1, Data structure Preface
1. Data structure: data and organization between data
2. Program (data and function composition) = data structure + algorithm
3. Time complexity
Concept: the number of execution times of a statement of an algorithm program (rather than the running time of the algorithm);
Time complexity is a function T (n). For convenience, the standard of large o representation is generally used: progressive time complexity O (f (n));
Time complexity of common algorithms:
- Time complexity of recursive algorithm = time complexity of single call + total recursion times
- Bubble sort time complexity = O(n^2)
- Binary search time complexity = O(log(n))
- Recursive Fibonacci number time complexity prime = O(2^n)
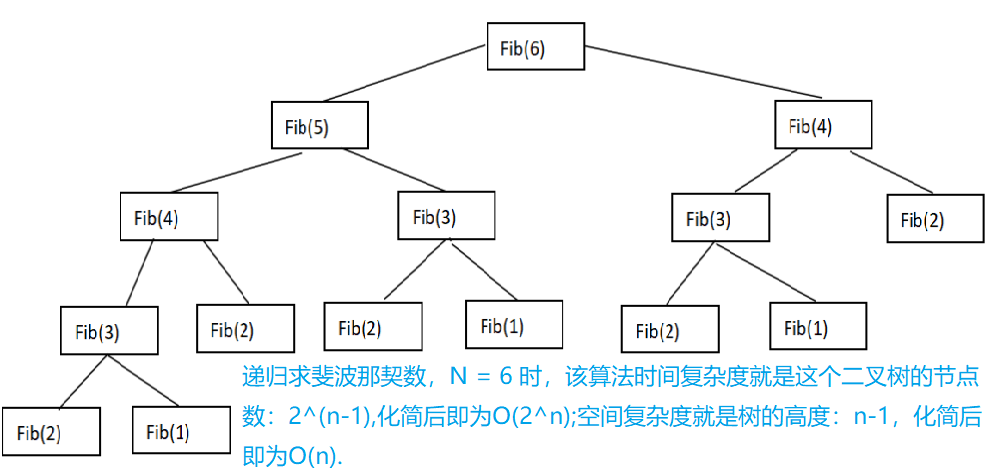
4. Space complexity
Concept: the amount of space temporarily occupied by an algorithm during operation (i.e. the newly opened space after operation);
Spatial complexity is a function S (n). For convenience, the standard of large o representation is generally used: progressive spatial complexity O (f (n));
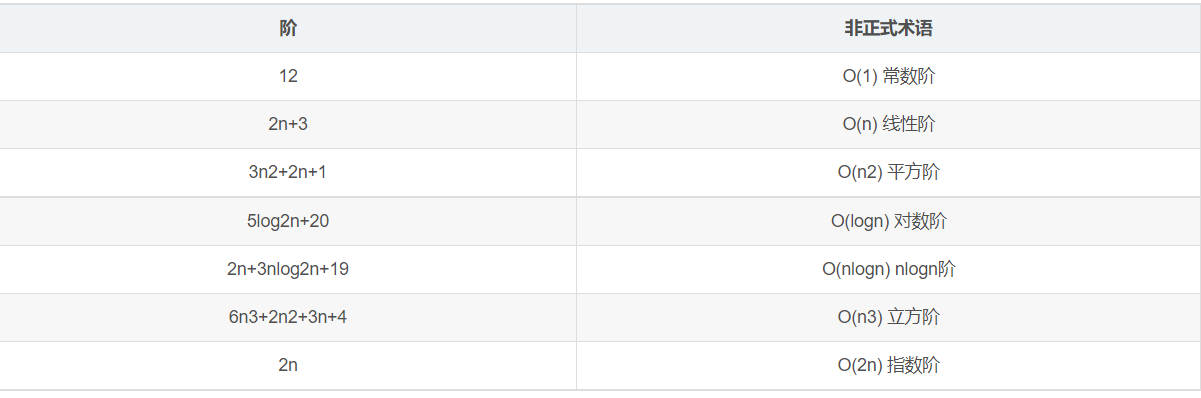
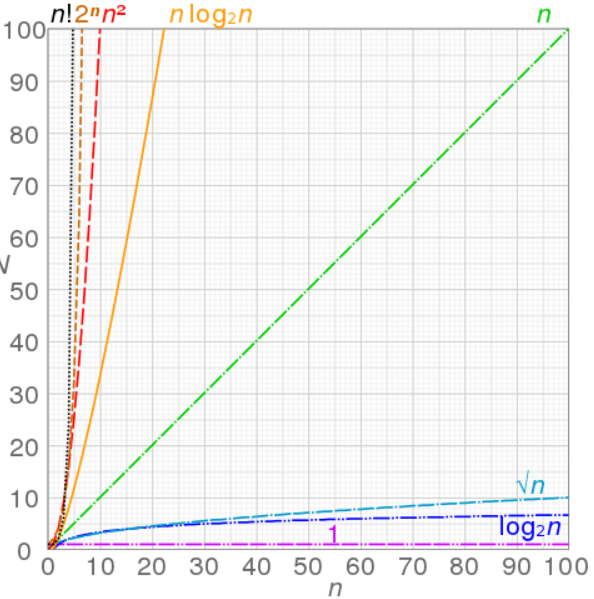
Common complexity performance
2, Sequence table
- Sequential table is a linear structure in which data elements are stored in sequence with a storage unit with continuous physical addresses. Generally, array storage is used. In array
Complete data addition, deletion, query and modification on.
1. Two development methods of sequence table (data structure of sequence table)
Static sequence table
Put the data directly into a fixed length array
//Static storage of sequence table
#define N 7
struct SeqList
{
int array[N]; //Fixed length array
size_t size; //Number of valid data
}
Dynamic sequence table
Dynamically open up the array on the heap and return the starting position pointer
//Dynamic storage of sequence table
struct SeqList
{
int *array; //A pointer is used as the starting position of the array
size_t size; //Number of valid data
size_t capicticy; //Size of space on heap
}
2. Common functions of sequence table
1) Initialize dynamic sequence table
Open up a custom length sequence table on the heap, with a minimum of three elements by default
void SeqListInit(SeqList* ps, int initCapacity)
{
assert(ps); //Check whether the incoming address is legal
initCapacity = initCapacity <= 0 ? 3 : initCapacity; //Detect the second parameter. If it is illegal, three spaces are opened by default
ps->array = (DataType*)malloc(initCapacity * sizeof(DataType));
if (NULL == ps->array)
{
assert(0); //Display the cause of the error through assert
return;
}
ps->capacity = initCapacity;
ps->size = 0;
}
2) Release sequence table
Because the dynamic sequence table is opened on the heap, it needs to be released after the call to avoid memory overflow
void SeqListDestroy(SeqList* ps)
{
assert(ps);
if (ps->array)
{
free(ps->array); //The linked list memory is continuously opened up and released as a whole
ps->array = NULL;
ps->capacity = 0;
ps->size = 0;
}
}
3) Tail insertion and head insertion of sequence table
a. Before inserting the sequence table, you must check whether the space is sufficient. Customize the space detection function static void ChecKCapacity(SeqList* ps)
b. The header insert needs to move all the following elements backward in turn
c. Therefore, the tail insertion time complexity is O(1) and the head insertion time complexity is O(N)
d. Remember to add 1 to the effective size of the array after the insert operation
// Tail insertion
void SeqListPushBack(SeqList* ps, DataType data)
{
assert(ps);
//1. Check whether the space is sufficient
ChecKCapacity(ps);
//2. Insert data for the last element
ps->array[ps->size] = data;
ps->size++;
}
// Head insert
void SeqListPushFront(SeqList* ps, DataType data)
{
assert(ps);
//1. Check whether the space is sufficient
ChecKCapacity(ps);
//2. Move all elements back one bit as a whole
for (int i = ps->size - 1; i >= 0; i--)
{
ps->array[i + 1] = ps->array[i];
}
//3. Insert element
ps->array[0] = data;
ps->size++;
}
4) Sequential table space detection function
a. It is defined as static static function to make it valid only in the program of this document
b. If the space is insufficient, the new space opened each time is twice as large as the original space (here, use the shift left < < operator to expand it by 2 times)
c. Note that after the new space is opened, the original heap space should be released
static void ChecKCapacity(SeqList* ps)
{
assert(ps);
if (ps->size == ps->capacity)
{
//Open up new space
int newCapacity = (ps->capacity << 1); //One bit to the left is twice the size
DataType* temp = (DataType*)malloc(newCapacity * sizeof(DataType));
if (NULL == temp)
{
assert(0);
return;
}
//Copy the original space value to the new space
for (int i = 0; i < ps->size; i++)
{
temp[i] = ps->array[i];
}
//Free up original heap space
free(ps->array);
ps->array = temp;
ps->capacity = newCapacity;
}
}
5) Tail deletion and header deletion of sequence table
a. Before deleting the sequence list, you must first judge whether to operate on the empty linked list. If it is an empty list, it will jump out directly
b. To delete a header, you need to move all the following elements forward in turn
c. Therefore, the time complexity of head insertion is O(1) and the time complexity of tail insertion is O(N)
d. Remember to subtract 1 from the effective size of the array after the delete operation
// Tail deletion
void SeqListPopBack(SeqList* ps)
{
assert(ps);
//1. Check whether there are elements in the linked list
if (SeqListEmpty(ps))
{
printf("ERROR:The sequence table has no content\n");
return;
}
//2. Delete
ps->size--; //Just change the number of legal elements without releasing the space
}
// Header deletion
void SeqListPopFront(SeqList* ps)
{
assert(ps);
//1. Check whether there are elements in the linked list
if (SeqListEmpty(ps))
{
printf("ERROR:The sequence table has no content\n");
return;
}
//2. Move all elements forward one bit as a whole
for (int i = 0; i < ps->size; i++)
{
ps->array[i] = ps->array[i + 1];
}
ps->size--;
}
6) Insert and delete the specified position of the sequence table
Before inserting and deleting, first judge whether the pos position is within the effective length of the array
// Insert the element data in the pos position of the sequence table
// Note: the range of pos must be [0, PS - > size]
void SeqListInsert(SeqList* ps, int pos, DataType data) //pos is the subscript, starting from 0
{
assert(ps);
//1. Position detection
if (pos<0 || pos>ps->size)
{
printf("ERROR:Insertion position out of range\n");
return;
}
//2. Capacity test
ChecKCapacity(ps);
//3.pos element moves back one bit
for (int i = ps->size; i >= pos; i--)
{
ps->array[i + 1] = ps->array[i];
}
//4. Insert element
ps->array[pos] = data;
ps->size++;
}
// The sequence table deletes the value of pos position
// Note: the range of pos must be [0, PS - > size)
void SeqListErase(SeqList* ps, int pos) //pos is the subscript, starting from 0
{
assert(ps);
//1. Position detection
if (pos<0 || pos>ps->size)
{
printf("ERROR:Insertion position out of range\n");
return;
}
//2.pos and subsequent elements move forward one bit
for (int i = pos; i < ps->size; i++)
{
ps->array[i] = ps->array[i + 1];
}
ps->size--;
}
7) Other functions of the sequence table
// 9. Number of effective elements
int SeqListSize(SeqList* ps)
{
assert(ps);
return ps->size;
}
// 10. Total space size
int SeqListCapacity(SeqList* ps)
{
assert(ps);
return ps->capacity;
}
// 11. Find element location
int SeqListFind(SeqList* ps, DataType data)
{
assert(ps);
for (int i = 0; i < ps->size; i++)
{
if (data == ps->array[i])
{
return i;
}
}
return -1;
}
// 12. Check whether the sequence table is empty
int SeqListEmpty(SeqList* ps)
{
assert(ps);
return 0 == ps->size; //If it is empty, the equation is true and the return value is 1
}
// 13. Get the first element in the sequence table
DataType SeqListFront(SeqList* ps)
{
assert(ps);
return ps->array[0];
}
// 14. Get the last element in the sequence table
DataType SeqListBack(SeqList* ps)
{
assert(ps);
return ps->array[ps->size];
}
// 15. Get the element at any position in the sequence table
DataType SeqListGet(SeqList* ps, int pos)
{
assert(ps);
return ps->array[pos];
}
3. Sequence table summary
1) Because the sequential table is continuously opened in memory, it can be found directly when looking for data at any position
2) The header insertion and deletion of the sequence table need to move the data circularly, and the time complexity is high
3) In order to expand the capacity of the sequence table, the original data needs to traverse the new space of the copy value, which consumes a lot of energy
4) The sequence table will cause a waste of space, because the space is opened up in advance
source code
Header file
//The header file is used to declare the calling function
#pragma once
#include<stdio.h>
#include<Windows.h>
#include<malloc.h>
#include<assert.h>
#pragma warning(disable:4996)
/*
// 1.Static sequence table: the elements in the sequence table are stored in a fixed array
#define MAXSIZE 100
struct SeqList
{
int array[MAXSIZE];
int size;
};
*/
// 2. Dynamic sequence table: the underlying space is dynamically applied from the heap
typedef int DataType;
typedef struct SeqList
{
DataType* array; // Points to the starting position of the storage element space
int capacity; // Represents the total size of the space
int size; // Number of valid elements
}SeqList;
// typedef struct SeqList SeqList;
// 1. Initialize dynamic sequence table
void SeqListInit(SeqList* ps, int initCapacity);
// 2. Release linked list
void SeqListDestroy(SeqList* ps);
// 3. Tail plug
void SeqListPushBack(SeqList* ps, DataType data);
// 4. Deletion
void SeqListPopBack(SeqList* ps);
// 5. Head insert
void SeqListPushFront(SeqList* ps, DataType data);
// 6. Header deletion
void SeqListPopFront(SeqList* ps);
// 7. Insert the element data in the pos position of the sequence table
// Note: the range of pos must be [0, PS - > size]
void SeqListInsert(SeqList* ps, int pos, DataType data);
// 8. Delete the value of pos position in the sequence table
// Note: the range of pos must be [0, PS - > size)
void SeqListErase(SeqList* ps, int pos);
// 9. Number of effective elements
int SeqListSize(SeqList* ps);
// 10. Total space size
int SeqListCapacity(SeqList* ps);
// 11. Find element location
int SeqListFind(SeqList* ps, DataType data);
// 12. Check whether the sequence table is empty
int SeqListEmpty(SeqList* ps);
// 13. Get the first element in the sequence table
DataType SeqListFront(SeqList* ps);
// 14. Get the last element in the sequence table
DataType SeqListBack(SeqList* ps);
// 15. Get the element at any position in the sequence table
DataType SeqListGet(SeqList* ps, int pos);
///
// Test sequence table
void TestSeqList();
Function file
#include "seqlist.h"
// Detect sequential tablespaces
static void ChecKCapacity(SeqList* ps)
{
assert(ps);
if (ps->size == ps->capacity)
{
//Open up new space
int newCapacity = (ps->capacity << 1); //One bit to the left is twice the size
DataType* temp = (DataType*)malloc(newCapacity * sizeof(DataType));
if (NULL == temp)
{
assert(0);
return;
}
//Copy the original space value to the new space
for (int i = 0; i < ps->size; i++)
{
temp[i] = ps->array[i];
}
//Free up original heap space
free(ps->array);
ps->array = temp;
ps->capacity = newCapacity;
}
}
// Print function
static void SeqListPrint(SeqList* ps)
{
assert(ps);
for (int i = 0; i < ps->size; i++)
{
printf("%d ", ps->array[i]);
}
printf("\n");
}
///
// 1. Initialize dynamic sequence table
void SeqListInit(SeqList* ps, int initCapacity)
{
assert(ps); //Check whether the incoming address is legal
initCapacity = initCapacity <= 0 ? 3 : initCapacity; //Detect the second parameter. If it is illegal, three spaces are opened by default
ps->array = (DataType*)malloc(initCapacity * sizeof(DataType));
if (NULL == ps->array)
{
assert(0); //Display the cause of the error through assert
return;
}
ps->capacity = initCapacity;
ps->size = 0;
}
// 2. Release sequence table
void SeqListDestroy(SeqList* ps)
{
assert(ps);
if (ps->array)
{
free(ps->array); //The linked list memory is continuously opened up and released as a whole
ps->array = NULL;
ps->capacity = 0;
ps->size = 0;
}
}
// 3. Tail plug
void SeqListPushBack(SeqList* ps, DataType data)
{
assert(ps);
//1. Check whether the space is sufficient
ChecKCapacity(ps);
//2. Insert data for the last element
ps->array[ps->size] = data;
ps->size++;
}
// 4. Deletion
void SeqListPopBack(SeqList* ps)
{
assert(ps);
//1. Check whether there are elements in the linked list
if (SeqListEmpty(ps))
{
printf("ERROR:The sequence table has no content\n");
return;
}
//2. Delete
ps->size--; //Just change the number of legal elements without releasing the space
}
// 5. Head insert
void SeqListPushFront(SeqList* ps, DataType data)
{
assert(ps);
//1. Check whether the space is sufficient
ChecKCapacity(ps);
//2. Move all elements back one bit as a whole
for (int i = ps->size - 1; i >= 0; i--)
{
ps->array[i + 1] = ps->array[i];
}
//3. Insert element
ps->array[0] = data;
ps->size++;
}
// 6. Header deletion
void SeqListPopFront(SeqList* ps)
{
assert(ps);
//1. Check whether there are elements in the linked list
if (SeqListEmpty(ps))
{
printf("ERROR:The sequence table has no content\n");
return;
}
//2. Move all elements forward one bit as a whole
for (int i = 0; i < ps->size; i++)
{
ps->array[i] = ps->array[i + 1];
}
ps->size--;
}
// 7. Insert the element data in the pos position of the sequence table
// Note: the range of pos must be [0, PS - > size]
void SeqListInsert(SeqList* ps, int pos, DataType data) //pos is the subscript, starting from 0
{
assert(ps);
//1. Position detection
if (pos<0 || pos>ps->size)
{
printf("ERROR:Insertion position out of range\n");
return;
}
//2. Capacity test
ChecKCapacity(ps);
//3.pos element moves back one bit
for (int i = ps->size; i >= pos; i--)
{
ps->array[i + 1] = ps->array[i];
}
//4. Insert element
ps->array[pos] = data;
ps->size++;
}
// 8. Delete the value of pos position in the sequence table
// Note: the range of pos must be [0, PS - > size)
void SeqListErase(SeqList* ps, int pos) //pos is the subscript, starting from 0
{
assert(ps);
//1. Position detection
if (pos<0 || pos>ps->size)
{
printf("ERROR:Insertion position out of range\n");
return;
}
//2.pos and subsequent elements move forward one bit
for (int i = pos; i < ps->size; i++)
{
ps->array[i] = ps->array[i + 1];
}
ps->size--;
}
// 9. Number of effective elements
int SeqListSize(SeqList* ps)
{
assert(ps);
return ps->size;
}
// 10. Total space size
int SeqListCapacity(SeqList* ps)
{
assert(ps);
return ps->capacity;
}
// 11. Find element location
int SeqListFind(SeqList* ps, DataType data)
{
assert(ps);
for (int i = 0; i < ps->size; i++)
{
if (data == ps->array[i])
{
return i;
}
}
return -1;
}
// 12. Check whether the sequence table is empty
int SeqListEmpty(SeqList* ps)
{
assert(ps);
return 0 == ps->size; //If it is empty, the equation is true and the return value is 1
}
// 13. Get the first element in the sequence table
DataType SeqListFront(SeqList* ps)
{
assert(ps);
return ps->array[0];
}
// 14. Get the last element in the sequence table
DataType SeqListBack(SeqList* ps)
{
assert(ps);
return ps->array[ps->size];
}
// 15. Get the element at any position in the sequence table
DataType SeqListGet(SeqList* ps, int pos)
{
assert(ps);
return ps->array[pos];
}
///
//Test function 1
static void Test1()
{
SeqList s;
SeqListInit(&s, 3); //Note that the parameter here is the address
SeqListPushBack(&s, 1);
SeqListPushBack(&s, 2);
SeqListPushBack(&s, 3);
SeqListPushBack(&s, 4);
SeqListPushBack(&s, 5);
SeqListPushBack(&s, 6);
SeqListPrint(&s);
SeqListErase(&s, 4);
SeqListPushFront(&s, 0);
SeqListPrint(&s);
printf("Sequence table significant digits:%d\n", SeqListSize(&s));
printf("Sequential table space:%d\n", SeqListCapacity(&s));
printf("Subscript of number 5 in sequence table:%d\n", SeqListFind(&s, 5));
SeqListDestroy(&s);
}
//Test sequence table
void TestSeqList()
{
Test1();
}
Main function file
#include "seqlist.h"
int main()
{
TestSeqList();
system("pause");
return 0;
}