 )]
)]
What is DNS?
Domain Name System is the phone book of the whole Internet. It can translate the domain name that can be understood into the IP address that can be understood by the machine, so that Internet users no longer need to directly contact the IP address that is difficult to read and understand.
The domain name system is very important in the Internet today, because the IP address of the server may change frequently. Without DNS, the client of the current server will not be able to connect to the target server once the IP address changes. If we provide an alias for the IP address and modify the alias and IP when it changes Address relationship, then we can ensure that the external services provided by the cluster can be relatively stable accessed by other clients.
DNS is actually a distributed tree naming system. It is like a decentralized distributed database, which stores the mapping from domain name to IP address.
Local name resolution profile: hosts
linux: /etc/hosts
windows: %WINDIR%/system32/drivers/etc/hosts
DNS is based on C/S architecture, server side: 53/udp, 53/tcp
FQDN: full name domain name = host name (alias) + domain name (organization, independent namespace)
BIND: Bekerley Internet Name Domain, implemented by DNS software provided by ISC
DNS domain name structure
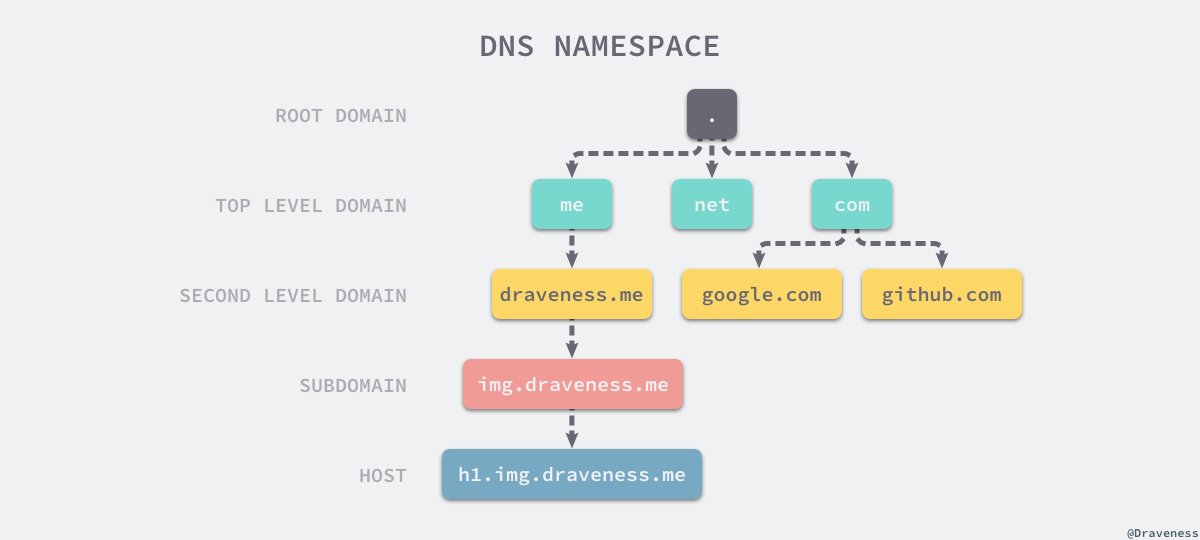
- Root domain
- TOP Level Domain - TLD
- com,edu,mil,gov,org...
- There are three types: organization domain and country domain ), reverse domain
- Secondary domain name: baidu.com
- Third level domain name: img.baidu.com
- Up to 127 domain names
How DNS works
Simply put: when you enter a domain name, DNS will return an IP address
Although only one IP address needs to be returned, the DNS query process is very complex and divided into many steps.
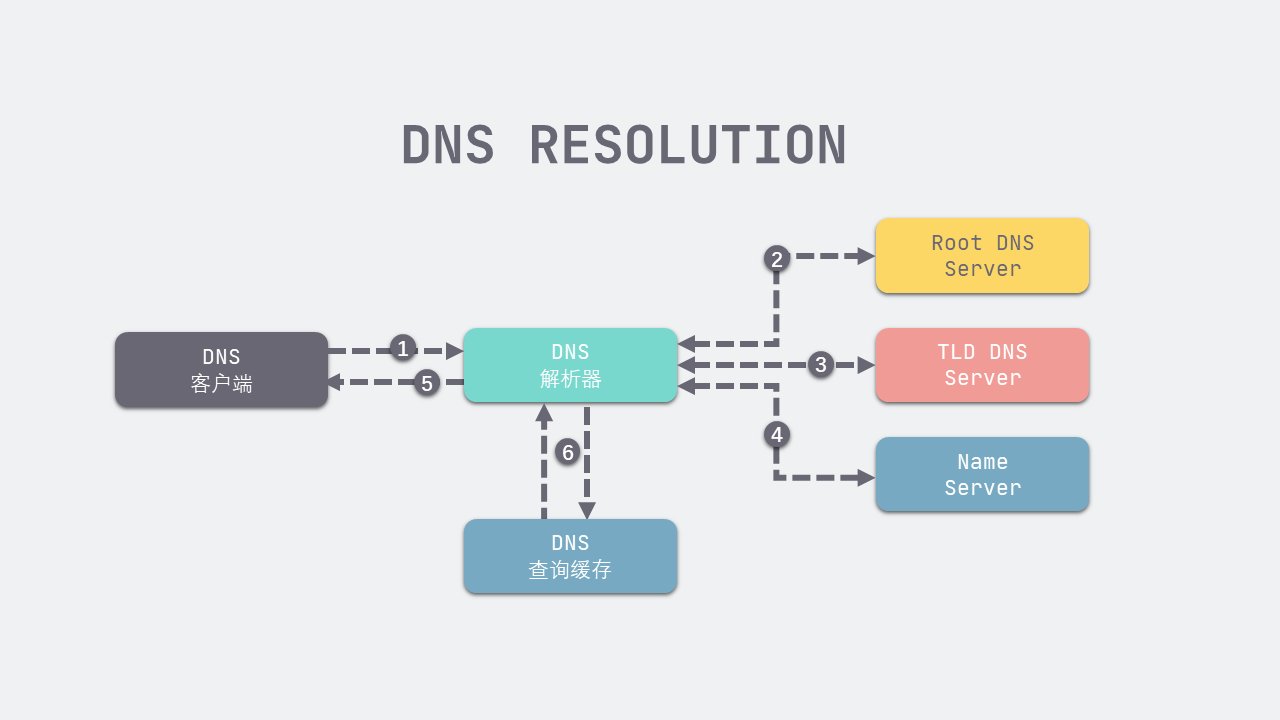
- DNS client sends resolution to DNS resolver www.baidu.com Domain name request
- The DNS resolver first requests the address of the top-level DNS server from the nearest root DNS server. Each DNS server knows the root server address
- After getting the address of the root domain DNS Service Com., you will ask the. COM domain name server for responsibility baidu.com . the name service of domain name resolution gets baidu.com . address information
- Get it baodu.com . the address of the domain name server is requested to be responsible to the domain name server www.baidu.com. Domain name resolution and return results to DNS resolver
- DNS resolver gives the result of resolution to DNS client
- The DNS resolver caches the resolution results in the DNS query cache, and then if you want to query the same domain name, you can directly read the cache content (the local machine also has a cache)
- window: ipconfig/display
- Linux: no cache by default, only local hosts file
Complete query request process
Client - hosts file - Client DNS Service Local Cache - DNS Server(recursion) - DNS Server Cache - Iteration - root - top level domain name DNS - secondary domain name DNS #recursion #iteration
After the DNS client receives the IP address, the whole DNS resolution process is over, and the client will send the request directly to the server through the current IP address.
For the DNS resolver, the DNS query method used here is iterative query. Each DNS service does not directly return DNS information, but returns the location of another DNS server. The client queries different levels of DNS services in turn until the expected results are obtained. Another query method is called recursive query, that is, DNS After receiving the client's request, the server will directly return accurate results. If the current server does not store DNS information, it will access other servers and return the results to the client.
Snowman project(Yeti DNS Project)
Root server It is the most important strategic infrastructure of the Internet and the "hub" of Internet communication. For a variety of reasons, the existing internet The number of root servers has been limited to 13. Global next generation Internet based on new technology architecture( IPv6 )Root server test and operation experiment project - "snowman plan". Officially released on June 23, 2015, Liu Dong, director of China's next generation Internet Engineering Center and the first executive chairman of the snowman plan, believes that the plan will break the root server dilemma and the global Internet is expected to achieve multilateral co governance.
In November 2017, it was reported that the "snowman plan" led by the next generation Internet National Engineering Center has completed the installation of 25 IPv6 (Internet Protocol version 6) root servers in the world, and 4 of them have been deployed in China, breaking the dilemma that China did not have root servers in the past.
DNS query type
- Recursive query: query to return the final result
- Iterative query: partial results are found and distributed query returns results
Resolution type
- FQDN > IP forward resolution
- IP - > FQDN reverse resolution
be careful
Forward and reverse parsing are two different namespaces, generally speaking, two different parse trees
DNS service related concepts and technologies
Type of DNS server
-
Primary DNS server
-
From DNS server
-
Cache DNS server (forwarder)
Primary DNS server
Manage and maintain the server of the domain resolution library responsible for resolution
From DNS server
"Copy" (zone transfer) resolution of a library copy from the primary server or from the server "
Serial number: the version number of the resolution library. The change of the main server resolution library is that its sequence is increasing
Refresh interval: the interval between requests for synchronous resolution from the master server from the slave server
Retry interval: failed to request synchronization from server yes, retry interval
Expiration time: when the master service cannot be reached from the server, how long before the service is stopped
Notification mechanism: when the primary server resolution library changes, it will actively notify the secondary server
Internet domain name
Domain name registration:
- Wanwang: acquired by Alibaba
- Xinwang: acquired by Tencent
- godaddy
DNS build software BIND
DNS server software: bind, powerdns, unbound
BIND related packages
[root@localhost ~]# yum list all bind* bind # The server bind-libs # Related Library bind-utils # client bind-chroot # Security package, put DNS related files to / var/named/chroot [root@localhost ~]# rpm -qa bind* bind-libs-lite-9.11.4-9.P2.el7.x86_64 bind-license-9.11.4-9.P2.el7.noarch bind-export-libs-9.11.4-9.P2.el7.x86_64 bind-utils-9.11.4-9.P2.el7.x86_64 bind-libs-9.11.4-9.P2.el7.x86_64
Install bind and bind utils
[root@localhost ~]# yum install bind bind-utils -y [root@localhost ~]# systemctl enable --now named Created symlink /etc/systemd/system/multi-user.target.wants/named.service → /usr/lib/systemd/system/named.service.
Common client testing tools for bind utils
[root@localhost ~]# rpm -ql bind-utils /etc/trusted-key.key /usr/bin/delv /usr/bin/dig /usr/bin/host /usr/bin/mdig /usr/bin/nslookup /usr/bin/nsupdate ...
bind file list
[root@localhost ~]# rpm -ql bind /etc/logrotate.d/named /etc/named /etc/named.conf # Master profile /etc/named.iscdlv.key /etc/named.rfc1912.zones /etc/named.root.key /etc/rndc.conf /etc/rndc.key /etc/rwtab.d/named /etc/sysconfig/named /run/named /usr/bin/arpaname /usr/bin/named-rrchecker /usr/lib/python2.7/site-packages/isc /usr/lib/python2.7/site-packages/isc-2.0-py2.7.egg-info /usr/lib/python2.7/site-packages/isc/__init__.py /usr/lib/python2.7/site-packages/isc/__init__.pyc /usr/lib/python2.7/site-packages/isc/__init__.pyo /usr/lib/python2.7/site-packages/isc/checkds.py /usr/lib/python2.7/site-packages/isc/checkds.pyc /usr/lib/python2.7/site-packages/isc/checkds.pyo /usr/lib/python2.7/site-packages/isc/coverage.py /usr/lib/python2.7/site-packages/isc/coverage.pyc /usr/lib/python2.7/site-packages/isc/coverage.pyo /usr/lib/python2.7/site-packages/isc/dnskey.py /usr/lib/python2.7/site-packages/isc/dnskey.pyc /usr/lib/python2.7/site-packages/isc/dnskey.pyo /usr/lib/python2.7/site-packages/isc/eventlist.py /usr/lib/python2.7/site-packages/isc/eventlist.pyc /usr/lib/python2.7/site-packages/isc/eventlist.pyo /usr/lib/python2.7/site-packages/isc/keydict.py /usr/lib/python2.7/site-packages/isc/keydict.pyc /usr/lib/python2.7/site-packages/isc/keydict.pyo /usr/lib/python2.7/site-packages/isc/keyevent.py /usr/lib/python2.7/site-packages/isc/keyevent.pyc /usr/lib/python2.7/site-packages/isc/keyevent.pyo /usr/lib/python2.7/site-packages/isc/keymgr.py /usr/lib/python2.7/site-packages/isc/keymgr.pyc /usr/lib/python2.7/site-packages/isc/keymgr.pyo /usr/lib/python2.7/site-packages/isc/keyseries.py /usr/lib/python2.7/site-packages/isc/keyseries.pyc /usr/lib/python2.7/site-packages/isc/keyseries.pyo /usr/lib/python2.7/site-packages/isc/keyzone.py /usr/lib/python2.7/site-packages/isc/keyzone.pyc /usr/lib/python2.7/site-packages/isc/keyzone.pyo /usr/lib/python2.7/site-packages/isc/parsetab.py /usr/lib/python2.7/site-packages/isc/parsetab.pyc /usr/lib/python2.7/site-packages/isc/parsetab.pyo /usr/lib/python2.7/site-packages/isc/policy.py /usr/lib/python2.7/site-packages/isc/policy.pyc /usr/lib/python2.7/site-packages/isc/policy.pyo /usr/lib/python2.7/site-packages/isc/rndc.py /usr/lib/python2.7/site-packages/isc/rndc.pyc /usr/lib/python2.7/site-packages/isc/rndc.pyo /usr/lib/python2.7/site-packages/isc/utils.py /usr/lib/python2.7/site-packages/isc/utils.pyc /usr/lib/python2.7/site-packages/isc/utils.pyo /usr/lib/systemd/system/named-setup-rndc.service /usr/lib/systemd/system/named.service # Service Documents /usr/lib/tmpfiles.d/named.conf /usr/lib64/bind /usr/libexec/generate-rndc-key.sh /usr/sbin/ddns-confgen /usr/sbin/dnssec-checkds /usr/sbin/dnssec-coverage /usr/sbin/dnssec-dsfromkey /usr/sbin/dnssec-importkey /usr/sbin/dnssec-keyfromlabel /usr/sbin/dnssec-keygen /usr/sbin/dnssec-keymgr /usr/sbin/dnssec-revoke /usr/sbin/dnssec-settime /usr/sbin/dnssec-signzone /usr/sbin/dnssec-verify /usr/sbin/genrandom /usr/sbin/isc-hmac-fixup /usr/sbin/lwresd /usr/sbin/named # main program /usr/sbin/named-checkconf /usr/sbin/named-checkzone /usr/sbin/named-compilezone /usr/sbin/named-journalprint /usr/sbin/nsec3hash /usr/sbin/rndc # Implement service shutdown or reload /usr/sbin/rndc-confgen /usr/sbin/tsig-keygen /usr/share/doc/bind-9.11.4 /usr/share/doc/bind-9.11.4/Bv9ARM.ch01.html /usr/share/doc/bind-9.11.4/Bv9ARM.ch02.html /usr/share/doc/bind-9.11.4/Bv9ARM.ch03.html /usr/share/doc/bind-9.11.4/Bv9ARM.ch04.html /usr/share/doc/bind-9.11.4/Bv9ARM.ch05.html /usr/share/doc/bind-9.11.4/Bv9ARM.ch06.html /usr/share/doc/bind-9.11.4/Bv9ARM.ch07.html /usr/share/doc/bind-9.11.4/Bv9ARM.ch08.html /usr/share/doc/bind-9.11.4/Bv9ARM.ch09.html /usr/share/doc/bind-9.11.4/Bv9ARM.ch10.html /usr/share/doc/bind-9.11.4/Bv9ARM.ch11.html /usr/share/doc/bind-9.11.4/Bv9ARM.ch12.html /usr/share/doc/bind-9.11.4/Bv9ARM.ch13.html /usr/share/doc/bind-9.11.4/Bv9ARM.html /usr/share/doc/bind-9.11.4/Bv9ARM.pdf /usr/share/doc/bind-9.11.4/CHANGES /usr/share/doc/bind-9.11.4/README /usr/share/doc/bind-9.11.4/isc-logo.pdf /usr/share/doc/bind-9.11.4/man.arpaname.html /usr/share/doc/bind-9.11.4/man.ddns-confgen.html /usr/share/doc/bind-9.11.4/man.delv.html /usr/share/doc/bind-9.11.4/man.dig.html /usr/share/doc/bind-9.11.4/man.dnssec-checkds.html /usr/share/doc/bind-9.11.4/man.dnssec-coverage.html /usr/share/doc/bind-9.11.4/man.dnssec-dsfromkey.html /usr/share/doc/bind-9.11.4/man.dnssec-importkey.html /usr/share/doc/bind-9.11.4/man.dnssec-keyfromlabel.html /usr/share/doc/bind-9.11.4/man.dnssec-keygen.html /usr/share/doc/bind-9.11.4/man.dnssec-keymgr.html /usr/share/doc/bind-9.11.4/man.dnssec-revoke.html /usr/share/doc/bind-9.11.4/man.dnssec-settime.html /usr/share/doc/bind-9.11.4/man.dnssec-signzone.html /usr/share/doc/bind-9.11.4/man.dnssec-verify.html /usr/share/doc/bind-9.11.4/man.dnstap-read.html /usr/share/doc/bind-9.11.4/man.genrandom.html /usr/share/doc/bind-9.11.4/man.host.html /usr/share/doc/bind-9.11.4/man.isc-hmac-fixup.html /usr/share/doc/bind-9.11.4/man.lwresd.html /usr/share/doc/bind-9.11.4/man.mdig.html /usr/share/doc/bind-9.11.4/man.named-checkconf.html /usr/share/doc/bind-9.11.4/man.named-checkzone.html /usr/share/doc/bind-9.11.4/man.named-journalprint.html /usr/share/doc/bind-9.11.4/man.named-nzd2nzf.html /usr/share/doc/bind-9.11.4/man.named-rrchecker.html /usr/share/doc/bind-9.11.4/man.named.conf.html /usr/share/doc/bind-9.11.4/man.named.html /usr/share/doc/bind-9.11.4/man.nsec3hash.html /usr/share/doc/bind-9.11.4/man.nslookup.html /usr/share/doc/bind-9.11.4/man.nsupdate.html /usr/share/doc/bind-9.11.4/man.pkcs11-destroy.html /usr/share/doc/bind-9.11.4/man.pkcs11-keygen.html /usr/share/doc/bind-9.11.4/man.pkcs11-list.html /usr/share/doc/bind-9.11.4/man.pkcs11-tokens.html /usr/share/doc/bind-9.11.4/man.rndc-confgen.html /usr/share/doc/bind-9.11.4/man.rndc.conf.html /usr/share/doc/bind-9.11.4/man.rndc.html /usr/share/doc/bind-9.11.4/named.conf.default /usr/share/doc/bind-9.11.4/notes.html /usr/share/doc/bind-9.11.4/notes.pdf /usr/share/doc/bind-9.11.4/sample /usr/share/doc/bind-9.11.4/sample/etc /usr/share/doc/bind-9.11.4/sample/etc/named.conf /usr/share/doc/bind-9.11.4/sample/etc/named.rfc1912.zones /usr/share/doc/bind-9.11.4/sample/var /usr/share/doc/bind-9.11.4/sample/var/named /usr/share/doc/bind-9.11.4/sample/var/named/data /usr/share/doc/bind-9.11.4/sample/var/named/my.external.zone.db /usr/share/doc/bind-9.11.4/sample/var/named/my.internal.zone.db /usr/share/doc/bind-9.11.4/sample/var/named/named.ca /usr/share/doc/bind-9.11.4/sample/var/named/named.empty /usr/share/doc/bind-9.11.4/sample/var/named/named.localhost /usr/share/doc/bind-9.11.4/sample/var/named/named.loopback /usr/share/doc/bind-9.11.4/sample/var/named/slaves /usr/share/doc/bind-9.11.4/sample/var/named/slaves/my.ddns.internal.zone.db /usr/share/doc/bind-9.11.4/sample/var/named/slaves/my.slave.internal.zone.db /usr/share/man/man1/arpaname.1.gz /usr/share/man/man1/named-rrchecker.1.gz /usr/share/man/man5/named.conf.5.gz /usr/share/man/man5/rndc.conf.5.gz /usr/share/man/man8/ddns-confgen.8.gz /usr/share/man/man8/dnssec-checkds.8.gz /usr/share/man/man8/dnssec-coverage.8.gz /usr/share/man/man8/dnssec-dsfromkey.8.gz /usr/share/man/man8/dnssec-importkey.8.gz /usr/share/man/man8/dnssec-keyfromlabel.8.gz /usr/share/man/man8/dnssec-keygen.8.gz /usr/share/man/man8/dnssec-keymgr.8.gz /usr/share/man/man8/dnssec-revoke.8.gz /usr/share/man/man8/dnssec-settime.8.gz /usr/share/man/man8/dnssec-signzone.8.gz /usr/share/man/man8/dnssec-verify.8.gz /usr/share/man/man8/genrandom.8.gz /usr/share/man/man8/isc-hmac-fixup.8.gz /usr/share/man/man8/lwresd.8.gz /usr/share/man/man8/named-checkconf.8.gz /usr/share/man/man8/named-checkzone.8.gz /usr/share/man/man8/named-compilezone.8.gz /usr/share/man/man8/named-journalprint.8.gz /usr/share/man/man8/named.8.gz /usr/share/man/man8/nsec3hash.8.gz /usr/share/man/man8/rndc-confgen.8.gz /usr/share/man/man8/rndc.8.gz /usr/share/man/man8/tsig-keygen.8.gz /var/log/named.log /var/named /var/named/data /var/named/dynamic /var/named/named.ca /var/named/named.empty /var/named/named.localhost /var/named/named.loopback /var/named/slaves
Start service
[root@localhost ~]# systemctl start named [root@localhost ~]# systemctl enable named Created symlink from /etc/systemd/system/multi-user.target.wants/named.service to /usr/lib/systemd/system/named.service.
View port
[root@localhost ~]# ss -nutlp Netid State Recv-Q Send-Q Local Address:Port Peer Address:Port udp UNCONN 0 0 [::1]:53 [::]:* users:(("named",pid=67617,fd=513)) tcp LISTEN 0 128 [::1]:953 [::]:* users:(("named",pid=67617,fd=24)) tcp LISTEN 0 10 [::1]:53 [::]:* users:(("named",pid=67617,fd=22))
Build DNS master server
preparation
Two hosts, one as DNS server and one as client
Set / etc of DNS server/ resolv.conf File, point DNS to your own IP
[root@localhost ~]# vim /etc/sysconfig/network-scripts/ifcfg-ens33 PROXY_METHOD=none BROWSER_ONLY=no BOOTPROTO=dhcp DEFROUTE=yes IPV4_FAILURE_FATAL=no IPV6INIT=yes IPV6_AUTOCONF=yes IPV6_DEFROUTE=yes IPV6_FAILURE_FATAL=no IPV6_ADDR_GEN_MODE=stable-privacy NAME=ens33 UUID=fc4d728c-858c-41f2-9a0f-8bcbcdfdb804 DEVICE=ens33 ONBOOT=yes DNS1=127.0.0.1 DNS2=180.76.76.76
After the change, it will take effect
nmcli connection reload nmcli connection up ens33
After taking effect / etc/resolv.conf The DNS content of has changed
[root@localhost ~]# nmcli connection reload [root@localhost ~]# nmcli connection up ens33 Connection successfully activated (D-Bus active path: /org/freedesktop/NetworkManager/ActiveConnection/4) [root@localhost ~]# cat /etc/resolv.conf # Generated by NetworkManager search localdomain CentOS8 nameserver 127.0.0.1 nameserver 180.76.76.76
Use test tools host, dig, nslookup
host www.baidu.com DNSSERVER dig www.baidu.com @DNSSERVER nslookup Can be interactive
host
[root@localhost ~]# host www.baidu.com 127.0.0.1 Using domain server: Name: 127.0.0.1 Address: 127.0.0.1#53 Aliases: www.baidu.com is an alias for www.a.shifen.com. www.a.shifen.com has address 14.215.177.38 www.a.shifen.com has address 14.215.177.39
dig
[root@localhost ~]# dig www.baidu.com @127.0.0.1 ; <<>> DiG 9.11.13-RedHat-9.11.13-3.el8 <<>> www.baidu.com @127.0.0.1 ;; global options: +cmd ;; Got answer: ;; ->>HEADER<<- opcode: QUERY, status: NOERROR, id: 46479 ;; flags: qr rd ra; QUERY: 1, ANSWER: 3, AUTHORITY: 5, ADDITIONAL: 6 ;; OPT PSEUDOSECTION: ; EDNS: version: 0, flags:; udp: 4096 ; COOKIE: 49986308e0fe172f521523215ee786b8e2cf8877826cd9f9 (good) ;; QUESTION SECTION:# Request options, will www.baidu.com Resolve to A ;www.baidu.com. IN A ;; ANSWER SECTION:# Return results www.baidu.com. 1142 IN CNAME www.a.shifen.com. www.a.shifen.com. 244 IN A 14.215.177.38 www.a.shifen.com. 244 IN A 14.215.177.39 ;; AUTHORITY SECTION: a.shifen.com. 1143 IN NS ns2.a.shifen.com. a.shifen.com. 1143 IN NS ns1.a.shifen.com. a.shifen.com. 1143 IN NS ns5.a.shifen.com. a.shifen.com. 1143 IN NS ns4.a.shifen.com. a.shifen.com. 1143 IN NS ns3.a.shifen.com. ;; ADDITIONAL SECTION: ns1.a.shifen.com. 1143 IN A 61.135.165.224 ns4.a.shifen.com. 1143 IN A 14.215.177.229 ns5.a.shifen.com. 1143 IN A 180.76.76.95 ns3.a.shifen.com. 1143 IN A 112.80.255.253 ns2.a.shifen.com. 1143 IN A 220.181.33.32 ;; Query time: 0 msec ;; SERVER: 127.0.0.1#53(127.0.0.1) ;; WHEN: Mon Jun 15 10:33:28 EDT 2020 ;; MSG SIZE rcvd: 299
nslookup: both windows and linux support and are interactive
[root@localhost ~]# nslookup > server 127.0.0.1 Default server: 127.0.0.1 Address: 127.0.0.1#53 > www.baidu.com Server: 127.0.0.1 Address: 127.0.0.1#53 Non-authoritative answer:# Non authoritative result www.baidu.com canonical name = www.a.shifen.com. Name: www.a.shifen.com Address: 14.215.177.38 Name: www.a.shifen.com Address: 14.215.177.39
Whether the content queried is an authoritative result
[root@localhost ~]# dig www.baidu.com @106.11.211.61 ; <<>> DiG 9.11.13-RedHat-9.11.13-3.el8 <<>> www.baidu.com @106.11.211.61 ;; global options: +cmd ;; Got answer: ;; ->>HEADER<<- opcode: QUERY, status: NXDOMAIN, id: 675 ;; flags: qr aa rd; QUERY: 1, ANSWER: 0, AUTHORITY: 1, ADDITIONAL: 1 #aa here is the authoritative result ;; WARNING: recursion requested but not available ;; OPT PSEUDOSECTION: ; EDNS: version: 0, flags:; udp: 4096 ;; QUESTION SECTION: ;www.baidu.com. IN A ;; AUTHORITY SECTION: baidu.com. 600 IN SOA ns1.alidns.com. hostmaster.hichina.com. 2019090319 3600 1200 86400 360 ;; Query time: 34 msec ;; SERVER: 106.11.211.61#53(106.11.211.61) ;; WHEN: Mon Jun 15 10:43:10 EDT 2020 ;; MSG SIZE rcvd: 114
[root@localhost ~]# nslookup > server 106.11.211.61 Default server: 106.11.211.61 Address: 106.11.211.61#53 > www.baidu.com Server: 106.11.211.61 Address: 106.11.211.61#53 www.baidu.com canonical name = www.a.shifen.com. Name: www.a.shifen.com Address: 14.215.177.38 Name: www.a.shifen.com Address: 14.215.177.39
Listen to all addresses by DNS Service
Modify profile
[root@localhost ~]# rpm -qc bind /etc/logrotate.d/named /etc/named.conf /etc/named.rfc1912.zones /etc/named.root.key /etc/rndc.conf /etc/rndc.key /etc/sysconfig/named /var/named/named.ca /var/named/named.empty /var/named/named.localhost /var/named/named.loopback # /etc/named.conf
[root@localhost ~]# vim /etc/named.conf // // named.conf // // // See /usr/share/doc/bind*/sample/ for example named configuration files. // listen-on port 53 { 127.0.0.1; };//Modify the configuration localhost or 0.0.0.0; note that this line has the same effect listen-on-v6 port 53 { ::1; }; directory "/var/named";//Specify default file path dump-file "/var/named/data/cache_dump.db"; statistics-file "/var/named/data/named_stats.txt"; memstatistics-file "/var/named/data/named_mem_stats.txt"; secroots-file "/var/named/data/named.secroots"; recursing-file "/var/named/data/named.recursing"; allow-query { localhost; };//Who is allowed to query can be changed to any; comments in this line have the same effect /* - If you are building an AUTHORITATIVE DNS server, do NOT enable recursion. - If you are building a RECURSIVE (caching) DNS server, you need to enable recursion. control to limit queries to your legitimate users. Failing to do so will cause your server to become part of large scale DNS amplification attacks. Implementing BCP38 within your network would greatly reduce such attack surface */ recursion yes; dnssec-enable yes; //It is better to change these two items to no, encryption option dnssec-validation yes; managed-keys-directory "/var/named/dynamic"; pid-file "/run/named/named.pid"; session-keyfile "/run/named/session.key"; /* https://fedoraproject.org/wiki/Changes/CryptoPolicy */ include "/etc/crypto-policies/back-ends/bind.config"; }; logging { channel default_debug { file "data/named.run"; severity dynamic; }; }; zone "." IN { type hint; file "named.ca";// There are 13ipv4 root server addresses on the Internet, and the file path is in the directory "/ var / named" above }; // Refer to the configuration files of other regions. We should also use this reference method when adding our own domain include "/etc/named.rfc1912.zones"; include "/etc/named.root.key";
Check syntax
[root@localhost ~]# named-checkconf [root@localhost ~]# rndc reload server reload successful
At this time, DNS forwarder function can be realized
see named.ca content
[root@localhost ~]# cat /var/named/named.ca ; <<>> DiG 9.11.3-RedHat-9.11.3-3.fc27 <<>> +bufsize=1200 +norec @a.root-servers.net ; (2 servers found) ;; global options: +cmd ;; Got answer: ;; ->>HEADER<<- opcode: QUERY, status: NOERROR, id: 46900 ;; flags: qr aa; QUERY: 1, ANSWER: 13, AUTHORITY: 0, ADDITIONAL: 27 ;; OPT PSEUDOSECTION: ; EDNS: version: 0, flags:; udp: 1472 ;; QUESTION SECTION: ;. IN NS ;; ANSWER SECTION:# 13 root servers . 518400 IN NS a.root-servers.net. . 518400 IN NS b.root-servers.net. . 518400 IN NS c.root-servers.net. . 518400 IN NS d.root-servers.net. . 518400 IN NS e.root-servers.net. . 518400 IN NS f.root-servers.net. . 518400 IN NS g.root-servers.net. . 518400 IN NS h.root-servers.net. . 518400 IN NS i.root-servers.net. . 518400 IN NS j.root-servers.net. . 518400 IN NS k.root-servers.net. . 518400 IN NS l.root-servers.net. . 518400 IN NS m.root-servers.net. ;; ADDITIONAL SECTION: # IPV4 address a.root-servers.net. 518400 IN A 198.41.0.4 b.root-servers.net. 518400 IN A 199.9.14.201 c.root-servers.net. 518400 IN A 192.33.4.12 d.root-servers.net. 518400 IN A 199.7.91.13 e.root-servers.net. 518400 IN A 192.203.230.10 f.root-servers.net. 518400 IN A 192.5.5.241 g.root-servers.net. 518400 IN A 192.112.36.4 h.root-servers.net. 518400 IN A 198.97.190.53 i.root-servers.net. 518400 IN A 192.36.148.17 j.root-servers.net. 518400 IN A 192.58.128.30 k.root-servers.net. 518400 IN A 193.0.14.129 l.root-servers.net. 518400 IN A 199.7.83.42 m.root-servers.net. 518400 IN A 202.12.27.33 # IPV6 address cache time 518400 in seconds a.root-servers.net. 518400 IN AAAA 2001:503:ba3e::2:30 b.root-servers.net. 518400 IN AAAA 2001:500:200::b c.root-servers.net. 518400 IN AAAA 2001:500:2::c d.root-servers.net. 518400 IN AAAA 2001:500:2d::d e.root-servers.net. 518400 IN AAAA 2001:500:a8::e f.root-servers.net. 518400 IN AAAA 2001:500:2f::f g.root-servers.net. 518400 IN AAAA 2001:500:12::d0d h.root-servers.net. 518400 IN AAAA 2001:500:1::53 i.root-servers.net. 518400 IN AAAA 2001:7fe::53 j.root-servers.net. 518400 IN AAAA 2001:503:c27::2:30 k.root-servers.net. 518400 IN AAAA 2001:7fd::1 l.root-servers.net. 518400 IN AAAA 2001:500:9f::42 m.root-servers.net. 518400 IN AAAA 2001:dc3::35 ;; Query time: 24 msec ;; SERVER: 198.41.0.4#53(198.41.0.4) ;; WHEN: Thu Apr 05 15:57:34 CEST 2018 ;; MSG SIZE rcvd: 811
Try to reload instead of restarting the service after changing the configuration
- The PID will be changed after restarting the service, resulting in the disconnection of the user in use
rndc reload
Implement forward parsing
take flamenca.cn Resolve to IP
Primary forward resolution DNS server
type: master
type: hint
Primary DNS server configuration
// In / etc/named.conf in // Comment out the following two lines // listen-on port 53 { 127.0.0.1; }; // allow-query { localhost; }; // Domain name resolution scope zone "ZONE_NAME" IN { type {hint|master|slave|forward}; file "ZONE_NAME.zone"; }; // Import data configuration through include include "/etc/named.XXX.zones"; // as include "/etc/named.rfc1912.zones";
View the file include "/etc/named.rfc1912.zones";
[root@localhost ~]# vim /etc/named.rfc1912.zones // named.rfc1912.zones: // // Provided by Red Hat caching-nameserver package // // ISC BIND named zone configuration for zones recommended by // RFC 1912 section 4.1 : localhost TLDs and address zones // and https://tools.ietf.org/html/rfc6303 // (c)2007 R W Franks // // See /usr/share/doc/bind*/sample/ for example named configuration files. // // Note: empty-zones-enable yes; option is default. // If private ranges should be forwarded, add // disable-empty-zone "."; into options // zone "flamenca.com" IN { type master; file "flamenca.com.zone" //Prepare to create the directory } zone "localhost.localdomain" IN { type master; file "named.localhost"; allow-update { none; }; }; zone "localhost" IN { type master; file "named.localhost"; allow-update { none; }; }; zone "1.0.0.0.0.0.0.0.0.0.0.0.0.0.0.0.0.0.0.0.0.0.0.0.0.0.0.0.0.0.0.0.ip6.arpa" IN { type master; file "named.loopback"; allow-update { none; }; }; zone "1.0.0.127.in-addr.arpa" IN { type master; file "named.loopback"; allow-update { none; }; }; zone "0.in-addr.arpa" IN { type master; file "named.empty"; allow-update { none; }; };
Set zone file permissions, all groups
When creating a zone file, you need to pay attention to permission matching: permissions are generally 640, and all groups are named
[root@localhost named]# cd /var/named/ [root@localhost named]# ll total 16 drwxrwx---. 2 named named 23 Jun 15 10:31 data drwxrwx---. 2 named named 60 Jun 17 06:50 dynamic -rw-r-----. 1 root named 2253 Apr 24 09:54 named.ca -rw-r-----. 1 root named 152 Apr 24 09:54 named.empty -rw-r-----. 1 root named 152 Apr 24 09:54 named.localhost -rw-r-----. 1 root named 168 Apr 24 09:54 named.loopback drwxrwx---. 2 named named 6 Apr 24 09:54 slaves
Why not run the permissions of other users? If other users have permissions, hackers will know the company's network architecture and attack it
Create my zone file
[root@localhost named]# pwd /var/named [root@localhost named]# touch flamenca.com.zone [root@localhost named]# id named uid=25(named) gid=25(named) groups=25(named) # Modify group [root@localhost named]# chgrp named flamenca.com.zone [root@localhost named]# ll total 16 drwxrwx---. 2 named named 23 Jun 15 10:31 data drwxrwx---. 2 named named 60 Jun 17 06:50 dynamic # My new file -rw-r--r-- 1 root named 0 Jun 17 07:41 flamenca.com.zone -rw-r-----. 1 root named 2253 Apr 24 09:54 named.ca -rw-r-----. 1 root named 152 Apr 24 09:54 named.empty -rw-r-----. 1 root named 152 Apr 24 09:54 named.localhost -rw-r-----. 1 root named 168 Apr 24 09:54 named.loopback drwxrwx---. 2 named named 6 Apr 24 09:54 slaves [root@localhost named]# chmod o= flamenca.com.zone [root@localhost named]# ll flamenca.com.zone -rw-r----- 1 root named 0 Jun 17 07:41 flamenca.com.zone
zone file content reference
# You can refer to namd.localhost [root@localhost named]# pwd /var/named [root@localhost named]# cat named.localhost ############### SOA ####################### $TTL 1D # 1D=1 day # Managed local domain @ IN SOA @ rname.invalid. ( 0 ; serial # serial number 1D ; refresh 1H ; retry 1W ; expire 3H ) ; minimum # TTL value of negative answer # The previous IP does not write, i.e. inherits from the previous one@ NS @ A 127.0.0.1 AAAA ::1 ###############################################
Various resource records
Regional resolution Library: it is composed of many RR s:
Resource Record: Resource Record, RR
Record type: A, AAAA, RTP, SOA, NS, CNAME, MX
-
SOA: Start Of Authority, start authorization record; an area resolution library has and can only have one SOA record, which must be in the first record of the resolution Library
-
A: Internet Address, function, FQDN -- > IP
-
AAAA: FQDN->IPv6
-
PTR: PoinTeR,IP->FQDN
-
NS: Name Server, specifically used to indicate the DNS server of the current zone
-
CNAME: Canonical Name, alias record
-
MX: Mail eXchange
-
TXT: a way to identify and explain the domain name. Generally, this item is used when making verification records, such as SPF (anti spam) records, https verification, etc., as follows:
_dnsauth TXT XXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXX
Format of resource record (RR) definition
name [TTL] IN rr_type value #Domain name cache time fixed value above resource type IP
be careful:
- TTL can inherit from the global
- Use the "@" symbol to refer to the name of the current area
- The same name can define multiple different values through multiple records. At this time, the DNS server will respond by polling
- The same value may have multiple different definition names, which are defined by multiple different names pointing to the same value; this only means that the same host can be found by multiple different names
Master-slave server synchronization mechanism
PUSH:
The master server pushes the data to the slave server for synchronization
PULL:
The slave server pulls the data of the master server to itself for synchronization; there is a time interval
Slave server serial number mechanism
- Resolution library version number: when the resolution library changes from the server, its sequence is incremented
- Refresh interval: the interval between requests for synchronous resolution from the master server from the slave server
- Retry interval: when synchronization from the server fails, retry interval
- Expiration time: when the secondary server cannot reach the primary server, how long before the service is stopped
- Notification mechanism (push operation): when the primary server resolution library changes, it will actively notify the secondary server
Judge the condition of data update: serial number of database
SOA record
- Name: the name of the current area. For example " flamenca.com "
- value: there are many parts
be careful:
-
FQDN of the primary DNS server of the current zone, or the name of the current zone
-
The mailbox address of the current area administrator; however, the @ symbol cannot be used in the address. For example: admin.flamenca.com
-
Transfer the unified TTL of related definitions and negative answers from the main service area
example:
# Primary DNS server name administrator mailbox flameca.com. 86400 IN SOA ns.flamenca.com. admin.flamenca.com. ( 1234 ;# serial number 2H ;# Refresh time 10M ;# Retry time 1W ;# Expiration time Week 1D ;# The TTL value of the negative answer will cache the nonexistent and wrong records )
Start copywriting
$TTL 1D @ IN SOA ns1.flamenca.com. admin.flamenca.com.( 20200618 ; 1D ; 10M ; 3D ; 2H) ; NS ns1 ns1 A 192.168.33.129 webserv A 192.168.33.130 www CNAME webserv app A 1.1.1.1 db A 2.2.2.2
Check whether the format of configuration file and zone file is correct
[root@localhost named]# named-checkconf [root@localhost named]# named-checkzone flamenca.com /var/named/flamenca.com.zone zone flamenca.com/IN: loaded serial 20200618 OK
Configuration complete reload
[root@localhost named]# rndc reload server reload successful
dig test www.flamenca.com
[root@localhost named]# dig www.flamenca.com ; <<>> DiG 9.11.13-RedHat-9.11.13-3.el8 <<>> www.flamenca.com ;; global options: +cmd ;; Got answer: ;; ->>HEADER<<- opcode: QUERY, status: NOERROR, id: 45146 ;; flags: qr aa rd ra; QUERY: 1, ANSWER: 2, AUTHORITY: 1, ADDITIONAL: 2 ;; display aa ;; OPT PSEUDOSECTION: ; EDNS: version: 0, flags:; udp: 4096 ; COOKIE: 92156a57011b8a24f1b619f95eeb77481eedcaa191394c91 (good) ;; QUESTION SECTION: ;www.flamenca.com. IN A ;; ANSWER SECTION: ;;CNAME Resolution successful www.flamenca.com. 86400 IN CNAME webserv.flamenca.com. webserv.flamenca.com. 86400 IN A 192.168.33.130 ;; AUTHORITY SECTION: flamenca.com. 86400 IN NS master.flamenca.com. ;; ADDITIONAL SECTION: master.flamenca.com. 86400 IN A 192.168.33.129 ;; Query time: 0 msec ;; SERVER: 192.168.33.129#53(192.168.33.129) ;; WHEN: Thu Jun 18 10:16:40 EDT 2020 ;; MSG SIZE rcvd: 148
Open another virtual machine 192.168.33.130
# Install httpd service [root@localhost ~]# echo www.flamenca.com > /var/www/html/index.html [root@localhost ~]# systemctl start httpd
curl visit website content
[root@localhost named]# curl www.flamenca.com www.flamenca.com
Forward resolution is now complete.
A record
name: FQDN of a host
value: IP address of the host corresponding to the host name
To avoid giving wrong answers when users write wrong names, they can resolve to specific addresses through pan domain name resolution
www.flamenca.com. IN A 192.168.33.129 $GENERATE 1-254 HOST$ IN A 1.2.3.$ *.flamenca.com. IN A 192.168.33.129
Allow dynamic updates
Dynamic update: the resource records of the regional database can be updated remotely. There are security risks
To implement dynamic update, you need to add the specified zone statement block
Allow-update {any;} # IP can be added in braces to specify the host that can change the database remotely

Implement reverse parsing area
ARPA top level domain
IP > FQDN
# 192.168.33.130->www.flamenca.com # Parse according to the reverse format of: 130.33.168.192 # Domain name: 33.168.192.in-addr.arpa
Establish reverse area
[root@localhost named]# vim /etc/named.rfc1912.zones // named.rfc1912.zones: // // Provided by Red Hat caching-nameserver package // // ISC BIND named zone configuration for zones recommended by // RFC 1912 section 4.1 : localhost TLDs and address zones // and https://tools.ietf.org/html/rfc6303 // (c)2007 R W Franks // // See /usr/share/doc/bind*/sample/ for example named configuration files. // // Note: empty-zones-enable yes; option is default. // If private ranges should be forwarded, add // disable-empty-zone "."; into options // zone "localhost.localdomain" IN { type master; file "named.localhost"; allow-update { none; }; }; ... // Example of reverse region zone "1.0.0.127.in-addr.arpa" IN { type master; file "named.loopback"; allow-update { none; }; }; // Parody zone "33.168.192.in-addr.arpa" IN { type master; file "192.168.33.zone" }; zone "0.in-addr.arpa" IN { type master; file "named.empty"; allow-update { none; }; }; zone "flamenca.com" IN { type master; file "flamenca.com.zone"; };
Create the corresponding 192.168.33.zone file
[root@localhost named]# cd /var/named [root@localhost named]# vim 192.168.33.zone $TTL 1D @ IN SOA master.flamenca.com. admin.flamenca.com. ( 0 ; serial 1D ; refresh 1H ; retry 1W ; expire 3H ) ; minimum NS master.flamenca.com. ; master.flamenca.com master.flamenca.com. A 192.168.33.129 ; DNS server IP 130 PTR www.flamenca.com. ; 130=192.168.33.130 129 PTR master.flamenca.com.
Dig-t PTR test
[root@localhost named]# dig -t ptr 130.33.168.192.in-addr.arpa ; <<>> DiG 9.11.13-RedHat-9.11.13-3.el8 <<>> -t ptr 130.33.168.192.in-addr.arpa ;; global options: +cmd ;; Got answer: ;; ->>HEADER<<- opcode: QUERY, status: NOERROR, id: 57764 ;; flags: qr aa rd ra; QUERY: 1, ANSWER: 1, AUTHORITY: 1, ADDITIONAL: 2 ;; OPT PSEUDOSECTION: ; EDNS: version: 0, flags:; udp: 4096 ; COOKIE: 4144c2e7128bcbfe71b5ddc85eeb903f2aff58e8dfc42c99 (good) ;; QUESTION SECTION: ;130.33.168.192.in-addr.arpa. IN PTR ;; ANSWER SECTION: 130.33.168.192.in-addr.arpa. 86400 IN PTR www.flamenca.com. ;; AUTHORITY SECTION: 33.168.192.in-addr.arpa. 86400 IN NS master.flamenca.com. ;; ADDITIONAL SECTION: master.flamenca.com. 86400 IN A 192.168.33.129 ;; Query time: 0 msec ;; SERVER: 192.168.33.129#53(192.168.33.129) ;; WHEN: Thu Jun 18 12:03:11 EDT 2020 ;; MSG SIZE rcvd: 151
Dig-x reverse parsing command
[root@localhost named]# dig -x 192.168.33.130 ; <<>> DiG 9.11.13-RedHat-9.11.13-3.el8 <<>> -x 192.168.33.130 ;; global options: +cmd ;; Got answer: ;; ->>HEADER<<- opcode: QUERY, status: NOERROR, id: 48564 ;; flags: qr aa rd ra; QUERY: 1, ANSWER: 1, AUTHORITY: 1, ADDITIONAL: 2 ;; OPT PSEUDOSECTION: ; EDNS: version: 0, flags:; udp: 4096 ; COOKIE: 89904e21ae5e908c7364f7c45eeb90b72b27912d58d0fa0c (good) ;; QUESTION SECTION: ;130.33.168.192.in-addr.arpa. IN PTR ;; ANSWER SECTION: 130.33.168.192.in-addr.arpa. 86400 IN PTR www.flamenca.com. ;; AUTHORITY SECTION: 33.168.192.in-addr.arpa. 86400 IN NS master.flamenca.com. ;; ADDITIONAL SECTION: master.flamenca.com. 86400 IN A 192.168.33.129 ;; Query time: 0 msec ;; SERVER: 192.168.33.129#53(192.168.33.129) ;; WHEN: Thu Jun 18 12:05:11 EDT 2020 ;; MSG SIZE rcvd: 151
In the mail, it can check whether it is a legal host through reverse parsing to eliminate spam
Multiple hosts
Build multiple DNS servers to realize fault tolerance
One host points to multiple IP S
$TTL 1D @ IN SOA ns1.flamenca.com. admin.flamenca.com.( 20200618 ; 1D ; 10M ; 3D ; 2H) ; NS ns1 ns1 A 192.168.33.129 ##########One host points to multiple IP Fault tolerance########### webserv A 192.168.33.130 webserv A 192.168.33.131 webserv A 192.168.33.132 #####It is a domain name externally and multiple servers behind it to achieve load balancing##### www CNAME webserv app A 1.1.1.1 db A 2.2.2.2
Fault tolerance
The user clicks the wrong domain name and points to the set host with the pan domain name
$TTL 1D @ IN SOA ns1.flamenca.com. admin.flamenca.com.( 20200618 ; 1D ; 10M ; 3D ; 2H) ; NS ns1 ns1 A 192.168.33.129 webserv A 192.168.33.130 www CNAME webserv app A 1.1.1.1 db A 2.2.2.2 ########Pan domain name############## * CNAME webserv ########################### # Enter other content to point to the webserv host
Note: * cannot match empty content
*Can't match without prefix flamenca.com
Solution
$TTL 1D @ IN SOA ns1.flamenca.com. admin.flamenca.com.( 20200618 ; 1D ; 10M ; 3D ; 2H) ; NS ns1 ns1 A 192.168.33.129 webserv A 192.168.33.130 www CNAME webserv app A 1.1.1.1 db A 2.2.2.2 ########Pan domain name############## * CNAME webserv ########################### # Enter other content to point to the webserv host #########@wildcard A record############ @ A 192.168.33.129 ##########Cannot point to alias CNAME######

Set up slave server
The main function is to realize data synchronization
Virtual machine 192.168.33.130 is the slave server
[root@localhost ~]# yum install bind -y
Modify profile
[root@localhost ~]# vim /etc/named.conf // // named.conf // options { // listen-on port 53 { 127.0.0.1; }; ... // allow-query { localhost; }; }; # Comment out these two lines
modify named.rfc1912.zones file to create the same zones as the primary server
[root@localhost ~]# vim /etc/named.rfc1912.zones // named.rfc1912.zones: // // zone "flamenca.com" IN { type slave;# # masters {192.168.33.129;};# Primary server address file "slaves/flamecna.com.zone.slave";# The path is relative }; ...
From the server's data store / var/named/slaves
Restart named
[root@localhost ~]# systemctl restart named [root@localhost ~]# ll /var/named/slaves/ total 4 -rw-r--r-- 1 named named 422 Jun 19 09:00 flamecna.com.zone.slave # success # The file cannot be opened. It is not a text file. It is only a data file
Add load balancing of slave server in master server setting
Add master service push data setting: add NS record in the setting
$TTL 1D @ IN SOA master.flamenca.com. admin.flamenca.com. ( 20200618 ; 1D ; 10M ; 3D ; 2H) ; NS master NS slave # Naming doesn't matter. You need a record pointing to the slave server master A 192.168.33.129 slave A 192.168.33.130 # Resolve IP from server webserv A 192.168.33.130 webserv A 192.168.33.129 www CNAME webserv app A 1.1.1.1 db A 2.2.2.2
Method of timely synchronization from service
#Delete the original downloaded slave file and restart the named service #To let the slave service update the service, first update the serial number of the configuration of the master server
View log file information
[root@localhost ~]# tail /var/log/messages
View on. 129
[root@localhost named]# dig www.flamenca.com @192.168.33.130 ; <<>> DiG 9.11.13-RedHat-9.11.13-3.el8 <<>> www.flamenca.com @192.168.33.130 ;; global options: +cmd ;; Got answer: ;; ->>HEADER<<- opcode: QUERY, status: NOERROR, id: 37118 ;; flags: qr aa rd ra; QUERY: 1, ANSWER: 2, AUTHORITY: 1, ADDITIONAL: 2 ;; OPT PSEUDOSECTION: ; EDNS: version: 0, flags:; udp: 4096 ; COOKIE: d486ed5b13c2f6b138aafd7d5eec0f245ea686e6c545bf36 (good) ;; QUESTION SECTION: ;www.flamenca.com. IN A ;; ANSWER SECTION: www.flamenca.com. 86400 IN CNAME webserv.flamenca.com. webserv.flamenca.com. 86400 IN A 192.168.33.130 ;; AUTHORITY SECTION: flamenca.com. 86400 IN NS master.flamenca.com. ;; ADDITIONAL SECTION: master.flamenca.com. 86400 IN A 192.168.33.129 ;; Query time: 0 msec ;; SERVER: 192.168.33.130#53(192.168.33.130) ;; WHEN: Thu Jun 18 13:04:39 EDT 2020 ;; MSG SIZE rcvd: 148
Resolution successful
Security of the primary server
How to restrict the slave service?
CentOS 6 can directly grab DNS data information
dig -t axfr flamenca.com @192.168.33.129
Specify to grab data from server host
vim /etc/named.conf allow-transfer {192.168.33.130;}; # From the service should also be relevant allow-transfer {none;};
Implementation subdomain
Configuration file in parent domain / var/named/flamenca.com.zone Add subdomain information to
[root@localhost named]# vim flamenca.com.zone $TTL 1D @ IN SOA master.flamenca.com. admin.flamenca.com. ( $TTL 1D @ IN SOA master.flamenca.com. admin.flamenca.com. ( 20200618 ; 1D ; 10M ; 3D ; 2H) ; NS master NS slave www.ziyu01.flamenca.com. A 1.1.1.2 blog.ziyu01.flamenca.com. A 1.1.1.3 master A 192.168.33.129 slave A 192.168.33.130 webserv A 192.168.33.130 webserv A 192.168.33.129 www CNAME webserv app A 1.1.1.1 db A 2.2.2.2
Restart service after creation
systemctl restart named
dig test
[root@localhost named]# dig www.ziyu01.flamenca.com ; <<>> DiG 9.11.13-RedHat-9.11.13-3.el8 <<>> www.ziyu01.flamenca.com ;; global options: +cmd ;; Got answer: ;; ->>HEADER<<- opcode: QUERY, status: NOERROR, id: 34439 ;; flags: qr aa rd ra; QUERY: 1, ANSWER: 1, AUTHORITY: 2, ADDITIONAL: 3 ;; OPT PSEUDOSECTION: ; EDNS: version: 0, flags:; udp: 4096 ; COOKIE: bdfe8b341c9306586f9e1aae5eec4993aef5ff24ca69e188 (good) ;; QUESTION SECTION: ;www.ziyu01.flamenca.com. IN A ;; ANSWER SECTION: www.ziyu01.flamenca.com. 86400 IN A 1.1.1.2 ;; AUTHORITY SECTION: flamenca.com. 86400 IN NS master.flamenca.com. flamenca.com. 86400 IN NS slave.flamenca.com. ;; ADDITIONAL SECTION: master.flamenca.com. 86400 IN A 192.168.33.129 slave.flamenca.com. 86400 IN A 192.168.33.130 ;; Query time: 0 msec ;; SERVER: 127.0.0.1#53(127.0.0.1) ;; WHEN: Fri Jun 19 01:13:55 EDT 2020 ;; MSG SIZE rcvd: 169
success
DNS servers for subdomains
Separate parent domain from child domain
# Set the IP address of the subdomain named ziyu02 to 192.168.33.131 [root@localhost named]# vim flamenca.com.zone $TTL 1D @ IN SOA master.flamenca.com. admin.flamenca.com. ( 20200618 ; 1D ; 10M ; 3D ; 2H) ; NS master NS slave ziyu02 NS ziyu02serv www.ziyu01.flamenca.com. A 1.1.1.2 blog.ziyu02.flamenca.com. A 1.1.1.3 ziyu02serv A 192.168.33.131 master A 192.168.33.129 slave A 192.168.33.130 webserv A 192.168.33.130
Establishment of sub domain DNS server 192.168.33.131
[root@centos8 named]# vim /etc/named.conf // options { // listen-on port 53 { 127.0.0.1; }; listen-on-v6 port 53 { ::1; }; directory "/var/named"; dump-file "/var/named/data/cache_dump.db"; statistics-file "/var/named/data/named_stats.txt"; memstatistics-file "/var/named/data/named_mem_stats.txt"; secroots-file "/var/named/data/named.secroots"; recursing-file "/var/named/data/named.recursing"; // allow-query { localhost; }; allow-transfer {none;};
/etc/ named.rfc1912 Add zone subdomain to. Zones
zone "ziyu02.flamenca.com" IN { type master; file "ziyu02.flamenca.com.zone"; };
Enter / var/named / to create ziyu02 flamenca.com.zone
[root@centos8 named]# vim ziyu02.flamenca.com.zone $TTL 1D @ IN SOA ziyu02 admin ( 1 1H 5M 1D 3H ); NS ziyu02 ziyu02 A 192.168.33.131 www A 192.33.33.33 ~ ### [root@centos8 named]# chmod 640 ziyu02.flamenca.com.zone [root@centos8 named]# chgrp named ziyu02.flamenca.com.zone ###Start service### [root@centos8 named]# systemctl enable --now named Created symlink /etc/systemd/system/multi-user.target.wants/named.service → /usr/lib/systemd/system/named.service. ## ## ###Check syntax### [root@centos8 named]# named-checkconf [root@centos8 named]# named-checkzone ziyu02.flamenca.com ziyu02.flamenca.com.zone zone ziyu02.flamenca.com/IN: loaded serial 1 OK
dig test
[root@centos8 named]# dig www.ziyu02.flamenca.com @192.168.33.129 ; <<>> DiG 9.11.13-RedHat-9.11.13-3.el8 <<>> www.ziyu02.flamenca.com @192.168.33.129 ;; global options: +cmd ;; Got answer: ;; ->>HEADER<<- opcode: QUERY, status: NOERROR, id: 7516 ;; flags: qr rd ra; QUERY: 1, ANSWER: 1, AUTHORITY: 1, ADDITIONAL: 2 ;; OPT PSEUDOSECTION: ; EDNS: version: 0, flags:; udp: 4096 ; COOKIE: 8c25356f918d2b2e5f6f471d5eec62c946fc6fc46dc582d5 (good) ;; QUESTION SECTION: ;www.ziyu02.flamenca.com. IN A ;; ANSWER SECTION: www.ziyu02.flamenca.com. 86400 IN A 192.33.33.33 ;; AUTHORITY SECTION: ziyu02.flamenca.com. 86400 IN NS ziyu02serv.flamenca.com. ;; ADDITIONAL SECTION: ziyu02serv.flamenca.com. 86400 IN A 192.168.33.131 ;; Query time: 1 msec ;; SERVER: 192.168.33.129#53(192.168.33.129) ;; WHEN: Fri Jun 19 03:01:29 EDT 2020 ;; MSG SIZE rcvd: 137
success
Implement forwarding
DNS forwarding
With DNS forwarding, users' DNS requests can be forwarded to the specified DNS service instead of the default root DNS server, and the returned results of the specified server query can be cached to improve efficiency
be careful:
- The server to be forwarded needs to be able to recurse for the requester, otherwise the forwarding request will not be carried out
- In the global configuration block, turn off the dnssec function
dnssec-enable no; dnssec-validation no;
Forwarding method
Global Forwarding
All requests for non local resolution areas are forwarded to the designated server
In global configuration:
// named.conf // options { listen-on port 53 { localhost; }; // Point this server to the root server or forward server listen-on-v6 port 53 { ::1; }; directory "/var/named"; dump-file "/var/named/data/cache_dump.db"; statistics-file "/var/named/data/named_stats.txt"; memstatistics-file "/var/named/data/named_mem_stats.txt"; secroots-file "/var/named/data/named.secroots"; recursing-file "/var/named/data/named.recursing"; allow-query { any; }; forward fist|only;//First, forward the specified dns server first. If you can't check it, ask the root server in person // Only forward to the specified dns server only. If the query fails, an error message will be returned forwarders {ip;}; };
Forwarding of specific areas
Realize intelligent DNS
Move the website to the door and set up a host in each city
GSLB: Global Server Load Balance
GSLB is a comprehensive judgment of servers and links to decide which location servers provide services and realize remote server groups to ensure service quality. Generally, large companies will distribute most traffic on DNS servers to ensure service speed
The main purpose of GSLB is to direct the user's request to the nearest node (or region) in the whole network
GSLB is divided into implementation based on DNS, implementation based on redirection and Implementation Based on routing protocol. The general way is based on DNS resolution, which is the logic of Intelligent DNS
[root@localhost named]# dig www.taobao.com ; <<>> DiG 9.11.13-RedHat-9.11.13-3.el8 <<>> www.taobao.com ;; global options: +cmd ;; Got answer: ;; ->>HEADER<<- opcode: QUERY, status: NOERROR, id: 19239 ;; flags: qr rd ra; QUERY: 1, ANSWER: 3, AUTHORITY: 0, ADDITIONAL: 1 ;; OPT PSEUDOSECTION: ; EDNS: version: 0, flags:; MBZ: 0x0005, udp: 4096 ;; QUESTION SECTION: ;www.taobao.com. IN A ;; ANSWER SECTION: www.taobao.com. 5 IN CNAME www.taobao.com.danuoyi.tbcache.com. www.taobao.com.danuoyi.tbcache.com. 5 IN A 182.106.155.238 www.taobao.com.danuoyi.tbcache.com. 5 IN A 182.106.155.237 ;; Query time: 11 msec ;; SERVER: 192.168.33.2#53(192.168.33.2) ;; WHEN: Fri Jun 19 12:01:41 EDT 2020 ;; MSG SIZE rcvd: 120
Take Taobao for example, enter www.taobao.com When DNS server returns another server address www.taobao.com.danuoyi.tbcache.com.
CDN content distribution network
CDN service providers charge by traffic. For example, if a 1K picture is visited, it will cost 1K, and if a 1M picture is visited, it will cost 1M, so it is very important for resource compression. We will talk about this later
How CDN works
- User input to browser www.taobao.com For this domain name, the browser finds that there is no local DNS cache for the first time (Note: the command to clear DNS cache in bind is rndc flush), and then requests the DNS server of Taobao website
- CNAME is set in the DNS domain name resolver of Taobao website, which points to www.taobao.com.danuoyi.tbcache.com. That is, the request points to the Intelligent DNS load balancing system in CDN network
- The Intelligent DNS load balancing system resolves the domain name and returns the corresponding fast IP node to the user
- The user issues a request to the returned IP node (CDN server)
- As this is the first visit, the CDN server will obtain the IP address of the original web site of this domain name through the internal dedicated DNS resolution of Cache, send a request to the original site server, and Cache the content on the CDN server
- Request result sent to user
Intelligent DNS service implementation
ACL in bind
acl combines one or more addresses into a set and calls it by a unified name
Note: it can only be defined before use; therefore, it is generally defined in the configuration file before option
The format is as follows:
acl acl_name { ip; net/prelen; ... };
example
acl shanghai { 127.16.0.0/16; # Suppose this segment is a damage segment 10.10.10.10;# The assigned address is 10.10.10.10, and other IPS can be added };
bind has four built-in ACLS (access list)
- none: no host
- Any: any host
- localhost: Native
- localnet: the network address obtained by the local IP mask operation
Instructions for access control
allow-query {}# Hosts allowed to query: white list allow-transfer {}# Allowed hosts for zone transfer: white list allow-recursion {}# Recursive hosts are allowed. It is recommended to use them globally, which means whether to run to find DNS servers on the Internet to return results allow-updata {}# Allow content in the zone database to be updated
VIEW view
Realize the corresponding relationship between ACL and zone database, and realize the Intelligent DNS
- A bind server can define multiple views, and each view can define one or more zone s
- Each view is used to match a set of clients
- The same region may need to be resolved in multiple view s. dan uses different regions to resolve library files
be careful
- Once view is enabled, all zone s can only be defined in view
- Only define the root area in the view of the client that allows recursive requests
- When a client request arrives, it checks the list of clients served by each view from top to bottom
view format
# VIEW in Beijing view VIEW_NAME { match-clients {beijingnet; }; zone "flamenca.com" { type master; file "flamenca.com.zone.bj"; }; include "/etc/named.rfc1912.zones"; }; # VIEW in Shanghai view VIEW_NAME { match-clients {shanghainet; }; zone "flamenca.com" { type master; file "flamenca.com.zone.bj"; }; include "/etc/named.rfc1912.zones"; };
Experimental steps
Configure a domain name to return 1.1.1.1 when accessing from beijing network segment, 2.2.2.2 when accessing shanghai, 3.3.3.3 when other
In / etc/named.conf Three ACLS are defined in: beijing, shanghai, and other
acl beijingnet { }; acl shanghainet { }; acl other { }; options { //listen-on port 53 { localhost; }; listen-on-v6 port 53 { ::1; }; directory "/var/named"; dump-file "/var/named/data/cache_dump.db"; statistics-file "/var/named/data/named_stats.txt"; memstatistics-file "/var/named/data/named_mem_stats.txt"; secroots-file "/var/named/data/named.secroots"; recursing-file "/var/named/data/named.recursing"; //allow-query { any; };
Prepare two virtual machines and create two different network segments
# Add network card # 192.168.0.8/24 [root@localhost ~]# ip a a 192.168.0.3/24 dev ens33 [root@localhost ~]# ip a 1: lo: <LOOPBACK,UP,LOWER_UP> mtu 65536 qdisc noqueue state UNKNOWN group default qlen 1000 link/loopback 00:00:00:00:00:00 brd 00:00:00:00:00:00 inet 127.0.0.1/8 scope host lo valid_lft forever preferred_lft forever inet6 ::1/128 scope host valid_lft forever preferred_lft forever 2: ens33: <BROADCAST,MULTICAST,UP,LOWER_UP> mtu 1500 qdisc fq_codel state UP group default qlen 1000 link/ether 00:0c:29:9a:35:c7 brd ff:ff:ff:ff:ff:ff inet 192.168.33.129/24 brd 192.168.33.255 scope global dynamic noprefixroute ens33 valid_lft 1643sec preferred_lft 1643sec inet 192.168.0.3/24 scope global ens33 valid_lft forever preferred_lft forever inet6 fe80::5f95:77de:7cad:df9e/64 scope link noprefixroute valid_lft forever preferred_lft forever
Add address 192.168.0.6/24 to CentOS7
[root@localhost ~]# ip a a 192.168.0.6/24 dev eth0 [root@localhost ~]# ip a 1: lo: <LOOPBACK,UP,LOWER_UP> mtu 65536 qdisc noqueue state UNKNOWN group default qlen 1000 link/loopback 00:00:00:00:00:00 brd 00:00:00:00:00:00 inet 127.0.0.1/8 scope host lo valid_lft forever preferred_lft forever inet6 ::1/128 scope host valid_lft forever preferred_lft forever 2: eth0: <BROADCAST,MULTICAST,UP,LOWER_UP> mtu 1500 qdisc pfifo_fast state UP group default qlen 1000 link/ether 00:0c:29:b6:94:7d brd ff:ff:ff:ff:ff:ff inet 192.168.33.130/24 brd 192.168.33.255 scope global noprefixroute dynamic eth0 valid_lft 1013sec preferred_lft 1013sec inet 192.168.0.6/24 scope global eth0 valid_lft forever preferred_lft forever inet6 fe80::28d1:a712:6021:917a/64 scope link noprefixroute valid_lft forever preferred_lft forever
Assumption:
- 192.168.33.130/24 segment is beijing segment
- 192.168.0.6/27 segment is shanghai segment
- 127.0.0.1/8 network segment is other
Then start to configure DNS server / etc/named.com acl in
acl beijingnet { 192.168.33.0/24; }; acl shanghainet { 192.168.0.0/24; }; acl other { any; }; options { //listen-on port 53 { localhost; }; listen-on-v6 port 53 { ::1; }; directory "/var/named"; dump-file "/var/named/data/cache_dump.db"; statistics-file "/var/named/data/named_stats.txt"; memstatistics-file "/var/named/data/named_mem_stats.txt"; secroots-file "/var/named/data/named.secroots"; recursing-file "/var/named/data/named.recursing"; //allow-query { any; }; ...
Configure three sets of zone files
[root@localhost ~]# vim /etc/named.conf [root@localhost ~]# cd /var/named/ [root@localhost named]# cp -p flamenca.com.zone flamenca.com.zone.bj [root@localhost named]# cp -p flamenca.com.zone flamenca.com.zone.sh [root@localhost named]# cp -p flamenca.com.zone flamenca.com.zone.other
configuration file flamenca.com.zone.bj
$TTL 1D @ IN SOA master.flamenca.com. admin.flamenca.com. ( 20200618 ; 1D ; 10M ; 3D ; 2H) ; NS master master A 192.168.33.129 webserv A 1.1.1.1 www CNAME webserv
configuration file flamenca.com.zone.sh
$TTL 1D @ IN SOA master.flamenca.com. admin.flamenca.com. ( 20200618 ; 1D ; 10M ; 3D ; 2H) ; NS master master A 192.168.33.129 webserv A 2.2.2.2 www CNAME webserv
configuration file flamenca.com.zone.other
$TTL 1D @ IN SOA master.flamenca.com. admin.flamenca.com. ( 20200618 ; 1D ; 10M ; 3D ; 2H) ; NS master master A 192.168.33.129 webserv A 3.3.3.3 www CNAME webserv
Associate database to configuration file / etc/named.conf
acl beijingnet { 192.168.33.0/24; }; acl shanghainet { 192.168.0.0/24; }; acl other { any; }; ################################### ... ################################### VIEW beijingVIEW { match-clients {beijingnet; }; include "/etc/named.rfc1912.zones.bj"; }; VIEW shanghaiVIEW { match-clients {shanghai; }; include "/etc/named.rfc1912.zones.sh"; }; VIEW otherVIEW { match-clients {other; }; include "/etc/named.rfc1912.zones.other"; };
Note: once VIEW is available, other zone configuration information must be put into VIEW
So we put all the original zone configuration information in the configuration file into vim /etc/named.rfc1912.zones
Put / etc/ named.rfc1912 Three copies of. Zones file with suffix. BJ. Sh. Other
[root@localhost named]# cp -p /etc/named.rfc1912.zones /etc/named.rfc1912.zones.bj [root@localhost named]# cp -p /etc/named.rfc1912.zones /etc/named.rfc1912.zones.sh [root@localhost named]# cp -p /etc/named.rfc1912.zones /etc/named.rfc1912.zones.other
Modify contents respectively
[root@localhost named]# vim /etc/named.rfc1912.zones.bj zone "." IN { type hint; file "named.ca"; }; ... zone "flamenca.com" IN { type master; file "flamenca.com.zone.bj";# Point the corresponding database file to the corresponding area, and so on sh.other };
Restart the service after configuration
[root@localhost named]# systemctl restart named
Start testing
Using dig, access 192.168.33.129 (only access from network card 192.168.33.130), 192.168.0.3 (only access from network card 192.168.0.3), 127.0.0.1 respectively;
[root@localhost ~]# dig www.flamenca.com @192.168.33.129 ; <<>> DiG 9.11.4-P2-RedHat-9.11.4-9.P2.el7 <<>> www.flamenca.com @192.168.33.129 ;; global options: +cmd ;; Got answer: ;; ->>HEADER<<- opcode: QUERY, status: NOERROR, id: 8069 ;; flags: qr aa rd ra; QUERY: 1, ANSWER: 2, AUTHORITY: 1, ADDITIONAL: 2 ;; OPT PSEUDOSECTION: ; EDNS: version: 0, flags:; udp: 4096 ;; QUESTION SECTION: ;www.flamenca.com. IN A ;; ANSWER SECTION: www.flamenca.com. 86400 IN CNAME webserv.flamenca.com. webserv.flamenca.com. 86400 IN A 1.1.1.1 # 1.1.1.1 is displayed here successfully ;; AUTHORITY SECTION: flamenca.com. 86400 IN NS master.flamenca.com. ;; ADDITIONAL SECTION: master.flamenca.com. 86400 IN A 192.168.33.129 ;; Query time: 0 msec ;; SERVER: 192.168.33.129#53(192.168.33.129) ;; WHEN: Sun Jun 21 09:24:11 CST 2020 ;; MSG SIZE rcvd: 120
[root@localhost ~]# dig www.flamenca.com @192.168.0.3 ; <<>> DiG 9.11.4-P2-RedHat-9.11.4-9.P2.el7 <<>> www.flamenca.com @192.168.0.3 ;; global options: +cmd ;; Got answer: ;; ->>HEADER<<- opcode: QUERY, status: NOERROR, id: 13911 ;; flags: qr aa rd ra; QUERY: 1, ANSWER: 2, AUTHORITY: 1, ADDITIONAL: 2 ;; OPT PSEUDOSECTION: ; EDNS: version: 0, flags:; udp: 4096 ;; QUESTION SECTION: ;www.flamenca.com. IN A ;; ANSWER SECTION: www.flamenca.com. 86400 IN CNAME webserv.flamenca.com. webserv.flamenca.com. 86400 IN A 2.2.2.2 # 2.2.2.2 is displayed here successfully ;; AUTHORITY SECTION: flamenca.com. 86400 IN NS master.flamenca.com. ;; ADDITIONAL SECTION: master.flamenca.com. 86400 IN A 192.168.33.129 ;; Query time: 0 msec ;; SERVER: 192.168.0.3#53(192.168.0.3) ;; WHEN: Sun Jun 21 09:24:41 CST 2020 ;; MSG SIZE rcvd: 120
[root@localhost named]# dig www.flamenca.com @127.0.0.1 ; <<>> DiG 9.11.13-RedHat-9.11.13-3.el8 <<>> www.flamenca.com @127.0.0.1 ;; global options: +cmd ;; Got answer: ;; ->>HEADER<<- opcode: QUERY, status: NOERROR, id: 53370 ;; flags: qr aa rd ra; QUERY: 1, ANSWER: 2, AUTHORITY: 1, ADDITIONAL: 2 ;; OPT PSEUDOSECTION: ; EDNS: version: 0, flags:; udp: 4096 ; COOKIE: 57b53af9b14534f9083ddf865eee47ff9a65289e3c32efd0 (good) ;; QUESTION SECTION: ;www.flamenca.com. IN A ;; ANSWER SECTION: www.flamenca.com. 86400 IN CNAME webserv.flamenca.com. webserv.flamenca.com. 86400 IN A 3.3.3.3 # 3.3.3.3.3 is displayed successfully. Note that the address is the loopback network card address, so it is only tested on the DNS server ;; AUTHORITY SECTION: flamenca.com. 86400 IN NS master.flamenca.com. ;; ADDITIONAL SECTION: master.flamenca.com. 86400 IN A 192.168.33.129 ;; Query time: 0 msec ;; SERVER: 127.0.0.1#53(127.0.0.1) ;; WHEN: Sat Jun 20 13:31:43 EDT 2020 ;; MSG SIZE rcvd: 148
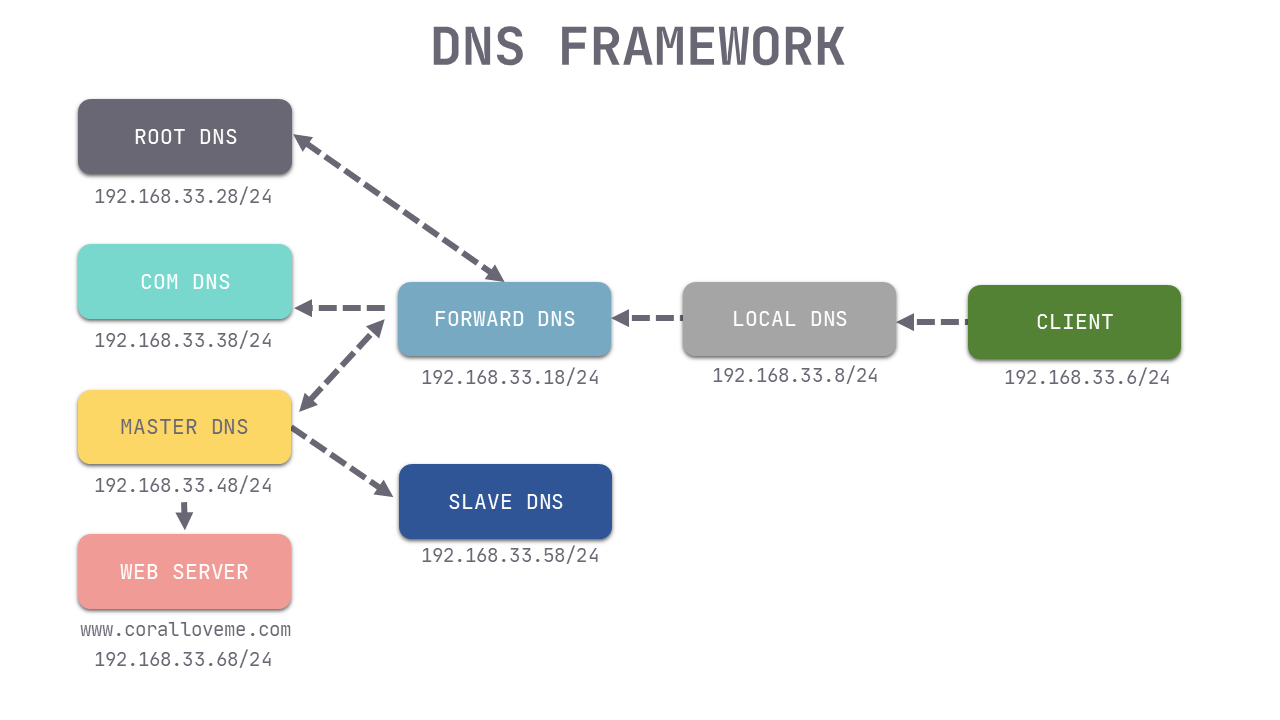
DNS architecture of Internet
Experiment preparation
Use cobbler to install 8 virtual machines and configure yum source
Prepare 8 virtual machines
So for the convenience of testing, the order of server setup is
# Client 192.168.33.6 # WEB SERVER 192.168.33.68 # MASTER DNS 192.168.33.48 # SLAVE DNS 192.168.33.58 # COM DNS 192.168.33.38 # ROOT DNS 192.168.33.28 # FORWARD DNS 192.168.33.18 # LOCAL DNS 192.168.33.8
- webserv 192.168.33.68 install http and bind services
- client192.168.33.6 install bind utils service
- bind is installed for everything else
Start configuration
webserv
[root@webserv ~]# curl 192.168.33.68 www.coralloveme.com # Install http service, create www.coralloveme.com Home page. as a mere token
to configure named.conf
options { // listen-on port 53 { 127.0.0.1; }; listen-on-v6 port 53 { ::1; }; directory "/var/named"; dump-file "/var/named/data/cache_dump.db"; statistics-file "/var/named/data/named_stats.txt"; memstatistics-file "/var/named/data/named_mem_stats.txt"; recursing-file "/var/named/data/named.recursing"; secroots-file "/var/named/data/named.secroots"; // allow-query { localhost; }; dnssec-enable no; dnssec-validation no;
Client
# Configure dns to point to local dns [root@client ~]# vim /etc/sysconfig/network-scripts/ifcfg-eth0 TYPE=Ethernet DEVICE=eth0 BOOTPROTO=static IPADDR=192.168.33.6 NETMASK=255.255.255.0 ONBOOT=yes DNS1=192.168.33.8 #### [root@client ~]# systemctl restart network [root@client ~]# cat /etc/resolv.conf # Generated by NetworkManager nameserver 192.168.33.8 #### [root@client ~]# curl 192.168.33.68 www.coralloveme.com
Test domain name resolution after setting DNS to LOCAL DNS
[root@client ~]# dig www.coralloveme.com ; <<>> DiG 9.11.4-P2-RedHat-9.11.4-9.P2.el7 <<>> www.coralloveme.com ;; global options: +cmd ;; Got answer: ;; ->>HEADER<<- opcode: QUERY, status: NOERROR, id: 12868 ;; flags: qr rd ra; QUERY: 1, ANSWER: 1, AUTHORITY: 2, ADDITIONAL: 3 ;; OPT PSEUDOSECTION: ; EDNS: version: 0, flags:; udp: 4096 ;; QUESTION SECTION: ;www.coralloveme.com. IN A ;; ANSWER SECTION: www.coralloveme.com. 85918 IN A 192.168.33.68 ;; AUTHORITY SECTION: coralloveme.com. 85918 IN NS slave.com. coralloveme.com. 85918 IN NS master.com. ;; ADDITIONAL SECTION: master.com. 85918 IN A 192.168.33.48 slave.com. 85918 IN A 192.169.33.58 ;; Query time: 0 msec ;; SERVER: 192.168.33.8#53(192.168.33.8) ;; WHEN: Sun Jun 21 17:20:51 CST 2020 ;; MSG SIZE rcvd: 137
curl test
[root@client ~]# curl www.coralloveme.com www.coralloveme.com
MASTER DNS
# to configure named.conf options { // listen-on port 53 { 127.0.0.1; }; ... // allow-query { localhost; }; allow-transfer {192.168.33.58; }; dnssec-enable no; dnssec-validation no;
[root@master-dns ~]# vim /etc/named.rfc1912.zones zone "coralloveme.com" IN { type master; file "coralloveme.com.zone"; };
[root@master-dns ~]# cd /var/named/ [root@master-dns named]# cp named.localhost coralloveme.com.zone [root@master-dns named]# ll coralloveme.com.zone -rw-r----- 1 root root 152 Jun 21 15:37 coralloveme.com.zone ################ [root@master-dns named]# vim coralloveme.com.zone $TTL 1D @ IN SOA master admin ( 0 ; serial 1D ; refresh 1H ; retry 1W ; expire 3H ) ; minimum NS master NS slave master A 192.168.33.48 slave A 192.168.33.58 www A 192.168.33.68 ##### # Note that the group to which the file belongs is set to named ##### [root@master-dns named]# systemctl restart named
client test
[root@client ~]# dig www.coralloveme.com @192.168.33.48 ; <<>> DiG 9.11.4-P2-RedHat-9.11.4-9.P2.el7 <<>> www.coralloveme.com @192.168.33.48 ;; global options: +cmd ;; Got answer: ;; ->>HEADER<<- opcode: QUERY, status: NOERROR, id: 23461 ;; flags: qr aa rd ra; QUERY: 1, ANSWER: 1, AUTHORITY: 2, ADDITIONAL: 3 ;; OPT PSEUDOSECTION: ; EDNS: version: 0, flags:; udp: 4096 ;; QUESTION SECTION: ;www.coralloveme.com. IN A ;; ANSWER SECTION: www.coralloveme.com. 86400 IN A 192.168.33.68 ;; AUTHORITY SECTION: coralloveme.com. 86400 IN NS slave.coralloveme.com. coralloveme.com. 86400 IN NS master.coralloveme.com. ;; ADDITIONAL SECTION: master.coralloveme.com. 86400 IN A 192.168.33.48 slave.coralloveme.com. 86400 IN A 192.168.33.58 ;; Query time: 2 msec ;; SERVER: 192.168.33.48#53(192.168.33.48) ;; WHEN: Sun Jun 21 16:10:37 CST 2020 ;; MSG SIZE rcvd: 137
SLAVE DNS
options { // listen-on port 53 { 127.0.0.1; }; listen-on-v6 port 53 { ::1; }; directory "/var/named"; dump-file "/var/named/data/cache_dump.db"; statistics-file "/var/named/data/named_stats.txt"; memstatistics-file "/var/named/data/named_mem_stats.txt"; recursing-file "/var/named/data/named.recursing"; secroots-file "/var/named/data/named.secroots"; // allow-query { localhost; }; allow-transfer {none;}; dnssec-enable no; dnssec-validation no;
// named.rfc1912.zones: // // zone "coralloveme.com" IN { type slave; masters {192.168.33.48;}; file "slaves/coralloveme.com.zone.bak"; }; # What's the name here? What's the name of the backup file [root@slave-dns ~]# systemctl restart named
Check if the database has been copied
[root@slave-dns ~]# ll /var/named/slaves total 4 -rw-r--r-- 1 named named 364 Jun 21 16:19 coralloveme.com.zone.bak
client test slave
[root@client ~]# dig www.coralloveme.com @192.168.33.58 ; <<>> DiG 9.11.4-P2-RedHat-9.11.4-9.P2.el7 <<>> www.coralloveme.com @192.168.33.58 ;; global options: +cmd ;; Got answer: ;; ->>HEADER<<- opcode: QUERY, status: NOERROR, id: 13335 ;; flags: qr aa rd ra; QUERY: 1, ANSWER: 1, AUTHORITY: 2, ADDITIONAL: 3 ;; OPT PSEUDOSECTION: ; EDNS: version: 0, flags:; udp: 4096 ;; QUESTION SECTION: ;www.coralloveme.com. IN A ;; ANSWER SECTION: www.coralloveme.com. 86400 IN A 192.168.33.68 ;; AUTHORITY SECTION: coralloveme.com. 86400 IN NS slave.coralloveme.com. coralloveme.com. 86400 IN NS master.coralloveme.com. ;; ADDITIONAL SECTION: master.coralloveme.com. 86400 IN A 192.168.33.48 slave.coralloveme.com. 86400 IN A 192.168.33.58 ;; Query time: 0 msec ;; SERVER: 192.168.33.58#53(192.168.33.58) ;; WHEN: Sun Jun 21 16:21:17 CST 2020 ;; MSG SIZE rcvd: 137
Note: when the master changes and the serial number changes, it will be backed up to slave
COM DNS
options { // listen-on port 53 { 127.0.0.1; }; listen-on-v6 port 53 { ::1; }; directory "/var/named"; dump-file "/var/named/data/cache_dump.db"; statistics-file "/var/named/data/named_stats.txt"; memstatistics-file "/var/named/data/named_mem_stats.txt"; recursing-file "/var/named/data/named.recursing"; secroots-file "/var/named/data/named.secroots"; // allow-query { localhost; }; dnssec-enable no; dnssec-validation no;
// named.rfc1912.zones: // // zone "com" IN { type master; file "com.zone"; };
Regional database file
[root@com-dns named]# vim com.zone $TTL 1D @ IN SOA com admin ( 0 ; serial 1D ; refresh 1H ; retry 1W ; expire 3H ) ; minimum NS com coralloveme NS master coralloveme NS slave com A 192.168.33.38 master A 192.168.33.48 slave A 192.169.33.58 #### [root@com-dns named]# systemctl restart named
client test
[root@client ~]# dig www.coralloveme.com @192.168.33.38 ; <<>> DiG 9.11.4-P2-RedHat-9.11.4-9.P2.el7 <<>> www.coralloveme.com @192.168.33.38 ;; global options: +cmd ;; Got answer: ;; ->>HEADER<<- opcode: QUERY, status: NOERROR, id: 50700 ;; flags: qr rd ra; QUERY: 1, ANSWER: 1, AUTHORITY: 2, ADDITIONAL: 3 ;; OPT PSEUDOSECTION: ; EDNS: version: 0, flags:; udp: 4096 ;; QUESTION SECTION: ;www.coralloveme.com. IN A ;; ANSWER SECTION: www.coralloveme.com. 86400 IN A 192.168.33.68 ;; AUTHORITY SECTION: coralloveme.com. 86400 IN NS master.com. coralloveme.com. 86400 IN NS slave.com. ;; ADDITIONAL SECTION: master.com. 86400 IN A 192.168.33.48 slave.com. 86400 IN A 192.169.33.58 ;; Query time: 3 msec ;; SERVER: 192.168.33.38#53(192.168.33.38) ;; WHEN: Sun Jun 21 16:44:47 CST 2020 ;; MSG SIZE rcvd: 137
ROOT DNS
options { // listen-on port 53 { 127.0.0.1; }; listen-on-v6 port 53 { ::1; }; directory "/var/named"; dump-file "/var/named/data/cache_dump.db"; statistics-file "/var/named/data/named_stats.txt"; memstatistics-file "/var/named/data/named_mem_stats.txt"; recursing-file "/var/named/data/named.recursing"; secroots-file "/var/named/data/named.secroots"; // allow-query { localhost; }; dnssec-enable no; dnssec-validation no; ####be careful zone "." IN { type master; file "root.zone"; };
[root@root-dns named]# vim root.zone $TTL 1D @ IN SOA master admin ( 0 ; serial 1D ; refresh 1H ; retry 1W ; expire 3H ) ; minimum NS master com NS com master A 192.168.33.28 com A 192.168.33.38
client test
[root@client ~]# dig www.coralloveme.com @192.168.33.28 ; <<>> DiG 9.11.4-P2-RedHat-9.11.4-9.P2.el7 <<>> www.coralloveme.com @192.168.33.28 ;; global options: +cmd ;; Got answer: ;; ->>HEADER<<- opcode: QUERY, status: NOERROR, id: 22151 ;; flags: qr rd ra; QUERY: 1, ANSWER: 1, AUTHORITY: 2, ADDITIONAL: 3 ;; OPT PSEUDOSECTION: ; EDNS: version: 0, flags:; udp: 4096 ;; QUESTION SECTION: ;www.coralloveme.com. IN A ;; ANSWER SECTION: www.coralloveme.com. 86400 IN A 192.168.33.68 ;; AUTHORITY SECTION: coralloveme.com. 86400 IN NS slave.com. coralloveme.com. 86400 IN NS master.com. ;; ADDITIONAL SECTION: master.com. 86400 IN A 192.168.33.48 slave.com. 86400 IN A 192.169.33.58 ;; Query time: 2 msec ;; SERVER: 192.168.33.28#53(192.168.33.28) ;; WHEN: Sun Jun 21 17:04:01 CST 2020 ;; MSG SIZE rcvd: 137
FORWARD DNS
options { // listen-on port 53 { 127.0.0.1; }; listen-on-v6 port 53 { ::1; }; directory "/var/named"; dump-file "/var/named/data/cache_dump.db"; statistics-file "/var/named/data/named_stats.txt"; memstatistics-file "/var/named/data/named_mem_stats.txt"; recursing-file "/var/named/data/named.recursing"; secroots-file "/var/named/data/named.secroots"; // allow-query { localhost; }; ######### #Note that the forwarding service must be set to no ######### dnssec-enable no; dnssec-validation no;
FORWARD DNS queries directly from the root directory recursively, so it directly named.ca Just change the root server address
[root@forward-dns ~]# vim /var/named/named.ca ; <<>> DiG 9.11.3-RedHat-9.11.3-3.fc27 <<>> +bufsize=1200 +norec @a.root-servers.net ; (2 servers found) ;; global options: +cmd ;; Got answer: ;; ->>HEADER<<- opcode: QUERY, status: NOERROR, id: 46900 ;; flags: qr aa; QUERY: 1, ANSWER: 13, AUTHORITY: 0, ADDITIONAL: 27 ;; OPT PSEUDOSECTION: ; EDNS: version: 0, flags:; udp: 1472 ;; QUESTION SECTION: ;. IN NS ;; ANSWER SECTION: . 518400 IN NS a.root-servers.net. ;; ADDITIONAL SECTION: a.root-servers.net. 518400 IN A 192.168.33.28 ;; Query time: 24 msec ;; SERVER: 198.41.0.4#53(198.41.0.4) ;; WHEN: Thu Apr 05 15:57:34 CEST 2018 ;; MSG SIZE rcvd: 811 ##### [root@forward-dns ~]# systemctl restart named
client test
[root@client ~]# dig www.coralloveme.com @192.168.33.18 ; <<>> DiG 9.11.4-P2-RedHat-9.11.4-9.P2.el7 <<>> www.coralloveme.com @192.168.33.18 ;; global options: +cmd ;; Got answer: ;; ->>HEADER<<- opcode: QUERY, status: NOERROR, id: 25600 ;; flags: qr rd ra; QUERY: 1, ANSWER: 1, AUTHORITY: 2, ADDITIONAL: 3 ;; OPT PSEUDOSECTION: ; EDNS: version: 0, flags:; udp: 4096 ;; QUESTION SECTION: ;www.coralloveme.com. IN A ;; ANSWER SECTION: www.coralloveme.com. 86400 IN A 192.168.33.68 ;; AUTHORITY SECTION: coralloveme.com. 86400 IN NS master.com. coralloveme.com. 86400 IN NS slave.com. ;; ADDITIONAL SECTION: master.com. 86400 IN A 192.168.33.48 slave.com. 86400 IN A 192.169.33.58 ;; Query time: 3 msec ;; SERVER: 192.168.33.18#53(192.168.33.18) ;; WHEN: Sun Jun 21 17:12:48 CST 2020 ;; MSG SIZE rcvd: 137
LOCAL DNS
Set a forwarding function for local dns
[root@local-dns ~]# vi /etc/named.conf // // named.conf // // Provided by Red Hat bind package to configure the ISC BIND named(8) DNS // server as a caching only nameserver (as a localhost DNS resolver only). // // See /usr/share/doc/bind*/sample/ for example named configuration files. // // See the BIND Administrator's Reference Manual (ARM) for details about the // configuration located in /usr/share/doc/bind-{version}/Bv9ARM.html options { // listen-on port 53 { 127.0.0.1; }; listen-on-v6 port 53 { ::1; }; directory "/var/named"; dump-file "/var/named/data/cache_dump.db"; statistics-file "/var/named/data/named_stats.txt"; memstatistics-file "/var/named/data/named_mem_stats.txt"; recursing-file "/var/named/data/named.recursing"; secroots-file "/var/named/data/named.secroots"; // allow-query { localhost; }; ########### #Add forward option ########### forward only; forwarders { 192.168.33.18;}; ... ######### #Note that the forwarding service must be set to no ######### dnssec-enable no; dnssec-validation no; # [root@forward-dns ~]# systemctl restart named
client test
[root@client ~]# dig www.coralloveme.com @192.168.33.8 ; <<>> DiG 9.11.4-P2-RedHat-9.11.4-9.P2.el7 <<>> www.coralloveme.com @192.168.33.8 ;; global options: +cmd ;; Got answer: ;; ->>HEADER<<- opcode: QUERY, status: NOERROR, id: 42512 ;; flags: qr rd ra; QUERY: 1, ANSWER: 1, AUTHORITY: 2, ADDITIONAL: 3 ;; OPT PSEUDOSECTION: ; EDNS: version: 0, flags:; udp: 4096 ;; QUESTION SECTION: ;www.coralloveme.com. IN A ;; ANSWER SECTION: www.coralloveme.com. 86019 IN A 192.168.33.68 ;; AUTHORITY SECTION: coralloveme.com. 86019 IN NS slave.com. coralloveme.com. 86019 IN NS master.com. ;; ADDITIONAL SECTION: master.com. 86019 IN A 192.168.33.48 slave.com. 86019 IN A 192.169.33.58 ;; Query time: 1 msec ;; SERVER: 192.168.33.8#53(192.168.33.8) ;; WHEN: Sun Jun 21 17:19:10 CST 2020 ;; MSG SIZE rcvd: 137
Now that the DNS architecture has been set up, you can change the DNS of the client to the IP of the LOCAL DNS
DNS troubleshooting
A window verification DNS operation process
I have configured the domain name on the Linux host as flamenca.com DNS information for
But in windows computer, the content of domain name resolution is other IP
Check the hosts file. There is no relevant information
Then find out the reason:
- The IP in the network card is obtained automatically, which is not the same network segment as the IP in the virtual machine. Therefore, add DNS192.168.33.129, the Linux host address, to the network card VM8 in NAT mode
- Set DNS of network card to 192.168.33.129
- At this time, I ping 192.168.33.129 to get my own test interface