
mvn spring-boot:run -Dspring.profiles.active=https
Visit https://localhost:8766/

You can see that the client project has been successfully registered with the server service.