Article directory
Preface
It is too cumbersome (or lazy) to transplant mysql in the development board, so we need to migrate the required libraries to the development board for C language programs.
Final effect: connect the Exynos4412 development board to Alibaba cloud database
1, libmysql source download
1. Download on official website
Click to download
2. Baidu online disk
Let me know if the link fails
Link: https://pan.baidu.com/s/1AlOxQozi4TmDvlG6cxD5yA Extraction code: j052
2, Unzip and configure
1. Copy it to ubuntu, unzip it, and view the files in the directory
2. Install cmake
The cmake tool is used for configuration, so it needs to be installed
sudo apt-get install cmake
3. Configure CMakeLists.txt
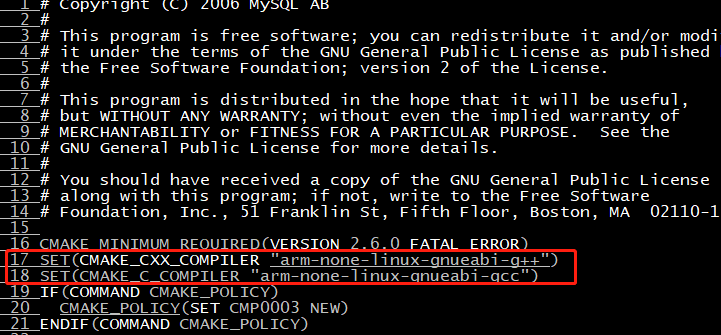
Join at the beginning (top)
Change the cross compilation tool to its own path
SET(CMAKE_CXX_COMPILER "arm-none-linux-gnueabi-g++") SET(CMAKE_C_COMPILER "arm-none-linux-gnueabi-gcc")
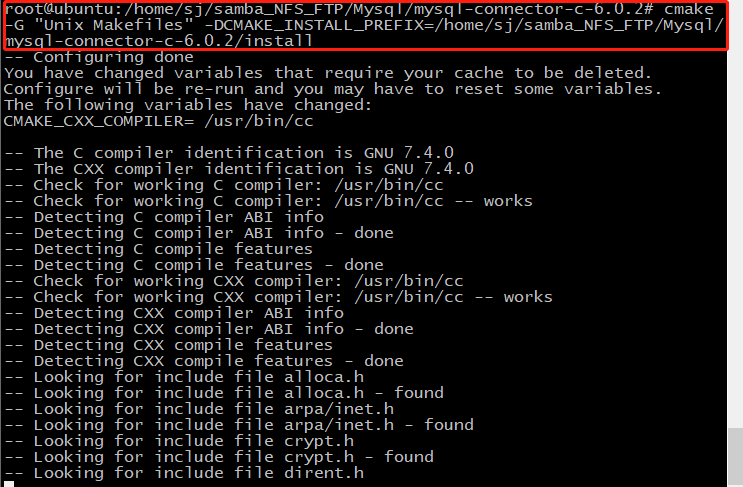
4. Configure with Cmake
Cmake - G "UNIX makefiles" - dcmake "Install" prefix = install path
3, Build install
1. make directly
* * mistakes 1 * *
error: static declaration of 'rint' follows non-static declaration
Solution: just comment out the rint function in include / my "global. H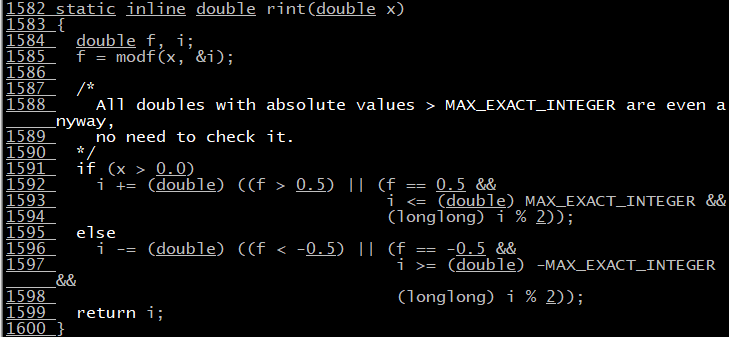
Error 2
Undefined when compiling to 95%
erro:undefined reference floor
Solution: add an environment variable to the Makefile, and link these functions together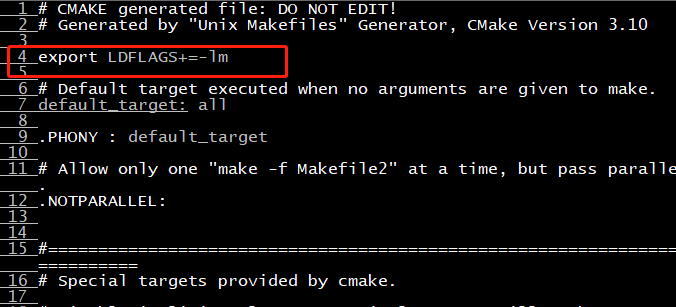
To solve the above two problems, you need to re use cmake for configuration, and then make to compile successfully.
Problem solving reference blog: Click to enter (it's been bothered for a long time. You can see the analysis of the great God.)
2, installation
2.1. make install. I found that it was not installed according to the previous installation path (even installed in my mysql)
Finally, find a file cmake? Install.cmake to configure the installation path
It is found that / usr/local/mysql is the default configuration path (it is clear that cmake "Install" prefix has been defined). Finally, change the default path to the path you want and make install again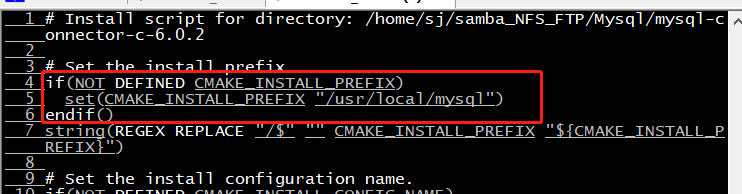
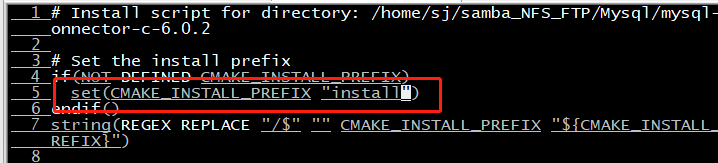
2.2. Copy the files in include and lib under the installation directory to the folder corresponding to the cross compiler, and you can compile happily (the files in lib should also be copied to Lib in the file system of the development board, and the corresponding library can only be found when the program is running in the development board)
4, Program testing
1. A simple database connection program is written to output the data in the test table in the test database.
#include <stdio.h> #include <stdlib.h> #include <string.h> #include <time.h> #include "mysql.h" #define MAX_BUF_SIZE 1024 //Maximum number of bytes in buffer MYSQL *g_conn;//mysql links MYSQL_RES *g_res;//mysql Recordset MYSQL_ROW g_row;//String array, mysql record line /* host name password db_name port */ const char *g_host_name = "";//Host address const char *g_user_name = "root";//Database user name const char *g_password = "";//Password const char *g_db_name = "test";//database name of the connection const unsigned int g_db_port = 3306; /* Buffer for commands */ char sql[MAX_BUF_SIZE]; char Time[MAX_BUF_SIZE]; int iNum_rows = 0;//Initial value of the number of rows returned from the execution result of mysql statement int flag = 0;//Administrator authority switch int i = 1;//System operation switch /* Print error function */ void print_mysql_error(const char *msg) { if(msg) printf("%s: %s\n",msg,mysql_error(g_conn)); else puts(mysql_error(g_conn)); } /* Execute MySql statement function */ int executesql(const char * sql) { if(mysql_real_query(g_conn,sql,strlen(sql))) return -1; return 0; } /* Initialize database connection */ int init_mysql(const char *g_host_name,const char *g_user_name,const char *g_password,const char *g_db_name,const unsigned int g_db_port) { //Initializing G g_conn = mysql_init(NULL); //connection the database if(!mysql_real_connect(g_conn,g_host_name,g_user_name,g_password,g_db_name,g_db_port,NULL,0)) return -1;//link failure return 0; //Return to success } int connect_db(const char *g_host_name,const char *g_user_name,const char *g_password,const char *g_db_name,const unsigned int g_db_port) { if(init_mysql(g_host_name,g_user_name,g_password,g_db_name,g_db_port)) { print_mysql_error(NULL);//Errors will be reported when linking to the database return -1; } else { printf("Connect OK!\n"); return 0; } } int main() { int iNum_rows,iNum_fields,res; res = connect_db(g_host_name, g_user_name, g_password, g_db_name, g_db_port); if(res!=0) { printf("Can not connect!\n"); return -1; } if(executesql("select * from test")) print_mysql_error(NULL); g_res = mysql_store_result(g_conn); // Transfer the result set from the server to the local. MySQL use result directly uses the record set on the server iNum_rows = mysql_num_rows(g_res); // Get the number of rows of records iNum_fields = mysql_num_fields(g_res); // Get the number of columns recorded while ((g_row=mysql_fetch_row(g_res))) // Print result set printf("%s\n",g_row[0]); mysql_free_result(g_res); // Release result set mysql_close(g_conn); return 0; }
2. Configure mysql on the server side (you need to configure to allow remote connection)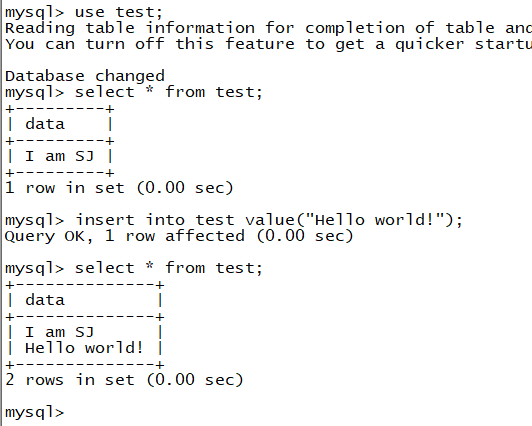
3. Compile
The parameter - lmysqlclient needs to be added when compiling
4. Running compiled executable files on the development board
Show that the connection is successful and read out the data in the test table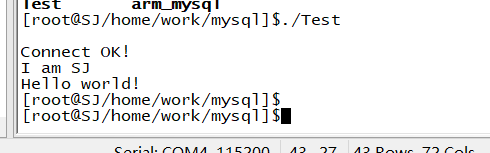
At this point, you can exchange data with remote database on the development board

