catalogue
2 array as parameter of method
2.2 understanding of references
2.4 understand JVM memory area division
3 array as the return value of the method
4.2 find the specified element in the array (binary search)
1 basic usage of array
1.1 what is an array
An array uses a continuous space to store some data of the same type.
Each data in the array has its own unique index, which is also the identification of accessing the element. Subscripts start at 0
For example, there are five numbers in the array, and the data in it corresponds to the sub subscript of the data, as shown in the figure
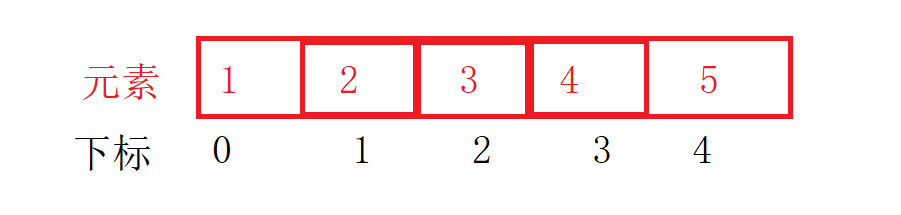
For example:
1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6 and 7 can be stored in an array
1.2 creating arrays
Basic syntax:
Data type [] array name = {initialization data};
Data type [] array name = new data type [number of data to be stored] {initialization data};
Example code:
int[]array1={1,2,3,4,5};
int[]array2=new int[5]={1,2,3,4,5};1.3 use of arrays
There are two basic uses of arrays: 1 is the length of the array or de array, and 2 is to access each element of the array
Example code:
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[]array={1,2,3,4,5};
//Gets the length of the array
int len=array.length;
System.out.println(len);
//Access the array through the index of the array
System.out.println(array[0]);
}
matters needing attention
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[]array={1,2,3,4,5};
//for loop traversal
for(int i=0;i<array.length;i++){
System.out.print(array[i]+" ");
}
System.out.println();
//foreach traverses the array,
for (int x:
array) {
System.out.print(x);
}
System.out.println();
}
2 array as parameter of method
2.1 basic usage
Example code: traversal of array
public static void playArray(int[]array){
for (int i = 0; i <array.length ; i++) {
System.out.print(array[i]+" ");
}
System.out.println();
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] arr = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5};
playArray(arr);
}
In this code, arr is an argument, array is a formal parameter, and array.length can also obtain the length of the array
2.2 understanding of references
First, let's look at the following code:
public static void change(int num){
num=20;
System.out.println("num="+num);
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
int a=10;
change(a);
System.out.println("a="+a);
}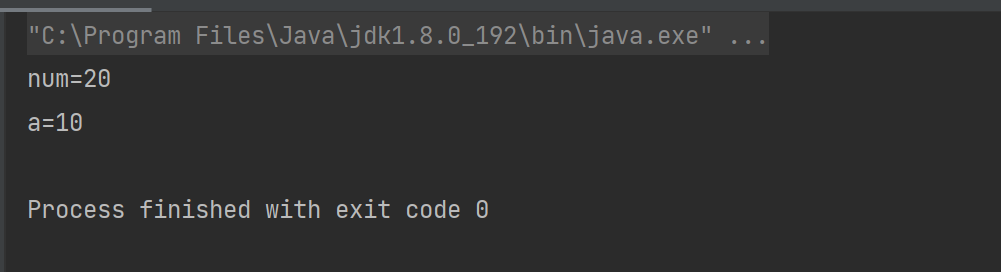
Obviously, we can't change a through methods, because num is just a copy of A. they just have the same value
So what should we do if we want to modify a spatial data through a method?
The concept of reference is introduced here
Reference: reference is also a variable, but it stores the address of an object (the concept of object will be discussed later).
Let's look at a piece of code
public static void change(int[]array){
for(int i=0;i<array.length;i++){
array[i]*=2;
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
int arr[]={1,2,3,4,5};
change(arr);
playArray(arr);
}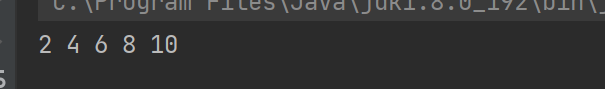
We can see that the data in the array has been changed. Why is this? Let's discuss this problem below.
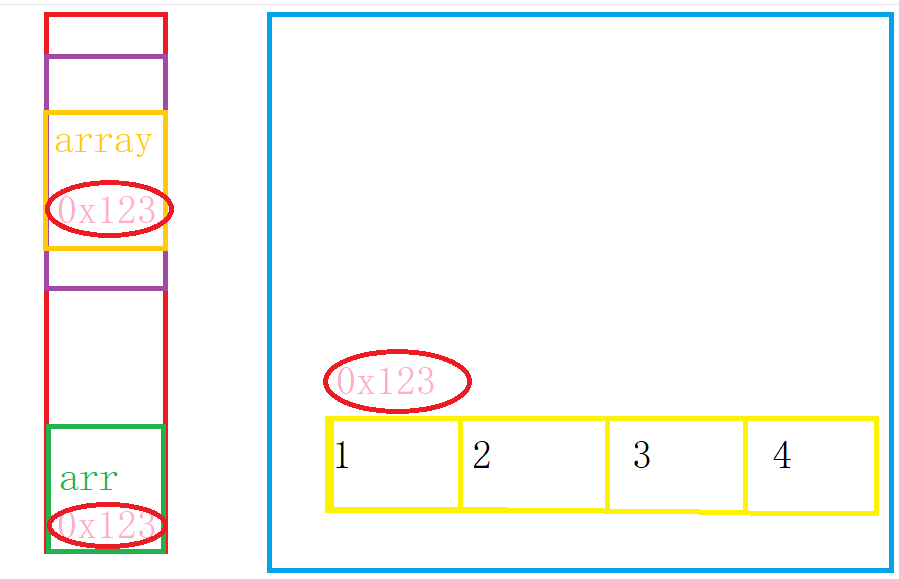
First of all, I want to tell you that an array is a reference type. The array name is the variable name of the reference type, and the address of the elements in the array is stored in the variable. Then, a copy of array to arr, that is, the same address is also stored in array. Through the address, the value of the space corresponding to the address can be changed.
As shown in the figure:
2.3 understanding
2.4 understand JVM memory area division

The inner dimension of the JVM is divided into several different regions
3 array as the return value of the method
Example code: expand each element in an array by 2 times and return
public static int[]toDouble(int[]array){
int[]returnArray=new int[array.length];
for (int i = 0; i <array.length ; i++) {
returnArray[i]=array[i];
}
return returnArray;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
int arr[]={1,2,3,4,5};
playArray(toDouble(arr));
}
4 array exercises
4.1 array to string
code:
/**
* Array to string
* @param array Array to convert
* @return Converted String
*/
public static String toString(int[]array){
String str="[";
for(int i=0;i<array.length;i++){
str+=array[i];
if(i<array.length-1){
str+=",";
}
}
str+="]";
return str;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
int arr[]={1,2,3,4,5};
System.out.println(toString(arr));
}
4.2 find the specified element in the array (binary search)
/**
* Binary search
* @param array Array to find
* @param key Number of to find
* @return If it is found, it returns the subscript of the number to be found. If it is not found, it returns an error message
*/
public static int binarySearch(int[]array,int key){
int left=0;
int right=array.length-1;
while(left<=right){
int mid=(left+right)/2;
if(array[mid]>key){
right=mid-1;
}else if(array[mid]<key){
left=mid+1;
}else{
return mid;
}
}
return -1;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
int arr[]={1,2,3,4,5};
System.out.println(binarySearch(arr,2));
}