In previous articles“ Elasticsearch: use Spring Boot to create REST APIs to access elasticsearch ”, I described in detail how to use it in Spring Boot applications Elasticsearch rest high level client library to connect with elasticsearch. In today's article, I'll use another library spring-boot-starter-data-elasticsearch To connect to elasticsearch. This method is very simple and direct.
For your convenience, I put the final code into github GitHub - liu-xiao-guo/SpringBootElasticsearch-demo . You can get it in the following ways:
git clone https://github.com/liu-xiao-guo/SpringBootElasticsearch-demo
Code interpretation
pom.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0 https://maven.apache.org/xsd/maven-4.0.0.xsd">
<modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion>
<parent>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-parent</artifactId>
<version>2.5.5</version>
<relativePath/> <!-- lookup parent from repository -->
</parent>
<groupId>com.liuxg</groupId>
<artifactId>SpringBootElasticsearch-demo</artifactId>
<version>0.0.1-SNAPSHOT</version>
<name>SpringBootElasticsearch-demo</name>
<description>SpringBootElasticsearch-demo</description>
<properties>
<java.version>1.8</java.version>
<elastic.version>7.15.0</elastic.version>
</properties>
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-thymeleaf</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-devtools</artifactId>
<scope>runtime</scope>
<optional>true</optional>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.projectlombok</groupId>
<artifactId>lombok</artifactId>
<optional>true</optional>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-test</artifactId>
<scope>test</scope>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-configuration-processor</artifactId>
<optional>true</optional>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-data-elasticsearch</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.elasticsearch.client</groupId>
<artifactId>elasticsearch-rest-high-level-client</artifactId>
<version>${elastic.version}</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.elasticsearch.client</groupId>
<artifactId>elasticsearch-rest-client</artifactId>
<version>${elastic.version}</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.elasticsearch</groupId>
<artifactId>elasticsearch</artifactId>
<version>${elastic.version}</version><!--$NO-MVN-MAN-VER$-->
</dependency>
</dependencies>
<build>
<plugins>
<plugin>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-maven-plugin</artifactId>
<configuration>
<excludes>
<exclude>
<groupId>org.projectlombok</groupId>
<artifactId>lombok</artifactId>
</exclude>
</excludes>
</configuration>
</plugin>
</plugins>
</build>
</project>Above, please note that we need dependency spring-boot-starter-data-elasticsearch. In my Elasticsearch cluster, I started Basic security authentication. The password of superuser elastic is set to password. In the application, we have passed RestHighLevelClient for authentication, so I also Elastic search rest high level client is introduced.
configuration file
Because the default port address 8080 conflicts with the port of my computer, I use port 9999. In addition, we can also configure the address and port of Elasticsearch. At the same time, we also define the password of super user elastic:
application.properties
server.port = 9999 elasticsearch.url=localhost:9200 elasticsearch.username=elastic elasticsearch.password=password
document
Employee.java
package com.liuxg.springbootelasticsearchdemo.document;
import org.springframework.data.annotation.Id;
import org.springframework.data.elasticsearch.annotations.Document;
import org.springframework.data.elasticsearch.annotations.Field;
import org.springframework.data.elasticsearch.annotations.FieldType;
@Document(indexName = "employees", shards = 1, replicas = 0, refreshInterval = "5s")
public class Employee {
@Id
@Field(type = FieldType.Keyword)
private String id;
@Field(type = FieldType.Text)
private String name;
public String getId() {
return id;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setId(String id) {
this.id = id;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
}Above, we defined the name of the index employees. It contains two fields id and name. Their attributes are keyword and text respectively. When we run the Spring Boot application, it will automatically help us produce the employees index in Elasticsearch.
Repository
EmployeeRepository.java
import com.liuxg.springbootelasticsearchdemo.document.Employee;
import org.springframework.data.elasticsearch.annotations.Query;
import org.springframework.data.elasticsearch.repository.ElasticsearchRepository;
import java.util.List;
public interface EmployeeRepository extends ElasticsearchRepository<Employee, String> {
List<Employee> findAllByName(String name);
@Query("{\"match\":{\"name\":\"?0\"}}")
List<Employee> findAllByNameUsingAnnotations(String name);
}Here, we decide how to access Elasticsearch. Elastic search repository contains many designed methods for us to use.
Service
EmployeeService.java
package com.liuxg.springbootelasticsearchdemo.service;
import com.liuxg.springbootelasticsearchdemo.document.Employee;
import com.liuxg.springbootelasticsearchdemo.repository.EmployeeRepository;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;
import java.util.List;
@Service
public class EmployeeService {
private final EmployeeRepository repository;
@Autowired
public EmployeeService(EmployeeRepository repository) {
this.repository = repository;
}
public void save(final Employee employee) { repository.save(employee); }
public Employee findById(final String id) { return repository.findById(id).orElse(null); }
public List<Employee> findByName(final String name) { return repository.findAllByName(name);}
public List<Employee> getEmployeesByNameUsingAnnotation(String name) {
return repository.findAllByNameUsingAnnotations(name);
}
public void deleteEmployee(String id) {
repository.deleteById(id);
}
}Controller
EmployeeController.java
package com.liuxg.springbootelasticsearchdemo.controller;
import com.liuxg.springbootelasticsearchdemo.document.Employee;
import com.liuxg.springbootelasticsearchdemo.service.EmployeeService;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.*;
import java.util.List;
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/api/employee")
public class EmployeeController {
private final EmployeeService service;
@Autowired
public EmployeeController(EmployeeService service) {
this.service = service;
}
@PostMapping
public void save(@RequestBody final Employee employee) {
service.save(employee);
}
@GetMapping("/{id}")
public Employee findById(@PathVariable final String id) {
return service.findById(id);
}
@DeleteMapping("/{id}")
public boolean deleteById(@PathVariable String id) {
service.deleteEmployee(id);
return true;
}
@GetMapping("/name/{name}")
public List<Employee> findAllByName(@PathVariable String name) {
return service.findByName(name);
}
@GetMapping("/name/{name}/annotations")
public List<Employee> findAllByNameAnnotations(@PathVariable String name) {
return service.getEmployeesByNameUsingAnnotation(name);
}
}Some REST interfaces are defined here to facilitate our access to Elasticsearch.
Configuration
Config.java
package com.liuxg.springbootelasticsearchdemo.configuration;
import lombok.RequiredArgsConstructor;
import org.elasticsearch.client.RestHighLevelClient;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Value;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.ComponentScan;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import org.springframework.data.elasticsearch.client.ClientConfiguration;
import org.springframework.data.elasticsearch.client.RestClients;
import org.springframework.data.elasticsearch.config.AbstractElasticsearchConfiguration;
import org.springframework.data.elasticsearch.repository.config.EnableElasticsearchRepositories;
@Configuration
@EnableElasticsearchRepositories(basePackages = "com.liuxg.springbootelasticsearchdemo.repository")
@ComponentScan(basePackages = {"com.liuxg.springbootelasticsearchdemo"})
@RequiredArgsConstructor
public class Config extends AbstractElasticsearchConfiguration {
@Value("${elasticsearch.url}")
public String elasticsearchUrl;
@Value("${elasticsearch.username}")
public String elasticsearchUsername;
@Value("${elasticsearch.password}")
public String elasticsearchPassword;
@Override
@Bean
public RestHighLevelClient elasticsearchClient() {
final ClientConfiguration clientConfiguration = ClientConfiguration.builder()
.connectedTo(elasticsearchUrl)
.withBasicAuth(elasticsearchUsername, elasticsearchPassword)
.build();
return RestClients.create(clientConfiguration).rest();
}
}Here, we use the configuration parameters in application.properties to establish a connection with Elasticsearch and return a RestHighLevelClient. Its use can be seen in my previous article“ Elasticsearch: use Spring Boot to create REST APIs to access elasticsearch ”. In this example, it is only used as authentication.
Spring Boot Application
SpringBootElasticsearchDemoApplication.java
package com.liuxg.springbootelasticsearchdemo;
import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication;
@SpringBootApplication
public class SpringBootElasticsearchDemoApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(SpringBootElasticsearchDemoApplication.class, args);
}
}The structure of the whole code is as follows:
$ tree
.
├── README.md
├── pom.xml
└── src
├── main
│ ├── java
│ │ └── com
│ │ └── liuxg
│ │ └── springbootelasticsearchdemo
│ │ ├── SpringBootElasticsearchDemoApplication.java
│ │ ├── configuration
│ │ │ └── Config.java
│ │ ├── controller
│ │ │ └── EmployeeController.java
│ │ ├── document
│ │ │ └── Employee.java
│ │ ├── repository
│ │ │ └── EmployeeRepository.java
│ │ └── service
│ │ └── EmployeeService.java
│ └── resources
│ ├── application.properties
│ ├── static
│ └── templates
└── test
└── java
└── com
└── liuxg
└── springbootelasticsearchdemo
└── SpringBootElasticsearchDemoApplicationTests.javaTest application
We compile the application and run it. In this test, I will use Postman as a test tool for REST interface.
View index created
After the reference is started, it will automatically help us create an index called employees. We can enter the following address in the browser:
http://localhost:9200/_cat/indices
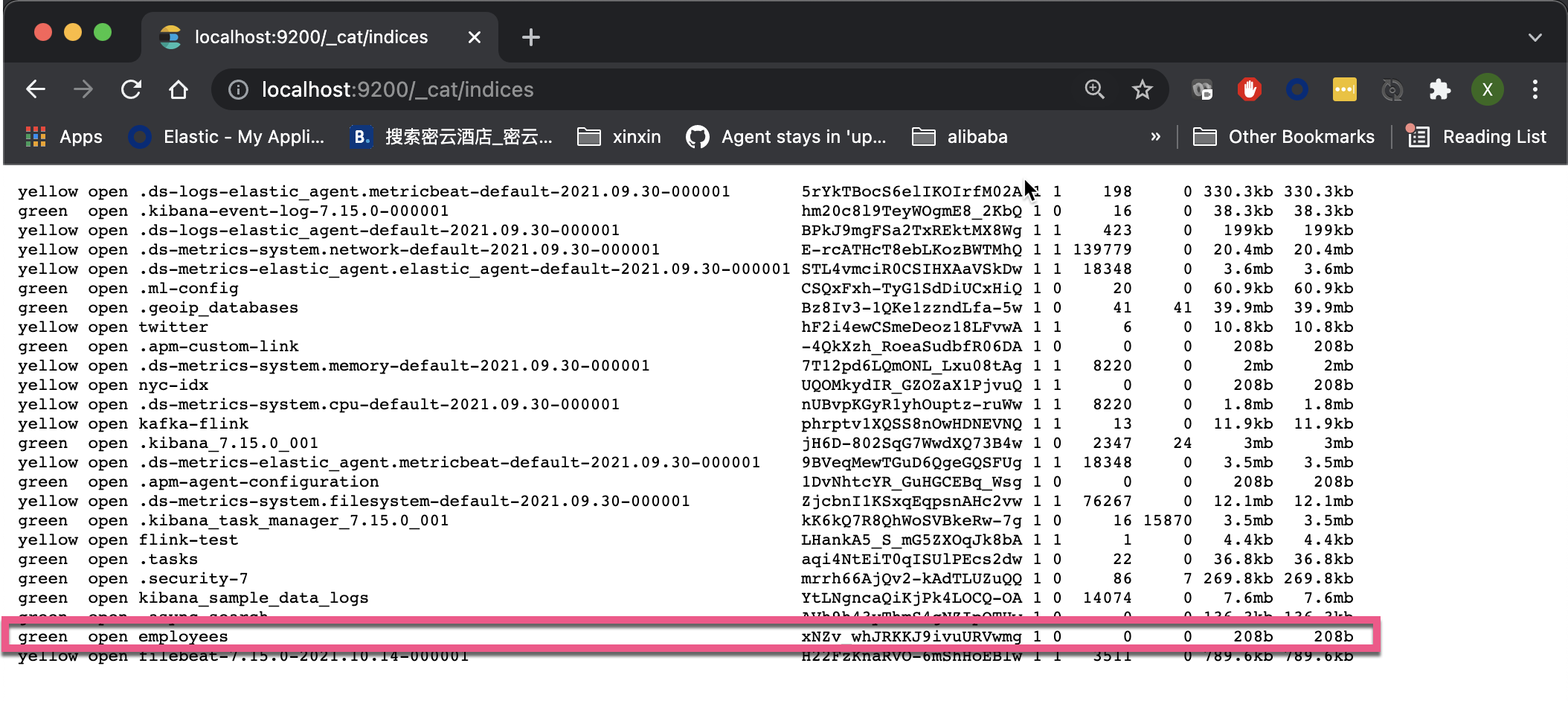
From the above, we can see the employees index that has been created. We can also search in the following ways:
http://localhost:9200/employees/_search
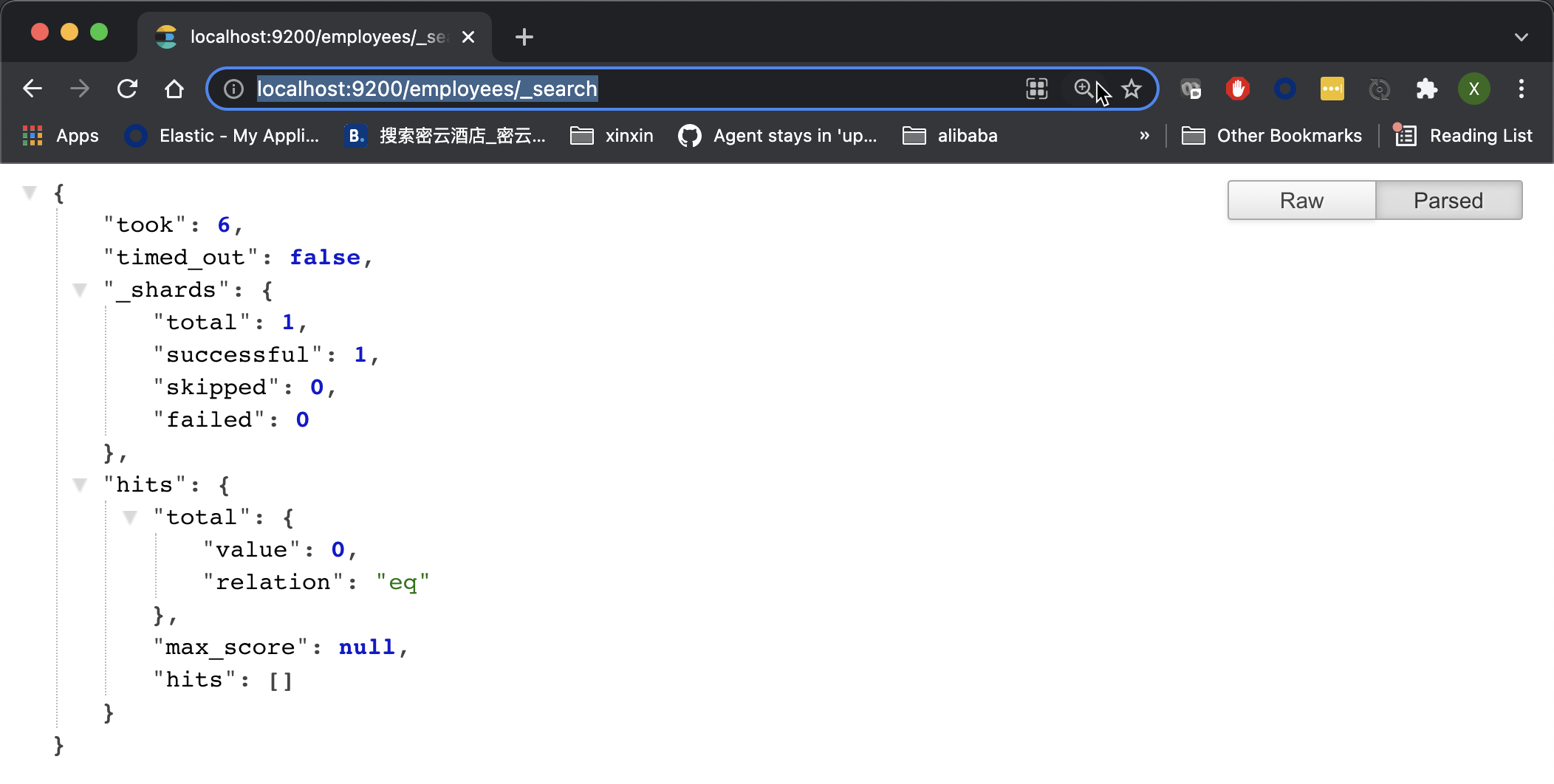
From the above returned results, we can see that there is no data in employees. If the results are not displayed in this very nice indented format in your browser, it is recommended that you install it JSON formatter plug-in unit.
Next, we send the request and save the data through the API interface of Spring Boot.
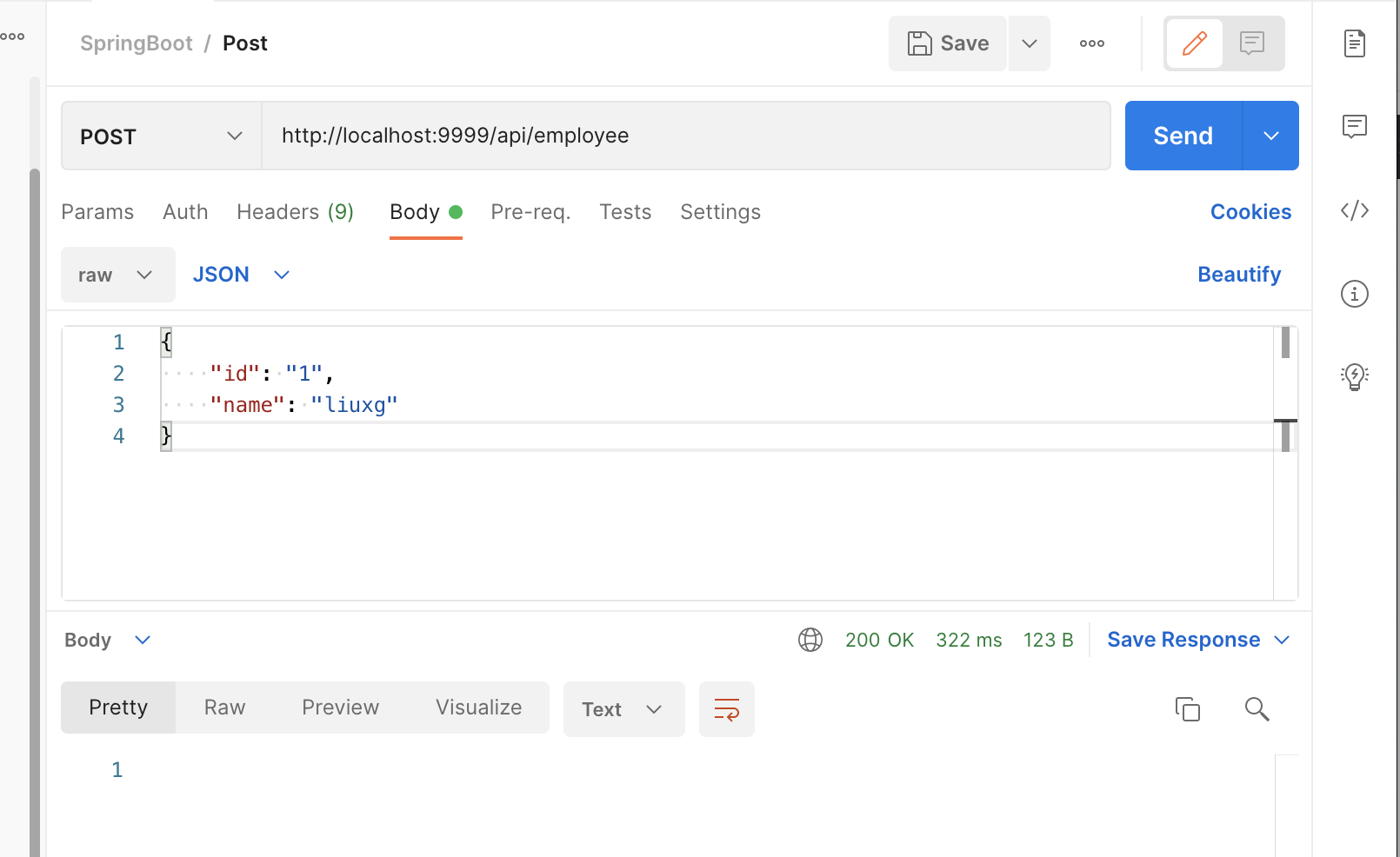
Above, we pass the interface http://localhost:9999/api/employee towards Elasticsearch sends the following data:
{
"id": "1",
"name": "liuxg"
}The data structure is the format we defined in document. We view the data through the browser again:
http://localhost:9200/employees/_search
We can see the following results:
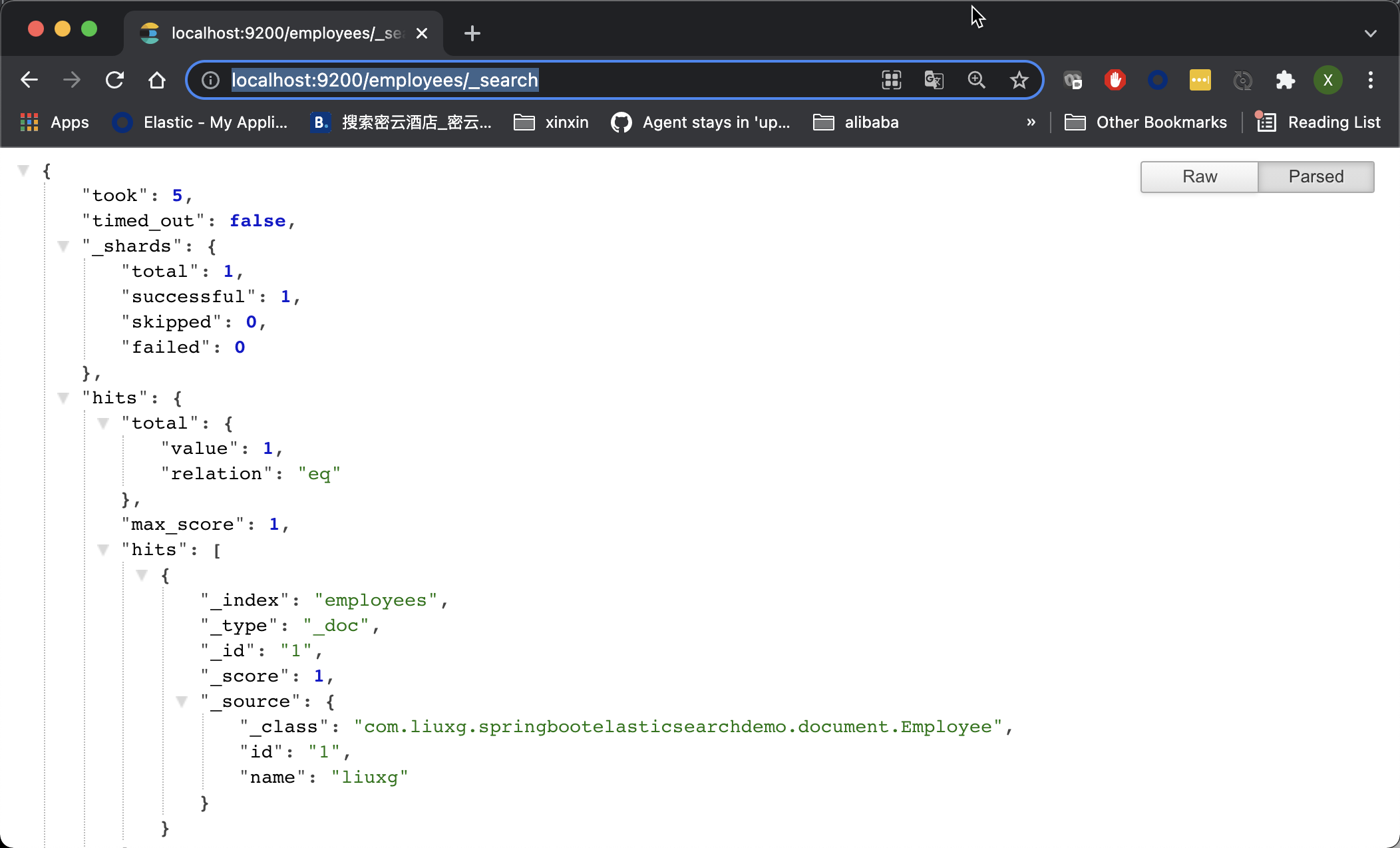
From the above, we can see that a data has been written in.
Next, we use the following interface to obtain the data just written:
http://localhost:9999/api/employee/1
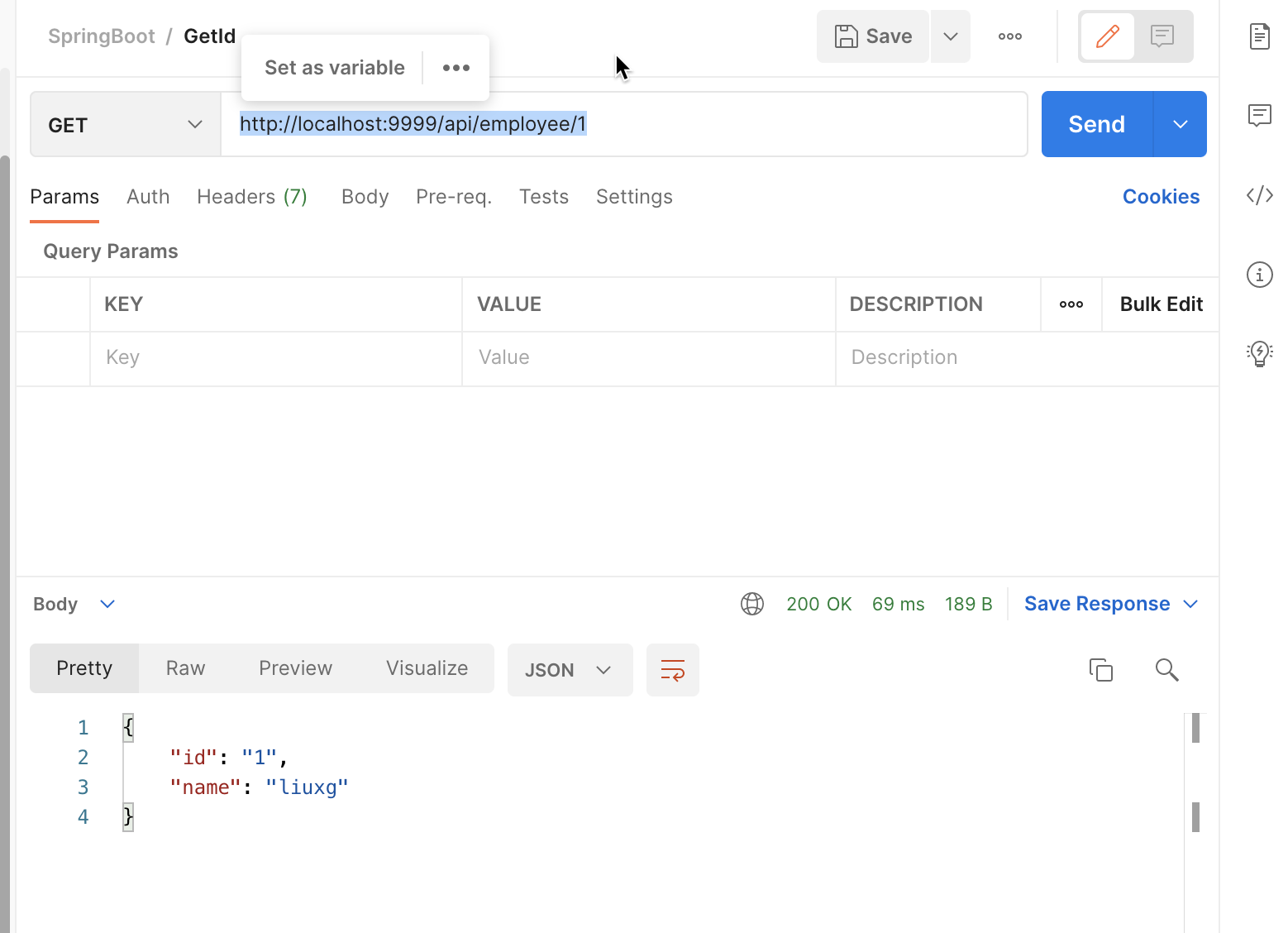
It can be seen that our interface works normally.
We can also query a document by searching name:
http://localhost:9999/api/employee/name/liuxg
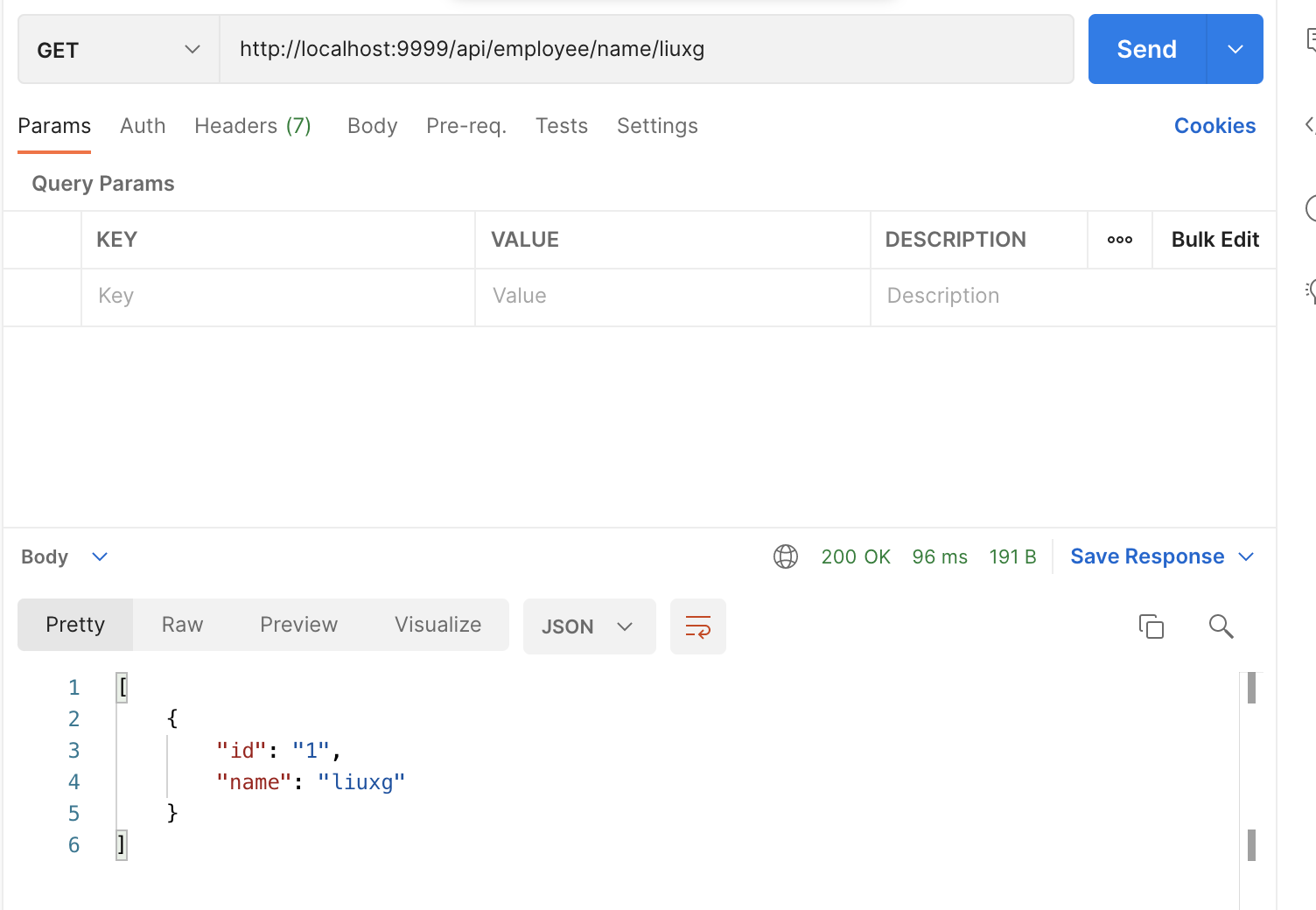
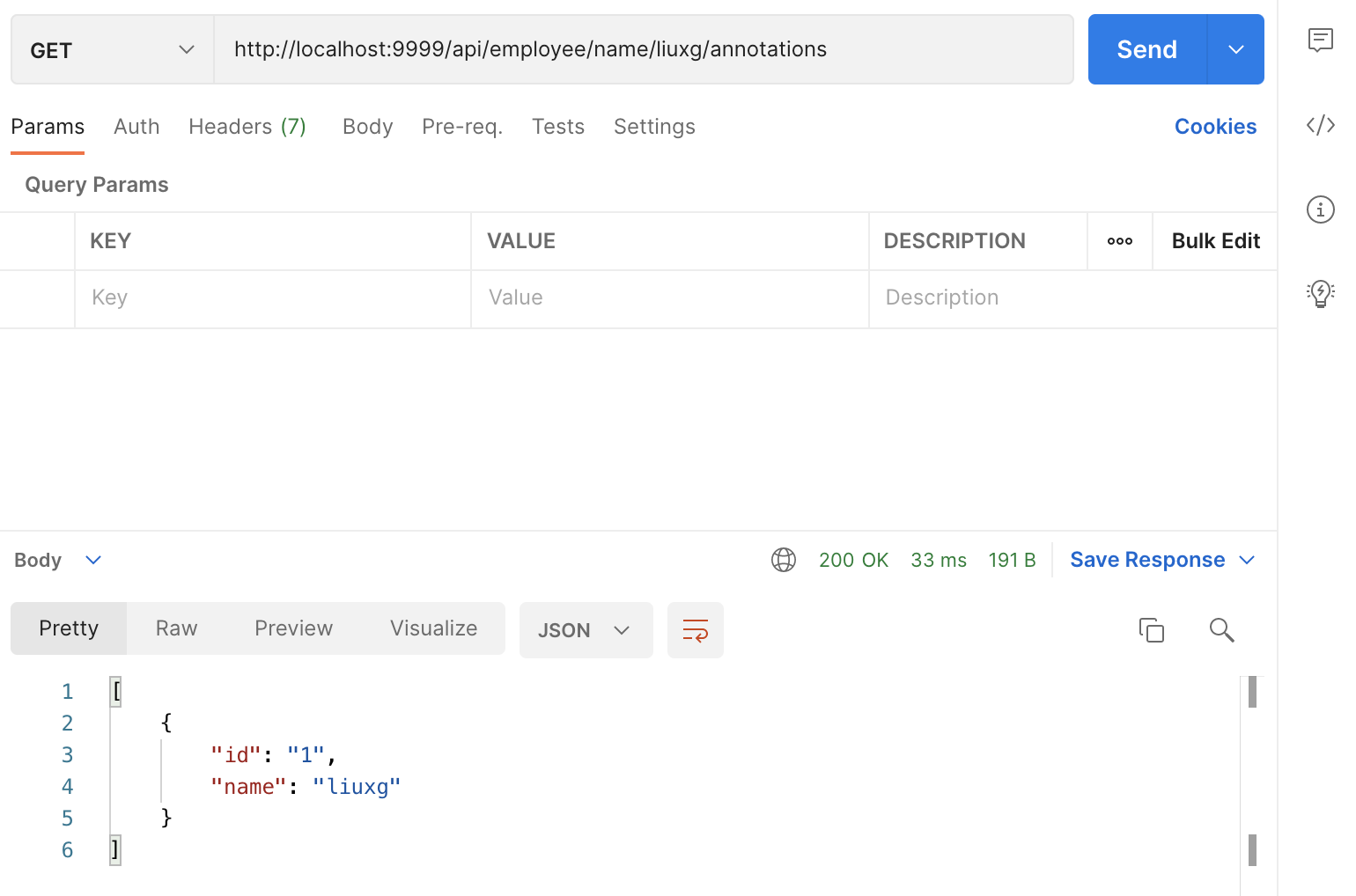
We can also query through annotations:
http://localhost:9999/api/employee/name/liuxg/annotations
Finally, we can delete the created documents through the API:
http://localhost:9999/api/employee/1
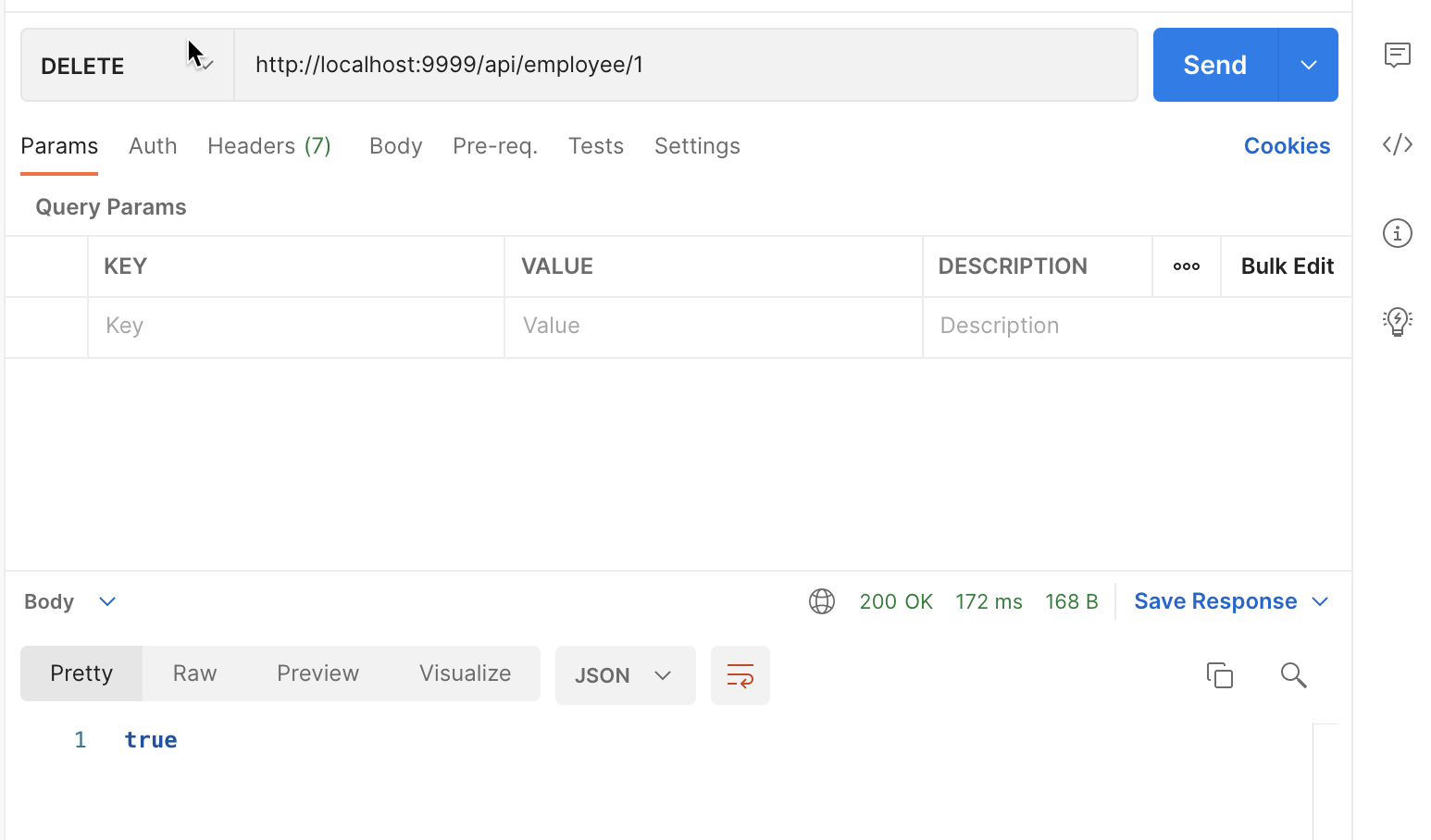
We then query the data of employees through the browser:
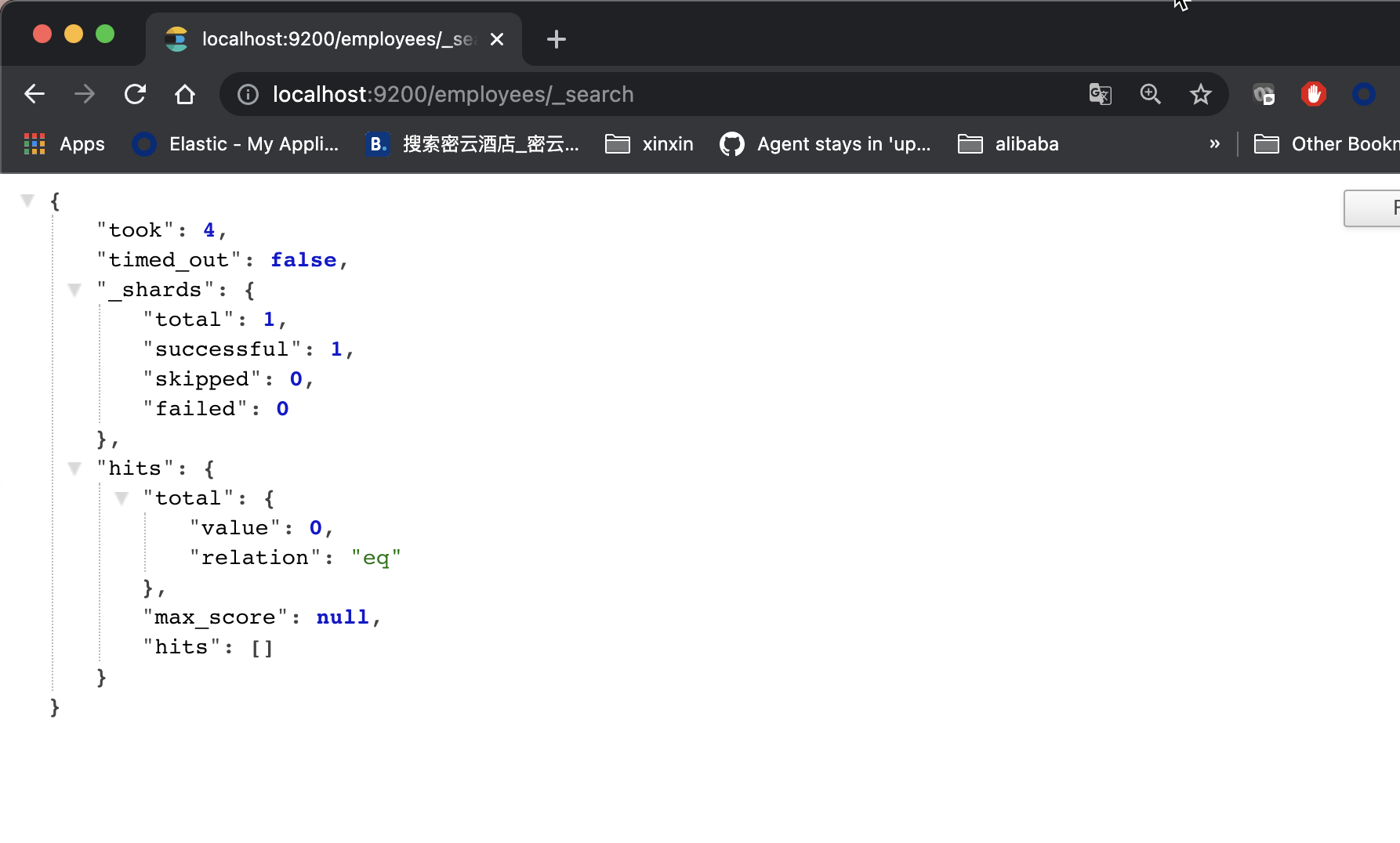
From the above, we can see that the previously created file has been successfully deleted.
reference resources: