Give me warm eyes
character string:
A string of data composed of multiple characters is called a string
It can also be regarded as a character array
Is a constant whose value cannot be changed once initialized
1, Construction method
1.1 public String()
Create an empty string with a length of 0, which is meaningless, so it is generally not used
String s1 = new String(); System.out.println(s1); System.out.println(s1 + " + " + s1.length()); // + 0
1.2 public String(byte[] bytes)
Converts a byte array into a string
Because the array needs to be converted into ascii code, the members in the array should be legal
byte[] a = {97, 98, 99, 100, 101};
String s2 = new String(a);
System.out.println(s2 + " + " + s2.length());
// abcde + 5
1.3 public String(byte[] bytes,int offset,int length)
Truncate a part of the byte array into a string
offset is the starting index position and length is the interception length
byte[] b = {97, 98, 99, 100, 101};
String s3 = new String(a,1,3);
System.out.println(s3 + " + " + s3.length());
// bcd + 3
1.4 public String(char[] value)
Converts a character array into a string
char[] c = {'f','g','h','Leek','food','box','son'};
String s4 = new String(c);
System.out.println(s4 + " + " + s4.length());
// fgh leek box + 7
1.5 public String(char[] value,int offset,int count)
Truncate a part of the character array as a string
offset is the starting index position and count is the intercept length
char[] d = {'f','g','h','Leek','food','box','son'};
String s5 = new String(d,3,4);
System.out.println(s5 + " + " + s5.length());
// Leek box + 4
1.6 public String(String original)
Converts a string to a new string
String e = "fgh Leek box "; String s6 = new String(e); System.out.println(s6 + " + " + s6.length()); // fgh leek box + 7
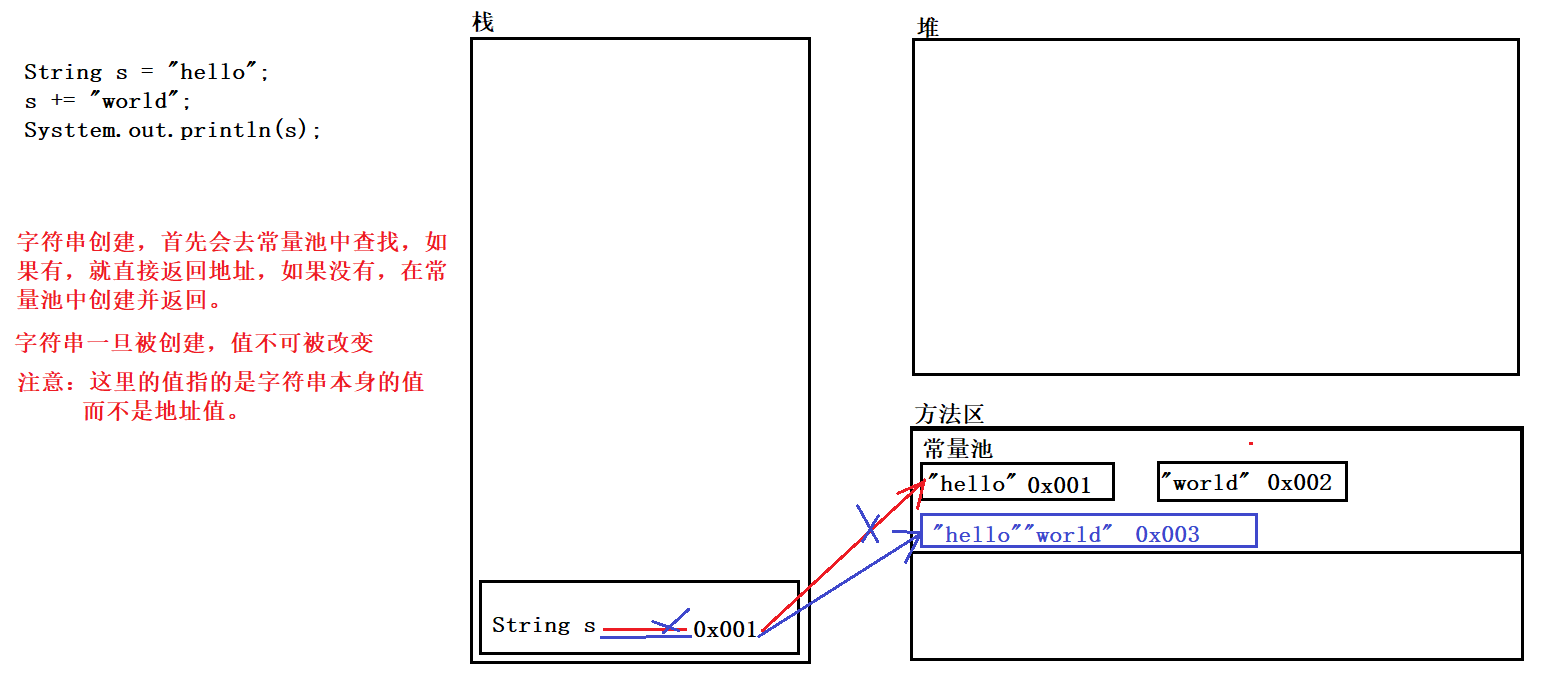
2, The String value cannot be changed
String s = "hello"; s += "world"; System.out.println(s); // helloworld
At this time, helloworld is output because:
The variable s here is a reference type and points to the address of "hello" in the constant pool
When the + = operation is performed on it in the second step, space will be opened up in the constant pool to store "helloworld"
Then point s to the address of "Hello world"
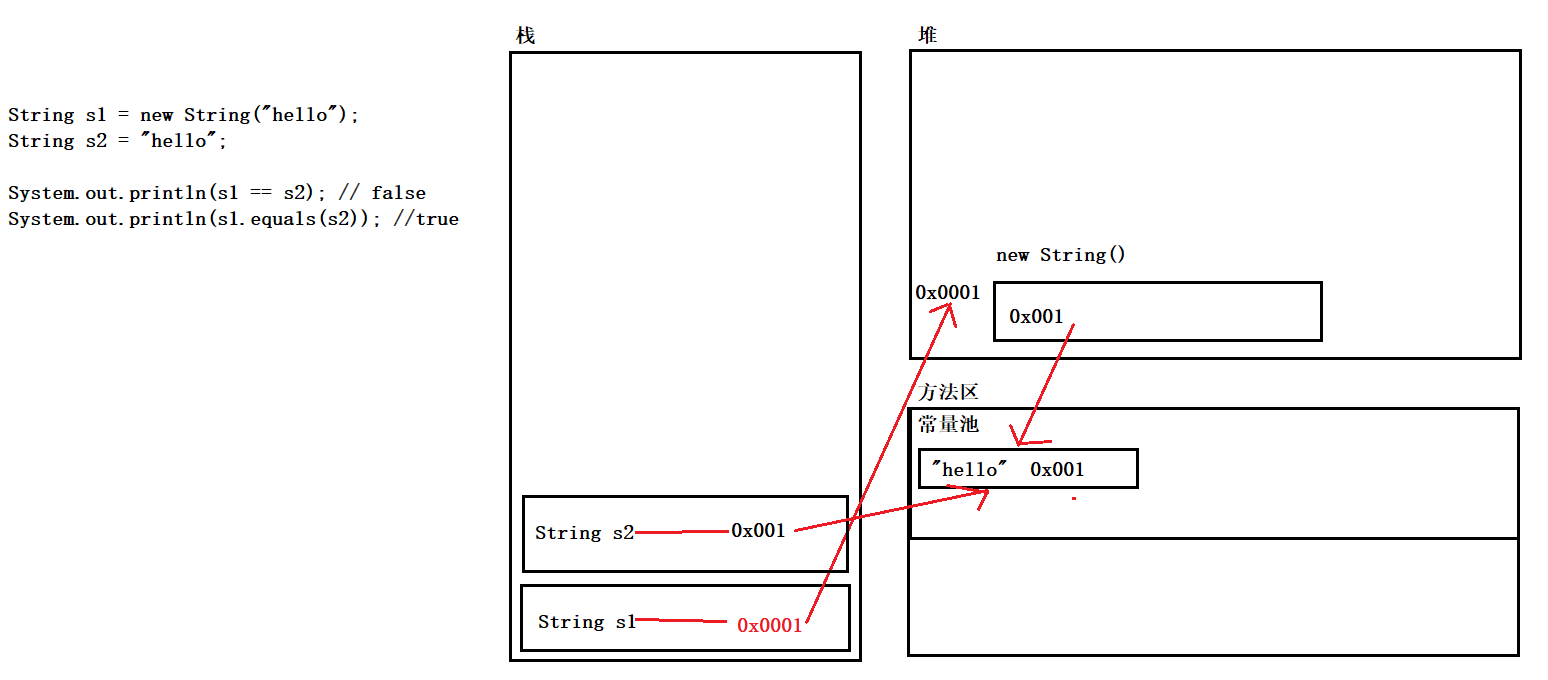
2, The difference between String and new String
String s1 = "hello";
String s2 = new String("hello");
System.out.println(s1 == s2); // false
System.out.println(s1.equals(s2)); // ture
s1 points to the address of "hello" in the constant pool
s2 is an object created in heap memory and points to the address of "hello" in the constant pool
One is the address of the constant pool and the other is the address of the heap memory, so the addresses are different
The equals() method is overridden by default in the String class. At this time, the addresses in the two final constant pools are compared
3, String addition
1. If the string is a variable addition, it will open up space first, and then splice
2. If the string is a constant addition, add it first, and then look for it in the constant pool. If it is found, it will be returned. If it is not found, it will be created
String a = "hello"; String b = "world"; String c = "helloworld"; String d = a + b; String e = "helloworld"; String f = a + b; //Get string address value System.out.println(System.identityHashCode(c)); // 1163157884 System.out.println(System.identityHashCode(d)); // 1956725890 System.out.println(System.identityHashCode(e)); // 1163157884 System.out.println(System.identityHashCode(f)); // 356573597 System.out.println(d == a + b); //false System.out.println(d == "helloworld"); //false
4, Judgment function of String class
4.1 boolean equals(Object obj)
Compares whether the contents of the string are the same, and is case sensitive
String a = "helloworld"; String b = "helloworld"; System.out.println(a.equals(b)); // true
4.2 boolean equalsIgnoreCase(String str)
Compares whether the contents of the string are the same, ignoring case
String a = "helloworld"; String c = "Helloworld"; System.out.println(a.equalsIgnoreCase(c)); // true
4.3 boolean contains(String str)
Judge whether the large string contains the string str. if so, it returns true, otherwise it is false
Case sensitive
String a = "helloworld"; String d = "world"; System.out.println(a.contains(d)); // true
4.4 boolean startsWith(String str)
Tests whether this string starts with the specified prefix
Case sensitive
String a = "helloworld"; String e = "hel"; String f = "ello"; System.out.println(a.startsWith(e)); // true System.out.println(a.startsWith(f)); // fales
##4.5 Boolean endswith (string STR) > test whether the string ends with the specified suffix > case sensitive ` ` ` java String a = "helloworld"; String e = "rld"; String f = "Rld"; System.out.println(a.startsWith(e)); // true System.out.println(a.startsWith(f)); // false ```
4.6 boolean isEmpty()
Determine whether the string is empty
String g = ""; String h = null; System.out.println(g == h); // false System.out.println(g.isEmpty()); // true System.out.println(h.isEmpty()); // true
5, Judgment function of String class
5.1 int length()
Gets the length of the string
String s = "helloworld"; System.out.println(s.length()); // 10
5.2 char charAt(int index)
Returns the value at the index specified by char
String s = "helloworld"; System.out.println(s.charAt(1)); // e //An error will be reported when crossing the boundary
5.3 int indexOf(int ch)
Returns the index within the string where the specified character first appears
String s = "helloworld";
System.out.println(s.indexOf('e')); // 1
//Return - 1 not found
5.4 int indexOf(String str)
Returns the index within the string where the specified substring first appears
Index of the first character of the string
String s = "helloworld";
System.out.println(s.indexOf("ello")); // 1
//Return - 1 not found
5.5 int indexOf(int ch,int fromIndex)
Returns the index within the string where the specified character first appears, starting the search with the specified index
String s = "helloworld";
System.out.println(s.indexOf('o',4)); // 4
//Return - 1 not found
5.6 int indexOf(String str,int fromIndex)
Returns the index within the string where the specified string first appears, and starts the search with the specified index
String s = "helloworld";
System.out.println(s.indexOf("wo",3)); // 5
//Return - 1 not found
5.6 String substring(int start)
Returns a string that is a substring of this string
A substring starts with a character at the specified index and extends to the end of the string
String s = "helloworld"; System.out.println(s.substring(5)); // world //An error will be reported when crossing the boundary
5.7 String substring(int start,int end)
Returns a string that is a substring of this string
The substring starts at the specified index start and extends to the index end - 1
Left closed right open [start, end)
String s = "helloworld"; System.out.println(s.substring(5,10)); // world //An error will be reported when crossing the boundary
summary
boolean equals(Object obj)
Compare whether the contents of the string are the same
Case sensitive
boolean contains(String str)
Judge whether the large string contains the string str. if so, it returns true, otherwise it is false
Case sensitive
boolean startsWith(String str)
Tests whether this string starts with the specified prefix
Case sensitive
boolean isEmpty()
Determine whether the string is empty
int length()
Gets the length of the string
String substring(int start)
Returns a string that is a substring of this string
A substring starts with a character at the specified index and extends to the end of the string
String substring(int start,int end)
Returns a string that is a substring of this string
The substring starts at the specified index start and extends to the index end - 1
Left closed right open [start, end)