Reference:
"Deep and Simple DPDK"
DPDK
https://software.intel.com/en-us/articles/introduction-to-the-data-plane-development-kit-dpdk-packet-framework
...........................................................................................................
This part belongs to the core part of DPDK. For the whole life cycle of a message, how to access the router from the external interface of the docking operator, connect the network card of the computer, and send the process, maybe this is what we are doubtful about, and it is also the key part of this study. Only by understanding each step and link, can we understand the network message office thoroughly. Reason, and then solve the problems that arise.
I. Division of DPDK Network Processing Modules
Processing and forwarding of network messages are mainly divided into hardware and software processing parts, which are composed of the following modules:
- packet input
- pre-processing: coarse-grained processing of messages
- input classification: fine-grained shunting of messages
- ingress queuing: Provides a descriptor-based queue FIFO
- delivery/scheduling: Scheduling based on queue priority and CPU status
- accelerator: provides hardware functions such as encryption, decryption and compression/decompression
- egress queuing: Scheduling at export according to the QoS level
- post processing: Late message processing releases the cache
- packet output: Send from hardware
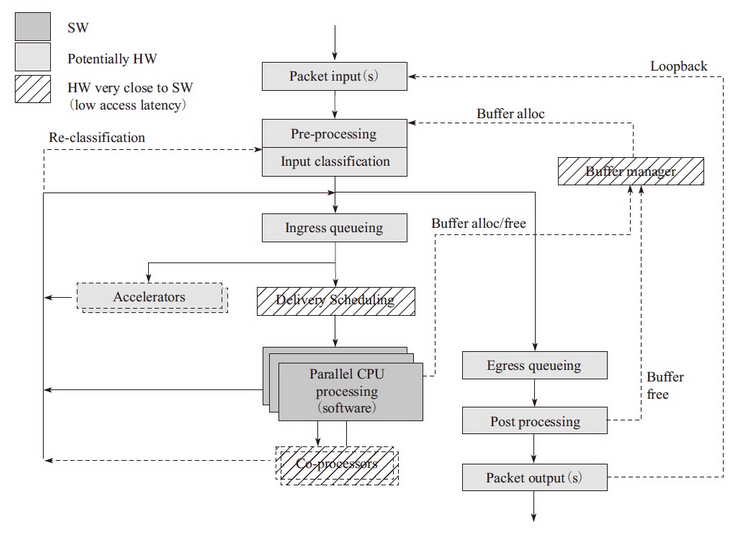
Figure 1
As shown in Figure 1, the light and shadow parts are related to the corresponding modules and hardware, so the best choice to improve the performance of this part is to choose as many uninstall features related to network specific functions as possible on the network card or the device chip. The dark software part can improve network performance by improving the efficiency of the algorithm and combining CPU-related parallel instructions to understand the network. After the basic components of the processing module, let's look at how different forwarding frameworks enable these modules to work together to complete network packet processing.
Introduction of forwarding framework
Traditional Network Process forwarding models can be divided into run to comletion (RTC) model and pipeline (pipeline) model.
2.1 pipeline Model
Pipeline refers to the industrial pipeline model, dividing the whole function into several independent stages, and delivering products through queues in different stages. In this way, for some CPU-intensive and I/O-intensive applications, I/O-intensive operations will be executed on another microprocessor engine. Through filters, different threads can be allocated for different operations, and two speeds can be matched by queues to achieve the best concurrency.

We can see that in the figure, the TOP(Task Optimized Processor) unit, each TOP unit is a special micro-unit for optimizing a particular thing.
2.2 run to completion Model
This model is DPDK's operation method for general programs. A program is divided into several different logical functions. Several logical functions will run on a CPU core. Let's look at the view of the model below.

This model has no special processing unit for messages, only two NP cores, two NP cores use the burned microcodes to process messages.
2.3 Forwarding Model Comparison
From the run to completion model, we can clearly see that each IA's physical core is responsible for processing the entire message life cycle from RX to TX, which is very similar to the role of the nP core of AMCC mentioned earlier. In pipeline model, message processing can be divided into different logical function units A, B and C. A message needs to go through three stages: A, B and C. These three stages can be divided into more than one functional unit and distributed on different physical cores. Different functional units can be distributed on the same core (or distributed on different cores). It can be seen that the classification and invocation of modules are more flexible than EZchip's hardware scheme.
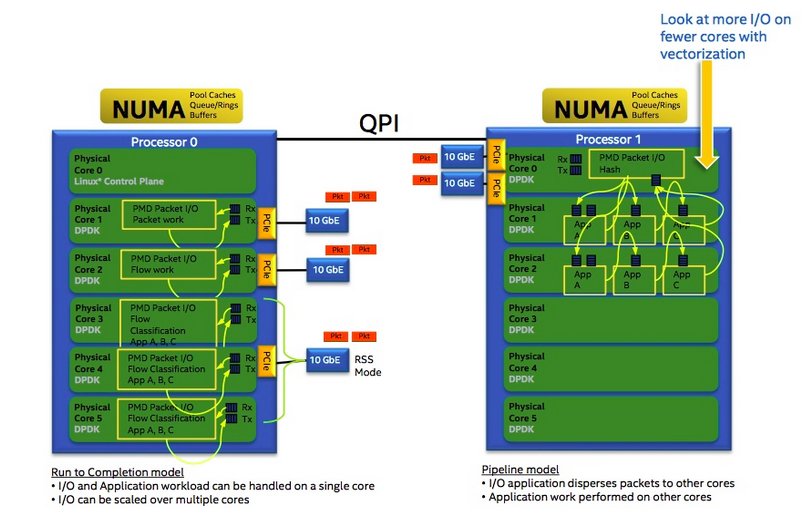
Two advantages and disadvantages:

3. Forwarding algorithm
In addition to a good forwarding framework, a very important part of forwarding is the matching and recognition of message segments. In DPDK, Exact Match (Exact Match) algorithm and Longest Prefix Matching (LPM) algorithm are mainly used to match messages to obtain corresponding information. Accurate matching mainly needs to solve two problems: data signature (hashing) and hash conflict. CRC32 and J hash are mainly supported in DPDK.
Longest Prefix Matching (LPM) algorithm refers to an algorithm used by routers in IP protocol for routing table selection. The LPM algorithm currently used by DPDK uses memory consumption to improve the performance of LPM lookup. When the prefix length of the lookup table entries is less than 24 bits, only one memory access is needed to find the next one. According to probability statistics, this is a relatively probabilistic one. When the current prefix is larger than 24 bits, two memory visits are required, but this is a small probability event.
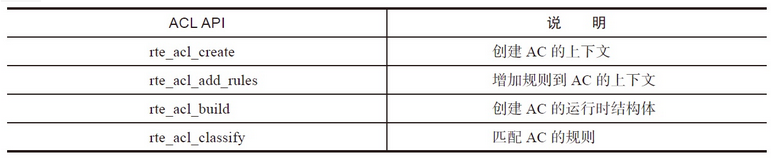
The ACL library uses the matching rules of N tuples to perform type matching, providing the following basic operations:
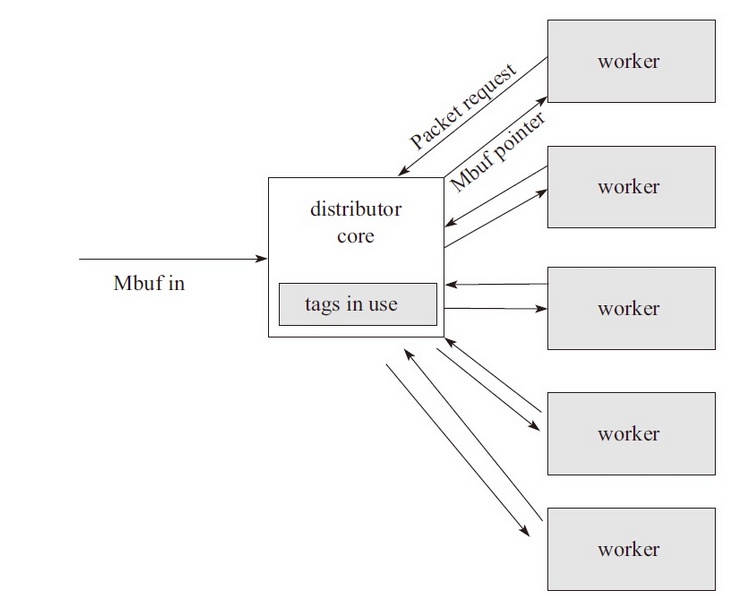
Packet distributor (Packet Distribution) is an API library provided by DPDK to users for package distribution. The main functions can be described in the following figure:
Examples (refer to Intel website: https://software.intel.com/en-us/articles/introduction-to-the-data-plane-development-kit-dpdk-package-framework)
The ip_pipline application shows how to use the pipeline module by providing several sample applications and configuration files
The following figure shows the three-tier forwarding configuration application
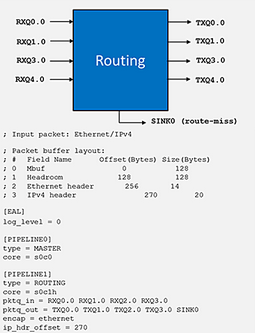
In this example, it sets up simple routing.
The "core" entry thread ID (socket ID, physical CPU ID and hyperthreading ID) determines the CPU core used to run the pipeline.
The parameters "pktq_in" and "pktq_out" define the interface for data packet transmission, which refers to receiving and transmitting data packets.
The "encap" parameter can be set to "ethernet", "qinq" or "mpls" to encapsulate appropriate headers for all outbound packages.
The last parameter "ip_hdr_offset" can be used to set the offset bytes required for the starting position of ip-header in DPDK packet structure (mbuf).
The following figure is a script file of ip_pipeline, in which the contents will be added as routing table entries to the longest matching table of the routing pipeline:
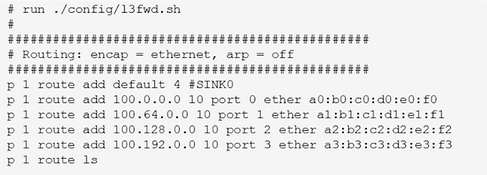
p <pipeline_id> route add <ip_addr> <depth> port <port_id> ether <next hop mac_addr>
The following commands can be used to run L3 forwarding applications:
$./build/ip_pipeline -f l3fwd.cfg -p 0xf -s l3fwd.sh
Sometimes, applications have complex topologies when they are interconnected between different functional modules. Once the application configuration file is ready, run the following commands to generate the topology diagram
$./diagram-generator.py -f <configuration file>
Topology generated by the ip_pipeline sample program:

Various network functions (pipelines) built using this standard pipeline model can be used as part of the DPDK ip_pipeline sample application.
DPDK supports pipeline in the following ways:
1)Packet I/O
2)Flow classification
3)Firewall
4)Routing
5)Metering
6)Traffic Mgmt
Let's take an example of Guan l2 forwarding to see how the whole code works.
Source download: http://core.dpdk.org/download/
Code path: dpdk/examples/l2fwd
1 #include <stdio.h> 2 #include <stdlib.h> 3 #include <string.h> 4 #include <stdint.h> 5 #include <inttypes.h> 6 #include <sys/types.h> 7 #include <sys/queue.h> 8 #include <netinet/in.h> 9 #include <setjmp.h> 10 #include <stdarg.h> 11 #include <ctype.h> 12 #include <errno.h> 13 #include <getopt.h> 14 #include <signal.h> 15 #include <stdbool.h> 16 17 #include <rte_common.h> 18 #include <rte_log.h> 19 #include <rte_malloc.h> 20 #include <rte_memory.h> 21 #include <rte_memcpy.h> 22 #include <rte_memzone.h> 23 #include <rte_eal.h> 24 #include <rte_per_lcore.h> 25 #include <rte_launch.h> 26 #include <rte_atomic.h> 27 #include <rte_cycles.h> 28 #include <rte_prefetch.h> 29 #include <rte_lcore.h> 30 #include <rte_per_lcore.h> 31 #include <rte_branch_prediction.h> 32 #include <rte_interrupts.h> 33 #include <rte_pci.h> 34 #include <rte_random.h> 35 #include <rte_debug.h> 36 #include <rte_ether.h> 37 #include <rte_ethdev.h> 38 #include <rte_mempool.h> 39 #include <rte_mbuf.h> 40 41 static volatile bool force_quit; 42 43 /* MAC updating enabled by default */ 44 static int mac_updating = 1; 45 46 #define RTE_LOGTYPE_L2FWD RTE_LOGTYPE_USER1 47 48 #define NB_MBUF 8192 49 50 #define MAX_PKT_BURST 32 51 #define BURST_TX_DRAIN_US 100 /* TX drain every ~100us */ 52 #define MEMPOOL_CACHE_SIZE 256 53 54 /* 55 * Configurable number of RX/TX ring descriptors 56 */ 57 #define RTE_TEST_RX_DESC_DEFAULT 128 58 #define RTE_TEST_TX_DESC_DEFAULT 512 59 static uint16_t nb_rxd = RTE_TEST_RX_DESC_DEFAULT; 60 static uint16_t nb_txd = RTE_TEST_TX_DESC_DEFAULT; 61 62 /* ethernet addresses of ports */ 63 //Ethernet address of port 64 static struct ether_addr l2fwd_ports_eth_addr[RTE_MAX_ETHPORTS]; 65 66 /* mask of enabled ports */ 67 //Port-enabled mask 68 static uint32_t l2fwd_enabled_port_mask = 0; 69 70 /* list of enabled ports */ 71 //Enable Port List 72 static uint32_t l2fwd_dst_ports[RTE_MAX_ETHPORTS]; 73 74 static unsigned int l2fwd_rx_queue_per_lcore = 1; 75 76 #define MAX_RX_QUEUE_PER_LCORE 16 77 #define MAX_TX_QUEUE_PER_PORT 16 78 struct lcore_queue_conf { 79 unsigned n_rx_port; 80 unsigned rx_port_list[MAX_RX_QUEUE_PER_LCORE]; 81 } __rte_cache_aligned; 82 struct lcore_queue_conf lcore_queue_conf[RTE_MAX_LCORE]; 83 84 static struct rte_eth_dev_tx_buffer *tx_buffer[RTE_MAX_ETHPORTS]; 85 86 static const struct rte_eth_conf port_conf = { 87 .rxmode = { 88 .split_hdr_size = 0, 89 .header_split = 0, /**< Header Split disabled */ //Header separation 90 .hw_ip_checksum = 0, /**< IP checksum offload disabled */ //IP Checksum offload 91 .hw_vlan_filter = 0, /**< VLAN filtering disabled */ //vlan filter 92 .jumbo_frame = 0, /**< Jumbo Frame Support disabled */ //Supporting Giant Star Frames 93 .hw_strip_crc = 0, /**< CRC stripped by hardware */ //Use Hardware Clearance CRC 94 }, 95 .txmode = { 96 .mq_mode = ETH_MQ_TX_NONE, 97 }, 98 }; 99 100 struct rte_mempool * l2fwd_pktmbuf_pool = NULL; 101 102 /* Per-port statistics struct */ 103 struct l2fwd_port_statistics { 104 uint64_t tx; 105 uint64_t rx; 106 uint64_t dropped; 107 } __rte_cache_aligned; 108 struct l2fwd_port_statistics port_statistics[RTE_MAX_ETHPORTS]; 109 110 #define MAX_TIMER_PERIOD 86400 /* 1 day max */ 111 /* A tsc-based timer responsible for triggering statistics printout */ 112 static uint64_t timer_period = 10; /* default period is 10 seconds */ 113 114 /* Print out statistics on packets dropped */ 115 //Printed attributes skip... 116 static void 117 print_stats(void) 118 { 119 uint64_t total_packets_dropped, total_packets_tx, total_packets_rx; 120 unsigned portid; 121 122 total_packets_dropped = 0; 123 total_packets_tx = 0; 124 total_packets_rx = 0; 125 126 const char clr[] = { 27, '[', '2', 'J', '\0' }; 127 const char topLeft[] = { 27, '[', '1', ';', '1', 'H','\0' }; 128 129 /* Clear screen and move to top left */ 130 printf("%s%s", clr, topLeft); 131 132 printf("\nPort statistics ===================================="); 133 134 for (portid = 0; portid < RTE_MAX_ETHPORTS; portid++) { 135 /* skip disabled ports */ 136 if ((l2fwd_enabled_port_mask & (1 << portid)) == 0) 137 continue; 138 printf("\nStatistics for port %u ------------------------------" 139 "\nPackets sent: %24"PRIu64 140 "\nPackets received: %20"PRIu64 141 "\nPackets dropped: %21"PRIu64, 142 portid, 143 port_statistics[portid].tx, 144 port_statistics[portid].rx, 145 port_statistics[portid].dropped); 146 147 total_packets_dropped += port_statistics[portid].dropped; 148 total_packets_tx += port_statistics[portid].tx; 149 total_packets_rx += port_statistics[portid].rx; 150 } 151 printf("\nAggregate statistics ===============================" 152 "\nTotal packets sent: %18"PRIu64 153 "\nTotal packets received: %14"PRIu64 154 "\nTotal packets dropped: %15"PRIu64, 155 total_packets_tx, 156 total_packets_rx, 157 total_packets_dropped); 158 printf("\n====================================================\n"); 159 } 160 161 static void 162 l2fwd_mac_updating(struct rte_mbuf *m, unsigned dest_portid) 163 { 164 struct ether_hdr *eth; 165 void *tmp; 166 167 eth = rte_pktmbuf_mtod(m, struct ether_hdr *); 168 169 /* 02:00:00:00:00:xx */ 170 tmp = ð->d_addr.addr_bytes[0]; 171 *((uint64_t *)tmp) = 0x000000000002 + ((uint64_t)dest_portid << 40); 172 173 /* src addr */ 174 ether_addr_copy(&l2fwd_ports_eth_addr[dest_portid], ð->s_addr); 175 } 176 177 //Processing incoming packets 178 static void 179 l2fwd_simple_forward(struct rte_mbuf *m, unsigned portid) 180 { 181 unsigned dst_port; 182 int sent; 183 struct rte_eth_dev_tx_buffer *buffer; 184 185 //Get the destination port ID 186 dst_port = l2fwd_dst_ports[portid]; 187 188 //To update MAC address 189 if (mac_updating) 190 l2fwd_mac_updating(m, dst_port); 191 192 //Getting the destination port tx cache 193 buffer = tx_buffer[dst_port]; 194 //Send a packet to the destination port tx cache 195 sent = rte_eth_tx_buffer(dst_port, 0, buffer, m); 196 197 if (sent) 198 port_statistics[dst_port].tx += sent; //If the outgoing is successful, the outgoing number+1 199 } 200 201 /* main processing loop */ 202 static void 203 l2fwd_main_loop(void) 204 { 205 struct rte_mbuf *pkts_burst[MAX_PKT_BURST]; 206 struct rte_mbuf *m; 207 int sent; 208 unsigned lcore_id; 209 uint64_t prev_tsc, diff_tsc, cur_tsc, timer_tsc; 210 unsigned i, j, portid, nb_rx; 211 struct lcore_queue_conf *qconf; 212 const uint64_t drain_tsc = (rte_get_tsc_hz() + US_PER_S - 1) / US_PER_S * 213 BURST_TX_DRAIN_US; 214 struct rte_eth_dev_tx_buffer *buffer; 215 216 prev_tsc = 0; 217 timer_tsc = 0; 218 219 //Acquiring the Current Core ID 220 lcore_id = rte_lcore_id(); 221 //Get the current core configuration 222 qconf = &lcore_queue_conf[lcore_id]; 223 224 //If rx_port The number of logs is 0. (It's actually a mistake) 225 if (qconf->n_rx_port == 0) { 226 RTE_LOG(INFO, L2FWD, "lcore %u has nothing to do\n", lcore_id); 227 return; 228 } 229 230 //Logging, 231 RTE_LOG(INFO, L2FWD, "entering main loop on lcore %u\n", lcore_id); 232 233 //Traveling through all port 234 for (i = 0; i < qconf->n_rx_port; i++) { 235 //Obtained portID 236 portid = qconf->rx_port_list[i]; 237 //Logging 238 RTE_LOG(INFO, L2FWD, " -- lcoreid=%u portid=%u\n", lcore_id, 239 portid); 240 241 } 242 243 //If it does not time out (the run time of the first two-tier forwarding set) 244 while (!force_quit) { 245 246 //Get the timestamp 247 cur_tsc = rte_rdtsc(); 248 249 /* 250 * TX burst queue drain 251 */ 252 //Contrast timestamps 253 diff_tsc = cur_tsc - prev_tsc; 254 if (unlikely(diff_tsc > drain_tsc)) { 255 256 for (i = 0; i < qconf->n_rx_port; i++) { 257 //Get portid and buffer 258 portid = l2fwd_dst_ports[qconf->rx_port_list[i]]; 259 buffer = tx_buffer[portid]; 260 261 //hold buffer Data sent in portid Corresponding port 262 sent = rte_eth_tx_buffer_flush(portid, 0, buffer); 263 if (sent) 264 port_statistics[portid].tx += sent; //If the outgoing is successful, the outgoing number+1 265 266 } 267 268 /* if timer is enabled */ 269 //If the timer is turned on 270 if (timer_period > 0) { 271 272 /* advance the timer */ 273 //Adjust timer 274 timer_tsc += diff_tsc; 275 276 /* if timer has reached its timeout */ 277 //If the timer times out 278 if (unlikely(timer_tsc >= timer_period)) { 279 280 /* do this only on master core */ 281 //The main thread prints some properties, and only the main thread executes them. print_stats 282 if (lcore_id == rte_get_master_lcore()) { 283 print_stats(); //Print attributes, 284 /* reset the timer */ 285 timer_tsc = 0; //Set timer to 0 286 } 287 } 288 } 289 290 prev_tsc = cur_tsc; 291 } 292 293 /* 294 * Read packet from RX queues //Packet Receiving Module 295 */ 296 for (i = 0; i < qconf->n_rx_port; i++) { 297 //Obtain portID 298 portid = qconf->rx_port_list[i]; 299 //from portID Corresponding Port Received nb_rx Package 300 nb_rx = rte_eth_rx_burst((uint8_t) portid, 0, 301 pkts_burst, MAX_PKT_BURST); 302 303 port_statistics[portid].rx += nb_rx; //Packet Receiving Count+=nb_rx 304 305 for (j = 0; j < nb_rx; j++) { //Traverse the received package 306 m = pkts_burst[j]; 307 rte_prefetch0(rte_pktmbuf_mtod(m, void *)); //Prefetch pktmbuf 308 l2fwd_simple_forward(m, portid); //Call functions to process incoming packages 309 } 310 } 311 } 312 } 313 314 //__attribute__((unused))Represents that this parameter may not be available and that the compiler will not report errors 315 static int 316 l2fwd_launch_one_lcore(__attribute__((unused)) void *dummy) 317 { 318 l2fwd_main_loop(); //Layer 2 Forwarding main loop 319 return 0; 320 } 321 322 /* display usage */ 323 static void 324 l2fwd_usage(const char *prgname) 325 { 326 printf("%s [EAL options] -- -p PORTMASK [-q NQ]\n" 327 " -p PORTMASK: hexadecimal bitmask of ports to configure\n" 328 " -q NQ: number of queue (=ports) per lcore (default is 1)\n" 329 " -T PERIOD: statistics will be refreshed each PERIOD seconds (0 to disable, 10 default, 86400 maximum)\n" 330 " --[no-]mac-updating: Enable or disable MAC addresses updating (enabled by default)\n" 331 " When enabled:\n" 332 " - The source MAC address is replaced by the TX port MAC address\n" 333 " - The destination MAC address is replaced by 02:00:00:00:00:TX_PORT_ID\n", 334 prgname); 335 } 336 337 static int 338 l2fwd_parse_portmask(const char *portmask) 339 { 340 char *end = NULL; 341 unsigned long pm; 342 343 /* parse hexadecimal string */ 344 //Resolve hexadecimal strings and convert them to hexadecimal strings unsigned long 345 pm = strtoul(portmask, &end, 16); 346 if ((portmask[0] == '\0') || (end == NULL) || (*end != '\0')) 347 return -1; 348 349 if (pm == 0) 350 return -1; 351 352 return pm; 353 } 354 355 static unsigned int 356 l2fwd_parse_nqueue(const char *q_arg) 357 { 358 char *end = NULL; 359 unsigned long n; 360 361 /* parse hexadecimal string */ 362 n = strtoul(q_arg, &end, 10); 363 if ((q_arg[0] == '\0') || (end == NULL) || (*end != '\0')) 364 return 0; 365 if (n == 0) 366 return 0; 367 if (n >= MAX_RX_QUEUE_PER_LCORE) 368 return 0; 369 370 return n; 371 } 372 373 static int 374 l2fwd_parse_timer_period(const char *q_arg) 375 { 376 char *end = NULL; 377 int n; 378 379 /* parse number string */ 380 n = strtol(q_arg, &end, 10); 381 if ((q_arg[0] == '\0') || (end == NULL) || (*end != '\0')) 382 return -1; 383 if (n >= MAX_TIMER_PERIOD) 384 return -1; 385 386 return n; 387 } 388 389 //Parsing command-line parameters 390 /* Parse the argument given in the command line of the application */ 391 static int 392 l2fwd_parse_args(int argc, char **argv) 393 { 394 int opt, ret, timer_secs; 395 char **argvopt; 396 int option_index; 397 char *prgname = argv[0]; 398 static struct option lgopts[] = { 399 { "mac-updating", no_argument, &mac_updating, 1}, 400 { "no-mac-updating", no_argument, &mac_updating, 0}, 401 {NULL, 0, 0, 0} 402 }; 403 404 argvopt = argv; //copy argv Pointer 405 406 //Parse the command line, getopt_long()Can parse command line parameters 407 while ((opt = getopt_long(argc, argvopt, "p:q:T:", 408 lgopts, &option_index)) != EOF) { 409 410 //The command line has three parameters. p:portmask,n:nqueue,T: timer period 411 switch (opt) { 412 /* portmask */ 413 //port Number, expressed in hexadecimal, as 0. x0f Representation 15 414 case 'p': 415 //l2fwd_parse_portmask()Functions are custom functions 416 //Put the hexadecimal mask String conversion unsigned long. 417 //Port enablement 418 l2fwd_enabled_port_mask = l2fwd_parse_portmask(optarg); 419 if (l2fwd_enabled_port_mask == 0) { //mask 0 represents error 420 printf("invalid portmask\n"); 421 l2fwd_usage(prgname); //Print user options, similar to --help 422 return -1; //The parameter passing error returns-1,The result is an exit procedure. 423 } 424 break; 425 426 /* nqueue */ 427 //The number of queues is also expressed in hexadecimal strings. 428 case 'q': 429 //Several for each core configuration rx Queue. 430 l2fwd_rx_queue_per_lcore = l2fwd_parse_nqueue(optarg); 431 if (l2fwd_rx_queue_per_lcore == 0) { //lcore 0 Represent an error 432 printf("invalid queue number\n"); 433 l2fwd_usage(prgname); 434 return -1; //Return-1,The result is withdrawal from the process. 435 } 436 break; 437 438 /* timer period */ //Timer cycle 439 440 case 'T': 441 //Configure timer cycle in seconds 442 //Namely l2fwd How many seconds to run, expressed in hexadecimal. 443 timer_secs = l2fwd_parse_timer_period(optarg); 444 if (timer_secs < 0) { 445 printf("invalid timer period\n"); 446 l2fwd_usage(prgname); 447 return -1; 448 } 449 //timer_period Represents the test time of Layer 2 forwarding, which defaults to 10 seconds.-T To regulate time 450 timer_period = timer_secs; 451 break; 452 453 /* long options */ 454 //--The first option is not handled 455 case 0: 456 break; 457 458 default: 459 //Parameter Passing Error, Printing--help 460 l2fwd_usage(prgname); 461 return -1; 462 } 463 } 464 465 if (optind >= 0) 466 argv[optind-1] = prgname; 467 468 ret = optind-1; 469 optind = 0; /* reset getopt lib */ 470 return ret; 471 } 472 473 /* Check the link status of all ports in up to 9s, and print them finally */ 474 static void 475 check_all_ports_link_status(uint8_t port_num, uint32_t port_mask) 476 { 477 #define CHECK_INTERVAL 100 /* 100ms */ 478 #define MAX_CHECK_TIME 90 /* 9s (90 * 100ms) in total */ 479 uint8_t portid, count, all_ports_up, print_flag = 0; 480 struct rte_eth_link link; 481 482 printf("\nChecking link status"); 483 fflush(stdout); 484 for (count = 0; count <= MAX_CHECK_TIME; count++) { 485 if (force_quit) 486 return; 487 all_ports_up = 1; 488 for (portid = 0; portid < port_num; portid++) { 489 if (force_quit) 490 return; 491 if ((port_mask & (1 << portid)) == 0) 492 continue; 493 memset(&link, 0, sizeof(link)); 494 rte_eth_link_get_nowait(portid, &link); 495 /* print link status if flag set */ 496 if (print_flag == 1) { 497 if (link.link_status) 498 printf("Port %d Link Up - speed %u " 499 "Mbps - %s\n", (uint8_t)portid, 500 (unsigned)link.link_speed, 501 (link.link_duplex == ETH_LINK_FULL_DUPLEX) ? 502 ("full-duplex") : ("half-duplex\n")); 503 else 504 printf("Port %d Link Down\n", 505 (uint8_t)portid); 506 continue; 507 } 508 /* clear all_ports_up flag if any link down */ 509 if (link.link_status == ETH_LINK_DOWN) { 510 all_ports_up = 0; 511 break; 512 } 513 } 514 /* after finally printing all link status, get out */ 515 if (print_flag == 1) 516 break; 517 518 if (all_ports_up == 0) { 519 printf("."); 520 fflush(stdout); 521 rte_delay_ms(CHECK_INTERVAL); 522 } 523 524 /* set the print_flag if all ports up or timeout */ 525 if (all_ports_up == 1 || count == (MAX_CHECK_TIME - 1)) { 526 print_flag = 1; 527 printf("done\n"); 528 } 529 } 530 } 531 532 static void 533 signal_handler(int signum) 534 { 535 if (signum == SIGINT || signum == SIGTERM) { 536 printf("\n\nSignal %d received, preparing to exit...\n", 537 signum); 538 force_quit = true; //Forced exit button is true 539 } 540 } 541 542 int 543 main(int argc, char **argv) 544 { 545 /* 546 //Customized structure in front of the program 547 // __rte_cache_aligned Is a macro that represents memory for it 548 struct lcore_queue_conf { 549 unsigned n_rx_port; //rx_port Number 550 unsigned rx_port_list[MAX_RX_QUEUE_PER_LCORE]; //rx_port list 551 } __rte_cache_aligned; 552 struct lcore_queue_conf lcore_queue_conf[RTE_MAX_LCORE]; 553 //One computer, with multiple cores, and one core processing multiple rx_port s 554 */ 555 struct lcore_queue_conf *qconf; 556 557 558 struct rte_eth_dev_info dev_info; //Equipment Information 559 int ret; //Return value 560 uint8_t nb_ports; //total port Number 561 uint8_t nb_ports_available; //available port Number 562 uint8_t portid, last_port; //current portid,Previous portid. 563 unsigned lcore_id, rx_lcore_id; //core id,rx_lcore_id 564 unsigned nb_ports_in_mask = 0; //?? 565 566 /* init EAL */ 567 //Initialization environment 568 ret = rte_eal_init(argc, argv); 569 if (ret < 0) 570 rte_exit(EXIT_FAILURE, "Invalid EAL arguments\n"); 571 argc -= ret; //??Unknown, seemingly useless, so unknown 572 argv += ret; //??Unknown, seemingly useless, so unknown 573 574 force_quit = false; //Mandatory push button is false 575 //When captured SIGINT or SIGTERM When signal, push button is true. See details. signal_handler 576 //signal_handler For custom functions 577 signal(SIGINT, signal_handler); //Signal acquisition processing 1 578 signal(SIGTERM, signal_handler); //Signal acquisition processing 2 579 580 /* parse application arguments (after the EAL ones) */ 581 //Analytical Reference Transfer (Must be eal_init After that, this is a custom function, as detailed in the function definition 582 ret = l2fwd_parse_args(argc, argv); 583 if (ret < 0) 584 rte_exit(EXIT_FAILURE, "Invalid L2FWD arguments\n"); 585 586 printf("MAC updating %s\n", mac_updating ? "enabled" : "disabled"); 587 588 /* convert to number of cycles */ 589 //Getting the clock cycle of the timer 590 timer_period *= rte_get_timer_hz(); 591 592 /* create the mbuf pool */ 593 //Create a cache pool for storing data packets. 594 l2fwd_pktmbuf_pool = rte_pktmbuf_pool_create("mbuf_pool", NB_MBUF, 595 MEMPOOL_CACHE_SIZE, 0, RTE_MBUF_DEFAULT_BUF_SIZE, 596 rte_socket_id()); 597 if (l2fwd_pktmbuf_pool == NULL) 598 rte_exit(EXIT_FAILURE, "Cannot init mbuf pool\n"); 599 600 //Obtain Eth Number of mouths 601 nb_ports = rte_eth_dev_count(); 602 if (nb_ports == 0) 603 rte_exit(EXIT_FAILURE, "No Ethernet ports - bye\n"); 604 605 /* reset l2fwd_dst_ports */ 606 //Reset (clear 0) destination port. This block of code is used to initialize l2fwd_dst_ports 607 //Personal Comparisons of Writing low 608 for (portid = 0; portid < RTE_MAX_ETHPORTS; portid++) 609 l2fwd_dst_ports[portid] = 0; 610 last_port = 0; 611 612 /* 613 * Each logical core is assigned a dedicated TX queue on each port. 614 */ 615 //Set each port The purpose of the received packet to be forwarded port. 616 for (portid = 0; portid < nb_ports; portid++) { 617 /* skip ports that are not enabled */ 618 //Skip the Unenabled Port 619 if ((l2fwd_enabled_port_mask & (1 << portid)) == 0) 620 continue; 621 622 //Every two port Two-tier forwarding for one pair 623 //Send singular to singular+1,Send a digit to a digit-1 624 if (nb_ports_in_mask % 2) { 625 l2fwd_dst_ports[portid] = last_port; 626 l2fwd_dst_ports[last_port] = portid; 627 } 628 else 629 last_port = portid; //Yes last_port Assignment. 630 631 nb_ports_in_mask++; //Marking ++ 632 633 rte_eth_dev_info_get(portid, &dev_info); //Acquire correspondence portid Of dev information 634 } 635 //If there is only one network port left, the network port forwards itself to itself. 636 if (nb_ports_in_mask % 2) { 637 printf("Notice: odd number of ports in portmask.\n"); 638 l2fwd_dst_ports[last_port] = last_port; 639 } 640 641 rx_lcore_id = 0; 642 qconf = NULL; 643 644 //Initialize the queue configuration for each core 645 /* Initialize the port/queue configuration of each logical core */ 646 //Travel through all port 647 for (portid = 0; portid < nb_ports; portid++) { 648 /* skip ports that are not enabled */ 649 //Skip the Unenabled Port 650 if ((l2fwd_enabled_port_mask & (1 << portid)) == 0) 651 continue; 652 653 /* get the lcore_id for this port */ 654 //port Allocate one lcore_id. 655 //rte_lcore_is_enabled(rx_lcore_id) test core Enabling or not 656 //lcore_queue_conf Is a custom structure that contains port Number sum portid 657 //Meaning is one core, for multiple port Of rx queue 658 //Here, a core can only match one port 659 while (rte_lcore_is_enabled(rx_lcore_id) == 0 || 660 lcore_queue_conf[rx_lcore_id].n_rx_port == 661 l2fwd_rx_queue_per_lcore) { 662 rx_lcore_id++; 663 if (rx_lcore_id >= RTE_MAX_LCORE) 664 rte_exit(EXIT_FAILURE, "Not enough cores\n"); 665 } 666 667 //assignment qconf,qconf Start with NULL 668 if (qconf != &lcore_queue_conf[rx_lcore_id]) 669 /* Assigned a new logical core in the loop above. */ 670 qconf = &lcore_queue_conf[rx_lcore_id]; 671 672 //current lcore Add a port 673 //current lcore Management rx_port Total+1 674 qconf->rx_port_list[qconf->n_rx_port] = portid; 675 qconf->n_rx_port++; 676 printf("Lcore %u: RX port %u\n", rx_lcore_id, (unsigned) portid); 677 } 678 679 //Enabling port Total 680 nb_ports_available = nb_ports; 681 682 /* Initialise each port */ 683 //Getting Available port Number 684 for (portid = 0; portid < nb_ports; portid++) { 685 /* skip ports that are not enabled */ 686 //If it is not available, it will be cut off. 687 if ((l2fwd_enabled_port_mask & (1 << portid)) == 0) { 688 printf("Skipping disabled port %u\n", (unsigned) portid); 689 nb_ports_available--; 690 continue; 691 } 692 /* init port */ 693 //Initialization port 694 printf("Initializing port %u... ", (unsigned) portid); 695 fflush(stdout); 696 //To configure port,among port_conf Is a structure that contains information about port Configuration 697 //vlan Separation, crc Hardware validation considers these two useful. 698 ret = rte_eth_dev_configure(portid, 1, 1, &port_conf); 699 if (ret < 0) 700 rte_exit(EXIT_FAILURE, "Cannot configure device: err=%d, port=%u\n", 701 ret, (unsigned) portid); 702 703 //Obtain port Of mac address 704 //l2fwd_ports_eth_addr[] The type is a structure and is a global array. 705 rte_eth_macaddr_get(portid,&l2fwd_ports_eth_addr[portid]); 706 707 /* init one RX queue */ 708 //Initialization RX queue 709 fflush(stdout); 710 //rx The queue is bound to the current port Up, l2fwd_pktmbuf_pool For memory pool 711 ret = rte_eth_rx_queue_setup(portid, 0, nb_rxd, 712 rte_eth_dev_socket_id(portid), 713 NULL, 714 l2fwd_pktmbuf_pool); 715 if (ret < 0) 716 rte_exit(EXIT_FAILURE, "rte_eth_rx_queue_setup:err=%d, port=%u\n", 717 ret, (unsigned) portid); 718 719 /* init one TX queue on each port */ 720 //Initialization tx queue 721 fflush(stdout); 722 //tx Queues are bound to port upper 723 ret = rte_eth_tx_queue_setup(portid, 0, nb_txd, 724 rte_eth_dev_socket_id(portid), 725 NULL); 726 if (ret < 0) 727 rte_exit(EXIT_FAILURE, "rte_eth_tx_queue_setup:err=%d, port=%u\n", 728 ret, (unsigned) portid); 729 730 /* Initialize TX buffers */ 731 //malloc tx Caching, tx_buffer For pointer arrays, each port Correspond to one tx cache 732 tx_buffer[portid] = rte_zmalloc_socket("tx_buffer", 733 RTE_ETH_TX_BUFFER_SIZE(MAX_PKT_BURST), 0, 734 rte_eth_dev_socket_id(portid)); 735 if (tx_buffer[portid] == NULL) 736 rte_exit(EXIT_FAILURE, "Cannot allocate buffer for tx on port %u\n", 737 (unsigned) portid); 738 739 //Initialization tx cache 740 rte_eth_tx_buffer_init(tx_buffer[portid], MAX_PKT_BURST); 741 742 //tx When the cache is full, set the callback function 743 ret = rte_eth_tx_buffer_set_err_callback(tx_buffer[portid], 744 rte_eth_tx_buffer_count_callback, 745 &port_statistics[portid].dropped); 746 if (ret < 0) 747 rte_exit(EXIT_FAILURE, "Cannot set error callback for " 748 "tx buffer on port %u\n", (unsigned) portid); 749 750 /* Start device */ 751 //Start-up equipment 752 ret = rte_eth_dev_start(portid); 753 if (ret < 0) 754 rte_exit(EXIT_FAILURE, "rte_eth_dev_start:err=%d, port=%u\n", 755 ret, (unsigned) portid); 756 757 printf("done: \n"); 758 759 //Setting Network Card to Hybrid Mode 760 rte_eth_promiscuous_enable(portid); 761 762 //Printing port Of MAC address 763 printf("Port %u, MAC address: %02X:%02X:%02X:%02X:%02X:%02X\n\n", 764 (unsigned) portid, 765 l2fwd_ports_eth_addr[portid].addr_bytes[0], 766 l2fwd_ports_eth_addr[portid].addr_bytes[1], 767 l2fwd_ports_eth_addr[portid].addr_bytes[2], 768 l2fwd_ports_eth_addr[portid].addr_bytes[3], 769 l2fwd_ports_eth_addr[portid].addr_bytes[4], 770 l2fwd_ports_eth_addr[portid].addr_bytes[5]); 771 772 /* initialize port stats */ 773 //Initialization port attribute 774 memset(&port_statistics, 0, sizeof(port_statistics)); 775 } 776 777 //If the network card can be made to zero, then an error will be reported. 778 if (!nb_ports_available) { 779 rte_exit(EXIT_FAILURE, 780 "All available ports are disabled. Please set portmask.\n"); 781 } 782 783 //Check all port Of link attribute 784 check_all_ports_link_status(nb_ports, l2fwd_enabled_port_mask); 785 786 ret = 0; 787 /* launch per-lcore init on every lcore */ 788 //Start all lcore,Callback l2fwd_launch_one_lcore Function, parameter is NULL 789 rte_eal_mp_remote_launch(l2fwd_launch_one_lcore, NULL, CALL_MASTER); 790 //Travel through all lcore_id 791 RTE_LCORE_FOREACH_SLAVE(lcore_id) { 792 //Wait for all threads to end 793 if (rte_eal_wait_lcore(lcore_id) < 0) { 794 ret = -1; 795 break; 796 } 797 } 798 799 //Stop and close all port 800 for (portid = 0; portid < nb_ports; portid++) { 801 if ((l2fwd_enabled_port_mask & (1 << portid)) == 0) 802 continue; 803 printf("Closing port %d...", portid); 804 rte_eth_dev_stop(portid); 805 rte_eth_dev_close(portid); 806 printf(" Done\n"); 807 } 808 printf("Bye...\n"); 809 810 return ret; 811 }