Encapsulate MyBatis Output results
resultType
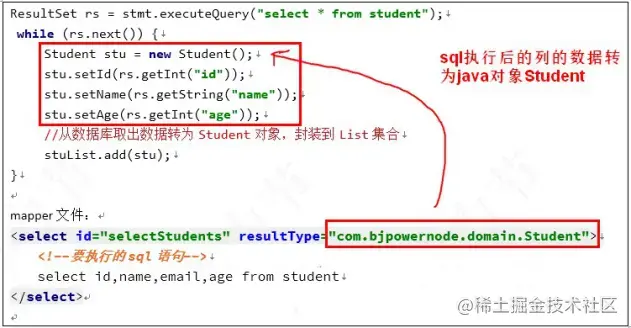
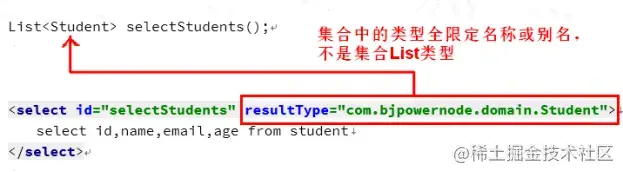
Resulttype: execute sql to get the type of ResultSet conversion, using the fully qualified name or alias of the type. Note that if a collection is returned, it should be set to the type contained in the collection, not the collection itself. resultType And resu ltMap cannot be used at the same time.
A. Simple type
Interface method:
int countStudent(); mapper File: < select id="countStudent" resultType="int"> select count(*) from student < /select> Copy code
Test method:
@Test
public void testRetunInt(){
int count = studentDao.countStudent();
System.out.println("Total number of students:"+ count);
}
Copy codeB. Object type
Interface method:
Student selectById(int id);
mapper file:
<select id="selectById"
resultType="com.bjpowernode.domain.Student"> select
id,name,email,age from student where id=#{studentId}
</select>
Copy codeFrame processing: create objects using construction methods. Call setXXX to assign a value to the property.
Student student = new Student();

Note: the Dao interface method returns a collection type. You need to specify the type in the collection, not the collection itself.
C,Map
The query result of sql is used as the key and value of map. Map < object, Object > is recommended.
Note: Map is the return value of the interface, and the query result of sql statement can only have one record at most. Greater than one record is an error.
Interface method:
Map<Object,Object> selectReturnMap(int id);
mapper file:
<select id="selectReturnMap" resultType="java.util.HashMap">
select name,email from student where id = #{studentId}
</select>
Copy codeTest method:
@Test
public void testReturnMap(){
Map<Object,Object> retMap = studentDao.selectReturnMap(1002);
System.out.println("The query result is Map:"+retMap);
}
Copy coderesultMap
resultMap can customize the mapping relationship between sql results and java object attributes. More flexible assignment of column values to specified attributes.
It is often used when the column name is different from the java object attribute name.
Usage:
1. Define resultMap first and specify the corresponding relationship between column name and attribute.
2. Replace resultType with resultMap in < Select >.
Interface method:
List< Student> selectUseResultMap(QueryParam param);
mapper file:

Test method:

Entity class attribute names and column names are handled differently
(1) Use column aliases and < resulttype >
Steps:
one Create a new entity class PrimaryStudent

two Interface method
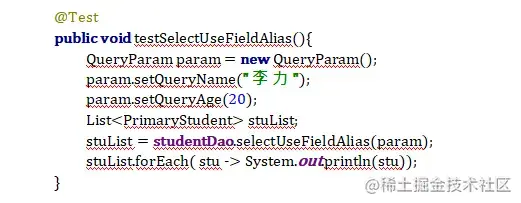
List< PrimaryStudent> selectUseFieldAlias(QueryParam param);
three mapper File:

four test method
(2) Use < resultmap >
Steps:
one Interface method
List<PrimaryStudent> selectUseDiffResultMap(QueryParam param);
two mapper File:

3. Test method

Fuzzy like
There are two ways to implement fuzzy query. One is to add "%" to the query data in java code; The second is in mapper File sql Add '%' to the conditional position of the statement
Demand: query names with "force"
Example 1: the "% force%" to be queried is provided in the Java code
Interface method:
List<Student> selectLikeFirst(String name);
mapper file:
<select id="selectLikeFirst"
resultType="com.bjpowernode.domain.Student"> select
id,name,email,age from student
where name like #{studentName}
</select>
Copy codeTest method:
@Test
public void
testSelectLikeOne(){ String
name="%power%";
List<Student> stuList = studentDao.selectLikeFirst(name);
stuList.forEach( stu -> System.out.println(stu));
}
Copy codeExample 2: use like name "%" #{xxx} "%" in mapper file
Interface method:
List<Student> selectLikeSecond(String name);
mapper file:
<select id="selectLikeSecond"
resultType="com.bjpowernode.domain.Student"> select id,name,email,age
from student
where name like "%" #{studentName} "%"
</select>
Copy codeTest method:
@Test
public void
testSelectLikeSecond(){ String
name="power";
List<Student> stuList = studentDao.selectLikeSecond(name);
stuList.forEach( stu -> System.out.println(stu));
}
Author: Ling Xiaoke
Link: https://juejin.cn/post/7021350272463011870