Data collection jsoup
-jsoup introduction:
1. jsoup is a Java HTML parser, which can directly parse a URL address and HTML text content.
2. The main functions of jsoup are as follows:
-Parsing HTML from a URL or string;
-Use DOM or CSS selector to find and retrieve data;
-Operable HTML elements, attributes and text;
3. jsoup is released based on MIT protocol and can be safely used in commercial projects.
-
jsoup environment configuration:
- idea jsoup environment configuration:
-
Import jar package:
-
Download jar package: Official website

-
Import jar package:

-
-
Creating Maven projects using dependency
-
Insert the following code into the section in the pom.xml file:
<dependency> <!-- jsoup HTML parser library @ https://jsoup.org/ --> <groupId>org.jsoup</groupId> <artifactId>jsoup</artifactId> <version>1.13.1</version> </dependency>
-
-
- idea jsoup environment configuration:
-
Important classes of jsup:

-
Jsup parsing web pages
-
Load html file by connecting to the given URL
-
Method 1: use the jsup. Connect (string URL) method to load HTML from the URL.
-
Method description: establish a new connection with the given url to obtain and parse the HTML page.
-
Case study:
Document doc = Jsoup.connect("http://www.hnkjxy.net.cn/").get(); System.out.println(doc.text());//Output web page System.out.println(doc.title());//Output titleDocument doc = Jsoup.connect("https://www.educoder.net/") .data("query","java")//Request parameters .userAgent("I'm jsoup")//Set up user agent .cookie("auth","token")//Set cookie s .timeout(3000)//Set connection timeout .post()//Use the POST method to access the URL .get()//Use the GET method to access the URL- Method 2: get the URL and parse it into HTML. In most cases, we use connect(String) instead.
- Method description:

-
-
Parsing local file contents into html documents
-
Load from the file into HTML using the jsup. Parse () method
-
Method introduction:
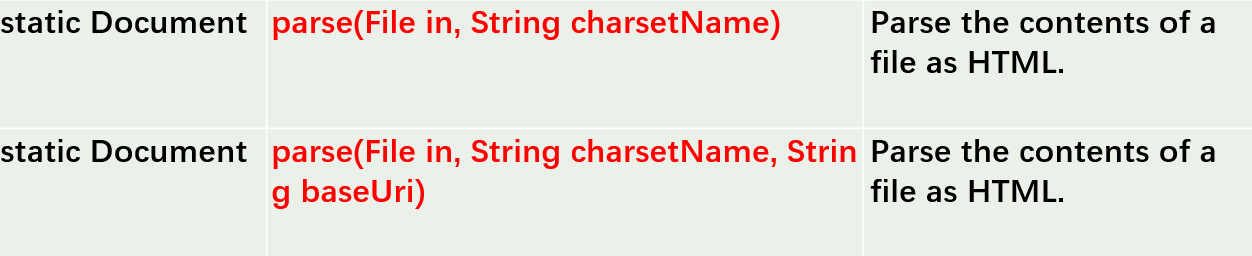
Note: in: file location, charsetName: encoding format, baseUri based URL address to solve the relative link problem. -
Case study:
//1. Crawl the web page and save it Document doc = Jsoup.connect("http://www.hnkjxy.net.cn/").get(); FileWriter fw = new FileWriter("Official website.html"); fw.write(doc.toString()); fw.close(); //2. Parse the local file and save the output Document doc2 = Jsoup.parse(new File("D:\\bigDataDevelop\\index.html"),"utf-8","http://www.hnkjxy.net.cn/"); System.out.println(doc2.text()); System.out.println(doc2.title());
-
-
Parsing a given string into an html document
-
Use the jsup. Parse () method to load HTML from a string.
-
Method introduction:

This method can parse the input HTML into a new Document. The parameter baseUri is used to convert the relative URL into an absolute URL and specify which website to obtain the Document from. -
Case study:
Document doc = Jsoup.parse("<html><head><title>First parse</title>" + "</head>body><p>Parsed HTML into a doc.</p></body>" + "</html>\r\n"); System.out.println(doc.toString()); System.out.println(doc.title());
-
-
Summary: jsoup is a Java HTML parser. It can parse HTML from URL s, local files and strings.

-
-
DOM method to find elements
-
Find element
-
Introduction to basic methods:
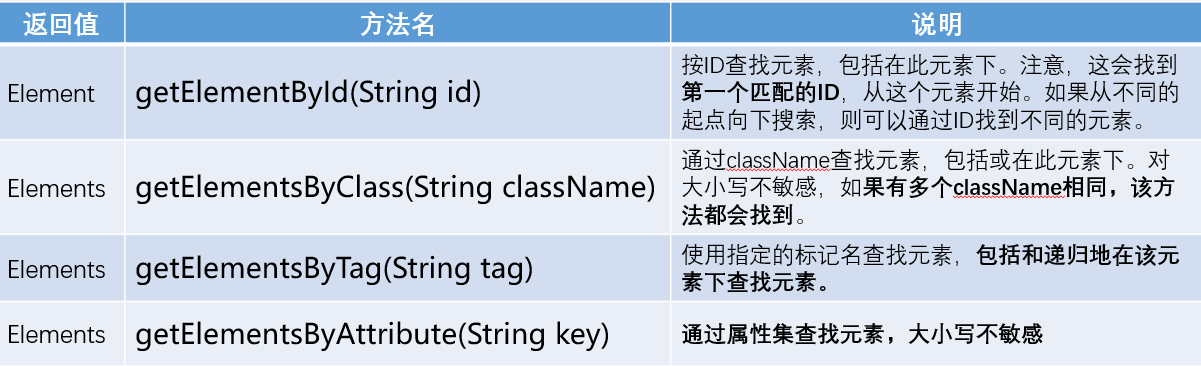
-
Case study:
// There is a local file example.com.html. Parse the file and find HTML elements. // Extract the element with id=one? // Extract the element of class=lianjie? // Extract the element labeled a? // Extract elements labeled div? // Extract element with attribute href try { Document doc = Jsoup.parse(new File("example.com.html"),"utf-8"); Element id_one = doc.getElementById("one"); Elements class_lianjie = doc.getElementsByClass("lianjie"); Elements tag_a = doc.getElementsByTag("a"); Elements tag_div = doc.getElementsByTag("div"); Elements attr_href = doc.getElementsByAttribute("href"); System.out.println("id_one:"+id_one+"\ntag_a:"+tag_a+"\nclass_lianjie:"+class_lianjie+"\ntag_div:"+tag_div+"\n"+"attr_href:"+attr_href); }catch (Exception e){ System.out.println("report errors!"); } -
Introduction to peer element method:

-
Case study:
// Gets the sibling element. // Get the sibling element of the first element whose className is equal to "lianjie"? // Get the previous sibling of the second element whose className is equal to "lianjie"? try { Document doc = Jsoup.parse(new File("example.com.html"),"utf-8"); Elements siblingElements = doc.getElementsByClass("lianjie").get(0).siblingElements(); System.out.println("siblingElements:"+siblingElements); Element previousElementSibling = doc.getElementsByClass("lianjie").get(1).previousElementSibling(); System.out.println("previousElementSibling:"+previousElementSibling); }catch (Exception e){ System.out.println("report errors!"); } -
Introduction to Graph method:

-
Case study:
// Find elements by graph // Gets the sub tag of the div tag with id "two". try { Document doc = Jsoup.parse(new File("example.com.html"),"utf-8"); Elements id_two = doc.getElementById("two").getElementsByTag("div"); Elements div = id_two.get(0).children(); System.out.println(div); }catch (Exception e){ System.out.println("report errors!"); }
-
-
Find element data
- Method introduction:
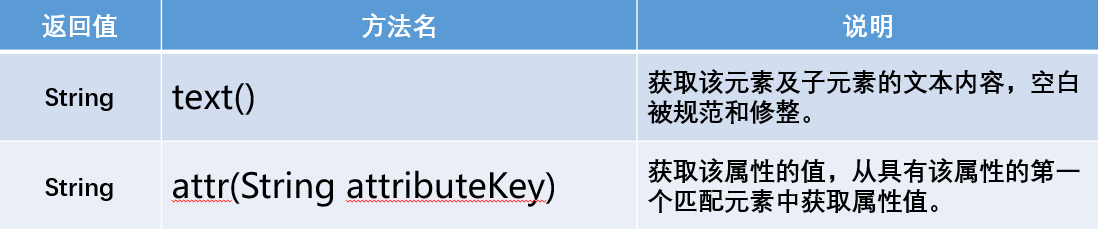
- Method introduction:


- Method introduction:
-
Manipulate HTML and text:

-
-
Slector selector method finds elements
The jsoup elements object supports a selector syntax similar to CSS (or jquery) to achieve very powerful and flexible lookup functions. It can be implemented using the Element.select(String selector) and Elements.select(String selector) methods
-
Selector foundation 1
tagname: find elements through tags, such as: a
ns|tag: find elements in namespace r through tags. For example, you can use fb|name syntax to find fb:name elements
#ID: find elements by ID, such as: #logo
. class: find elements by class name, for example:. masthead
[attribute]: use attributes to find elements, such as: [href] -
Selector combination
el#id: element + ID, such as div#logo
el.class: element + class, for example: div.masthead
el[attr]: element + class, for example: a[href]
Any combination, such as a[href].highlight
ancestor child: find the child elements of an element. For example, you can use. body p to find all P elements under the "body" element
Parent > child: find the direct child element under a parent element. For example, you can use div.content > p to find the P element or body > * to find all the direct child elements under the body tag
siblingA + siblingB: find the first sibling element B before element A, such as div.head + div
siblingA ~ siblingX: find the sibling X element before element A, such as h1 ~ p
el, el, el: a combination of multiple selectors to find the only element matching any selector, such as div.masthead, div.logo -
Pseudo selector selectors
: lt(n): find out which element's peer index value (its position is relative to its parent node in the DOM tree) is less than N, for example: td:lt(3) indicates elements with less than three columns
: gt(n): find out which elements have a sibling index value greater than N. for example: div p:gt(2) indicates which div contains more than 2 p elements
: eq(n): find out which elements have the same sibling index value as N, for example: form input:eq(1) indicates a Form element containing an input tag
: has(seletor): find the elements that match the elements contained in the selector. For example, div:has § indicates which div contains the p element
: not(selector): find elements that do not match the selector. For example: div:not(.logo) indicates a list of all div that do not contain a class = "logo" element
: contains(text): find the element containing the given text. The search is not big or write sensitive, such as: p:contains(jsoup)
: containsOwn(text): finds the element that directly contains the given text
: matches(regex): find which element text matches the specified regular expression, such as: div:matches((?i)login)
: matchesOwn(regex): finds an element that contains text that matches the specified regular expression
Note: the above pseudo selector index starts from 0
-