1. Introduction to Matplotlib
Matplotlib is a Python 2D drawing library that can generate publication quality data in various hard copy formats and cross platform interactive environments. Matplotlib can be used for Python scripts, Python and IPython shell s, Jupyter notebooks, Web application servers, and four GUI toolkits.
2. matplotlib installation
matplotlib installation can use source installation and pip installation. Pip is installed as follows:
pip install matplotlib
Install the latest version by default, or install the specified version
pip install matplotlib==2.2.0
3. Maplotlib drawing example
3.1 common statistical graphs
- Scatter plot
x = np.arange(50)
y = x + 5 * np.random.rand(50)
plt.scatter(x, y)
plt.title('Scatter plot') # Add title
plt.xlabel('independent variable') # Add abscissa
plt.ylabel('dependent variable') # Add ordinate
plt.xlim(xmin=0, xmax=50) # Add abscissa range
plt.ylim(ymin=0, ymax=50) # Add ordinate range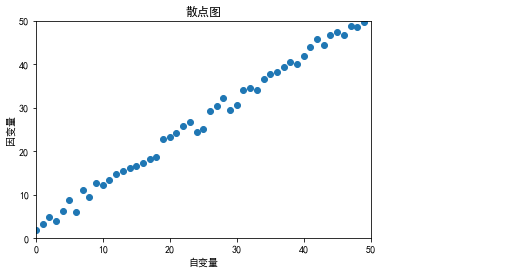
-
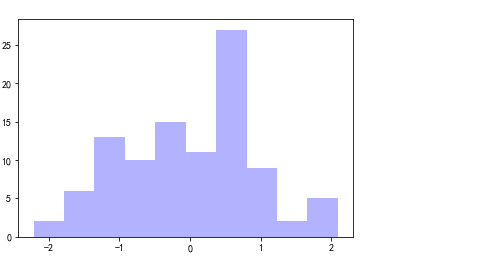
histogram
plt.hist(x=np.random.randn(100), bins=10, color='b', alpha=0.3)
-
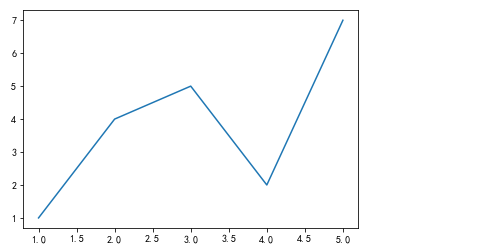
Broken line diagram
plt.plot([1,2,3,4,5],[1,4,5,2,7])
-
Histogram
x = np.arange(5) y1, y2 = np.random.randint(1, 25, size=(2, 5)) width = 0.25 plt.bar(x, y1, width, color='r') plt.bar(x+width, y2, width, color='g')
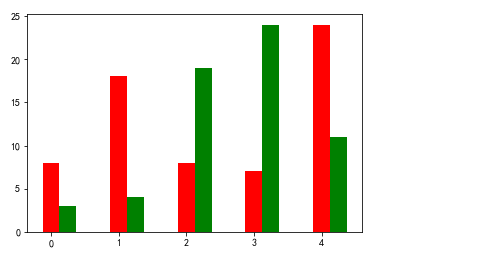
- Pie chart
explode=(0,0.1,0,0,0) partions = [0.30,0.20,0.1,0.15,0.25] labels = ['Apple','Samsung','millet','HUAWEI','others'] plt.pie(partions,labels=labels,explode=explode,autopct='%1.0f%%')
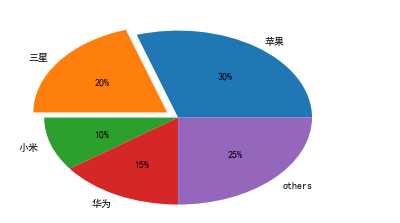
3.2 compilation of mathematical function curve
-
trigonometric function
x = np.arange(-np.pi,np.pi,0.01) y1 = np.sin(x) y2 = np.cos(x) plt.plot(x,y1,color='green',linewidth=1,linestyle='-',label='Sinusoidal curve') plt.plot(x,y2,color='blue',linewidth=1,linestyle='--',label='Cosine curve') plt.legend() # Add annotation
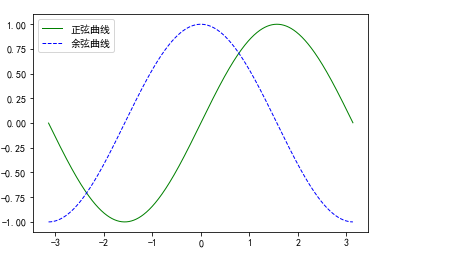
-
exponential function
t = np.linspace(-50.0,50.0,1000) func_exp = np.exp(-0.1*t) plt.plot(t,func_exp) plt.title('exp(-0.1*t)')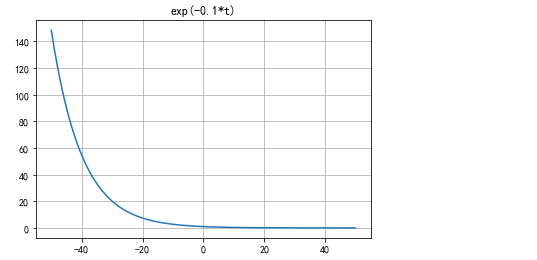
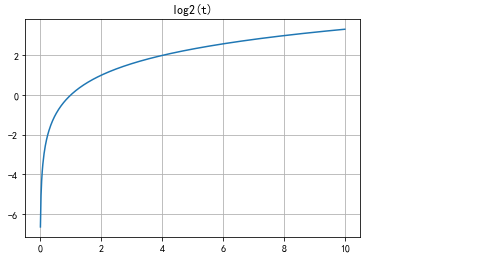
- Logarithmic function
t = np.linspace(-10.0,10.0,1000) func_log2 = np.log2(t) plt.plot(t,func_log2) plt.title('log2(t)') plt.grid()