@3 month concentrated essence Django and Vue joint project development
Project environment construction
1. Build a virtual environment
Virtual environment establishment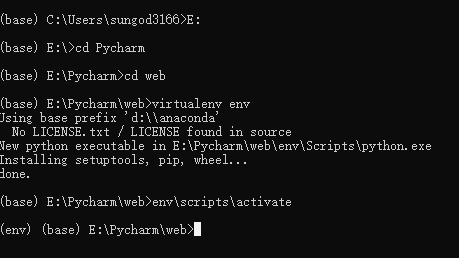
2. Install django
Activate virtual environment, install Django, build myweb project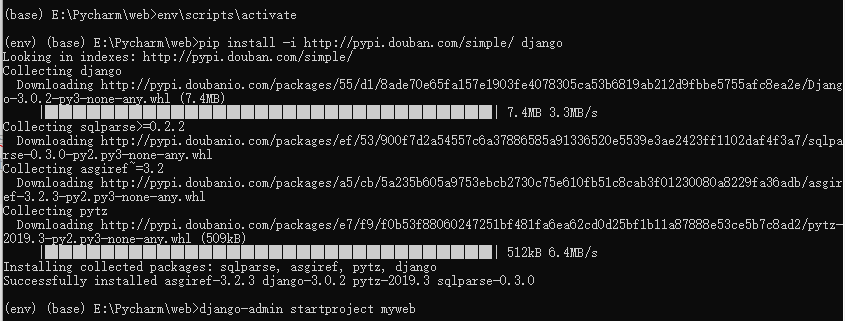
pip installation slow reference:
https://blog.csdn.net/zywvvd/article/details/100607820
Detailed usage of django-admin.py and manage.py
https://blog.csdn.net/weixin_42134789/article/details/80753001
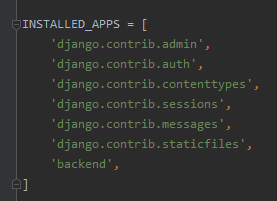
3. Enter the project and establish the project backend

Registered items
4. Database settings
My mysql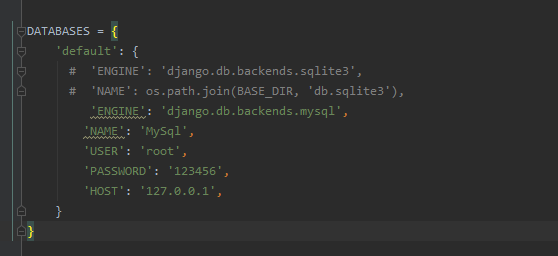
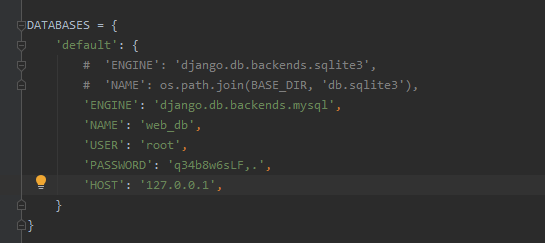
Configuration database
Conduct the next test after the configuration is successful
The MySQL DB library has been removed in Python 3.6.5. mysqlclient needs to be installed
MySQL Python: that is, MySQL dB. It is a simple package for C language to operate MySQL database. Python DB API v2 is followed. However, it only supports Python 2 and currently does not support Python 3.
mysqlclient: another branch of MySQL python. Support for Python 3 and fixed some bug s.
pymysql: a driver for pure Python implementation. Because it is written in pure python, the execution efficiency is not as efficient as MySQL python. And because it is written in pure python, it can be seamlessly connected with Python code.
MySQL Connector/Python: the official MySQL driver that uses pure Python to connect mysql. Because it's pure python. Not efficient.
Create a new database web dB in pycharm.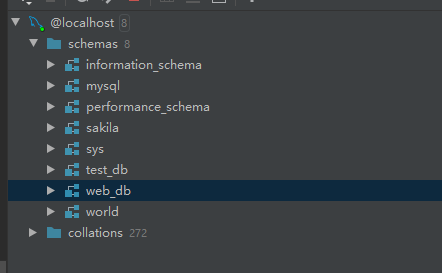
Change the database name name in settings.py to web dB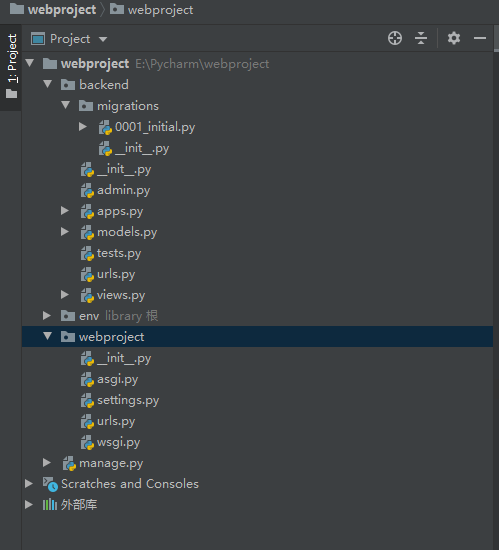
The following 5, 6 and 7 are respectively introduced according to Django MVT architecture
5. [M] in models.py under the app directory, we simply write a model
from django.db import models # Create your models here. class Book(models.Model): book_name = models.CharField(max_length=64) add_time = models.DateTimeField(auto_now_add=True) def __str__(self): return self.book_name
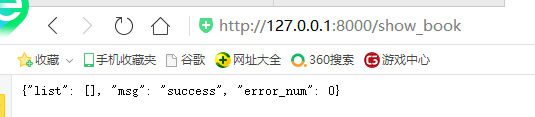
6. [V] write view control API in views.py: add book and show book
from django.views.decorators.http import require_http_methods from django.http import JsonResponse from .models import Book from django.core import serializers import json # Create your views here. @require_http_methods(["GET"]) def add_book(request): response = {} try: book = Book(book_name=request.GET.get('book_name', '')) book.save() response['msg'] = 'success' response['error_num'] = 0 except Exception as e: response['msg'] = 'success' response['error_num'] = 1 return JsonResponse(response) @require_http_methods(['GET']) def show_book(request): response = {} try: books = Book.objects.filter() response['list'] = json.loads(serializers.serialize("json", books)) response['msg'] = 'success' response['error_num'] = 0 except Exception as e: response['msg'] = str(e) response['error_num'] = 1 return JsonResponse(response)
The template is replaced by the front-end framework Vue, and url routing is introduced here
7 [T] add a urls.py file in backend to add our two new interfaces to the route.
Set the following in the url of the backend project
from django.urls import path from backend import views urlpatterns = [ # path('', views.index, name='index'), path('add_book', views.add_book, name='add_book'), path('show_book', views.show_book, name='show_book') ]
Set the following in the url of the Django project
from django.contrib import admin from django.urls import path, include import backend.urls urlpatterns = [ path('admin/', admin.site.urls), path('', include(backend.urls)) ]
8 data migration and running tests
Perform data migration.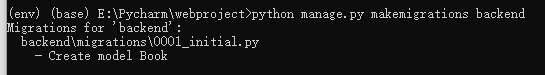
Test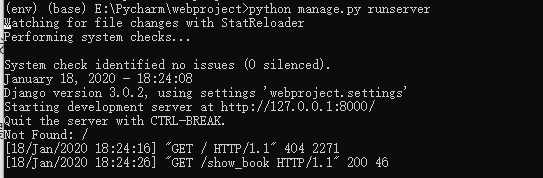
Run successfully, return json data. The next step is to interact with the front end through data