1. Definition:
Convert the interface of a class to another interface that the customer wants. The adapter pattern allows classes that could not work together because of incompatible interfaces to work together.
II. Classification:
1. Object adapter: loose coupling
UML diagram:
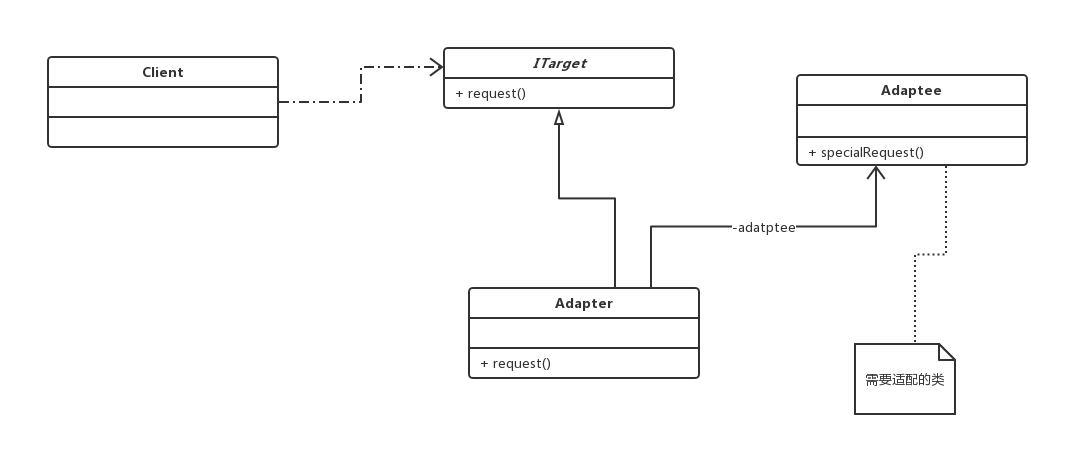
2. Class adapter: high coupling
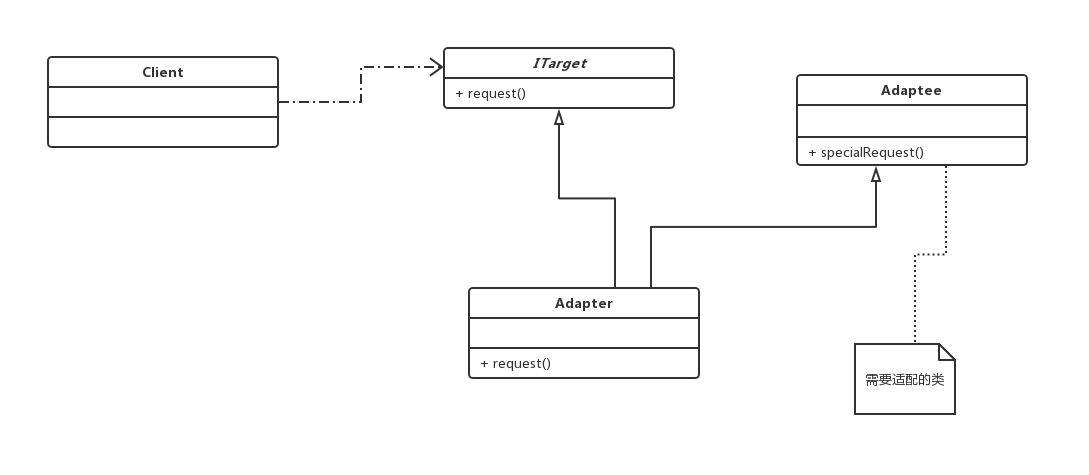
III. composition:
1. Target role: the interface expected by target customers
2. Adapter role: adapter: an adapter object is wrapped internally to convert the source interface to the target interface.
3. Source role: Adaptee
IV. schematic Code:
public class Adaptee {
public void specialRequest() {
System.out.println("this is a special request!");
}
}
public class Adapter extends Target {
Adaptee adaptee=new Adaptee();
@Override
public void request() {
this.adaptee.specialRequest();
}
}
public abstract class Target {
public void request(){
System.out.println("this is a normal request!");
}
}
public class Client {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Target t=new Adapter();
t.request();
}
}
V. advantages and disadvantages:
Advantage:
Better reusability
Better scalability
When implementing adapter functions, you can call your own developed functions, so as to naturally expand the functions of the system
Disadvantages:
Excessive use of adapters will make the system very messy and not easy to grasp as a whole.
6. Textbook example: Yao Ming plays basketball in NBA:
1. UML diagram:
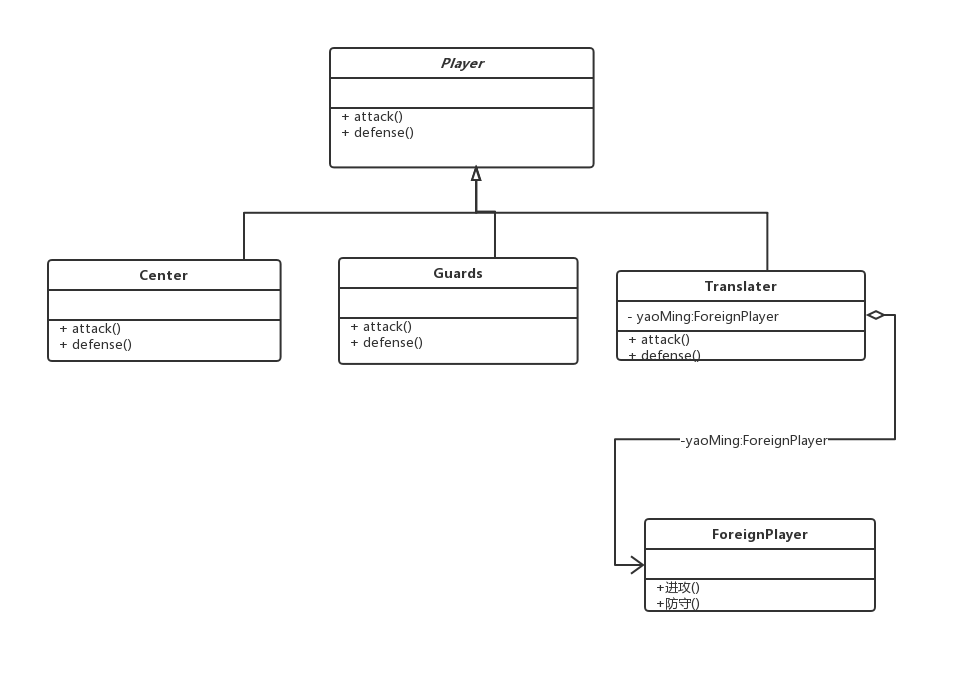
2. Code implementation:
//Target role
public abstract class Player {
protected String name=null;
public Player(String name) {
this.name=name;
}
public void defense() {
System.out.println(name+"denfense");
}
public void attack() {
System.out.println(name+"attack");
}
}
//Specific,,,
public class Guards extends Player {
public Guards(String name) {
super(name);
}
}
public class Center extends Player {
public Center(String name) {
super(name);
}
}
//Adapter role
public class Translate extends Player{
ForeignCenter yaoMing=null;
public Translate(String name) {
super(name);
yaoMing=new ForeignCenter(name);
}
public void attack() {
yaoMing.attack();//Call Chinese method of foreign player
}
public void defense() {
yaoMing.Defense();
}
}
//Source role
public class ForeignCenter {
private String name=null;
public ForeignCenter(String name) {
this.name=name;
}
public void attack() { //-----------Foreign players can only understand Chinese
System.out.println(name+"attack");
}
public void Defense() {
System.out.println(name+"Defense");
}
}
//Scenario class
public class Client {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Player p=new Translate("Yao Ming");
p.attack();
p.defense();
p=new Guards("tracy mcgrady ");
p.attack();
p.defense();
}
}
The end;