Buffer flow (high efficiency flow)
BufferedOutputStream buffered output byte stream
Construction method: BufferedOutputStream(OutputStream out)
Parameter: parent class of byte output stream (common class FileOutputStream)
Code formula:
// Throw anomaly
FileOutputStream fos = new FileOutputStream("/Users/james/Desktop/level/001.txt");
BufferedOutputStream bos = new BufferedOutputStream(fos);
bos.write("Hello World".getBytes());
bos.close();BufferedIntputStream buffered input byte stream
Construction method: BufferedInputStream(InputStream in)
Parameter: parent class of byte input stream (common class FileInputStream)
Code formula:
// Throw anomaly
FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream("/Users/james/Desktop/level/001.txt");
BufferedInputStream bis = new BufferedInputStream(fis);
byte[] bs = new byte[1024];
int len = 0;
while ((len = bis.read(bs)) != -1) {
System.out.println(new String(bs,0,len));
}
bis.close();Buffer character stream
Only text can be written
BufferedWrite
Constructor: parameter: BufferedWriter(Writer out)
Passable: FileWriter OutputStreamWriter
Code formula:
FileWriter fw = new FileWriter("/Users/james/Desktop/level/001.txt");
BufferedWriter bw = new BufferedWriter(fw);
bw.write("Hello James");
// Unique method line feed independent platform of all platforms common!
bw.newLine();
// Refresh every write
bw.flush();
bw.close();BufferedReader
BufferedReader(Reader in)
Same as above
Code formula:
FileReader fw = new FileReader("/Users/james/Desktop/level/001.txt");
BufferedReader bw = new BufferedReader(fw);
// readLine() reads by line, but cannot read newline
String string ="";
while ((string = bw.readLine()) != null) {
System.out.println(string);
}
bw.close();Properties collection
It indicates that a persistent property set is the only class in the collection that can cooperate with IO flow
When the parent class Hashtable reads and writes parameters, the character / byte can be used
Code example:
public class Demo06 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
// fun1();
// read
fun2();
// fun3();
}
/**
* @throws IOException
*/
public static void fun3() throws IOException {
Properties properties = new Properties();
properties.setProperty("name", "james");
properties.setProperty("sex", "male");
properties.setProperty("addres", "china");
// Suffixes can be anything, but in general. properties is used as the suffix of a file
//To identify that the file can be read using the properties class
FileWriter fw = new FileWriter("/Users/james/Desktop/level/001.properties");
// Write using methods in the properties class
// Parameter 2 is equivalent to a comment written to a file. Generally, nothing is written
// You can use ා to write comments in properties
properties.store(fw, "james");
fw.close();
}
/*
#\u4E01\u9E4F
#Thu Feb 01 14:44:24 CST 2018
addres=china
name=james
sex=male
*/
/**
* @throws FileNotFoundException
* @throws IOException
*/
public static void fun2() throws FileNotFoundException, IOException {
Properties properties = new Properties();
// Read the file and write it to properties
properties.load(reader);
Set<String> set = properties.stringPropertyNames();
for (String key : set) {
String value = properties.getProperty(key);
System.out.println(key + "=" + value);
}
reader.close();
}
public static void fun1() {
Properties properties = new Properties();
// Note: the best use of this collection is String string type
// PUT method inheriting parent class
properties.put("name", "james");
// Calling methods of this class
properties.setProperty("sex", "man");
System.out.println(properties);
// Ergodic set
Set<String> set = properties.stringPropertyNames();
for (String key : set) {
String value = properties.getProperty(key);
System.out.println(key + "=" + value);
}
}
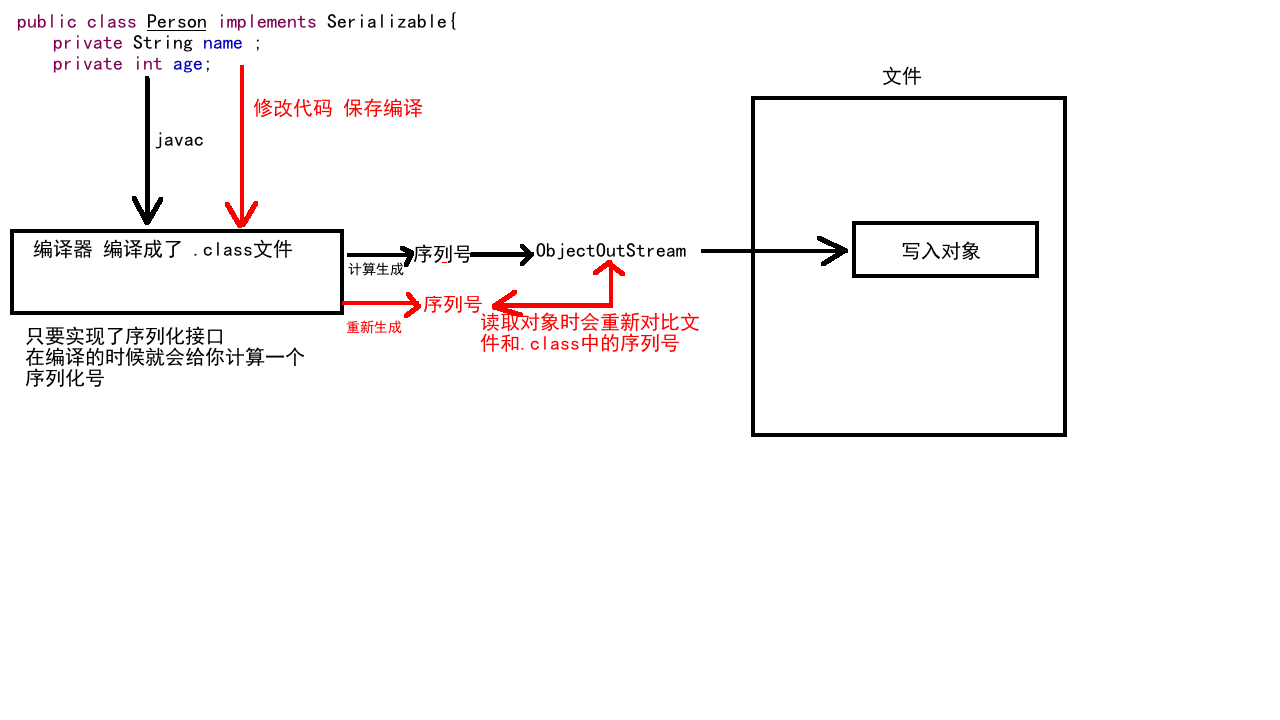
}Serialization stream and deserialization stream
Serialization writes objects into a file ObjectOutputStream
Deserialization reads objects from files ObjectInputStream
Attention points
Static member variables cannot be persisted (serialized)
Serialized is the input class's
transient
Do not want to write as static or serialize, use transient keyword
Function: can prevent member variable serialization
Serialization general formula:
public static void writeObject() throws FileNotFoundException, IOException {
// Note 1. Write objects use byte stream to operate
//2. If you want to instantiate an object, you must implement the Serializable interface
// Serializable this interface belongs to tag interface
FileOutputStream fos = new FileOutputStream("/Users/lanou/Desktop/level/person.txt");
// Create object output stream (serialization stream)
ObjectOutputStream oos = new ObjectOutputStream(fos);
oos.writeObject(new Person("james", 17));
oos.close();
}Deserialization formula:
public static void readObject() throws FileNotFoundException, IOException, ClassNotFoundException {
// Read serialization file (deserialization)
// When deserializing (reading), you need to rely on the compiled file. class file to read
FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream("/Users/lanou/Desktop/level/person.txt");
ObjectInputStream ois = new ObjectInputStream(fis);
// read file
// An exception ClassNotFoundException will be reported here
Object object = ois.readObject();
System.out.println(object);
ois.close();
}ClassNotFoundException
Class cannot find an exception. It will be reported when the accessed class changes