1. Preface
Earlier, we talked about how services are exported to the registry.In fact, one thing Dubbo does is publish the URL of the service to the registry.Now let's talk about how the consumer subscribes to the service from the registry and makes remote calls.
2. Reference Service Time Series Diagram
First, generally speaking the general internal mechanism in words
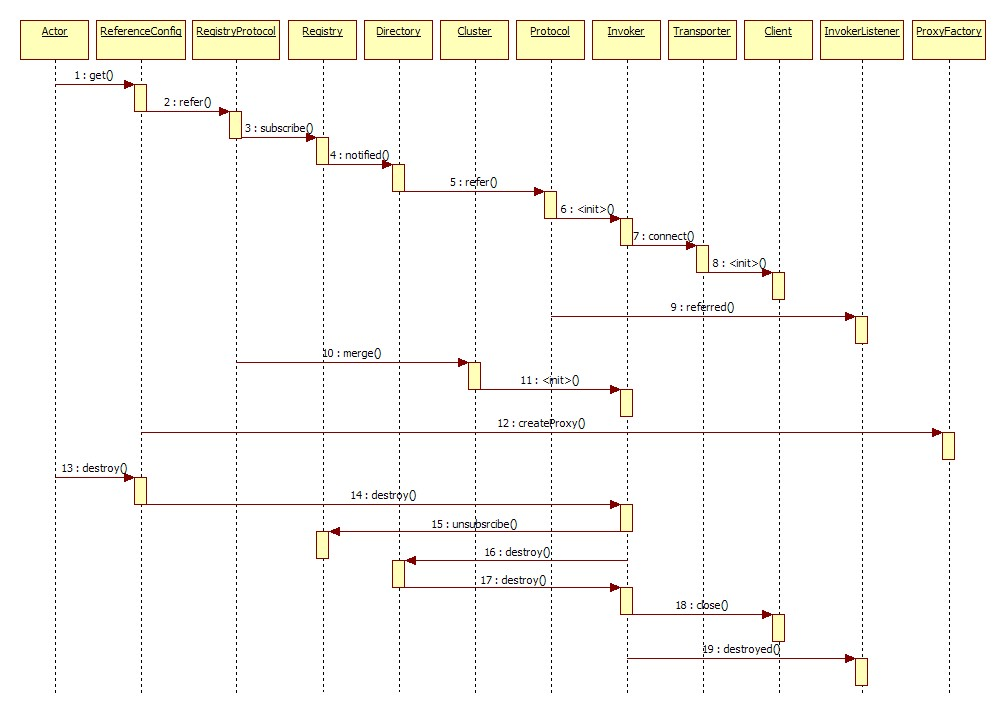
Actor: Can be our consumer.When we inject the corresponding service into another class using the @Reference annotation, Spring calls the getObject method for the first time, and the only method in getObject is get().This can be interpreted as the introduction of services by consumers.
Hungry Han: ReferenceBean's afterPropertiesSet method is called by the Spring container to reference the service.
Lazy: ReferenceBean is referenced when the corresponding service is injected into another class.Dubbo uses the lazy style by default.
ReferenceConfig: The get method actually goes into the ReferenceConfig class to execute the init() method.There are several main things to do in this method:
1. Check the validity of the @Reference labeled interface and whether it is generic
2. Get the file dubbo.resolve.file in the system, which is the interface for configuring consumer.Save the configured consumer information in the URL
3. Store the configured ApplicationConfig, ConsumerConfig, ReferenceConfig, MethodConfig, and the consumer's IP address in the system context
4. Next, start creating a proxy object into the createProxy of ReferenceConfig.This is still in the ReferenceConfig class.The above configurations are traditionally passed into this method.As mentioned above, resolve resolves consumer as a URL, and it is now up to you to decide whether to make a remote or local call first.
4.1 If called locally, call the refer method of InjvmProtocol to generate an InjvmInvoker instance
4.2 If called remotely, read the direct connection configuration key or registry URL and store the read URL in the urls.Then follow up based on the number of URLs elements.If the number of URLs elements is 1, the Invoker instance interface is built directly from the ProtocolAdaptive Extension class, RegistryProtocol class or DubboProtocol, depending on whether the URL starts with registry://or dubbo://.If the number of URLs elements is greater than 1, there are multiple registries or service direct-connect urls, then the Invoker is built from the URL first.Then merge multiple Invokers through Cluster, and finally call ProxyFactory to generate proxy classes.
RegistryProtocol: First set the protocol header for the url in the refer method, then load the registry instance according to the url parameter.Then get the group configuration to determine the type of the first parameter of the doRefer based on the group configuration.The doRefer method creates a RegistryDirectory instance, then generates a service consumer link, registers the consumer link to the registry through the registry.register method, and subscribes the data under providers, configurators, routers, and so on to the registry through the directory.subscribe.When the subscription is complete, RegistryDirectory receives information about the child nodes under these nodes.Since a service may be deployed on multiple servers, resulting in multiple nodes in providers, Cluster is required to merge multiple service nodes into one and generate an Invoker.Similarly, the Invoker creation process will not be analyzed first, but will be covered in a chapter later.
After the ProxyFactory: Invoker is created, the next thing to do is to generate the proxy object for the service interface.With a proxy object, remote calls can be made.The entry method generated by the proxy object is getProxy.Get the list of interfaces you need to create and group them into an array.The interface array is then passed into Proxy's getProxy method to get the Proxy subclass, then an InvokerInvocationHandler object is created and passed to newInstance to generate a Proxy instance.InvokerInvocationHandler implements the JDK's InvocationHandler interface for intercepting interface class calls.Can be understood as AOP or interceptor.That is, the Proxy instance is called before the object is acquired, rather than the corresponding class of the service provider.See the comments in the source code below for how to create proxy instances.
3. Dubbo Source
The getObject method of the service reference entry source ReferenceBean:
1 public Object getObject() throws Exception { 2 return get(); 3 } 4 5 public synchronized T get() { 6 if (destroyed) { 7 throw new IllegalStateException("Already destroyed!"); 8 } 9 // Testing ref Is it empty, empty passes through init Method Creation 10 if (ref == null) { 11 // init Methods are primarily used to handle configurations and to invoke createProxy Generate Proxy Class 12 init(); 13 } 14 return ref; 15 }
ReferenceConfig's init configures the consumer side:
Divide the source code to clarify logic
1 private void init() { 2 // Avoid duplicate initialization 3 if (initialized) { 4 return; 5 } 6 initialized = true; 7 // Detect interface name validity 8 if (interfaceName == null || interfaceName.length() == 0) { 9 throw new IllegalStateException("interface not allow null!"); 10 } 11 12 // Testing consumer Whether the variable is empty or not, an empty variable is created 13 checkDefault(); 14 appendProperties(this); 15 if (getGeneric() == null && getConsumer() != null) { 16 // Set up generic 17 setGeneric(getConsumer().getGeneric()); 18 } 19 20 // Detect if it is a generalized interface 21 if (ProtocolUtils.isGeneric(getGeneric())) { 22 interfaceClass = GenericService.class; 23 } else { 24 try { 25 // Load Class 26 interfaceClass = Class.forName(interfaceName, true, Thread.currentThread() 27 .getContextClassLoader()); 28 } catch (ClassNotFoundException e) { 29 throw new IllegalStateException(e.getMessage(), e); 30 } 31 checkInterfaceAndMethods(interfaceClass, methods); 32 } 33 34 // -------------------------------Split Line 1------------------------------ 35 36 // Get the property value corresponding to the interface name from the system variable 37 String resolve = System.getProperty(interfaceName); 38 String resolveFile = null; 39 if (resolve == null || resolve.length() == 0) { 40 // Get Parse File Path from System Properties 41 resolveFile = System.getProperty("dubbo.resolve.file"); 42 if (resolveFile == null || resolveFile.length() == 0) { 43 // Load profile from specified location 44 File userResolveFile = new File(new File(System.getProperty("user.home")), "dubbo-resolve.properties"); 45 if (userResolveFile.exists()) { 46 // Get absolute file path 47 resolveFile = userResolveFile.getAbsolutePath(); 48 } 49 } 50 if (resolveFile != null && resolveFile.length() > 0) { 51 Properties properties = new Properties(); 52 FileInputStream fis = null; 53 try { 54 fis = new FileInputStream(new File(resolveFile)); 55 // Load Configuration from File 56 properties.load(fis); 57 } catch (IOException e) { 58 throw new IllegalStateException("Unload ..., cause:..."); 59 } finally { 60 try { 61 if (null != fis) fis.close(); 62 } catch (IOException e) { 63 logger.warn(e.getMessage(), e); 64 } 65 } 66 // Gets the configuration corresponding to the interface name 67 resolve = properties.getProperty(interfaceName); 68 } 69 } 70 if (resolve != null && resolve.length() > 0) { 71 // take resolve Assign to url 72 url = resolve; 73 } 74 75 // -------------------------------Split Line 2------------------------------ 76 if (consumer != null) { 77 if (application == null) { 78 // from consumer Get in Application Example, same as below 79 application = consumer.getApplication(); 80 } 81 if (module == null) { 82 module = consumer.getModule(); 83 } 84 if (registries == null) { 85 registries = consumer.getRegistries(); 86 } 87 if (monitor == null) { 88 monitor = consumer.getMonitor(); 89 } 90 } 91 if (module != null) { 92 if (registries == null) { 93 registries = module.getRegistries(); 94 } 95 if (monitor == null) { 96 monitor = module.getMonitor(); 97 } 98 } 99 if (application != null) { 100 if (registries == null) { 101 registries = application.getRegistries(); 102 } 103 if (monitor == null) { 104 monitor = application.getMonitor(); 105 } 106 } 107 108 // Testing Application Legality 109 checkApplication(); 110 // Detect local stub configuration validity 111 checkStubAndMock(interfaceClass); 112 113 // -------------------------------Split Line 3------------------------------ 114 115 Map<String, String> map = new HashMap<String, String>(); 116 Map<Object, Object> attributes = new HashMap<Object, Object>(); 117 118 // Add to side,Protocol version information, timestamp, process number, etc. to map in 119 map.put(Constants.SIDE_KEY, Constants.CONSUMER_SIDE); 120 map.put(Constants.DUBBO_VERSION_KEY, Version.getProtocolVersion()); 121 map.put(Constants.TIMESTAMP_KEY, String.valueOf(System.currentTimeMillis())); 122 if (ConfigUtils.getPid() > 0) { 123 map.put(Constants.PID_KEY, String.valueOf(ConfigUtils.getPid())); 124 } 125 126 // Non-Generalized Services 127 if (!isGeneric()) { 128 // Get Version 129 String revision = Version.getVersion(interfaceClass, version); 130 if (revision != null && revision.length() > 0) { 131 map.put("revision", revision); 132 } 133 134 // Get a list of interface methods and add them to the map in 135 String[] methods = Wrapper.getWrapper(interfaceClass).getMethodNames(); 136 if (methods.length == 0) { 137 map.put("methods", Constants.ANY_VALUE); 138 } else { 139 map.put("methods", StringUtils.join(new HashSet<String>(Arrays.asList(methods)), ",")); 140 } 141 } 142 map.put(Constants.INTERFACE_KEY, interfaceName); 143 // take ApplicationConfig,ConsumerConfig,ReferenceConfig Field information of equal objects added to map in 144 appendParameters(map, application); 145 appendParameters(map, module); 146 appendParameters(map, consumer, Constants.DEFAULT_KEY); 147 appendParameters(map, this); 148 149 // -------------------------------Split Line 4------------------------------ 150 151 String prefix = StringUtils.getServiceKey(map); 152 if (methods != null && !methods.isEmpty()) { 153 // ergodic MethodConfig list 154 for (MethodConfig method : methods) { 155 appendParameters(map, method, method.getName()); 156 String retryKey = method.getName() + ".retry"; 157 // Testing map Whether to include methodName.retry 158 if (map.containsKey(retryKey)) { 159 String retryValue = map.remove(retryKey); 160 if ("false".equals(retryValue)) { 161 // Add Retry Number Configuration methodName.retries 162 map.put(method.getName() + ".retries", "0"); 163 } 164 } 165 166 // Add to MethodConfig From the Properties field to the attributes 167 // such as onreturn,onthrow,oninvoke etc. 168 appendAttributes(attributes, method, prefix + "." + method.getName()); 169 checkAndConvertImplicitConfig(method, map, attributes); 170 } 171 } 172 173 // -------------------------------✨ Split Line 5 ✨------------------------------ 174 175 // Get service consumers ip address 176 String hostToRegistry = ConfigUtils.getSystemProperty(Constants.DUBBO_IP_TO_REGISTRY); 177 if (hostToRegistry == null || hostToRegistry.length() == 0) { 178 hostToRegistry = NetUtils.getLocalHost(); 179 } else if (isInvalidLocalHost(hostToRegistry)) { 180 throw new IllegalArgumentException("Specified invalid registry ip from property..." ); 181 } 182 map.put(Constants.REGISTER_IP_KEY, hostToRegistry); 183 184 // storage attributes To System Context 185 StaticContext.getSystemContext().putAll(attributes); 186 187 // Create Proxy Class 188 ref = createProxy(map); 189 190 // According to the service name, ReferenceConfig,Agent Class Construction ConsumerModel, 191 // And will ConsumerModel Save in ApplicationModel in 192 ConsumerModel consumerModel = new ConsumerModel(getUniqueServiceName(), this, ref, interfaceClass.getMethods()); 193 ApplicationModel.initConsumerModel(getUniqueServiceName(), consumerModel); 194 }
createProxy for ReferenceConfig creates proxy objects:
Instead of creating proxy instances within this method, you create Invoker lines in three ways after parsing the URL, including refer in InjvmProtocol s, refer in DubboProtocol s, and refer in RegistryProtocol s, and finally call ProxyFactory to create proxy instances:
1 private T createProxy(Map<String, String> map) { 2 URL tmpUrl = new URL("temp", "localhost", 0, map); 3 final boolean isJvmRefer; 4 if (isInjvm() == null) { 5 // url Configuration is specified without local reference 6 if (url != null && url.length() > 0) { 7 isJvmRefer = false; 8 // according to url Agreements, scope as well as injvm And other parameters to detect whether a local reference is required 9 // For example, if the user explicitly configures the scope=local,here isInjvmRefer Return true 10 } else if (InjvmProtocol.getInjvmProtocol().isInjvmRefer(tmpUrl)) { 11 isJvmRefer = true; 12 } else { 13 isJvmRefer = false; 14 } 15 } else { 16 // Obtain injvm Configuration Value 17 isJvmRefer = isInjvm().booleanValue(); 18 } 19 20 // Local Reference 21 if (isJvmRefer) { 22 // Generate Local References URL,The agreement is injvm 23 URL url = new URL(Constants.LOCAL_PROTOCOL, NetUtils.LOCALHOST, 0, interfaceClass.getName()).addParameters(map); 24 // call refer Method Construction InjvmInvoker Example 25 invoker = refprotocol.refer(interfaceClass, url); 26 27 // Remote Reference 28 } else { 29 // url Not empty, indicating that the user may want to make point-to-point calls 30 if (url != null && url.length() > 0) { 31 // When multiple configurations are required url When you do this, you can use a semicolon, which is where you do this 32 String[] us = Constants.SEMICOLON_SPLIT_PATTERN.split(url); 33 if (us != null && us.length > 0) { 34 for (String u : us) { 35 URL url = URL.valueOf(u); 36 if (url.getPath() == null || url.getPath().length() == 0) { 37 // Set interface fully qualified name url Route 38 url = url.setPath(interfaceName); 39 } 40 41 // Testing url Is the agreement registry,If so, indicate that the user wants to use the specified registry 42 if (Constants.REGISTRY_PROTOCOL.equals(url.getProtocol())) { 43 // take map Converts to a query string and acts as a refer The value of the parameter is added to the url in 44 urls.add(url.addParameterAndEncoded(Constants.REFER_KEY, StringUtils.toQueryString(map))); 45 } else { 46 // merge url,Remove some configuration of the service provider from the user configuration url Attributes), 47 // For example, thread pool related configuration.And keep some configuration of the service provider, such as version, group,Timestamp, etc. 48 // Finally, set the merged configuration to url In the query string. 49 urls.add(ClusterUtils.mergeUrl(url, map)); 50 } 51 } 52 } 53 } else { 54 // Load Registry url 55 List<URL> us = loadRegistries(false); 56 if (us != null && !us.isEmpty()) { 57 for (URL u : us) { 58 URL monitorUrl = loadMonitor(u); 59 if (monitorUrl != null) { 60 map.put(Constants.MONITOR_KEY, URL.encode(monitorUrl.toFullString())); 61 } 62 // Add to refer Parameters to url And will url add to urls in 63 urls.add(u.addParameterAndEncoded(Constants.REFER_KEY, StringUtils.toQueryString(map))); 64 } 65 } 66 67 // Registry not configured, exception thrown 68 if (urls.isEmpty()) { 69 throw new IllegalStateException("No such any registry to reference..."); 70 } 71 } 72 73 // Single registry or service provider(Direct connection to service, same below) 74 if (urls.size() == 1) { 75 // call RegistryProtocol Of refer structure Invoker Example 76 invoker = refprotocol.refer(interfaceClass, urls.get(0)); 77 78 // Multiple registries, multiple service providers, or a mix of both 79 } else { 80 List<Invoker<?>> invokers = new ArrayList<Invoker<?>>(); 81 URL registryURL = null; 82 83 // Get All Invoker 84 for (URL url : urls) { 85 // adopt refprotocol call refer structure Invoker,refprotocol Will be running 86 // according to url Protocol Header Load Specified Protocol Instance, and calls the instance's refer Method 87 invokers.add(refprotocol.refer(interfaceClass, url)); 88 if (Constants.REGISTRY_PROTOCOL.equals(url.getProtocol())) { 89 registryURL = url; 90 } 91 } 92 if (registryURL != null) { 93 // If the registry link is not empty, the AvailableCluster 94 URL u = registryURL.addParameter(Constants.CLUSTER_KEY, AvailableCluster.NAME); 95 // Establish StaticDirectory And Cluster For multiple Invoker Merge 96 invoker = cluster.join(new StaticDirectory(u, invokers)); 97 } else { 98 invoker = cluster.join(new StaticDirectory(invokers)); 99 } 100 } 101 } 102 103 Boolean c = check; 104 if (c == null && consumer != null) { 105 c = consumer.isCheck(); 106 } 107 if (c == null) { 108 c = true; 109 } 110 111 // invoker Availability Check 112 if (c && !invoker.isAvailable()) { 113 throw new IllegalStateException("No provider available for the service..."); 114 } 115 116 // Generate Proxy Class 117 return (T) proxyFactory.getProxy(invoker); 118 }
Similarly, Invoker will be dedicated to one after its creation.For the time being, consider Invoker creation a black box, as long as we call it.
refer in RegistryProtocol:
1 public <T> Invoker<T> refer(Class<T> type, URL url) throws RpcException { 2 // take registry Parameter value and set it as protocol header 3 url = url.setProtocol(url.getParameter(Constants.REGISTRY_KEY, Constants.DEFAULT_REGISTRY)).removeParameter(Constants.REGISTRY_KEY); 4 // Get Registry Instance 5 Registry registry = registryFactory.getRegistry(url); 6 if (RegistryService.class.equals(type)) { 7 return proxyFactory.getInvoker((T) registry, type, url); 8 } 9 10 // take url Query string to Map 11 Map<String, String> qs = StringUtils.parseQueryString(url.getParameterAndDecoded(Constants.REFER_KEY)); 12 // Obtain group To configure 13 String group = qs.get(Constants.GROUP_KEY); 14 if (group != null && group.length() > 0) { 15 if ((Constants.COMMA_SPLIT_PATTERN.split(group)).length > 1 16 || "*".equals(group)) { 17 // adopt SPI Load MergeableCluster Instance and call doRefer Continue executing service reference logic 18 return doRefer(getMergeableCluster(), registry, type, url); 19 } 20 } 21 22 // call doRefer Continue executing service reference logic 23 return doRefer(cluster, registry, type, url); 24 } 25 private <T> Invoker<T> doRefer(Cluster cluster, Registry registry, Class<T> type, URL url) { 26 // Establish RegistryDirectory Example 27 RegistryDirectory<T> directory = new RegistryDirectory<T>(type, url); 28 // Set up a registry and protocol 29 directory.setRegistry(registry); 30 directory.setProtocol(protocol); 31 Map<String, String> parameters = new HashMap<String, String>(directory.getUrl().getParameters()); 32 // Generate service consumer links 33 URL subscribeUrl = new URL(Constants.CONSUMER_PROTOCOL, parameters.remove(Constants.REGISTER_IP_KEY), 0, type.getName(), parameters); 34 35 // Register service consumers at consumers New Node in Directory 36 if (!Constants.ANY_VALUE.equals(url.getServiceInterface()) 37 && url.getParameter(Constants.REGISTER_KEY, true)) { 38 registry.register(subscribeUrl.addParameters(Constants.CATEGORY_KEY, Constants.CONSUMERS_CATEGORY, 39 Constants.CHECK_KEY, String.valueOf(false))); 40 } 41 42 // Subscribe providers,configurators,routers Equal Node Data 43 directory.subscribe(subscribeUrl.addParameter(Constants.CATEGORY_KEY, 44 Constants.PROVIDERS_CATEGORY 45 + "," + Constants.CONFIGURATORS_CATEGORY 46 + "," + Constants.ROUTERS_CATEGORY)); 47 48 // A registry may have multiple service providers, so you need to merge multiple service providers into one 49 Invoker invoker = cluster.join(directory); 50 ProviderConsumerRegTable.registerConsumer(invoker, url, subscribeUrl, directory); 51 return invoker; 52 }
After the Invoker is created, it returns to the ReferenceConfig and enters the getProxy method in the ProxyFactory.
The getProxy method in ProxyFactory:
1 public <T> T getProxy(Invoker<T> invoker) throws RpcException { 2 // Calling overloaded methods 3 return getProxy(invoker, false); 4 } 5 6 public <T> T getProxy(Invoker<T> invoker, boolean generic) throws RpcException { 7 Class<?>[] interfaces = null; 8 // Get list of interfaces 9 String config = invoker.getUrl().getParameter("interfaces"); 10 if (config != null && config.length() > 0) { 11 // List of slicing interfaces 12 String[] types = Constants.COMMA_SPLIT_PATTERN.split(config); 13 if (types != null && types.length > 0) { 14 interfaces = new Class<?>[types.length + 2]; 15 // Setting up service interface classes and EchoService.class reach interfaces in 16 interfaces[0] = invoker.getInterface(); 17 interfaces[1] = EchoService.class; 18 for (int i = 0; i < types.length; i++) { 19 // Loading interface classes 20 interfaces[i + 1] = ReflectUtils.forName(types[i]); 21 } 22 } 23 } 24 if (interfaces == null) { 25 interfaces = new Class<?>[]{invoker.getInterface(), EchoService.class}; 26 } 27 28 // by http and hessian Protocol provides generic call support, reference pull request #1827 29 if (!invoker.getInterface().equals(GenericService.class) && generic) { 30 int len = interfaces.length; 31 Class<?>[] temp = interfaces; 32 // Create a new interfaces array 33 interfaces = new Class<?>[len + 1]; 34 System.arraycopy(temp, 0, interfaces, 0, len); 35 // Set up GenericService.class To Array 36 interfaces[len] = GenericService.class; 37 } 38 39 // Calling overloaded methods 40 return getProxy(invoker, interfaces); 41 } 42 43 public abstract <T> T getProxy(Invoker<T> invoker, Class<?>[] types);
The code above is mainly to get an array of interfaces and enter getProxy into Proxy through abstract getProxy.
1 public <T> T getProxy(Invoker<T> invoker, Class<?>[] interfaces) { 2 // generate Proxy Subclasses ( Proxy Is an abstract class).And call Proxy Subclass newInstance Method Creation Proxy Example 3 return (T) Proxy.getProxy(interfaces).newInstance(new InvokerInvocationHandler(invoker)); 4 }
Code-specific analysis is written above.Next to getProxy in the Proxy subclass
1 public static Proxy getProxy(Class<?>... ics) { 2 // Calling overloaded methods 3 return getProxy(ClassHelper.getClassLoader(Proxy.class), ics); 4 } 5 6 public static Proxy getProxy(ClassLoader cl, Class<?>... ics) { 7 if (ics.length > 65535) 8 throw new IllegalArgumentException("interface limit exceeded"); 9 10 StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder(); 11 // Traverse interface list 12 for (int i = 0; i < ics.length; i++) { 13 String itf = ics[i].getName(); 14 // Detect whether the type is an interface 15 if (!ics[i].isInterface()) 16 throw new RuntimeException(itf + " is not a interface."); 17 18 Class<?> tmp = null; 19 try { 20 // Reload Interface Class 21 tmp = Class.forName(itf, false, cl); 22 } catch (ClassNotFoundException e) { 23 } 24 25 // Detect if the interfaces are the same, here tmp Possibly empty 26 if (tmp != ics[i]) 27 throw new IllegalArgumentException(ics[i] + " is not visible from class loader"); 28 29 // Splice interface fully qualified name with delimiter ; 30 sb.append(itf).append(';'); 31 } 32 33 // Use the stitched interface name as the key 34 String key = sb.toString(); 35 36 Map<String, Object> cache; 37 synchronized (ProxyCacheMap) { 38 cache = ProxyCacheMap.get(cl); 39 if (cache == null) { 40 cache = new HashMap<String, Object>(); 41 ProxyCacheMap.put(cl, cache); 42 } 43 } 44 45 Proxy proxy = null; 46 synchronized (cache) { 47 do { 48 // Get from Cache Reference<Proxy> Example 49 Object value = cache.get(key); 50 if (value instanceof Reference<?>) { 51 proxy = (Proxy) ((Reference<?>) value).get(); 52 if (proxy != null) { 53 return proxy; 54 } 55 } 56 57 // Concurrency control to ensure that only one thread can perform subsequent operations 58 if (value == PendingGenerationMarker) { 59 try { 60 // Other threads are waiting here 61 cache.wait(); 62 } catch (InterruptedException e) { 63 } 64 } else { 65 // Place flag bits in the cache and jump out while Loop for subsequent action 66 cache.put(key, PendingGenerationMarker); 67 break; 68 } 69 } 70 while (true); 71 } 72 73 long id = PROXY_CLASS_COUNTER.getAndIncrement(); 74 String pkg = null; 75 ClassGenerator ccp = null, ccm = null; 76 try { 77 // Establish ClassGenerator object 78 ccp = ClassGenerator.newInstance(cl); 79 80 Set<String> worked = new HashSet<String>(); 81 List<Method> methods = new ArrayList<Method>(); 82 83 for (int i = 0; i < ics.length; i++) { 84 // Detect if interface access level is protected or privete 85 if (!Modifier.isPublic(ics[i].getModifiers())) { 86 // Get Interface Package Name 87 String npkg = ics[i].getPackage().getName(); 88 if (pkg == null) { 89 pkg = npkg; 90 } else { 91 if (!pkg.equals(npkg)) 92 // wrong public Level interface must be under the same package, or throw an exception 93 throw new IllegalArgumentException("non-public interfaces from different packages"); 94 } 95 } 96 97 // Add interface to ClassGenerator in 98 ccp.addInterface(ics[i]); 99 100 // Traversal interface method 101 for (Method method : ics[i].getMethods()) { 102 // Get a method description, which can be interpreted as a method signature 103 String desc = ReflectUtils.getDesc(method); 104 // If the method description string already exists worked Medium is ignored.Considering this situation, 105 // A Interfaces and B The interface contains an identical method 106 if (worked.contains(desc)) 107 continue; 108 worked.add(desc); 109 110 int ix = methods.size(); 111 // Get Method Return Value Type 112 Class<?> rt = method.getReturnType(); 113 // Get a list of parameters 114 Class<?>[] pts = method.getParameterTypes(); 115 116 // generate Object[] args = new Object[1...N] 117 StringBuilder code = new StringBuilder("Object[] args = new Object[").append(pts.length).append("];"); 118 for (int j = 0; j < pts.length; j++) 119 // generate args[1...N] = ($w)$1...N; 120 code.append(" args[").append(j).append("] = ($w)$").append(j + 1).append(";"); 121 // generate InvokerHandler Interface invoker The method call statement is as follows: 122 // Object ret = handler.invoke(this, methods[1...N], args); 123 code.append(" Object ret = handler.invoke(this, methods[" + ix + "], args);"); 124 125 // Return value is not void 126 if (!Void.TYPE.equals(rt)) 127 // Generate a return statement, such as return (java.lang.String) ret; 128 code.append(" return ").append(asArgument(rt, "ret")).append(";"); 129 130 methods.add(method); 131 // Add method name, access controller, parameter list, method code, etc. to ClassGenerator in 132 ccp.addMethod(method.getName(), method.getModifiers(), rt, pts, method.getExceptionTypes(), code.toString()); 133 } 134 } 135 136 if (pkg == null) 137 pkg = PACKAGE_NAME; 138 139 // Build interface proxy class name: pkg + ".proxy" + id,such as org.apache.dubbo.proxy0 140 String pcn = pkg + ".proxy" + id; 141 ccp.setClassName(pcn); 142 ccp.addField("public static java.lang.reflect.Method[] methods;"); 143 // generate private java.lang.reflect.InvocationHandler handler; 144 ccp.addField("private " + InvocationHandler.class.getName() + " handler;"); 145 146 // Add an interface proxy class with InvocationHandler Parameter construction methods, such as: 147 // porxy0(java.lang.reflect.InvocationHandler arg0) { 148 // handler=$1; 149 // } 150 ccp.addConstructor(Modifier.PUBLIC, new Class<?>[]{InvocationHandler.class}, new Class<?>[0], "handler=$1;"); 151 // Add default constructor for interface proxy class 152 ccp.addDefaultConstructor(); 153 154 // Generate interface proxy class 155 Class<?> clazz = ccp.toClass(); 156 clazz.getField("methods").set(null, methods.toArray(new Method[0])); 157 158 // structure Proxy Subclass names, such as Proxy1,Proxy2 etc. 159 String fcn = Proxy.class.getName() + id; 160 ccm = ClassGenerator.newInstance(cl); 161 ccm.setClassName(fcn); 162 ccm.addDefaultConstructor(); 163 ccm.setSuperClass(Proxy.class); 164 // by Proxy The abstract method of newInstance Generate implementation code, such as: 165 // public Object newInstance(java.lang.reflect.InvocationHandler h) { 166 // return new org.apache.dubbo.proxy0($1); 167 // } 168 ccm.addMethod("public Object newInstance(" + InvocationHandler.class.getName() + " h){ return new " + pcn + "($1); }"); 169 // generate Proxy Implementation Class 170 Class<?> pc = ccm.toClass(); 171 // Create by reflection Proxy Example 172 proxy = (Proxy) pc.newInstance(); 173 } catch (RuntimeException e) { 174 throw e; 175 } catch (Exception e) { 176 throw new RuntimeException(e.getMessage(), e); 177 } finally { 178 if (ccp != null) 179 // Release Resources 180 ccp.release(); 181 if (ccm != null) 182 ccm.release(); 183 synchronized (cache) { 184 if (proxy == null) 185 cache.remove(key); 186 else 187 // Write Cache 188 cache.put(key, new WeakReference<Proxy>(proxy)); 189 // Wake up other waiting threads 190 cache.notifyAll(); 191 } 192 } 193 return proxy; 194 }
CCP is used to generate proxy classes for service interfaces, such as we have a DemoService interface, which is generated by ccp.ccm is used to generate subclasses for the org.apache.dubbo.common.bytecode.Proxy Abstract class, mainly to implement the abstract method of the Proxy class.
This needs to be highlighted because concurrency control is used.The mechanism is that the Reference<Proxy>instance in the cache is first retrieved in synchronized.Because the cache is accessed by a HashMap structure.Key is the name of the interface corresponding to the Reference<Proxy>instance, value is the Reference<Proxy>instance, and note that the list of interfaces is stitched together.When the first thread enters, the key corresponds to the instance, not the Pending Generation Marker.So it goes into else, where the corresponding value of the key is set to the token Pending Generation nMarker.This allows other threads to wait and then produce subclasses of proxy and abstract classes for the service interface.When the resource is finally released, other threads are awakened and the Reference instance that has been generated is marked as a weak reference object, meaning it can be recycled.(Note: Weak references are weaker than soft references, and objects associated with them can only survive until the next garbage collection occurs.Weak reference objects are recycled when garbage collection occurs, regardless of whether there is enough memory.As you can see JVM garbage collection algorithm)
4. Summary:
This should be the end of the service reference mechanism in Dubbo.For Invoker, we'll talk about it later.One more sentence here is that service degradation starts if it is a cluster and load balancing selects only one Invoker call at a time, which is also discussed separately later.