Nginx common functions
1. Http proxy, reverse proxy:
As one of the most commonly used functions of web server, especially reverse proxy.
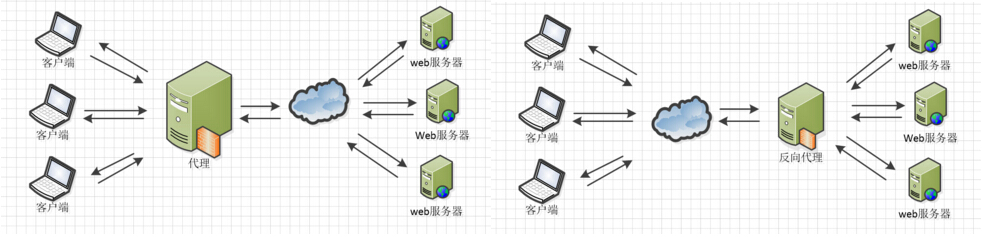
When working as a reverse proxy, nginx provides stable performance and flexible forwarding function. Nginx can adopt different forwarding strategies according to different regular matching, such as file server at the end of image file and web server for dynamic page. As long as you have no problem writing regular and have corresponding server solutions, you can play as you like. In addition, nginx performs error page Jump and exception judgment on the returned results. If the distributed server has an exception, it can re forward the request to another server, and then automatically remove the exception server.
2. Load balancing
There are two load balancing strategies provided by Nginx:
Built in and extended policies.
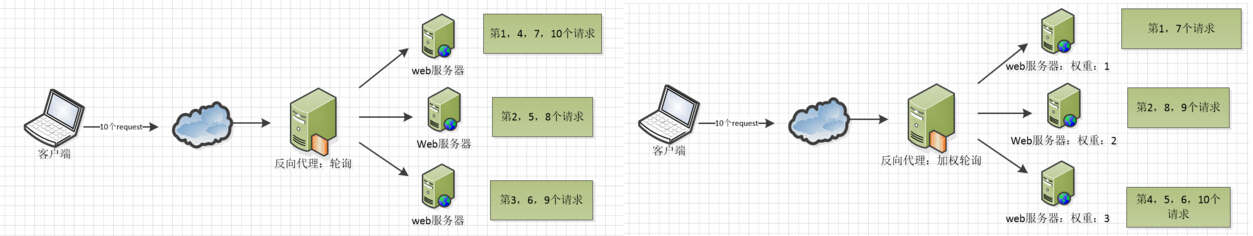
The built-in policies are polling, weighted polling and Ip hash.
The expansion strategy is unrestrained. There are only things you can't think of and nothing he can't do. You can refer to all load balancing algorithms and find them one by one for implementation.
In the above three figures, understand the implementation of these three load balancing algorithms
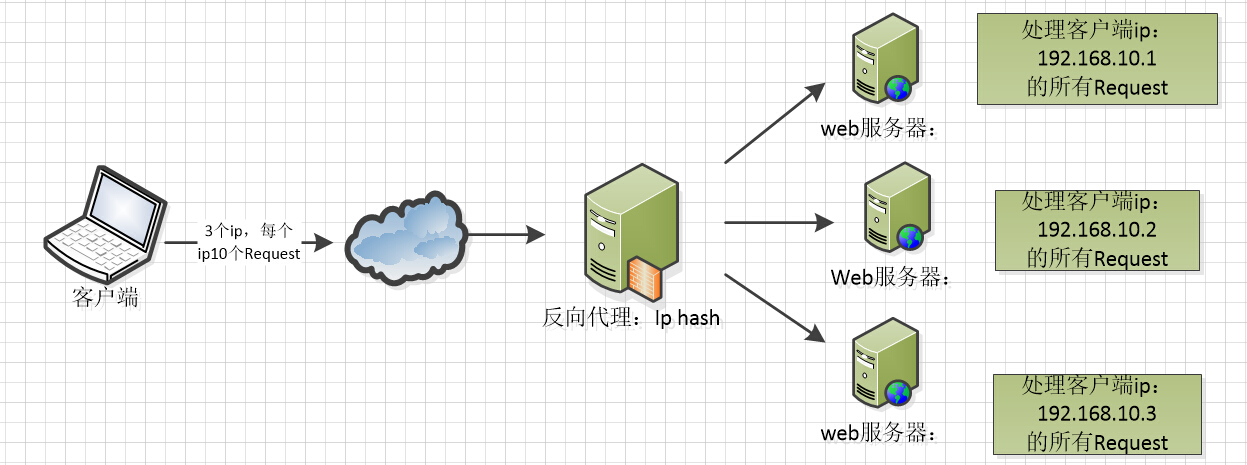
Ip hash algorithm, hash the ip requested by the client, and then distribute the request of the same client ip to the same server for processing according to the hash result, which can solve the problem of session non sharing.
3. web cache
Nginx can cache different files with flexible configuration and supports FastCGI_Cache is mainly used to cache the dynamic programs of FastCGI.
With the third party's ngx_cache_purge, which can add and delete the specified URL cache content.
Official website: http://www.nginx.org/
Nginx configuration file structure
If you download your installation file, you might as well open the nginx.conf file in the conf folder. The basic configuration of the Nginx server and the default configuration are also stored here.
The annotation symbol in nginx.conf is:#
The default nginx configuration file nginx.conf is as follows:
#user nobody;
worker_processes 1;
#error_log logs/error.log;
#error_log logs/error.log notice;
#error_log logs/error.log info;
#pid logs/nginx.pid;
events {
worker_connections 1024;
}
http {
include mime.types;
default_type application/octet-stream;
#log_format main '$remote_addr - $remote_user [$time_local] "$request" '
# '$status $body_bytes_sent "$http_referer" '
# '"$http_user_agent" "$http_x_forwarded_for"';
#access_log logs/access.log main;
sendfile on;
#tcp_nopush on;
#keepalive_timeout 0;
keepalive_timeout 65;
#gzip on;
server {
listen 80;
server_name localhost;
#charset koi8-r;
#access_log logs/host.access.log main;
location / {
root html;
index index.html index.htm;
}
#error_page 404 /404.html;
# redirect server error pages to the static page /50x.html
#
error_page 500 502 503 504 /50x.html;
location = /50x.html {
root html;
}
# proxy the PHP scripts to Apache listening on 127.0.0.1:80
#
#location ~ \.php$ {
# proxy_pass http://127.0.0.1;
#}
# pass the PHP scripts to FastCGI server listening on 127.0.0.1:9000
#
#location ~ \.php$ {
# root html;
# fastcgi_pass 127.0.0.1:9000;
# fastcgi_index index.php;
# fastcgi_param SCRIPT_FILENAME /scripts$fastcgi_script_name;
# include fastcgi_params;
#}
# deny access to .htaccess files, if Apache's document root
# concurs with nginx's one
#
#location ~ /\.ht {
# deny all;
#}
}
# another virtual host using mix of IP-, name-, and port-based configuration
#
#server {
# listen 8000;
# listen somename:8080;
# server_name somename alias another.alias;
# location / {
# root html;
# index index.html index.htm;
# }
#}
# HTTPS server
#
#server {
# listen 443 ssl;
# server_name localhost;
# ssl_certificate cert.pem;
# ssl_certificate_key cert.key;
# ssl_session_cache shared:SSL:1m;
# ssl_session_timeout 5m;
# ssl_ciphers HIGH:!aNULL:!MD5;
# ssl_prefer_server_ciphers on;
# location / {
# root html;
# index index.html index.htm;
# }
#}
}
nginx file structure
... #Global block
events { #events block
...
}
http #http block
{
... #http global block
server #server block
{
... #server global block
location [PATTERN] #location block
{
...
}
location [PATTERN]
{
...
}
}
server
{
...
}
... #http global block
}
1. Global block: configure instructions that affect nginx global.
Generally, there are user groups running nginx server, pid storage path of nginx process, log storage path, introduction of configuration file, number of worker process es allowed to be generated, etc.
2. events block: the configuration affects the nginx server or the network connection with the user.
There is the maximum number of connections per process, which event driven model is selected to process connection requests, whether multiple network connections are allowed to be accepted at the same time, and starting multiple network connection serialization.
3. http block: it can nest multiple server s, configure most functions such as proxy, cache and log definition, and configure third-party modules.
Such as file import, MIME type definition, log customization, whether to use sendfile to transfer files, connection timeout, number of single connection requests, etc.
4. server block: configure the relevant parameters of the virtual host. There can be multiple servers in one http.
5. location block: configure the routing of requests and the processing of various pages.
The following documents are for ease of understanding -
########### Each instruction must end with a semicolon.#################
#user administrator administrators; #Configure users or groups. The default is nobody.
#worker_processes 2; #The number of processes allowed to be generated. The default is 1
#pid /nginx/pid/nginx.pid; #Specify the storage address of nginx process running files
error_log log/error.log debug; #Make log path and level. This setting can be put into the global block, http block and server block. The level is: debug|info|notice|warn|error|crit|alert|emerg
events {
accept_mutex on; #Set the network connection serialization to prevent group panic. The default is on
multi_accept on; #Set whether a process accepts multiple network connections at the same time. The default is off
#use epoll; #Event driven model, select|poll|kqueue|epoll|resig|/dev/poll|eventport
worker_connections 1024; #The maximum number of connections is 512 by default
}
http {
include mime.types; #File extension and file type mapping table
default_type application/octet-stream; #The default file type is text/plain
#access_log off; #Cancel service log
log_format myFormat '$remote_addr–$remote_user [$time_local] $request $status $body_bytes_sent $http_referer $http_user_agent $http_x_forwarded_for'; #Custom format
access_log log/access.log myFormat; #combined is the default value for log format
sendfile on; #sendfile mode is allowed to transfer files. The default is off. It can be in http block, server block and location block.
sendfile_max_chunk 100k; #The number of transfers per call of each process cannot be greater than the set value. The default value is 0, that is, there is no upper limit.
keepalive_timeout 65; #The connection timeout, which is 75s by default, can be set in http, server and location blocks.
upstream mysvr {
server 127.0.0.1:7878;
server 192.168.10.121:3333 backup; #Hot standby
}
error_page 404 https://www.baidu.com; # Error page
server {
keepalive_requests 120; #Maximum number of single connection requests.
listen 4545; #Listening port
server_name 127.0.0.1; #Listening address
location ~*^.+$ { #Request url filtering, regular matching, ~ is case sensitive, ~ * is case insensitive.
#root path; #root directory
#index vv.txt; #Set default page
proxy_pass http://mysvr; # The request goes to the list of servers defined by mysvr
deny 127.0.0.1; #Rejected ip
allow 172.18.5.54; #Allowed ip
}
}
}
The above is the basic configuration of nginx. Note the following:
1. Several common configuration items:
- $remote_addr and $http_x_forwarded_for is used to record the ip address of the client;
- $remote_user: used to record the client user name;
- $time_local: used to record access time and time zone;
- $request: used to record the url and http protocol of the request;
- $status: used to record request status; Success is 200;
- $body_bytes_s ent: record the content size of the file body sent to the client;
- $http_referer: used to record the links accessed from that page;
- $http_user_agent: record the relevant information of the client browser;
2. Group startling phenomenon:
When a network connection arrives, multiple sleeping processes are awakened at the same time, but only one process can get the link, which will affect the system performance.