Database security and transaction operation
Article catalog
- Database security and transaction operation
- 1, Purpose and requirements
- 2, Experiment content
- 1. Design the security mechanism so that the user Wang Ming can only find the staff of the financial department
- 2 design a role_Emp ", this role can view employee number and name. And add Wang Ming to the role as a member
- 3. User Zhang Ming has the following permissions; he can only check the information in the purchase list, and has the permission to modify the information in his purchase list, but not the information in other tables.
- How to make employees in the purchasing department have the right to view the information in the purchase list and modify their own purchase information
- 5 bank transfer issues
- Encryption and decryption of database fields
- A user table is given. The code to create the table is as follows
- 3, Problems encountered and Solutions
- 4, Experiment summary
1, Purpose and requirements
- Master SQL security mechanism
- Master the management of server security
- Master the management of database users
- Master the management of authority
2, Experiment content
1. Design the security mechanism so that the user Wang Ming can only find the staff of the financial department
Idea: create a login SQL account Wang Ming, database user Wang Ming DB, create a view containing only employees of the financial department, and grant Wang the right to query the view
--establish SQL server Login account Wang Ming use Experiment 3 exec sp_addlogin 'Wang Ming' ,'123456' --Create database user Wang Ming DB exec sp_grantdbaccess 'Wang Ming','Wang Ming DB' go --Create a view that contains only the information of employees in the finance department CREATE VIEW view_FinanceEmp as SELECT * from Employees where Employees.dep_no = (select dep_no from Department where dep_name='Finance Department') go --Awarded to Wang Ming DB View permissions for this view GRANT SELECT ON view_FinanceEmp to Wang Ming DB
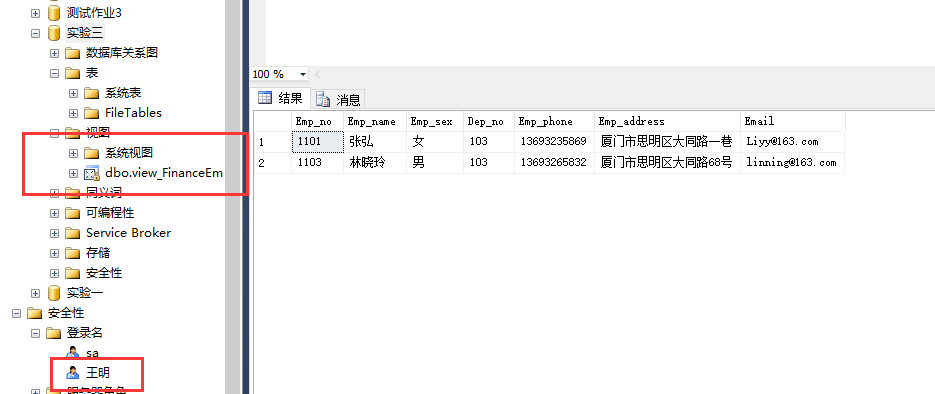
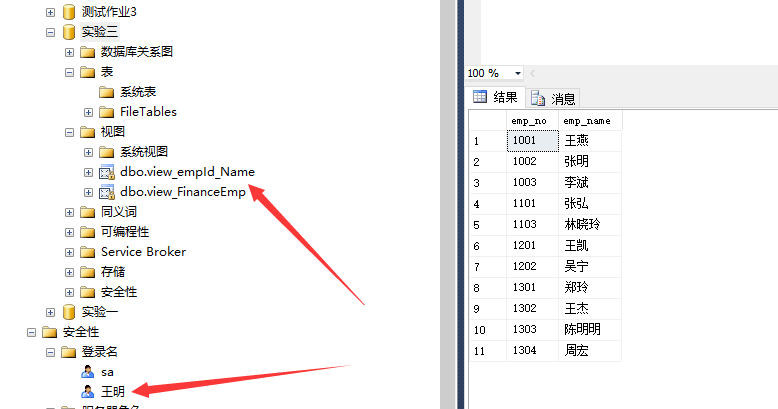
2 design a role_Emp ", this role can view employee number and name. And add Wang Ming to the role as a member
Ideas:
1 create role: sp_addrole ‘role_Emp ', create view
2 authorize the role
3 add Wang Ming DB to the role
--Create role exec sp_addrole 'role_Emp' --Create a view containing only employee number and name go CREATE VIEW view_empId_Name as select emp_no,emp_name from Employees go; select * from view_empId_Name go --Grant the role the right to query GRANT select on view_empId_Name to role_Emp --Add Wang Ming to the role exec sp_addrolemember 'role_Emp','Wang Ming DB'
3. User Zhang Ming has the following permissions; he can only check the information in the purchase list, and has the permission to modify the information in his purchase list, but not the information in other tables.
Give him permission to view the Purchase table
Give him permission to modify part (view) of purchase table
exec sp_addlogin 'Zhang Ming','123456'--establish sql Login account exec sp_grantdbaccess 'Zhang Ming','Zhang Ming DB'--Create database user Zhang Ming DB go create view view_zhangming as select * from Purchase where Emp_no in(select Emp_no from Employees where Emp_name='Zhang Ming') go Grant select on Purchase to Zhang Ming DB --Grant permission to query purchase list Grant select,update on view_zahngming to Zhang Ming DB --Grant permission to modify the information of own purchase
This view is exported from a single table, including the primary key and no aggregation function, so when you modify the view, the basic table will also be modified
How to make employees in the purchasing department have the right to view the information in the purchase list and modify their own purchase information
(write stored procedure Pro_purchase function: enter the name of the employee as the parameter, and search the product purchased by the employee from the purchase table. If not, return it. If yes, add the account and password in the login table accordingly. And create corresponding login account and database user)
go create proc proc_stu_grant @Emp_name varchar(30) as begin declare @view varchar(20) --View name declare @str varchar(255) --Execute statement if exists (select Pur_no from Purchase where Emp_no in (select Emp_no from Employees where Emp_name=@Emp_name))--Judge whether the employee has purchase information begin set @view =@Emp_name + '_v' set @str='create view '+@view+' as select * from Purchase where Emp_no in (select Emp_no from Employees where Emp_name='''+@Emp_name+''')' --Create your own purchase information view statement exec(@str) exec sp_addlogin @Emp_name,'123' --Create login account exec sp_grantdbaccess @Emp_name,@Emp_name --Create employee user set @str='Grant select on Purchase to '+@Emp_name --Grant permission statement to query purchase list exec(@str) set @str='Grant select,update on '+@view+' to '+@Emp_name--Grant query permission statement to modify the information of own purchase exec(@str) end else print 'No purchase information of the employee!!' end
exec proc_stu_grant 'Li Bin' select * from Li Bin_v
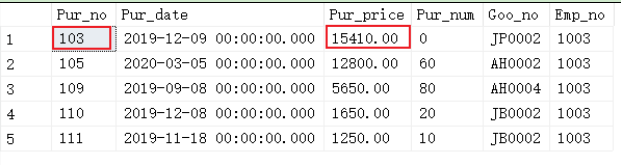
Summary:
(1)Create user CREATE USER 'user_name'@'host' IDENTIFIED BY 'password';
user_name: The name of the user to create.
host: Indicates which machine this newly created user is allowed to log in from. If only the local machine is allowed to log in, fill in the'localhost',If remote login is allowed, fill in'%'
password: The login database password of the newly created user. If there is no password, it can be left blank. (2)To delete a user command: DROP USER
'user_name'@'host' (3)Revoke user rights: Command: REVOKE privileges ON
database.tablename FROM 'username'@'host'
5 bank transfer issues
CREATE TABLE bank --Create account table to store user's account information (customerName CHAR(10), --Customer name currentMoney MONEY --Current balance ) go --Add constraint: according to the regulations of the bank, the account balance cannot be less than 1 yuan, otherwise it will be regarded as account cancellation ALTER TABLE bank ADD CONSTRAINT CK_currentMoney CHECK(currentMoney>=1) go --Zhang Hong opens an account with an account amount of 1000 yuan; Li Ming opens an account with an account amount of 1 yuan INSERT INTO bank(customerName,currentMoney) VALUES('Zhang Hong',1000) INSERT INTO bank(customerName,currentMoney) VALUES('Li Ming',1)
Write out the stored procedure of solving bank transfer with Transaction:
go create proc Bank_proc @send char(10),--Name of payer @receive char(10),--Name of payee @money money--Transfer amount as begin set nocount on --Do not return count begin try--Catch exception start begin tran--Transaction start update bank set currentMoney=currentMoney-@money where customerName=@send --Update amount of transfer out account update bank set currentMoney=currentMoney+@money where customerName=@receive --Update amount transferred to account print 'Transfer succeeded'+str(@money)+'Yuan.' commit tran --Normal commit transaction end try begin catch print'Account balance is insufficient, transfer failed!' rollback tran --Rollback transaction end catch --Catch exceptions end
Test data:
exec pro_bank 'Zhang Hong', 'Li Ming', 200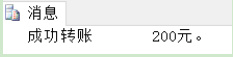
exec pro_bank 'Li Ming', 'Zhang Hong', 1000
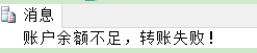
Summary:
There are four commands for controlling transactions: (1) COMMIT: COMMIT changes; (2) ROLLBACK: roll back changes;
(3) SAVEPOINT: create a series of ROLLBACK restore points within the transaction; (4) SET TRANSACTION: name the transaction;
SAVE TRANSACTION: SAVE TRANSACTION savepoint name -- name and location of custom savepoint ROLLBACK TRANSACTION
Savepoint name -- rollback to a custom savepoint
Encryption and decryption of database fields
(1) The empty table to create the reader table is called reader_bak, add a field: ID No
select * into Reader_bak from Reader where 1=2 alter table Reader_bak add ID number varbinary(150) select * from Reader_bak

(2) Create database master key
create master key encryption by password='1128'
result:
SELECT * FROM sys.symmetric_keys

(3) Establish certificate I, which is encrypted with the database master key
create certificate Cert_Demo with subject=N'cert encryption by database master key', start_date='2020-5-20', expiry_date='2020-6-20'
result:
(4) To reader_bak inserts a piece of data, library card No.: 210 ID card: 1234567891123456789, and encrypts the ID card
insert Reader_bak(Read_no,ID number) values('210',encryptbycert(cert_id(N'Cert_Demo'),N'350211199611020045'))

(5) Decrypt and display the encrypted ID card
select convert(nvarchar(50),decryptbycert(cert_id(N'Cert_Demo'),ID number)) from Reader_bak
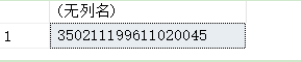
(6) Summarize the understanding of database field encryption and decryption
1. SQLSERVER Encryption and decryption function(Asymmetric key certificate encrypting symmetric key) ENCRYPTBYASYMKEY() --Asymmetric key ENCRYPTBYCERT() --Certificate encryption ENCRYPTBYKEY() --Symmetric key ENCRYPTBYPASSPHRASE() --Pass phrase( PassPhrase)encryption 2. --Create certificate CREATE CERTIFICATE CertTest with SUBJECT = 'Test Certificate' GO --Create asymmetric key CREATE ASYMMETRIC KEY TestAsymmetric WITH ALGORITHM = RSA_2048 ENCRYPTION BY PASSWORD = 'pa$$word'; GO --Create symmetric key CREATE SYMMETRIC KEY TestSymmetric WITH ALGORITHM = AES_256 ENCRYPTION BY PASSWORD = 'pa$$word'; GO
A user table is given. The code to create the table is as follows
create table users( Unumber INT IDENTITY(1,1), Uname varchar(20), sex char(2), Upassword char(10), CONSTRANIT PK_Unum PRIMARY KEY(Unumber), CONSTRAINT CK_sex CHECK(sex='male' OR sex='female'), CONSTRAINT CK_Upassword CHECK (LEN(Upassword)>=6) )
It is required to create a stored procedure to automatically convert the inserted password into plaintext (MD5 encryption is implemented with built-in function of SQL) when inserting user table data, and throw an exception in the Check constraint or trigger constraint caught in the stored procedure. In this way, data verification can be easily realized, and the judgment of many to many data in the stored procedure can be reduced.)
go create proc proc_insert_user @name varchar(20), @sex char(2), @pw char(10) as begin if(len(@pw)<6) begin raiserror('The length of the password entered is less than 6, please re-enter!',16,1) return end declare @errorMessage nvarchar(100) begin try insert into users(Uname,sex,Upassword) values(@name,@sex,substring(sys.fn_sqlvarbasetostr (HashBytes('MD5',@pw)),3,32)) end try begin catch --Returns a pointer to the string containing the error message, or if there is no error indication NULL. set @errorMessage=ERROR_MESSAGE() --adopt charindex If the corresponding string can be found, the position of the string will be returned, otherwise 0 will be returned if(charindex('CK_sex',@errorMessage)!=0) begin raiserror('Gender input error, please input again!',16,1) end end catch end
exec proc_insert_user 'Xiaozhang', '1', '123456'
exec proc_insert_user 'Xiaozhang', 'man', '1'
exec proc_insert_user 'Xiaozhang', 'man', '123456'
3, Problems encountered and Solutions
In the third question:


The last @ dbname is not recognized
Guess because the variable @ dbname string has Quotes
The scope of a local variable is the batch it is declared in
4, Experiment summary
Three layer security mechanism of SQL
| SQL operation security defense | Only when the user logs in successfully can he establish a connection with SQL server |
|---|---|
| Security defense of SQL database | Each database has its own users and roles, which can only be accessed by its users and roles, so as to avoid illegal users' access to the database |
| Security defense of SQL database objects | For authority management, legal users must operate data within their own authority. |
2 transaction management
Transaction control statement
--#Defining the start of a transaction BEGIN TRANSACTION T1 --#Commit transaction, end a transaction COMMIT TRAN --# Roll back the transaction to the beginning of the transaction or to a savepoint ROLLBACK TRAN --# Setting a savepoint in a transaction is a partial operation rollback within a transaction SAVE TRAN save_name --# @@ERROR a message that records the latest ERROR in the database --#@@The initial value of transmission is 0. Each time BEGIN TRAN is increased by 1, commit is decreased by 1, and rollback is directly returned to 0
Blocking mechanism sp_lock
Transaction log
Summary of three-tier security mechanism stored procedures
| Add SQL server server login account | exec sp_addlogin 'wmy' ,'123456' sp_droplogin |
|---|---|
| Add access user of a database | exec sp_grantdbaccess 'wmy','wmyDB' |
| Delete users of a database | exec sp_revokedbaccess 'wmyDB' |
| Have all operation rights to SQL server sysadmin | exec sp_addsrvrolemember 'wmy' ,'sysadmin' |
| Cancel all operation rights of a user to SQL server | exec sp_dropsrvrolemember 'wmy','sysadmin' |
| Have any operation permission on a database db_owner | exec sp_addrolemenber 'db_owner','wmyDB' |
| Grant some authority to a database user | GRANT SELECT ON TABLE1 TO wmyDB DENY INSER ,UPDATE ,DELETE ON TABLE1 TO wmyDB |
| Database creation role | exec sp_addrole ‘moniter_role '(role name) |
| Assign a role to a user | exec sp_addrolemember 'monitor_role','wmy' |