Derivation formula
We've learned the simplest list derivation and generator expressions before. But in addition, there are dictionary derivation, set derivation and so on.
The following is a detailed derivation format with list derivation as an example, which is also applicable to other derivation.

variable = [out_exp_res for out_exp in input_list if out_exp == 2] out_exp_res: List generates element expressions, which can be functions with return values. for out_exp in input_list: iteration input_list take out_exp afferent out_exp_res Expression. if out_exp == 2: Which values can be filtered according to the conditions.
List derivation
Example 1: all numbers within 30 that can be divided by 3
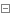 multiples = [i for i in range(30) if i % 3 is 0] print(multiples) # Output: [0, 3, 6, 9, 12, 15, 18, 21, 24, 27]
multiples = [i for i in range(30) if i % 3 is 0] print(multiples) # Output: [0, 3, 6, 9, 12, 15, 18, 21, 24, 27]