1. Implementation of edge detection:
(1) The image is transformed into gray scale image;
(2) Gauss filtering of images;
(3) Realization of convolution integral of pictures;
Code implementation:
import cv2
import numpy as np
import random
img = cv2.imread('image0.jpg',1)
imgInfo = img.shape
height = imgInfo[0]
width = imgInfo[1]
cv2.imshow('src',img)
#canny 1 gray 2 Gauss 3 canny
gray = cv2.cvtColor(img,cv2.COLOR_BGR2GRAY)
imgG = cv2.GaussianBlur(gray,(3,3),0)
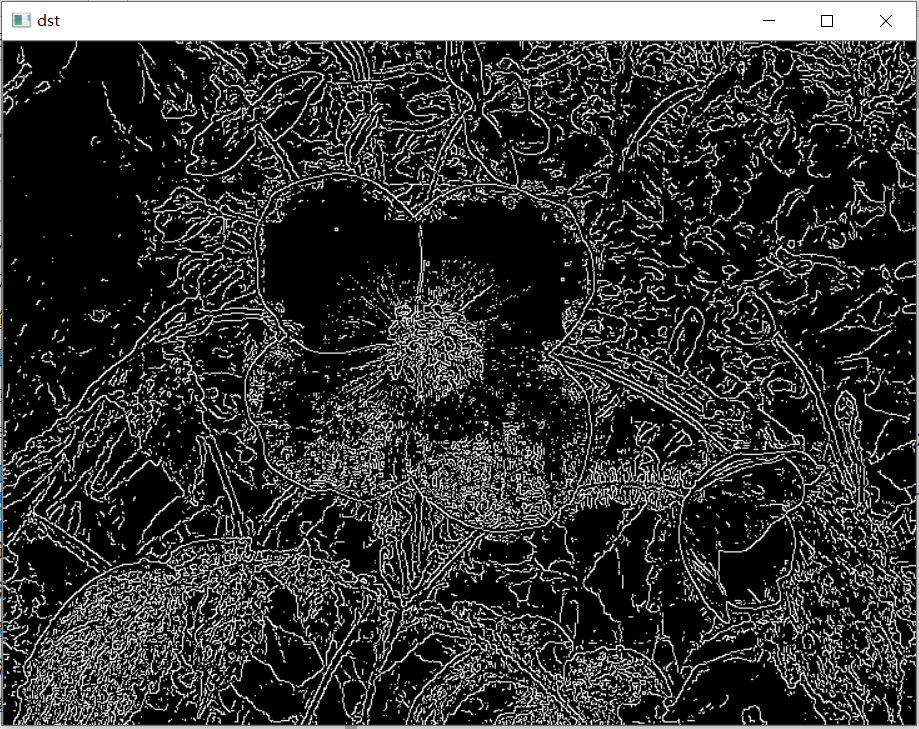
dst = cv2.Canny(img,50,50) #Picture Convolution --"th"
cv2.imshow('dst',dst)
cv2.waitKey(0)Achieving results:
2. Realization of convolution integral:
Assuming that there are matrices A and b, convolution is the multiplication of each element in a and each corresponding phase in B.
For example, suppose the operator template is a=[a1,a2,a3,a4]; the convolution matrix is b=[b1,b2,b3,b4]; and the convolution implementation is r=a1*b1+a2*b2+a3*b3+a4*b4.
Gradient calculation: horizontal gradient x, vertical gradient y, the total gradient z = sqrt(x^2+y^2);
Discriminant edge detection method: Discriminant Z and edge threshold f, if z > f, that point is the point of edge detection.
Algorithmic code implementation:
import cv2
import numpy as np
import random
import math
img = cv2.imread('image0.jpg',1)
imgInfo = img.shape
height = imgInfo[0]
width = imgInfo[1]
cv2.imshow('src',img)
# sobel 1 Operator Template 2 Picture Convolution 3 Threshold Decision
# [1 2 1 [ 1 0 -1
# 0 0 0 2 0 -2
# -1 -2 -1 ] 1 0 -1 ]
# [1 2 3 4] [a b c d] a*1+b*2+c*3+d*4 = dst
# sqrt(a*a+b*b) = f>th
gray = cv2.cvtColor(img,cv2.COLOR_BGR2GRAY)
dst = np.zeros((height,width,1),np.uint8)
for i in range(0,height-2):
for j in range(0,width-2):
gy = gray[i,j]*1+gray[i,j+1]*2+gray[i,j+2]*1-gray[i+2,j]*1-gray[i+2,j+1]*2-gray[i+2,j+2]*1
gx = gray[i,j]+gray[i+1,j]*2+gray[i+2,j]-gray[i,j+2]-gray[i+1,j+2]*2-gray[i+2,j+2]
grad = math.sqrt(gx*gx+gy*gy)
if grad>50:
dst[i,j] = 255
else:
dst[i,j] = 0
cv2.imshow('dst',dst)
cv2.waitKey(0)The result is the same as the picture above.